Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements is part of Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer . Here we have given Plus One Chemistry Previous Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements.
Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
Question 1.
a) How will you prepare Ca(OH)2 and CaC03 from quicklime (CaO)? (March – 2009)
b) Complete the following reactions:
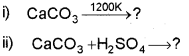
Answer:
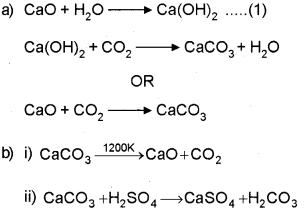
Question 2.
The group 1 metals of the periodic table of elements are collectively called alkali metals. (March – 2010)
a) Write the general electronic configuration of alkali metals.
b) Identify the alkali metal exhibiting anomalous properties. Explain.
C) Alkali metals are normally kept in kerosene. Why?
d) Alkali metals are never found free in nature. Give reason.
Answer:
a) n&
b) Li(Lithiuñi)
This is due to
- small size of the atom when compared to another elements in 1st group.
- Absence of d-orbital
- High polansing power
c) Because of their high reactivity towards air and water, they are normally kept in Kerosene oil.
d) Alkali metals react with water or air to form hydroxides, which are strongly alkaline in nature.
Question 3.
I) State whether the following sentences are true or false: (Say – 2010)
a) Metals in the second group are called alkali metals.
b) Alkali metals are not found in free state in nature.
c) Baking soda is chemically sodium hydrogen carbonate.
d) Portland cement is basically silicates and aluminates of calcium.
II) Fill in the blanks:
a) Molecular formula of Plaster of Paris
b) Beryllium shows the diagonal relationship with
c) The metal present in chlorophyll is
d) Solvay process is associated with the preparation of
Answer:
a) False
b) True
c) True
cTrue
II)
1) CaSO4, 1/2H2O
2) Aluminium
3) Magnesium
4) Sodium carbonate
Question 4.
Monovalent Na+, K+ ions and divalent Ca2+, Mg2+ ions are found in large proportions in biological fluids. (March – 2011)
a) In which part of our body are sodium and potassium ions prominently located?
b) What are the major roles of these Na+ and K+ions in our body?
c) For making which parts of our body is calcium is mainly used?
d) Give the name of the metal present in Chlorophyll.
Answer:
a) Outside the cells, blood plasma, intestinal fluid.
b) Transmission of nerve signals, regulating flow of water.
c) Bones and teeth
d) Magnesium
Question 5
Match the following (Say – 2011)
| A | B | C |
| a) Gypsum | 1) Magnesium | i) Solvay process |
| b) Milk of | 2) Magnesium magnesia | ii) Nerve signal hydroxide transmission |
| c) Washing soda | 3) Sodium | iii) Cement |
| d) Alkali metal | 4) Calcium sulphate | iv) Antacid |
| 5) Sodium carbonate | Violet flame |
Answer:
A – B – C
a – 4 – (iii)
b – 2 – (iv)
C – 5 – (i)
d – 3 – (ii) or (v)
Question 6.
Beryllium shows a diagonal relationship with aluminium. (March – 2012)
a) Mention any two similarities between beryllium and aluminium.
Match the following:
| A | B |
| Sodium carbonate | Chain structure in the solid-state |
| Beryllium chloride | Mild antiseptic |
| Sodium hydroxide | Solvay process |
| Sodium hydrogen carbonate | Castner-Kellnercell |
Answer:
a) 1) The oxides and hydroxides of both Be and Al are amphoteric
2) Both Be and Al reacts with electron-rich species to form complex compounds.
3) Both Becl2 and Alcl3 are strong Lewis acids,
b)
| A | B |
| Sodium Carbonate | Solvay process |
| Beryllium chloride | Chain Structure in the solid-state |
| Sodium hydroxide Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate | Castner- Kellner cell mild antiseptic |
Question 7.
a) Lithium and Magnesium belong to 1st and 2nd groups in the periodic table. They resemble each other in many respects.
i) Name such relationship.
ii) Give any one similarity between Li and Mg.
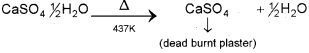
b) A compound of calcium is used in hospitals for setting fracture of bones.
i) Write the name and formula of the above compound.
ii) What is dead burnt plaster?
Answer:
a) 1) Diagonal Relationship
2) Similarity between Li and Mg.
1) Both are hard metals
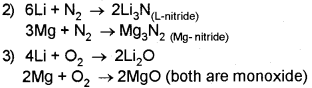
b) i) Plaster of paris – CaS04, 1/2H2O
ii) Plaster of paris on heating above 437K. It becomes anhydrous CaSO4 and is known as dead burnt plaster.
Question 8
Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals belong to the s-block of the periodic table. (March – 2013)
a) Name the process used for the industrial preparation of sodium carbonate.
b) The above-mentioned method is not suitable for the preparation of potassium carbonate. Give the reason.
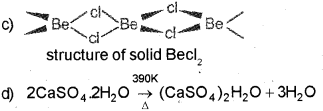
c) Draw the chain structure of beryllium chloride in solid-state.
d) Write the chemical equation showing the preparation of Plaster of Paris from gypsum.
Answer:
a) Solvay Ammonia Soda Process
b) Pot. Carbonate cannot be prepared by Solvay process because KHCO3 is much more soluble in water than NaHCO3
Question9
a) Fill in the blanks: (Say – 2013)
i) The suspension of a magnesium compound in water is used as an antacid. The compound is
ii) A mixture of calcium oxide (Quick lime) and Socia (NaOH) is called
b) When CO2 is passed through lime water ¡t turns milky. On passing excess of CO2, the milky colour disappears. Give the chemical reactions involved in the processes.
Answer:
a) i) Magnesium hydroxide
ii) Soda lime
b) When CO2 is passed through lime water it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 ↓ + H2O
On passing excess CO2, the precipitate dissolves to form calcium hydrogen carbonate.
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
Question 10.
a) Give reasons. (March – 2o14)
i) KO2 is paramagnetic.
ii) Solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia are blue in colour.
b) Match the following:
| A | B |
| Quicklime Plaster of Paris Bleaching powder Slaked lime | Ca(OCI)2 CaO Ca(OH)2 CaSO4. 1/4H20 CaCI2 CaCO3 |
Answer:
a) i) KO2 contains superoxide O2 which is para-magnetic because of one unpaired electron in π*2p molecular orbital.
ii) The blue colour of the solution is due to the ammoniated electron which absorbs energy in the visible region of light and thus imparts blue colour to the solution.
M + (x + y)NH3 → [M(NH3)+ + [e(NH3)y]
b) Quicklime – CaO
Plaster of Paris – CaSO4, 1/2 H2O
Bleaching powder – Ca(OCI)2
Slaked lime – Ca(OH)2
Question 11.
a) The reactivity of alkali metals towards air is different for different metals. How do alkali metals react with air? (August – 2014)
b) Match the following :
| A | B |
| i) Sodium Hydroxide | p) Dead burnt plaster |
| ii) Anhydrous calcium sulphate | q) Slaked lime |
| iii) Calcium hydroxide | r) Quick lime |
| iv) Sodium bicarbonate | s) Caustic soda |
| t) Baking soda |
Answer:
a) The alkali metals tarnish in dry air due to the formation of their oxides which in turn react with moisture to form hydroxides.
They burn vigorously in oxygen forming oxides. Lithium forms monoxide, sodium forms perox-ide, the other metals form superoxides.
The superoxide O2 ion is stable only in the presence of large cations such as K, Rb, Cs.
4Li + O2 → 2Li2O (oxide)
2Na + O2 → Na2O2 (peroxide)
M + O2 → MO2 (superoxide)
(M = K, Rb, Cs)
b)
| i) Sodium hydroxide | s) Caustic soda |
| ii) Anhydrous calcium sulphate | p) Dead burnt plaster |
| iii) Calcium hydroxide | q) Slaked lime |
| iv) Sodium bicarbonate | t) Baking soda |
Question 12.
a) The metal present in the chlorophyll of plants is …………… (March – 2015)
b) Give any two uses of caustic soda.
c) When sodium metal dissolves in liquid ammonia, it gives a deep blue coloured solution. Explain the reason.
Answer:
a) Magnesium (Mg)
b) 1) In the manufacture of soap, paper, artificial silk and a number of chemicals.
2) In petroleum refining.
c) It is due to the ammoniated electron which absorbs energy in the visible region of light and thus imparts blue colour to the solution.
Na + (x+y)NH2 → [NatNH3]x]+ + [e(NH3)y]
Question 13.
Alkali metals are highly reactive due to their low ionization enthalpies. (Say – 2015)
a) The alkali metal which acts as the strongest reducing agent in aqueous solution is ………….
b) How is sodium carbonate prepared using Solvay process? Is this method suitable for the preparation of potassium carbonate? Justify.
Answer:
a) Lithium.
b) In Solvay process, sodium carbonate is prepared by passing CO2 to a concentrated solution of sodium chloride saturated with ammonia to form ammonium hydrogen carbonate. This reacts with sodium chloride to form ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate on heating gives sodium carbonate.
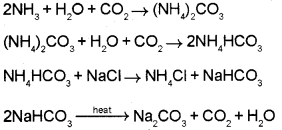
This method cannot be extended to the manufacture of potassium carbonate. Because potassium bicarbonate is too soluble to be precipitated by the addition of ammonoum hydrogen carbonate to a saturated solution of potassium chloride.
Question 14.
a) Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give blue coloured solutions. Why? (March – 2016)
b) Plaster of Paris is an important compound of Calcium.
i) Give the chemical formula of plaster of Paris.
ii) Identify the property of plaster of Paris which helps in plastering of broken bones.
Answer:
a) Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to the ammoniated electron which absorbs energy in the visible region of light and thus imparts blue colour to the solution.
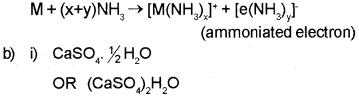
ii) Plaster of Paris has a remarkable property of setting with water. On mixing with an adequate quantity of water it forms a plastic mass that gets into a hard solid in 5 to 15 minutes. Hence, it is used for immobilising the affected part of the organ where there is a bone fracture or sprain.
Question 15.
a) Match the following: (Say – 2016)
| A | B |
| i) Caustic soda ii) Sodium carbonate iii) Magnesium hydroxide iv) Sodium bicarbonate | 1) Antacid 2) Mild antiseptic 3) Castnerkellnercell 4) Solvay process |
b) Cement is an important building material. Explain the manufacture of cement.
Answer:
a) i – 3;
ii – 3;
iii – 1;
iv – 2
b) The raw materials for the manufacture of cement are limestone and clay. When clay and lime stone are strongly heated together they fuse and react to form ‘cement clinker’. This clinker is mixed with 2-3% by weight of gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O) to regulate the setting time and is then ground to a very fine powder.
Question 16.
The s-block of periodic table constitutes alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. (March – 2017)
a) The hydroxides and carbonates of sodium and
potassium are more soluble than that of corresponding salts of Magnesium and Calcium. Explain.
b) Write the chemical name of the following:
i) Caustic soda
ii) Baking soda
iii) Slaked lime
iv) Milk of lime
Answer:
a) Due to the greater ionic size of Na+ and K+ ions compared to the Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions the hydroxides of sodium and potassium have lower lattice enthalpies than the hydroxides of calcium and magnesium [The anion being common (OH ) the cationic radius will influence the lattice enthalpy]. The decrease in lattice enthalpy is greater than the decrease in hydration enthalpy. Lower the lattice enthalpy greater will be the solubility,
b) i) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
ii) Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
iii) Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
iv) Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)
We hope the Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.