New Simplified Chemistry Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Water
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Simplified ChemistryChemistryPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Exercise
Question 1.
State the sources of water
(a) on the earth’s surface
(b) below the earth’s surface.
Answer:
(a) Sources of water on the earth’s surface are —
- Snow, frost — Snow and frost are the natural forms of water present. They are found in the solid state.
- Rain water — The purest form of natural water almost free from impurities is rain water.
Rain water may dissolve oxygen, nitrogen & carbon dioxide gas forming weak acids. In industrial regions, nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide evolved may dissolve in rain water forming nitric acid & sulphuric acid which causes acid rain. - River water — It is one of the impure forms of natural water since most forms of surface water enters into river water. It contains impurities such as sand partides, organic matter, bacteria, mineral salts which dissolve after soil erosion & dissolved gases.
- Lake water — It is another impure form of natural water which also contains impurities and other soluble salts.
- Sea water — The most impure form of natural water containing over 3% soluble salts including sodium chloride. It also contains salts of calcium & magnesium.
(b) Sources of Water below the earth’s surface are —
- Well water — Above the impervious rocky layers, of the earth’s surface is well water which contains soluble impurities.
- Spring water — Natural water accumulated above the rocky layers of the earth which forcefully comes out under pressure from the earth’s surface is spring water & contains soluble salts & minerals.
Question 2.
Give the importance of water in
(a) life processes
(b) household purpose
(c) fire fighting
(d) transportation.
Answer:
The importance of the Water is as follows :
(a) Life processes — Water is used by all plants, animals & humans for carrying out various metabolic processes including photosynthesis by plants & excretion by animals & humans.
(b) Household purposes — Water finds numerous applications, such as watering plants, washing clothes, cooking, bathing, cleaning etc.
(c) Fire fighting — Water is used for extinguishing fires either directly or as a constituent in a fire extinguisher.
(d) Transportation — Water serves as a habitat for marine life i.e. preferred place for an organism to live.
Question 3.
Explain how water plays an important role in
(a) industry
(b) agriculture.
Answer:
(a) Uses of Water in Industry :
- Water generates electricity in hydroelectric power stations.
- Water generates steam in boilers, used for various industrial purposes.
- Water finds application in chemical & other industries for cooling & cleaning operations.
(b) Uses of Water in Agriculture :
- In agriculture water finds importance in irrigation, production of crops & as a medium for spraying pesticides.
Question 4.
Give the occurrence of water in the three different states i.e. solid, liquid and gaseous.
Answer:
The Occurrence of water in three different states are :
- Solid state — As snow and frost.
- Liquid state — In sea water, river water and lake water.
- Gaseous state — As water vapour in air the amount depending on climatic conditions.
Question 5.
Draw a labelled diagram to show the change of state of water from solid state to liquid state to gaseous state starting from ice.
Answer:
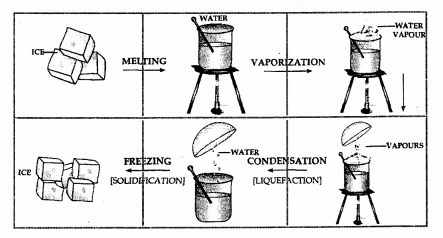
Question 6.
Explain the term water cycle. State the main points to show how water moves from the earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to the earth’s surface as rain.
Answer:
The water cycle is a natural process by which the circulation of water takes place from the earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to the earth’s surface as rain water.
The Process of water cycle is discussed below :
From The Earth’S Surface – To The Atmosphere
- Evaporation — The sun’s rays fall on the earth & warm its surface & the air above it.
The heat evaporates the water from the streams, rivers & the sea. - Water [mainly in the form of water vapour] is also added to the atmosphere by —
(a) Respiration by living organisims Glucose + Oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
(b) Burning of fossil fuels —
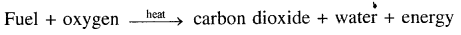
- Formation of clouds — The water vapour along with the warm air rises upwards, where at higher altitudes it condenses into small droplets of water forming clouds.
Back To The Earth’S Surface – As Rain Water
- Formation of rain — The clouds float in the atmosphere & when the size of the water droplets increases they fall down on the earth as rain water.
- Rain water falls into streams — The rain water is absorbed by the soil collects underground & flows into streams.
- Stream water enters rivers & seas — The stream water finds its outlets into rivers & later enters into the seas & oceans.
- River & sea water evaporates forming clouds and thus continuing the water cycle.
Question 7.
Give a reason why water is considered a universal solvent.
Answer:
Water is a polar covalent compound. When it comes in contact with any substance it breaks the electrostatic forces holding the molecules of that substance. Thus, the molecules break loose from the substance and hence dissolve in water. Thus, water is called a universal solvent and an alkali is not.
Question 8.
Define the term –
(a) solute
(b) solvent
(c) solution with reference to addition of sodium chloride to water.
Answer:
(a) Solute — The substance which dissolves or disappears in the solvent i.e. liquid to form a solution is called a solute. e.g. sodium chloride.
(b) Solvent — The liquid or medium of dissolution which allows the solute to dissolve in it, so as to form a solution is called a solvent, e.g. water.
(c) Solution — A homogenous mixture of a solute in a solvent is called a solution.
Question 9.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of addition of copper sulphate to water. Label the solute, solvent and solution in the same.
Answer:
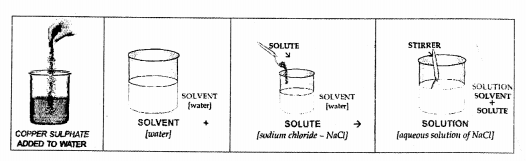
Question 10.
From the following substances given below state which will form a solution in the same.
(a) sodium carbonate
(b) calcium carbonate
(c) charcoal powder
(d) sodium sulphate
(e) table salt
(f) powdered particles of lead from a lead pencil
(g) iron powder
(h) copper filings
(i) sand particles
(j) honey
Answer:
(a) sodium carbonate
(d) sodium sulphate
(e) table salt
(j) honey
Question 11.
Name two gases each
(a) which are soluble in water
(b) which are insoluble in water.
Answer:
(a) The gases which are soluble in water are Carbon dioxide and chlorine
(b) The gases which are not soluble in water are Nitrogen, hydrogen
Question 12.
If ‘X’ g. of potassium nitrate is added to 100 g. of water at 60°C and the salt dissolves completely then —
(a) is ‘X’ g. the solubility of potassium nitrate at 60°C.
(b) is the solution formed – saturated or unsaturated
(c) if on addition ‘X’ + ‘Y’ g. of potassium nitrate to the same amount of water at the same temperature and the solute now just remains behind after stirring then –
(d) is the solution now – saturated or unsaturated
(e) is ‘X’ + ‘Y’ g. the solubility of potassium nitrate.
Answer:
Add ‘X’ g. of solute i.e. potassium nitrate to 100 g. of water 60°C.
- Stir the solute i.e. potassium nitrate in water thoroughly.
- ‘X’ g. of the solute completely dissolves in water.
- Add more solute and again stir thoroughly.
- The solute continues to dissolves.
- Water i.e. the solvent can dissolve more of the solute at the given temperature.
- The solution is therefore is said to be unsaturated.
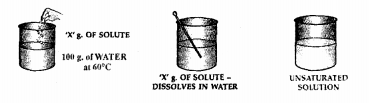
Add more solute to water till on adding an amount ‘X + Y’ g. of the solute i.e. potassium nitrate to 100 g. of water at 60°C.
- The solute just remains behind after stirring.
- The solution is now saturated.
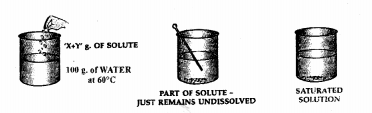
A saturated solution cannot dissolve more of the solute at a given temperature.
Question 13.
State whether the following statements are true or false. If false write the correct statement.
(a) Solubility of most solids – decrease with increase in temperature.
Answer:
False.
Correct — Solubility of most solids – increase in temperature.
(b) Distilled water is potable water.
Answer:
False.
Correct — Drinking water is potable water.
(c) The process to remove germs in water is also called sterilization.
Answer:
True.
Question 14.
Differentiate between chemical pollution and thermal pollution.
Answer:
(a) Chemical pollution — A large number of industrial chemicals which include chemicals from paint, textile & dyestuff industry & various acids & salt solutions enter into water when discharged as industrial wastes.
- Chemical pollutants include — Metallic salt solutions of mercury & lead which cause heavy devastation of marine & plant life.
- Agricultural wastes include — Poisonous pesticides namely fungicides & insecticides which may also enter underground water through the soil.
(b) Thermal pollution — Certain industries such as the iron & steel industry & numerous chemical plants use large amounts of water for varied functions.
- The discharged waste water after going through technical processes – is rendered hot & on entering streams of natural water – enhance growth of harmful biological organisms.
Question 15.
State some important steps to avoid pollution of water.
Answer:
Steps to avoid pollution of water are :
(a) Harmful wastes such as oils & chemicals should not enter into the water.
(b) Proper toilets & sewage systems should be used to prevent human excreta, containing disease causing organisms to enter into the water.
(c) Washing of clothes & bathing should be avoided near water sources.
(d) Planting of trees near water sources including river banks also minimizes pollution.
(e) To minimize thermal pollution the water should be cooled before being discharged as a waste.
(f) Man should be made aware through various awareness programmes & media about the harmful effects of water pollution & ways to control it.
Question 16.
State what is meant by the term ‘conservation of water’. State a few water saving methods, which may be used in the home to conserve water.
Answer:
Conservation of water is the means of preventing wastage of water so that clean water can be obtained by preventing pollution of water and by protecting the sources of water.
Need for conservation — Inspite of large quantities of water on the earth’s surface only a small percentage is potable water fit for human consumption and household purposes.
The need for water is ever increasing and hence all sources of water need to be conserved.
The various methods to conserve the water are :
- Well should be covered and washing and cleaning should be prevented near a well.
- Water saving devices must be used in homes
(a) such as closing running taps and using smaller cisterns in toilets.
(b) checking all leakages in household pipes.
(c) turning off the water tap while brushing teeth and while washing hands.
(d) using less electricity, since power plants also consume substantial amount of water.
Question 17.
Give a reason why :
(a) Conservation of water is essential in spite of the fact that three fourth of the earth’s surface is covered by water.
(b) Polluted water causes disease.
(c) Drip irrigation helps in conservation of water.
Answer:
(a) Because only a small percentage is potable water fit for human consumption and household purposes.
(b) Polluted water acts as a carrier for germs which causes various diseases.
(c) Drip irrigation in agriculture utilizes supply of water in small quantities.
Objective Type Questions
Q.1. Complete the statements by filling in the blanks with the correct word/s.
Question 1.
____is the purest form of water. It may dissolve gases like ____ forming weak acids, (sea water/ lake water/rain water ; chlorine/ammonia/carbon dioxide)
Answer:
Rain water is the purest form of water. It may dissolve gases like carbon dioxide forming weak acids.
Question 2.
Water generates ____ in hydroelectric power stations and ____ in boilers for industrial applications, (carbon dioxide/steam/heat/electricity)
Answer:
Water generates electricity in hydroelectric power stations and steam in boilers for industrial applications.
Question 3.
Water is added to the atmosphere by ____ and ____ (burning of fossil fuels/condensation of vapour/ respiration by living organisms/photosynthesis)
Answer:
Water is added to the atmosphere by burning of fossil fuels and respiration by living organisms.
Question 4.
If potassium nitrate is added to water in a beaker to give a homogeneous mixture, then potassium nitrate is referred to as the ____ water as the ____ and the homogeneous mixture as the ____ (solution/ solute/solvent/saturated solution).
Answer:
If potassium nitrate is added to water in a beaker to give a homogeneous mixture, then potassium nitrate is referred to as the solute, water as the solvent and the homogeneous mixture as the solution.
Question 5.
Water fit for human consumption and drinking purposes is called ____ (distilled water/potable water/rain harvested water).
Answer:
Water fit for human consumption and drinking purposes is called potable water.
Q.2. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, write the correct statement.
1. Sea water contains salts of calcium and magnesium.
Ans. True.
2. Water finds application as a means of transporting goods.
Ans. True.
3. On boiling water exists in the liquid state.
Ans. False.
Correct — On boiling water exists in the gaseous state.
4. Respiration uses up water from the atmosphere.
Ans. False.
Correct — Respiration add up water to the atmosphere.
5. Well water exists below the impervious rocky layers of earth.
Ans. False.
Correct — Well water exists above the impervious rocky layers of earth.
6. Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphate do not form an aqueous solution.
Ans. False.
Correct — Sodium carbonate and sodium sulphate form an aqueous solution.
7. If ‘X’ g. of solute is added to 100 g. of water at t°C and the solution formed is a saturated solution, then ‘X’ g. is the solubility of the solute.
Ans. True.
8. Purification of water is carried out to remove – dissolved gases e.g. carbon dioxide and dissolved minerals like magnesium salts.
Ans. True.
9. Water from rivers and lakes is – potable water.
Ans. False.
Correct — Water from rivers and lakes is impure water.
10. Chemical pollutants include metallic salt solution of mercury and lead.
Ans. True.
Q.3. Match the statements in List 1,1-10 with their correct answer in List II, A to J.

Answer:

Q.4. Explain the meaning of the following terms :
- Rain water harvesting
- Drip irrigation in agriculture
- Saturated solution
- Conservation of water
- Gaseous state of water in air
Answer:
- Rain water harvesting which is a means of utilizing rain water instead of allowing it to be wasted to be conducted by building tanks or pits in low lying areas and collecting roof top rain water through pipes into tanks.
- Drip irrigation in agriculture utilizes supply of water in small quantities.
- A saturated solution cannot dissolve more of the solute at a given temperature.
- Conservation of water is the means of preventing wastage of water so that clean water can be obtained by preventing pollution of water and by protecting the sources of water.
Polluted water acts as a carrier for germs which causes various diseases. - Gaseous state of water in air : Gaseous State as water vapour in air the amount depending on climatic conditions.
Q.5. Name the following :
Question 1.
A chemical used during chlorination of water.
Answer:
Chlorine.
Question 2.
An agricultural pollutant in water.
Answer:
Insecticides.
Question 3.
A solid, ‘natural form of water’.
Answer:
Snow.
Question 4.
The natural process by which circulation of water takes place from earth’s surface to atmosphere and back to earth’s surface.
Answer:
Water cycle.
Question 5.
The liquid or medium of dissolution which allows the solute to dissolve in it.
Answer:
Water (solvent).