Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 15 Communication Systems is part of Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Kerala. Here we have given Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Communication Systems.
Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Communication Systems
Question 1.
a) A 20kHz baseband signal is to be transmitted over a long distance. Comment on the size of the antenna required for this purpose. (March – 2019)
b) Explain the advantage of a high-frequency trans-mission for the above case
c) What is modulation? Why is it necessary?
d) Mention any two important properties of lasers.
Answer:
a) The size of the antenna should be comparable to the wavelength of signal (at least λ/4). The wavelength of the 20kHz wave is 15km and the antenna size should be at least 3.75km.
b) 1) Effective power radiation
2) Size of antenna reduces and transmission be comes practical
c) Modulation is the process of superimposing a low-frequency baseband signal with a high-frequency carrier wave.
It is necessary because
- To transmit a low-frequency signal, length of antenna should be several kilometers. It is not practically possible. So base band signal must be converted in to high-frequency signal.
- Low-frequency signals are more susceptible to interference than high-frequency signals.
- High radiation power is possible for a high-frequency wave (small wave length)
d) High monochromaticity, high degree of coherence, high output power, highly collimated beam.
Question 2.
Modulation is a process employed to superimpose a carrier wave with a signal wave. (March – 2010)
a) In amplitude modulation, which of the following will change?
i) Frequency
ii) Phase
iii) Amplitude
iv) Wavelength
b) A message signal of frequency 10 KHz and peak voltage of 10 volts is used to modulate a carrier wave of frequency 1 MHz and peak voltage of 20 volts.
Determine the modulation index and frequencies of side bands.
Answer:
a) Amplitude
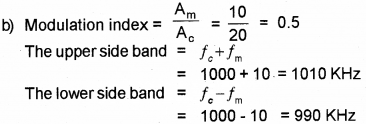
Question 3.
Communication is the process of sending information from one place to another by electric signals, (Say – 2010)
a) Name the two types of electric signal.
b) Differentiate these signals, giving one example each.
Answer:
a) i) Analog signal
ii) Digital signal
b) An analog signal is that in which current or voltage value varies continuously with time.

Example : Music Signal in TV and Radio.
Digital Signal: Digital signals are the signals that can take only discrete values.
![]()
Example:
1) Pulse shaped signal
2) Signals in computer
Question 4.
Television broadcast is done by space wave mode of propagation. (March – 2011)
a) What is the difference between sky wave and space wave modes of propagation?
b) A TV transmission antenna is 81 m tall. How much sevice area can it cover if the receiving antenna is at the ground level? (Radius of earth is 6400km)
Answer:
a) In sky wave the signal is reflected from the iono-sphere and received. In space wave signal is directly received by the receiving antenna.

Question 5.
Which of the following is used for line-of sight (LOS) communication? (Say – 2011)
a) Sky waves
b) ground waves
c) Space waves
d) Long waves
Answer:
Space wave
Question 6.
Power radiated by a transmitting antenna is proportional to (Say – 2011)
a) (λ/l)2
b) l2/λ
c) (l/λ)2
d) λ2/l
Answer:
c) (1/λ)2
Question 7.
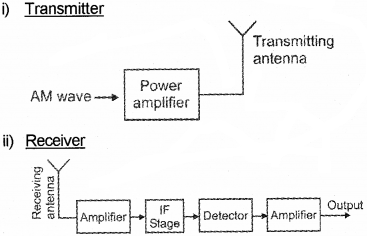
Spectrum allocations for communication are arrived at by an international agreement. (March – 2012)
Draw block diagrams of an amplitude modulated
i) transmitter and
ii) receiver
Answer:
Question 8.
In communication, signal is transmitted from a source to a receiver through a medium. Different types of media offer different band widths. (Say – 2012)
a) What do you understand by amplitude modulation?
b) Draw the block diagram of an AM receiver.
Answer:
a) In amplitude modulation the amplitude of the carrier is varied in accordance with the information signal.
b)

Question 9.
Various propagation modes are used in communication (March – 2013)
a) Mention two communication systems that uses space wave propagation.
b) Why modulation is necessary in communication?
c) If a signal of frequency ωs is used to modulate a carrier wave of frequency ωc which are the frequencies contained in the modulated signal other than ωc?
Answer:
a) Radio communication, Satellite communication.
b) Refer March – 2009, Question No. 1(c)
c) ωc + ωs, ωc, ωc – ωs
Question 10.
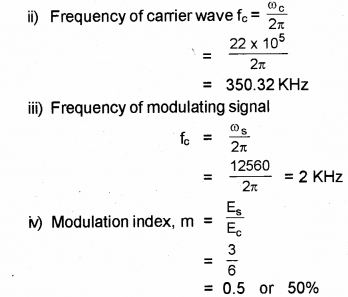
Ground waves, sky waves, surface waves and space waves are generally used in the communication process. (Say – 2013)
a) Which of the above waves is used in the UHF range?
b) An AM wave is represented by Cm(t) = 6(1 + Sin 0.5 12560t) Sin 22 x 106 volt.
Calculate:
i) PmpIitudeof carrier wave
ii) Frequency of camer wave
iii) Frequenc’ of the modulating signal
iv) Modulation index
Answer:
a) Space wave
b) Cm (t) 6(1 +O.5Sin 12560t) Sin 22 x 105 t V
i) The instantaneousvotge ofaAM wave is given t’
Cm(t) 6(1 + 0.5 Sin 12560t) Sin 22 x 105 t = (6 + 3 Sin 12560t) Sin 22 x 105 t
Comparing the standard A.M. wave
Cm(t) = (Ec + Es Sin ωst) Sin ωc t,
we getAmplitude of carrier wave
Ec = 6V
Question 11.
a) When a low flying aircraft passes over head, we sometimes notice a slight shaking of the picture on our TV screen. Identify the optical phenomenon behind it. (March – 2014)
b) In electro magnetic spectra, the wave length and frequencies are inversely related. A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. Determine the corresponding wave length band.
Answer:
a) Interference superposition of waves.
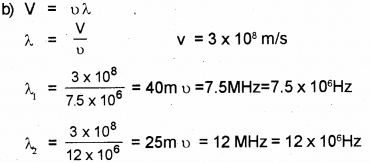
Question 12.
In ourdaily life, modulation plays an important role.
a) Discuss the amplitude modulation.
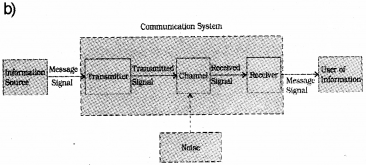
b) Give a block diagram of a generalized communication.
Answer:
a) In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of high frequency carrier wave is varied in accordance with modulating signal (information signal).
Question 13.
a) Describe how to detect an amplitude modulated wave.
b) Sketch a neat diagram for a detector for AM signal
Answer:
a) Detection is the process of recovering the modulating signal from the modulated carrier wave. The process of detection is shown in block diagram.
The modulated signal fig (a) is given to the rectifier. The rectifier removes the negative part of the A.M and gives the output as shown in figure (b) This output is given to the envelop detector. The envelop detector gives an output of the message signal as shown in figure (c).
The message signal from the detector is given to the amplifier. The amplifier, amplifies the signal and given to the loud speaker.

Question 14.
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves used for communication purpose. (Say – 2014)
a) Name the mode of propagation used for radio waves of frequencies ranging from 30-40 MHz.
b) Name two communication system that use space wave mode of propagation.
c) In standard radio broadcasting which modulation is commonly usen.
Answer:
a) Space wave propogation (Television broad casting)
b) TV, Radio
c) Amplitude modulation
Question 15.
A) Range of an electronic communication system is the (March – 2015)
a) distance to the nearest TV station.
b) distance to the nearest radio station.
c) largest distance the signal can travel.
d) largest distance between a source and destination up to which the signal is received with sufficient strength.
B) If the height of TV transmitting antenna is increased its coverage increases. Why?
Answer:
A) d
B) The distance travelled by the signal,
![]()
Where h is the height of antenna. The above equation shows that d increases with h. Hence if the height of TV transmitting antenna is increased its coverage increases.
Question 16.
a) A receiver in a communication system must have (March – 2016)
i) pick-up antenna
ii) demodulator
iii) amplifier
iv) all of these
b) Which of the following statements is wrong?
i) The attenuation of surface waves increases with an increase in frequency.
ii) The phenomenon involved in sky wave propagation is similar to total internal reflection.
iii) Space wave mode of propagation is used in satellite communication.
iv) Sky wave propagation is useful only in the range of frequencies 30 to 40 MHz,
Answer:
a) iv) all the these
b) iv) sky wave propagation is useful only in the range frequencies 30 to 40 MHz.
Question 17.
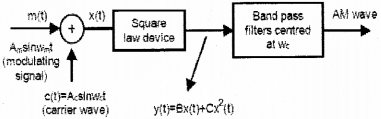
Draw the labeled block diagram of an amplitude modulator for obtaining AM wave. (Say – 2016)
Answer:
Question 18.
A message signal of frequency 10 KHz. and peak voltage 10V is used to modulate a carrier of frequency 1 MHz. and peak votage 20V. Find the modulation index. (March – 2017)
Answer:

We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Communication Systems help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Communication Systems, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.