Kerala Plus One Botany Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Respiration in Plants
Question 1.
Glycolysis and Krebs’ cycles are the two important steps in aerobic respiration. Suggest where exactly in the cell these events take place. (MARCH-2010)
Answer:
Glycolysis – Cytoplasm,
Krebs cycle – Mitochondria
Question 2.
Plants are living organisms respiring just like animals taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide. But, they are without any organ for this purpose. Mention any two reasons for it. (MARCH-2010)
Answer:
Plants have some pores on (stomata) its leaf, day time those pores gets open in sunlight and takes C02 and converts into 02.
In animals 02 transported with the help of Hb .that is not needed in plants. Hence organ system as animals is wasteful to plants. Therefore plants have mitochondria for cellular oxidation and takes 02 for this.
Question 3.
Suggest a method for finding out the biochemical compound used as the respiratory substrate in plants. (MARCH-2010)
Answer:
It mainly based on Respiratory quotient
(RQ= Volume of C02 evolved/ Volume of 02 consumed)
Question 4.
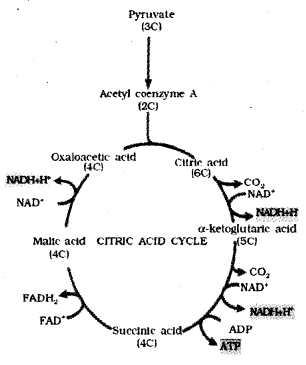
Diagrammatic representation of kerbs cycle is given below with some omissions. (SAY-2010)
a) Complete the diagram by filling the gaps.
b) Where does the substrate level phosphorylation occur in kerbs cycle?
Answer:
a) 4c – Oxaloacetic acid
4c – Malic acid / Fumaric acid
5c – α Ketoglutaric acid
b) During the formation of succinic acid / conversion of succinyl co.A to succinic acid/ Conversion of 5c to 4c compound.
Question 5.
Breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid is called glycolysis. Draw the scheme of glycolysis using the following, starting from glucose ending in pyruvic and 1,3-biphosphoglyceric acid, glyceraldehyde 3 phospate ![]() dihydroxy acetone phosphate, fructose, 1, 6- biphosphate, 3 phosphoglycerate, fructose-6, phosphate, phosphoenol pyruvate, glucose-6 phosphate, 3 phosphoglyceric acid. (MARCH-2011)
dihydroxy acetone phosphate, fructose, 1, 6- biphosphate, 3 phosphoglycerate, fructose-6, phosphate, phosphoenol pyruvate, glucose-6 phosphate, 3 phosphoglyceric acid. (MARCH-2011)
Answer:

Question 6.
Break down of glucose to pyruvic acid is glycolysis (SAY-2011)
a) How many molecules of pyruniv acid is produced from a glucose molecule?
b) Write the steps in which ATP is used during glycolysis.
c) The TCA cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl group with OAA and water to yield citric acid.
a) Name the enzyme catalysing the reaction.
b) How many NADH + H+ molecules are produced in TCA cycle?
c) How many FADH2 molecules are produced?
d) How many ATP molecules are produced?
Answer:
a) 2 molecules of pyruvic acid
b) 1) conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
2) fructose-6-phophate to fructose 1,6-biphosphate
c) a) citrate synthase
b) 6NADH2
c) 2FADH2
d) 2ATP
Question 7.
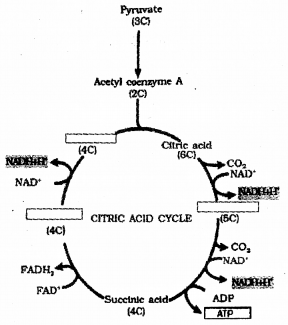
Observe the given figure and answer the questions. (MARCH-2012)
Answer:
a) Identify the cycle and name the scientist who traced the pathway.
b) Complete the cycle by filling A, B, C & D in the boxes.
c) How many NADH and FADH2 are yielded during the complete oxidation of one molecule of pyruvate by this pathway?
a) Kerb’s cycle / tricarboxylic acid cycle / Hans kreb
b) A – Acetyl co-enzyme
B – Citric acid
C – Succinic acid
D – Oxaloacetic acid / OAA
c) 4 molecules of NADH
1 molecule of FADH2
Question 8.
Observe the incomplete schematic representation given below and answer the questions. (MARCH-2012)
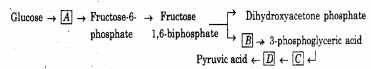
a) Identify this pathway common for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
b) Complete the scheme by filling the boxes A, B, CandD.
c) Mentionthethreemajorwaysinwhichdifferentcells handle pyruvic acid produced by this pathway.
Answer:
a) Glycolysis / EMP Pathway
b) A – Glucose 6 – phosphate
B – Triose phosphate / glyceraldehyde – 3 Phos-phate
C – 2 – Phosphoglyceric acid
D – 2 – Phosphoenolpyruvic acid
c) Lactic acid fermentation in muscle cells.
Alcoholic fermentation in Yeast.
Aerobic respiration.
Question 9.
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration starts with a common pathway. Identify the pathway and its end product. (SAY-2012)
Answer:
Glycolysis or EMP Pathway
Pyruvic acid
Question 10.
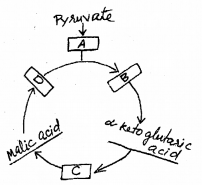
Observe the illustration given below and answer the following questions. (SAY-2012)
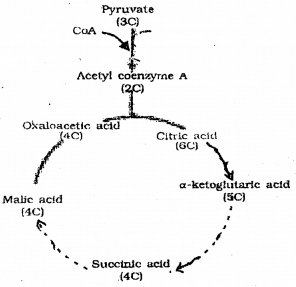
a) Identify the cyclic pathway.
b) Where does it occur?
c) Identify the steps of this pathway in which de-carboxylation takes place.
Answer:
a) Kreb’s cycle or T.C.A. or Citric acid cycle.
b) Mitochondria
c) Conversion of Pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co. A.
Conversion of citric acid to α – ketoglutaric acid.
Conversion of α – ketoglutaric acid to succinic acid.
Question 11.
Analyze the given statements and correct them with respect to the underlined words. (MARCH-2013)
a) Respiration is an anabolic pathway.
b) The site of perception of light by a plant for a photoperiodic response is a flower.
Answer:
a) amphibolic pathway
b) leaf
Question 12.
Breakdown of glucose in respiration is listed under glycolysis and Krebs cycle. (MARCH-2013)
a) Locate the site of glycolysis and Krebs cycle in the cell.
b) Glycolysis is a partial oxydation process. Justify.
Answer:
a) glycolysis-cytoplasm, krebs cycle-mitochondria
b) Glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form 2 molecules of pyruvic acid
Question 13.
A) Oxidative phosphorylation is an important event in cellular respiration. (SAY-2013)
a) Which organelle is associated with this process?
b) Name the phase of cellular respiration that is com-mon to both aerobic and anerobic condition.
c) Draw the schematic representation of that phase.
Answer:
A) a) Mitochondria
b) Glycolysis
c)
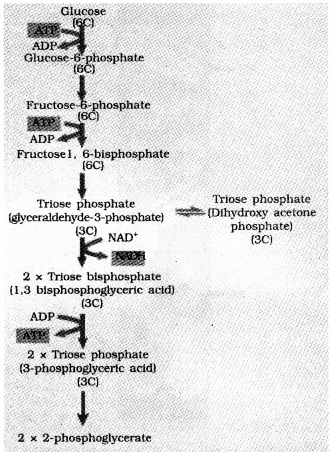

Question 14.
During terminla oxidation, electrons in the hydrogen atoms are transported to the oxygen through a series of electron carriers in ETS. The electron carriers are given below FMN, FAD, Ubiquinone, FeScyt a, cyt b, cyt c, cyt a3, etc. (SAY-2013)
a) Briefly explain ETS with schematic representation.
b) Where does ETS occur?
Answer:
a)
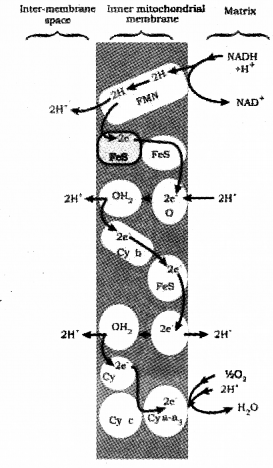
The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another is called the electron transport system (ETS).
Reduced coenzyme like NADH(complexl) in the mitochondrial matrix is oxidised and release 2 electrons and 2protons Electrons and protons are transferred to FMN, it reduced to FMNH2 It breaks and releases protons and electrons .protons goes to inter membrane space but electrons reaches ubiquinone. Ubiquinone also receives reducing equivalents via FADH2 (complex “).
The reduced ubiquinone is then oxidised with the transfer of electrons to cytochrome c via cytochrome Jbc1 complex(complex III). Cytochrome c acts as a mobile carrier for the transfer of electrons between complex III and IV. Complex IV refers to cytochrome c oxidase complex containing cytochromes a and a3, Oxygen acts as the final hydrogen acceptor.
In ETS the energy of oxidation-reduction is utilised for the production of proton gradient required for phosphorylation . This process is called oxidative phosphorylation.
b) It is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Question 15.
Anaerobic respiration is also occurs in animal cells. Suggest an occasion for this. (MARCH-2014)
Answer:
During streneous exercise 02 inedequecy is experi-ence in Skeletal tissues. In such a case the respira-tion is anaerobic.
Question 16.
Glycolysis is present in all organisms and it is the only process of respiration in anaerobic organisms. (MARCH-2014)
a) What is glycolysis?
b) Where does glycolysis occur?
c) Glycolysis is a partial oxidation. Justify.
d) Calculate the total number of ATP molecules synthesized in glycolysis by the partial oxidation of one molecule of glucose.
Answer:
a) It is the breakdown of glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid.
b) It is the partial oxidation takes place in cytoplasm
of the cell.
c) It takes place in the absence of 02.
d) The net gain of ATP formed is 10 – 2 = 8ATP molecules.
Question 17.
Various compounds in the citric acid cycle are given below: (Oxaloacetic acid, citric acid, succinyl CoA, pyruvate, Acetyl CoA, maleic acid, – Ketoglutaric acid, succinic acid) (SAY-2014)
a) Arrange them in order and draw a complete cycle.
b) Who traced this cycle?
c) Where does it take place?
Answer:
a)
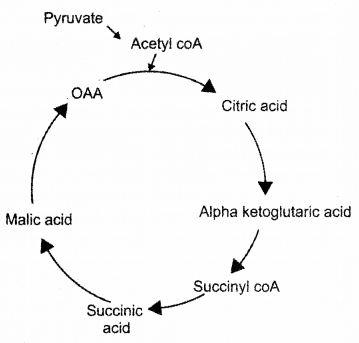
b) Hans kreb
c) Mitochondrial matrix
Question 18.
The metabolic pathway through which electrons pass from one electron carrier to another is called the electron transport system. Some electron acceptors are given below: (SAY-2014)
(Fes, Cyt b, FMN, FAD, cyt a, NADH, Ubiquinone, cyt c, cyt a3, H20).
a) Arrange them in the correct order.
b) Name the site of ETS.
c) What is the role of 02 in ETS?
Answer:
a)
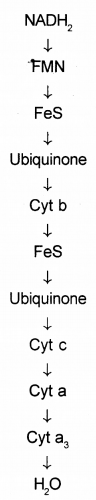
b) Inner membrane of mitochondria
c) 02 combines with electrons and protons forms .metabolic water. This is called Terminal oxidation.
Question 19.
Out of the four statements given below related to respiration, the correct statements are : (MARCH-2015)
i) Though respiration has traditionally been consid-ered a catabolic process, it would be better to consider it as an amphibolic pathway.
ii) In muscles when oxygen is inadequate, lactic acid is reduced to pyruvic acid.
iii) When fats are used in,respiration, the RQ is greater than one.
iv) In respiration, the energy of oxidation-reduction is utilized for phosphorylation.
a) i & ii
b) ii & iii
c) iii & iv
d) i & iv
Answer:
d) i & iv
Question 20.
Two crucial events of aerobic respiration takes place in two parts of mitochondria. Locate the two parts and mention the two events in one or two sentences each. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Matrix and inner membrane of mitochondria The complete oxidation of pyruvate by the stepwise removal of H2 atoms and leave three molecules of C02 that takesplace in matrix.
Oxidative phosphorylation and terminal oxidation occurs in inner membrane of mitochondria.
Question 21.
Mention the fate of pyruvic acid in respiration. (SAY-2015)
(Hint: Any two points)
Answer:
Pyruvic acid is used in three ways in respiration. Alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation and aerobic respiration.
In aerobic respiration pyruvic acid enters into krebs cycle and later forms C02 and water
Question 22.
The following compounds are intermediate in Glycolysis or in Kreb’s cycle. Write them in proper column of the table.
Fructose-6-phosphate, Citric acid, Phosphoenol pyruvate, Malic acid. (SAY-2015)
| Glycolysis’ | Kreb’s cycle |
Answer:
| GLYCOLYSIS | KREB’S CYCLE |
| Frucose -6 phosphate, phosphoenol pyruvate | Malic acid,citric acid |
Question 23.
“Respiration is an amphibolic pathway.” Evaluate the statement. (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
In amphibolic pathway both catabolism and anabolism are involved.
In respiratory pathway, fat is breakdown into fatty acid and glycerol, fatty acid again splits into acetyl coA. If body requires the synthesis of fat, acetyl CoA withdraws from the pathway and used in the synthesis of fat.
Question 24.
Fermentation if the incomplete oxidation of pyruvic acid. Find the difference between two types of fermentations in micro-organisms. (MARCH-2016)
Answer:
In alcoholic fermentation, glucose undergoes incomplete oxidation in the presence of yeast and forms ethyl alcohol and C02.
In lactic acid fermentation, glucose undergoes incomplete oxidation in the presence of lactobacillus and forms lactic acid.
Question 25.
Match the following (SAY-2016)
| A | B |
| a) Stomatal Closure | i) Cytoplasm |
| b) Citric Acid | ii) Plasticity |
| c) Glycolysis | iii) Ethylene |
| d) Heterophylly | iv) Kreb’s cycle |
| v) ABA |
Answer:
| A | B |
| a) Stomatal closure b) Citric acid c) Glycolysis d) Heterophylly | v) ABA iv) Kerb’s cycle i) Cytoplasm ii) Plasticity |
Question 26.
“There are several reasons why plants can get along without respiratory organs”. Justify the statement giving three reasons. (SAY-2016)
Answer:
a) Plant do not have great demands for gaseous exchange,the rate of respiration is far lower than that of animals.
b) The availability of oxygen is not a problem, because oxygen is released within the cell during photosynthesis.
c) Diffusion that helps the movement of gases.
Question 27.
Fill up the flow chart of glycolysis given below using the list of intermediary compounds given in the bracket. (SAY-2016)
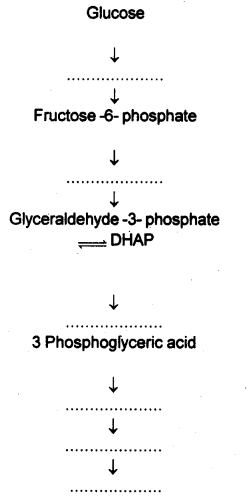
(Phosphoenol pyruvic acid, Glucose -6- phosphate, Pyruvic acid, Fructose -1,6- biphosphate, 2 Phosphoglyceric acid, 1,3 Biphosphoglyceric acid)
Answer:
- Glucose-6-phosphate
- Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
- 1,3- bisphosphog lyceric acid
- 2-phosphoglyceric acid
- Phosphoenol pyruvic acid
- Pyruvic acid
Question 28.
Glycolysis is the partial oxidation of glucose to produce two molecules of pyruvic acid. (MARCH-2017)
a) Where does glycolysis occur?
b) Steps of glycolysis are given below. Fill up the blank boxes.
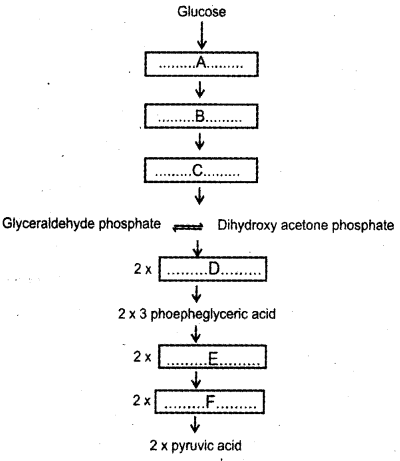
Answer:
Cytoplasm(Cytosol)
b) A. Glucose-6-phosphate
B. Fructose -6- phosphate
C. Fructose-1,6-biphosphate
D. 1,3bisphosphoglycericacid/Triosebisphosphate
E. 2 phosphoglycerate
F. Phosphoenol pyruvate
Question 29.
The complete oxidation of pyruvic acid yields three molecules of C02 by a cyclic process in the matrix of mitochondria. (MARCH-2017)
a) Who first develop this cycle?
b) Draw a diagrammatic sketch of the identified cycle.
Answer:
a) Hans Krebs
b)