What Is The Conservation Of Biodiversity
The preservation and careful management of plant and animal species in order to prevent their extinction is called conservation. Several steps have been taken by many national and international organizations towards conservation of biodiversity.
Forest Reserves
Forest reserves are large areas of forest cover that are protected from human exploitation. Strict laws have been enacted all over the world to prevent felling of trees in forest reserves. Thus, forest reserves have been established with an aim at serving the following purposes:
- prevention of deforestation;
- replenishment of lost forest cover by planting new trees (reforestation); and
- protection of food and shelter meant for wildlife.
Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks
Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are protected forests all across the world to preserve , certain plant and animal species. In India, there are more than four hundred wildlife sanctuaries and about a hundred national parks. Cutting trees and hunting animals in these areas is strictly prohibited.
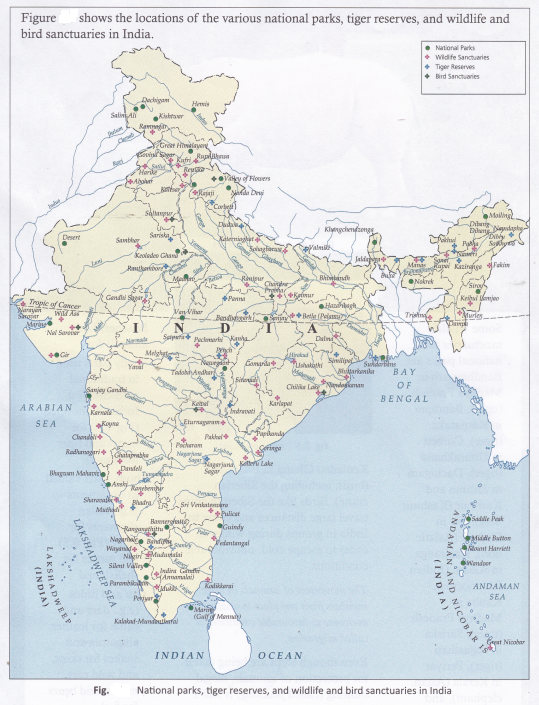
Some wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are: Bandhavgarh in Madhya Fradesh (tiger), Bandipur in Karnataka (tiger), Corbett in Uttarakhand (tiger), Dachigam in Jammu and Kashmir (Kashmir Stag), Oir in Gujarat (Asiatic lion), Kaziranga in Assam (Indian Rhinoceros), Kanha in Madhya Pradesh (tiger), Sariska in Rajasthan (tiger), Periyar in Kerala (Asian elephant), and Keoladeo Ghana in Bharatpur (birds, including the Siberian crane). Birds like the Siberian crane travel large distances and come to India in groups during winter in order to escape cold, unfavourable conditions.
The movement of animals in large numbers from one place to another to overcome unfavourable conditions is called migration. Even though steps are being taken for protection of animals, illegal hunting (called poaching) is still a major threat to wildlife.
Poachers hunt animals for
- body parts used in traditional medicine (e.g., Indian rhinoceros for horns and tiger for bones);
- body parts valued as ornaments (e.g., Asian elephants for ivory and turtles for shells); and
- fur and hides (e.g., deer and cattle for leather, alligators and snakes for skins, and wild cats, minks, and bears for fur).
Zoological Parks
A zoological park or zoo refers to any park, building, cage, enclosure, or premise in which animals are kept for public exhibition. Zoos play a major role in creating awareness among common people about the need to conserve nature. Some zoos serve as breeding centres for sawimfi ox Isaaks.
Botanical Gardens
Botanical gardens may be called ‘zoos’ of the plant world. They have been established to conserve rare and threatened plant species. There are about 1600 botanical gardens world over. Most botanical gardens also serve as seed banks and have reserves of seeds of several species of plants.
Organizations Involved in Conservation
Conserving the biodiversity is the duty of every human being. To promote conservation, government and non-government organizations at the international, national, and local levels are constantly organizing awareness programmes and issuing rules and regulations to protect, forests and wildlife.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) works towards assessing the global conservation status of plant and animal species. IUCN maintains a comprehensive list known as the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Here, species are classified into nine categories, on the basis of criteria like the rate of decline, population size, and area of geographical distribution.
The nine categories in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species are given below.
- Extinct
- Near threatened
- Extinct in the wild
- Least concern
- Critically endangered
- Data deficient
- Endangered
- Not evaluated
- Vulnerable
The main aim of the IUCN Red List is to focus the attention of conservationists towards species that are under threat of becoming extinct. Few of the animals listed in the IUCN Red List are blue whale, African elephant, sea turtle, and Bengal tiger. IUCN also publishes a catalogue, called the Red Data Book, which lists rare species and those in danger of extinction.
In India, some non-government organizations (NGOs) share the job of conserving the environment with the government. While some organizations aim at spreading awareness among people, some work towards implementation of rules and regulations set up by the government in this regard. Still others focus on restoring habitats through fieldwork and surveys. Some of the famous Indian conservation programmes that have gamed recognition m the recent past are Project Tiger, the Van Mahotsava programme, and the Chipko movement.
Recycling Paper
Recycling paper is one of the ways of conserving trees. Paper is made of cellulose fibre, the main source of which is wood pulp obtained from trees. The pulp and paper industry is so huge that trees are planted and grown specifically to make paper.
Besides avoiding wastage of paper, we can also reuse and recycle it. Waste paper can be made into useful products like packaging, writing paper, and tissue paper. Recycling refers to manufacturing new products from materials that would otherwise be considered waste. The process of recycling involves collecting waste materials, sorting them, and processing them into raw materials that could be used to make new products.

