ICSE Solutions for Class 6 History and Civics – Mahavira and Buddha – Great Preachers
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 6 History and Civics Chapter 6 Mahavira and Buddha – Great Preachers . You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 6 History & Civics Geography Biology Chemistry Physics Maths
Exercise
I. Fill in the blanks:
- The sixth century BC saw the rise of two new religions in India.
- The founders of both the new religions in India were Kshatriyas.
- Jainism was founded by Mahavira.
- The Jains believe Mahavira was the 24th and the last Tirthankara.
- At the age of 42, Mahavira conquered both misery and happiness and became Jina or the conqueror.
- Buddhism was founded by Gautam Buddha.
- His real name was Siddhartha.
- The tree under which Buddha attained Enlightenment is called Bodhi Tree.
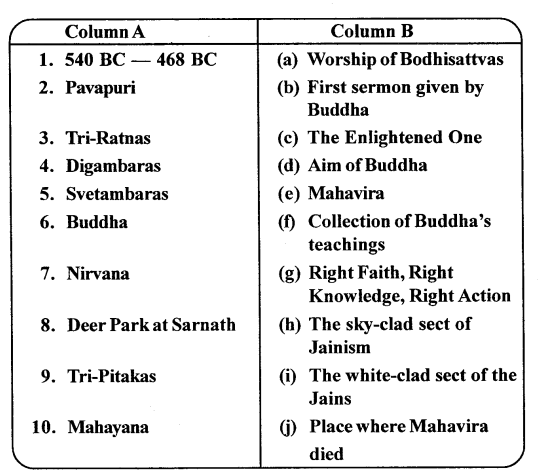
II. Match Column A with Column B
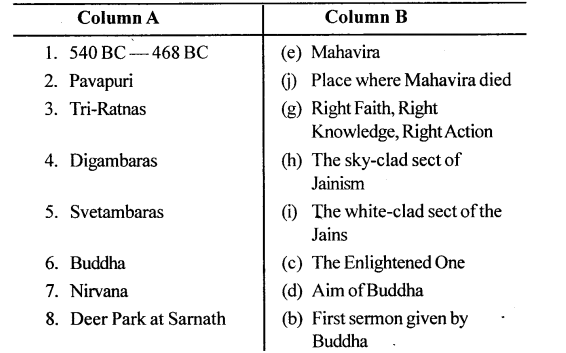
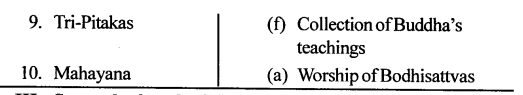
Answer:
III. State whether the following statements are True or False.
- By the 6th century BC the Vedic religion had become too complicated and common people could not understand it.
True - Mahavira was born at Pavapuri near Rajgir in Bihar.
False - The attainment of ‘Moksha’ should be the main goal of life according to Mahavira.
True - Jainism’s strict insistence on non-violence and penance made it popular in India.
False - Buddha’s teachings are included in the Four Noble Truths and the Eight-Fold Path.
True - Jatakas are stories about Buddha’s previous births.
True. - ‘Mahayana’ form of Buddhism started worshiping Buddha as a god.
True
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Why did new religions rise in India in the 6th century BC?
Answer:
By the 6th century BC the Vedic religion had become very complicated. There was a great deal of emphasis on rituals, yajnas and sacrifice. The Brahmanas had become very powerful and all the rituals had become too costly for the common man. Animal sacrifices affected the economy because it was based upon agriculture and animal husbandry. The language used for all rituals was Sanskrit and the common man could not understand it. The use of coins facilitated trade and commerce which added to the importance of the Vaishyas. They were ranked third in the society, the first two being Brahmanas and Kshatriyas. Naturally, they looked for a religion which would improve their position. Hence, new religions — Buddhism and Jainism — rose in India in the 6th century BC.
Question 2.
What are the five vows a Jain householder had to take?
Answer:
Five vows of Jainism are as follow:
- Ahimsa—non-violence
- Satya—Truth
- Achaurya orAsteya—Non-stealing
- Brahmacharya—Celibacy
- Aparigraha—Non-possession
Question 3.
Why did Buddha renounce the world?
Answer:
One day Prince Siddhartha, while on a chariot ride through the city, saw three sights — of an old man, a sick man and a dead body being carried by mourners. This disturbed and distressed him. Then he saw an ascetic who was serene and calm. No sorrow or worldly miseries affected him. These are the Four Great Sights that changed his life and he renounced the world.
Question 4.
Explain the main difference between Jainism and Buddhism.
Answer:
Compared to Jainism, Buddhism was moderate in its stress on the doctrine of non-violence. Buddhism emphasised on following the middle path whereas Jainism laid stress on extreme austerity. While the Buddha was silent about the existence of God, Mahavira denied his existence.
Question 5.
Why did Buddhism spread so rapidly?
Answer:
Buddhism spread rapidly because its teachings were very simple and it was taught in the language of the people. The patronage of two great emperors — Ashoka and Kanishka — made it a world religion. Its opposition to the caste system made it popular among the castes that were considered low.
Question 6.
What were the reasons behind the decline of Buddhism and Jainism?
Answer:
Buddhism became a victim to the evils of Brahmanism against which it had fought initially. The Buddhist monks were gradually cut off from the mainstream of the people’s life. They gave up Pali, the language of people and took to Sanskrit, the language of intellectuals. They also started practicing idol worship on a large scale and received material offerings from devotees. The rich offerings and generous royal grants made the life of monks luxurious. By the 7th century AD the Buddhist monasteries became centers of corrupt practices which Buddha had strictly prohibited. Undue emphasis on non-violence in Jainism checked its spread among the farming community as their profession necessarily involved killing insects and pests. Moreover, Mahavira’s ideas were not acceptable to those artisans and craftsmen whose occupation endangered the life of other creatures. Strict Jaina limitation of private property was interpreted as a ban on possession of landed property. All these factors led to the gradual decline of Jainism.
Question 7.
Name the religious texts of Buddhism and Jainism.
Answer:
Religious texts of Buddhism — Vinay Pitaka, Sutta Pitaka and Abhidhamma Pitaka Religious texts of Jainism — Angas and Purvas
Question 8.
Why is Buddhism called the Middle Path?
Answer:
Buddhism is called Middle Path because Buddha did not believe in extremes. Buddhism emphasised on following the middle
V. Picture study This is a picture of a temple.
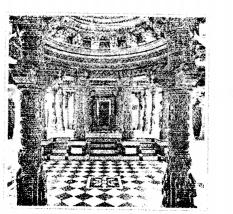
- Identify and name it.
Ans. Dilwara Jain Temple - Where is it situated?
Ans. Mount Abu (Rajasthan) - Who built it?
Ans. Vastupala - Write a paragraph about it.
Ans. The five legendary marble temples of Dilwara are a sacred pilgrimage place of the Jains. Many scholars consider them to be one of the most beautiful Jain pilgrimage sites in the world.
Textbook Keywords
- Tirthankaras: They were the religious teachers of Jainism who preached before Mahavira.
- Jina: It means conquerer of the self.
- Karma: It means that people’s actions decide their destiny. Moksha It means freedom from the cycle of birth and death.
- Digambara Sect of Jainism: The word means sky clad. They did not wear any clothes and followed the original teachings of Mahavira.
- Svetambaras: They were Jain monks who wore white clothes and did not believe in hard penance.
- Purvas and Angas: They are the religious literature of the Jains.
- Ashtangika marga: It means the eight fold path.
- Ahimsa: means non-violence. Both Jainism and Buddhism preached this principle.
- Nirvana: It means freedom from the cycle of birth and death.
- Sangha was the order of the Buddhist monks.
- Tripitakas and Jatakas Are Buddhist religious texts.
Additional Questions
A. Fill in the blanks.
- 1. Many evil customs crept into Hindu society.
- The shudras were denied the right to study religious texts.
- In the 6th century BCE two great religious reformers, Vardhamana Mahavira and Gautam a Buddha were bom.
- Two famous followers of Jainism were Bimbisara and Mahayana.
- The religious literature of the Buddhists is contained in the Tripitakas and Jatakas.
- Buddhism was divided into two sects, Hinayana and Mahayana
- Jainism was divided into two sects, Digambaras and Svetambaras.
B. Match the following.

Answer:

C. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
How did the new customs destroy the simplicity of the original Vedic religion?
Answer:
Costly sacrifices, superstitions and elaborate, meaningless rituals destroyed the simplicity and appeal of the original vedic religion.
Question 2.
How did the rigid caste system affect the shudras?
Answer:
Shudras were increasingly isolated and persecuted. They were denied the right to study the religious scriptures and were not even allowed to recite the Sanskrit hymns,
Question 3.
Mention the main teachings of Mahavira.
Answer:
- Ahimsa or Non-violence is the first great teaching of Mahavira.
- Mahavira did not accept the Veda and opposed all forms of religious rites and rituals.
- Mahavira believed that all people are equal.
- Mahavira denied that God was the creator of the universe,
- According to Mahavira the highest goal of a person’s life was to attain moksha.
Question 4.
Name the two Jain sects. What was the difference between the two?
Answer:
Digambaras and Svetambaras are two sects of Jainism.
The main difference between Digambaras and Svetambaras was that the followers of Digambaras did not wear any clothes and followed the original teaching of Mahavira. But the followers of Svetambaras wore white clothes and did not believe in hard penance.
Question 5.
In which parts of India is Jainism still popular?
Answer:
Jainism is still popular in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Question 6.
What were the ‘four great sights’ that proved to be a turning point in Gautama Buddha’s life?
Answer:
Once while Gautama Buddha was on an outing in his chariot,he saw an old man, a sick man, a dead man and an ascetic who was unaffected by the sorrow and misery around him. These four great sights proved to be a turning point in Gautama Buddha’s life.
Question 7.
Briefly explain the following events in Buddha’s life:
- Renunciation
- Enlightenment
Answer:
- Renunciation— At the ‘four great sights’ Gautam decided to renounce worldly life and go out in search for answers to the mysteries of life and death. He became an ascetic.
- Enlightenments— One day Gautam Buddha sat down under a pipal tree in Bodh Gaya and began to meditate. On the 49th day, true light dawned on him. He became the enlightened one. He had at last found the cause of human suffering and knew how to overcome it.
Question 8.
Explain the four noble truths of Buddhism.
Answer:
The four noble truths of Buddhism are following.
- The world is full of suffering.
- The cause of suffering is human desire.
- Suffering can be ended by overcoming desires.
- Desires can be overcome and freedom from the cycle of birth, death and rebirth can be achieved by nirvana. The eight fold path leads to nirvana.
Question 9.
What do you understand by the term eight fold path of Buddhism?
Answer:
The eight fold path of Buddhism are following:
- Right belief
- Right speech
- Right thought
- Right action
- Right efforts
- Right memory
- Right meditation
- Right means of livelihood
Question 10.
why did Buddhism spread so rapidly?
Answer:
Buddhism spread so rapidly because of following causes.
- The Simplicity of Gautam Buddha’s teachings and principle of equality greatly appealed to the common people.
- Buddhism was spread far and wide by monks and nuns.
- Buddhist universities established by king Ashoka (like Nalanda) were also other important reasons for rapid spread of Buddhism.
Question 11.
Explain the following terms:
- Ahimsa
- Karma
- Moksha
Answer:
- Ahimsa—Ahimsa means non-violence. Both Jainism and Buddhism preached this principle.
- Karma— People’s actions will decide their destiny. Good deeds are rewarded and evil deeds are punished.
- Moksha— The hightest goal of a person’s life was to attain Moksha freedom from the cycle of birth and death.
Question 12.
What were the reasons for the decline of Buddhism in India?
Answer:
Buddhism gradually declined in India for the following reasons.
- Hinduism was reformed and purified.
- The Gupta kings patronized Hinduism.
- India was invaded by the Huns who destroyed Buddhist viharas.
D. State whether the following are true or false.
- The brahmanas were very popular among the common people.
False. - Mahavira was the last tirthankara of the Jains.
True. - Mahavira believed in the existence of a supreme God.
False. - Buddhism was taught in Prakrit.
False. - Buddhism is the main religions of people in south-east Asia, Tibet. China and Japan.
True.