What is Molecular Mass
Molecular mass/Formula mass
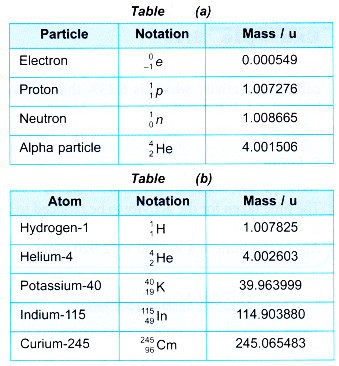
Molecular mass expresses as to how many times a molecule of a substance is heavier than th of the mass of an atom of carbon (carbon-12).
Thus, Molecular mass = \(\frac { Mass\quad of\quad a\quad molecule }{ \frac { 1 }{ 12 } th\quad mass\quad of\quad a\quad carbon\quad atom\quad (carbon-12) } \)
Molecular mass = 2 × vapour density
Example: A molecule of water is 18 times heavier than th of the mass of carbon atom. Therefore, the molecular mass of water is 18 u.
Calculation of molecular mass from atomic masses
The molecules are made up of two or more atoms of different elements. Therefore, the molecular mass may be calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of that substance.
Example: Ammonia has the formula, NH3. it consists of one atom of N and three atoms of H. The atomic mass of N and H are 14.0 and 1 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of NH3 is
Molecular mass of NH3 = Atomic mass of N + 3 × Atomic mass of H
= 14 + 3 × 1 = 17 u
Example: Sulphuric acid has the formula H2SO4. It consists of two H, one S and four O atoms. The atomic masses of H, S and O are 1,32 and 16 respectively. Therefore, the molecular mass of H2SO4 is
Molecular mass of H2SO4 = (2 × Atomic mass of H) + (1 × Atomic mass of S) + (4 × Atomic mass of O)
= (2 × 1) + (1 × 32) + (4 × 16) = 98 u
Gram molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance expressed in gram is called its gram molecular mass.
Example: Molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 u
So, gram molecular mass of oxygen, O2 = 32 grams.
People also ask
- What is the Definition of Atom and Molecule
- What is Atomic Mass
- What is the Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular Mass of an Element?
- What is One Mole and How many Particles are in a Mole?
- How do you Calculate the Molar Mass of a Substance?
- What is the Molar Volume of a Gas at STP?
- How do you know the Order of Elements in a Chemical Formula
- What is Empirical and Molecular Formula?
- How do you Write a Chemical Equation?