Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter is part of Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Kerala. Here we have given Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter.
Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Question 1.
Light meters in photographic cameras make use of photoelectric effect. (March – 2010)
a) What is photoelectric effect?
b) Which of the following is a photosensitive material?
a) Quartz
b) Caesium
c) Germanium
d) Silicon
c) Represent graphically the variation of photoelec-tric current with the intensity of incident radiation.
d) Red light however bright, cannot produce the emission of photoelectrons from a clean zinc sur-face. But even a weak ultraviolet radiation can do.
Do you agree with statement? Why?
Answer:
a) The phenomenon of emission of photoelectrons due to the interaction of matter with radiation is called photo electric effect,
b) Caesium
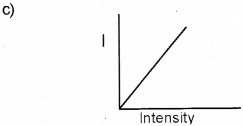
d) Yes, the frequency of ultraviolet light is greater than the red light.
Question 2.
According to de-Efroglie, matter exhibits particle as well as wave nature.
a) What will be the de Broglie wavelength of a mov-ing particle and that of a photon?
b) Name the experiment which proves the wave na-ture of electrons. Illustrate the experiment, with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
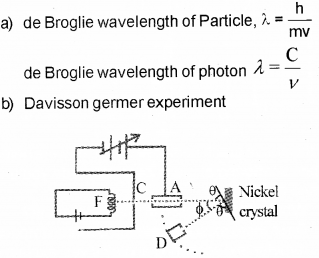
Aim
To confirm the wave nature of electron.
Experimental setup
The Davisson and Germer Experiment consists of filament ‘F’, which is connected to a low ten-sion battery. The Anode Plate (A) is used to accelerate the beam of electrons .A high voltage is applied in between A and C. ’N’ is a nickel crystal .D is an electron detector .It can be rotated on a circular scale. When electron incident on the nickel crystal, it undergose for interference. One of the important property of wave nature is interference. Thus wave nature of electron is established by this experiment.
Question 3.
To emit a free electron from a metal surface a minimum amount of energy must be supplied. (March – 2011)
a) This energy is called ………………
b) State three methods to supply this energy to the free electron.
c) When light of frequency 7.21 x 1014 Hz is incident on a metal surface, the maximum speed of the ejected electrons is 6 x 105 m/s. Calculate the threshold frequency forthe metal.
Answer:
a) Work function
b) Thermionic emission, field emission, photo electric emission.
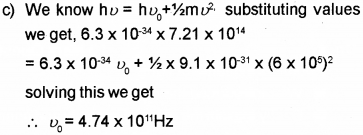
Question 4.
Einstein was awarded Nobel Prize in 1921 for his work on photoelectric effect. (Say – 2011)
a) What is meant by photoelectric work function?
b) Which of the following is not a photosensitive material for visible light?
a) Sodium
b) Magnesium
c) Rubidium
d) Caesium
c) Write down Einstein’s photoelectric equation and explain the symbols.
d) Following graph is obtained in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Which characteristics of incident radiation is kept constant in this experiment?
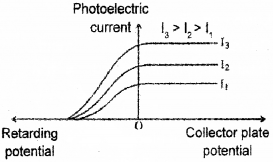
Answer:
a) The work function of a metal is the minimum energy required by light to liberate electrons from the surface of metal. It is given as f = hu0
b) Magnesium

d) Stopping potential is same. Hence fixed ¡s frequency.
Question 5.
Read the following statements and write whether they are TRUE or FALSE. (March – 2012)
a) Matter waves are electromagnetic.
b) When wavelength of incident light is decreased .the velocity of emitted photoelectrons increases.
c) Alkali metals are most suitable for photoelectric emission.
d) Davisson-Germer experiment proved the particle nature of electrons.
Answer:
a) False
b) True
c) True
d) False
Question 6.
Given below is the graph between frequency (u) of the incident light and maximum kinetic energy (EK) of emitted photoelectrons.
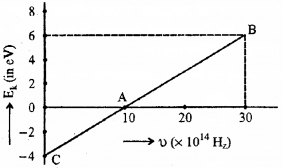
a) Define the terms-work function and threshold frequency.
b) Find the values of
i) threshold frequency and
ii) Work function from the graph,
Answer:
a) Work function
The minimum energy required by an electron to escape from the metal surface is called work function of the metal.
Threshold frequency
The minimum frequency required to produce photoelectric effect is called the threshold frequency.

Which means that the eq (1) gives straight line graph.
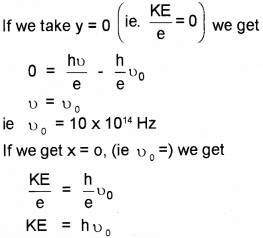
Which means that at x = 0, we get kinetic energy.
∴ Kinetic energy = 4 eV
Question 7.
The wavelength associated with a particle is called the de Broglie wavelength. From Bohr’s postulate of quantization of angular momentum arrive at an ex-pression for the wave length of an orbital electron. Comment of the result. (Say – 2012)
Answer:
According to Bohr’s postulate we can write
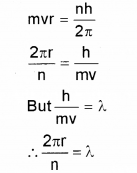
The quantised electron orbits and energy states are due to the wave nature of the electron.
Question 8.
Einstein got Nobel prize in physics in 1921 for his explanation of photoelectric effect.
a) Write down Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
b) Draw a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident readiation. How the value of Plank’s constant can be deter-mined from the graph?
Answer:
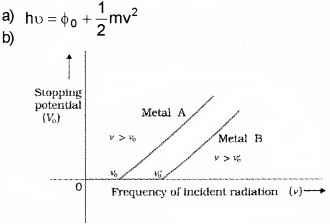
The slope of above graph gives h/e. when we multply slope with electronic charge, we get the value of h.
Question 9.
Photon is a quanta of light. (March – 2013)
a) Who introduced the concept of photon?
b) Briefly explain the effect of intensity and energy of the incident radiation of the photo electric effect.
Answer:
a) Max Plank
b) When the intensity of incident light increases, number of photons emitted from the metal surface also increases.
When the frequency of incident light increases, kinetic energy of emitted photon also increases.
Question 10.
Moving particles of matter should display wave like properties under suitable conditions. (Say – 2013)
a) Name the scientist who put toward this hypothesis.
b) Which experiment established the wave nature of particles?
c) A photon and electron have got the same wavelength. Explain which has greater total energy,
d) Calculate the frequency associated with a pho-ton of energy 3.3 x 10-20 J. [h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js]
Answer:
a) Louis – de – Brogle
b) Davisson and Germer experiment
c) Total energy of photon Ep = hu

Question 11.
Albert Einstein, the great physist proposed a clear picture to explain photoelectric effect. (March – 2014)
a) Explain Einstein’s photo electric equation.
b) Name the quanta of light.
Answer:
a) According to quantum theory, light contain photons having energy he:, when a photon of energy hvincidents on a metal surface, electrons are liberated. A small portion of the photon energy is used for work function (Φ)and remaining energy is appeared as K.E of the electron.
By law of conservation of energy, we can write, Photon energy = work function + K.E of electrons
![]()
b) Photon
Question 12.
De Brogue proposed the wave nature of electrons suggesting matter waves.
Find the momentum, speed and De-Brog lie wave length of an electron with Kinetic energy of 120 eV.
Answer:
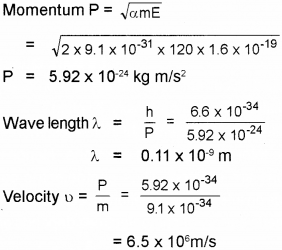
Question 13.
According to wave nature of matter, there is a wave associated with every material body. (Say – 2014)
a) What is the wavelength of electron when it is accelerated by a voltage of 54V.
b) Mention any two differences between light wave and matter wave.
Answer:
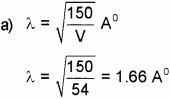
b)
| Lightwave | Matter Wave |
| i) Light wave is visible to human eye ii) Light wave can produce photo electric effect | Matter-wave is not visible to human eye Matter wave can’t produce photo electric effect |
Question 14.
A) Work function of a metal is the (March – 2015)
a) energy required by an electron to get absorbed in the metal surface.
b) minimum energy required by an electron to escape from the metal surface,
c) energy required by an electron to be retained in the metal surface.
d) maximum energy required by an electron to escape from the metal surface.
B) Write Einstein’s Photo-Electric Equation and explain the terms in it.
C) All Photo electrons are not emitted with the same energy as the incident photons. Why?
Answer:
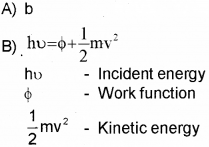
C) There is work function for every metal. Hence energy of incident photon is used for work function and K.E. Hence K.E. of emitted electron will not be same as incident photon.
Question 15.
a) What is the Broglie hypothesis?
b) Write the formula forde Broglie wavelength.
c) Calculate de Broglie wavelength associated with an electron accelerated by a potential difference of 100 volts.
Given mass of the electron = 9.1 x 10-31 kg, h = 6.634 x 10-34 JS, 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19J
Answer:
Moving particles of mattershould display wavelike properties under suitable conditions.
The waves associated with material particles are known as matterwaves or de-Broglie waves.
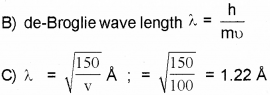
Question 16.
a) The work function of a metal is 6 eV. If two photons each having energy 4eV strike with the metal surface. (March – 2016)
i) will the emission be possible?
ii) why?
b) The waves associated with matter is called matter waves. Let Ae and Ap be the de-Broglie wavelengths associated with electron and proton respectively. If they are accelerated by same potential, then

Answer:
a) i) No
ii) The energy of incident photons is less than the work function (h1 < Φ0). Hence emission is not possible
b) λe > λp, (i)
Question 17.
A) The wavelength of matter waves is called de Broglie Wavelength. (Say – 2016)
a) An a-particle, a proton and an electron having de Broglie wavelengths la, lp and le respectively are moving with the same momentum. Then

b) Thede Broglie wavelength of a ball of mass 0.12 kg is 2.76 x 10-34m. Calculate the speed of the ball. (h = 6.625 x 10-34 Js)
OR
B) Photoelectric current depends on the intensity of incident light.
a) The maximum current emitted by a photoelectric material is called
i) Emitter current
ii) Collector current
iii) Saturation current
iv) Peak current
b) Work function of caesium and platinum are 2.14 eV and 5.65 eV respectively. Which one of the two metals has higher threshold wavelength? Justify.
Answer:
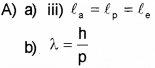
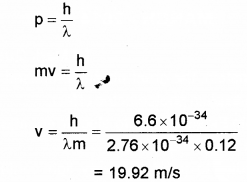
OR
B) a) iii) Saturation point
b) Threshold energy and threshold frequency of caesium is small. Hence caesium has higher threshold wavelength.
Question 18.
The momentum of a photon with wavelength λ is ………………. (March – 2017)
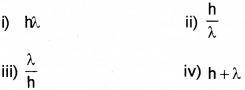
Answer:
![]()
Question 19.
Photoelectric current does not depend on energy of the radiation, but on its intensity. Explain.
Answer:
If the intensity of incident light increases, more num-ber of photons interact with electrons. Hence more electrons are emitted. Thus photoelectric current depends on intensity of radiation, not on its frequency. The kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends on frequency by the equation
![]()
Question 20.
Pick the correct material suited for exhibiting photoelectric effect from the following: (Say – 2017)
Arsenic, Copper, Zinc, Gold, Argon
Answer:
Zinc
Question 21.
If ‘h’ represents Planck’s constant, ‘c’ the velocity of light and v is Wave number, then the unit of h c v is (Say – 2017)
i) Newton
ii) Watt
iii) Electron Volt
iv) Pascal
Answer:
iii) Electron volt
Question 22.
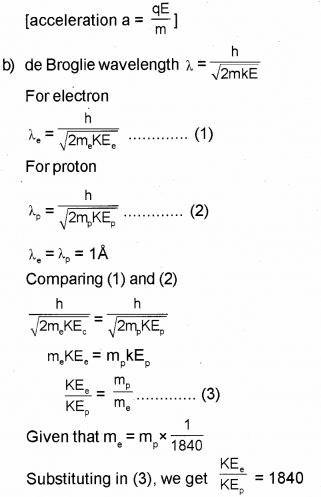
The mass of an electron is 1/1840 part of mass of a proton. When they are subjected to a uniform electric field, they start accelerating. (Say – 2017)
a) Which of them will heave large acceleration?
b) If they start from rest and have the same De Brogue wavelength of 1 angstrom unit, then determine the ratio of their kinetic energies.
Answer:
a) Electron
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.