What is the Structure and Function of the Golgi Apparatus
Golgi apparatus :
Golgi bodies are absent in prokaryotic cells. Golgi complex is found in all eukaryotic cells except RBCs.
Historical Account :
Camillo Golgi (1898), a zoologist, observed Golgi bodies in the form of a network in nerve cells of barn owl.
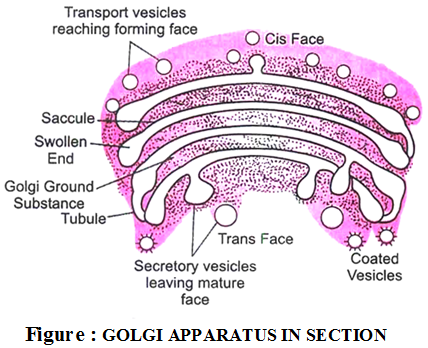
Ultrastructure :
- It is also called Golgi complex or Golgi apparatus or Dictyosome (in plants cell).
- It is made up of cisternae.
- Golgi bodies are interconnected with the tubules.
Functions of Golgi Apparatus :
- The main function of Golgi apparatus is secretory.
- It produces vacuoles or secretory vesicles which contain cellular secretions like enzymes, proteins, cellulose etc.
- Golgi apparatus is also involved in the synthesis of cell wall, plasma membrane and lysosomes.
Lysosomes :
Lysosomes are generally found in the cytoplasm of animal cells. Lysosomes exhibit polymorphism.
Historical Account :
The term lysosome was introduced by De Duve in 1955.
Ultrastructure :
- It is also called demolition squads, scavengers, cellular house keepers and suicidal bags.
- Lysosome are simple tiny spherical sac like structures evenly distributed in the cytoplasm.
- Lysosome is small vesicle surrounded by a single membrane and contains powerful enzymes.
Functions of Lysosomes :
- Lysosomes serve as interacellular digestive system, hence called digestive bags.
- Lysosomes also remove the worn out and poorly working cellular organelles by digesting them to make way for their new replacement.