New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions – Metallurgy
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Viraf J Dalal Chemistry Class 10 Solutions and Answers
Simplified ChemistryEnglishMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
For Objective and ICSE Board Type Questions Questions (Solved)
2002
Question 1.
Match the metals/alloys – brass, with its correct use.
Uses : (a) steel making (b) aeroplane wings (c) galvanizing (d) radiation shield (e) electrical fittings
Answer:

Question 2.
In order to obtain aluminium, the following inputs are required : Bauxite, sodium hydroxide and graphite. The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (III) oxide. Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite,
- When bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide solution what happens to the : (a) aluminium oxide (b) iron (c) oxide.
- Name the process used for the purification of bauxite.
- Write the equation for the action of heat on aluminium hydroxide
- Write the formula of cryolite.
Answer:
(i) (a) Aluminium oxide reacts with NaOH (aq.) at 150-200°C to give sodium aluminate which is soluble in water.
(b) Iron (II) oxide remains unaffected.
(ii) Baeyer’s method is used for removal of impurities.
![]()
Aluminium hydroxide write below Al2O3
(iv) Formula of cryolite – (Na3 Al F6)
Question 3.
Write down the word which correctly completes the following sentence : “By dissolving aluminium oxide in cryolite a __ [conducting / non-conducting] solution is produced.
State why is so much graphite is requires for this electrolytic process.
Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
Answer:
“By dissolving aluminium oxide in cryolite a conducting solution is produced.
The graphite anodes are periodically replaced during electrolysis process of fused alumina.
At cathode : 2Al3+ + 6e– → 2Al
Question 4.
In construction work, state why the alloy duralumin is used rather than pure aluminium.
Answer:
Duralumin is light, strong and corrosion resistant.
2003
Question 1.
Name an alloy of copper and zinc.
Answer:
Brass
2004
Question 1.
Element X is a metal with a valency 2. Element Y is a nonmetal with a valency 3.
Write equations to show how X and Y form ions.
Answer:
Y + 3e– → Y3– (cations formed)
Question 2.
Cations are formed by _____ (loss / gain) of electrons and anions are formed by _____ (loss / gain) of electrons.
Answer:
Cations are formed by loss of electrons and anions are formed by gain of electrons.
Question 3.
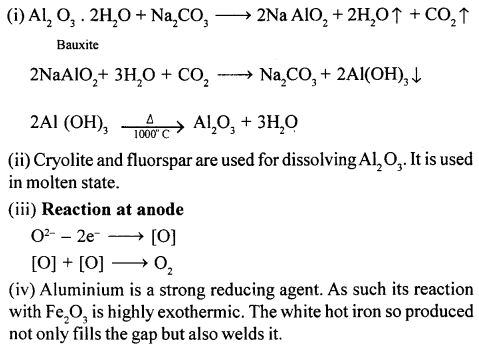
(i) Write three balanced equations for the purification of bauxite by Hall’s process in extraction of Al.
(ii) Name a chemical used for dissolving Al2O3. In which state of subdivision is the chemical used.
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction at the anode during the extraction of aluminium by the electrolytic process.
(iv) Mention one reason for the use of aluminium in thermite welding.
Answer:
2005
Question 1.
A to F below relate to the source and extraction of either Zinc or Aluminium. A : Bauxite, B : Coke, C : Cryolite, D : Froth floatation, E : Sodium hydroxide solution, F : Zinc blende.
- Write down the three letters each from the above list which are relevant to – Aluminium.
- Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate words from A to F : (a) The ore from which aluminium is extracted must first be treated with so that pure Aluminium oxide can be obtained. (b) Pure Aluminium oxide is dissolved in to make a conducting solution
- Write the formula of Cryolite.
Answer:
- Aluminium: Bauxite (A), Cryolite (C), Sodium hydroxide solution (F).
- (a) Sodium Hydroxide Solution (b) Cryolite
- Na3AlF6
Question 2.
Calcium, Copper, Lead, Aluminium, Zinc, Chromium, Magnesium, Iron.
Choose the major metals from the list given above to make the following alloys :
- Stainless steel
- Brass.
Answer:
- Iron, Chromium
- Copper, Zinc
2006
Question 1.
Name the following :
- A metal which is liquid at room temperature.
- A compound added to lower the fusion temp, of the electrolytic bath in the extraction of Al.
- The process of heating an ore to a high temperature in the presence of air.
Answer:
- Mercury or Gallium
- Cryolite [Na3 (AlF6)]
- Roasting
Question 2.
A strip of copper is placed in four different colourless salt solutions. They are KNO3, AgNO3, Zn(NO3)2, Ca(NO3)2.
Which one of the solutions will finaky turn blue.
Answer:
Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
Question 3.
When a metal atom becomes an ion
A : it loses electrons and is oxidized
B : it gains electrons and is reduced
C : it gains electrons and is oxidized
D : it loses electrons and is reduced
(Choose the correct answer from the choices A, B, C and D)
Answer:
A : it loses electrons and is oxidized
2007
Question 1.
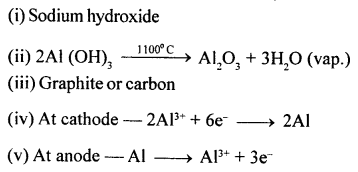
In the extraction of aluminium :
- Which soln. is used to react with bauxite as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide.
- The aluminium oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminium is obtained by heating aluminium hydroxide. Write the equation for this reaction.
- Name the element which serves as the anode and cathode in the extraction of aluminium.
- Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
- Give the equation for the reaction at the anode when aluminium is purified by electrolysis.
Answer:
2008
Question 1.
Brass is an alloy of :
A. Copper and tin
B. Copper and zinc
C. Zinc and lead
D. Lead and tin
Answer:
B. Copper and zinc
Question 2.
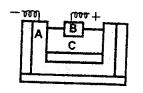
The following is a sketch of an electrolytic cell used in the extraction of aluminium :
- What is the substance of which the electrodes A and B are made?
- At which electrode (A or B) is the aluminium formed ?
- What are the two aluminium compounds in the electrolyte C ?
- Why is it necessary for electrode B to be continuously replaced ?
Answer:
- Electrodes A and B are made of graphite. Electrode B is carbon (graphite) lining while, electrode A is thick rods of graphite.
- Aluminium is formed at cathode in the molten state which can be taken out through a tapping hole.
- The two aluminium compounds in the electrolyte C are Alumina (Al2O3) and Cryolite (Na3AlF6).
- This is because electrode (B i.e. anode) is oxidised by the oxygen produced to carbon monoxide.
2009
Question 1.
The metal oxide which can react with acid as well as alkali is :
A. Silver oxide
B. Copper (II) oxide
C. Aluminium oxide
D. Calcium oxide
Answer:
C. Aluminium oxide
Question 2.
Correct the following statements. — Haematite is the chief ore of aluminium.
Answer:
Haematite is the chief ore of iron.
Or
Bauxite is the chief ore of aluminium.
Question 3.
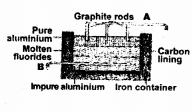
The sketch below illustrates the refining of aluminium by Hoope’s process.
- Which of A and B is the cathode and which one is the anode ?
- What is the electrolyte in the tank?
- What material is used for the cathode ?
Answer:
- A are graphite rods and they act as cathode, B act as anode.
- Molten Fluorides.
- Graphite rods dipped in pure molten aluminium.
Question 4.
State the property of the metal being utilized in the following :
- Zinc in Galvanization
- Aluminium in Thermite welding
Answer:
Use of metal :
(a) Zinc in Galvanization
(b) Aluminium in Thermite welding
Property :
(a) Zinc forms a protective layer of zinc oxide which prevents rusting of iron.
(b) Strong affinity for oxygen.
2010
Question 1.
State the main constituent metal in each alloy :
- Duralumin
- Brass
- Stainless steel
Answer:
- Aluminium
- Copper
- Iron
Question 2.
Select the correct answer from A, B, C and D – The property which is true for metals.
A : Metals are good conductors of electricity
B : Metals are malleable and ductile
C : Non-polar covalent compounds are formed from metals.
D : Metals have 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons.
Answer:
C : Non-polar covalent compounds are formed from metals.
2011
Question 1.
Choose from the following list of the substances, Acetylence gas, aqua fortis, coke, brass, barium chloride, bronze, platinum.
The substance which is an alloy of zinc, copper and tin.
Answer:
Bronze
Question 2.
(i) Name a metal which is found abundantly in the earth’s crust.
Answer:
Aluminium
(ii) Difference between calcination and roasting?
Answer:
Roasting :
- Ore is heated in the presence of air.
- Used generally for sulphide ores. SO2 gas is given off.
2ZnS+ 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2 - Volatile impurities are removed as oxides.
Calcination :
- Ore is heated in the absence of air.
- Hence Used generally for carbonate ores.
Hence, CO2 gas is given off. ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2. - Moisture, organic impurities and volatile impurities are removed.
(iii) Name the process used for the enrichment of sulphide ore.
Answer:
Froth floatation process
(iv) Write the chemical formulae of one main ore – of iron and aluminium.
Answer:
- Iron : Haematite → Fe2O3
- Aluminium : Bauxite → Al2,O3.2H2O
(v) Write the constituents of electrolyte for – the extraction of aluminium.
Answer:
- Fused Alumina (Al2O3) 1 part by weight.
- Cryolite fused (Na3 AlF6) 3 part by weight.
- Fluorspar (CaF2) 1 part by weight.
2012
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(i) An alkaline earth metal.
(A) Potassium
(B) Calcium
(C) Lead
(D) Copper
Answer:
(B) Calcium
(ii) Which of the following metallic oxides cannot be reduced by normal reducing agents ?
(A) Magnesium oxide
(B) Copper(II) oxide
(C) Zinc oxide
(D) Iron(III) oxide
Answer:
(A) Magnesium oxide
Question 2.
Match the properties and uses of alloys in List 1 with the appropriate answer from List 2.

Answer:
- (B) Brass
- (A) Duralumin
- (D) Stainless stell
- (E) Solder
- (C) Bronze
Question 3.
Name the following metals :
- A metal present in cryolite other than sodium.
- A metal which is unaffected by dilute or concentrated acids.
Answer:
- Aluminium
- Platinum
Question 4.
The following questions are relevant to the extraction of Aluminium :
- State the reason for addition of caustic alkali to bauxite ore during purification of bauxite.
- Give a balanced chemical equation for the above reaction.
- Along with cryolite and alumina, another substance is added to the electrolyte mixture. Name the substance and give one reason for the addition.
Answer:
- The caustic alkali dissolves aluminium oxide to form sodium aluminate.
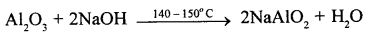
- Fluorspar is added. It helps in increasing the conductivity of the mixtures.
2013
Question 1.
The amphoteric metallic oxide is
(A) Calcium oxide
(B) Barium oxide
(C) Zinc oxide
(D) Copper (II) oxide
Answer:
(C) Zinc oxide is an amphoteric oxide
Question 2.
The metals zinc and tin are present in the alloy :
(A) Solder
(B) Brass
(C) Bronze
(D) Duralumin.
Answer:
(C) Bronze
Question 3.
Using the information below about X and Y – complete the following questions :

- ____ is the metallic element.
- Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of _____ electrons in the outermost energy level.
- Non-metallic elements tend to form _____ oxides while metals tend to form _____ oxides.
- Non-metallic elements tend to be _____ conductors of beat and electricity.
- Metals tend to _____ electrons and act as _____ agents in their reactions with elements and compounds,
Answer:
- Y is the metallic element.
- Metal atoms tend to have a maximum of three electrons in the outermost energy level.
- Non-metallic elements tend to form acidic oxides while metals tend to form basic oxides.
- Non-metallic elements tend to be bad conductors of heat and electricity.
- Metals tend to lose electrons and act as reducing agents in their reactions with elements and compounds.
Question 4.
The following questions relate to the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis :
(i) Name the other aluminium containing compound added to alumina and state its significance,
Answer:
The compound is cryolite [Na3AlF6]
The addition of cryolite lowers the melting point of alumina from 2050°C to 660 °C.
Furthermore, it increases the electrical conductivity of the molten alumina.
(ii) Give the equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode.
Answer:
Al3+ + 3e– → Al
(iii) Explain why is it necessary to renew the anode periodically.
Answer:
The anode (which is made of carbon) is attacked by nascent oxygen formed due to the discharge of O2- ions and changes to carbon dioxide. As the anode is gradually consumed, it is periodically renewed.
2014
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer from the choices :
(i) Heating an ore in a limited supply of air or in the absence of air at a temperature just below its melting point is known as :
(A) smelting
(B) ore dressing
(C) calcination
(D) bessemerisation
Answer:
(C) calcination
(ii) Aluminium powder is used in thermite welding because,
(A) it is a strong reducing agent
(B) it is a strong oxidising agent
(C) it is corrosion resistant
(D) it is a good conductor of heat.
Answer:
(A) it is a strong reducing agent
(iii) The main ore used for the extraction of iron is :
(A) Haematite
(B) Calamine
(C) Bauxite
(D) Cryolite
Answer:
(A) Haematite
Question 2.
State the main components of the following alloys :
- Brass
- Duralumin
- Bronze.
Answer:
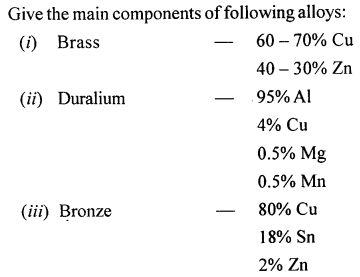
Question 3.
Name the following :
- The property possessed by metals by which they can be beaten into sheets.
- A compound added to lower the fusion temperature of electrolytic bath in the extraction of aluminium.
- The ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
Answer:
- Melleability
- Cryolite (Na3AlF6)
- The ore of zinc containing sulphide ZnS (Zinc Blende).
2015
Question 1.
Select which is not an alloy of copper :
(A) Brass
(B) Bronze
(C) Solder
(D) Duralumin.
Answer:
(C) Solder
Solder is an alloy of lead and tin.
Question 2.
Give scientific reasons for : Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc by using carbon monoxide, but aluminium oxide can – not be reduced by a reducing agent.
Answer:
Zinc ion is lower in electrochemical series. Thus, carbon monoxide provides enough energy and hence reduces zinc oxide to zinc. Aluminium ion is higher in electrochemical series. The carbon monoxide does not produce enough energy and hence aluminium oxide is not reduced to aluminium.
Question 3.
From the list of oxides — SO2, SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CO, Na2O — Select
- A basic oxide
- An amphoteric oxide.
Answer:
- Na2O
- Al2O3
Question 4.
A metal ‘X’ has a valency 2 and a non-metal ‘Y’ has a valency 3. Write an equation to show how ‘Y’ forms an ion.
Answer:
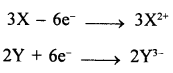
Question 5.
(i) Describe the role played in the extraction of aluminium by each of the substances listed.
(a) Cryolite
(b) Sodium hydroxide
(c) Graphite
(ii) Explain why :
(a) In the electrolysis of alumina using the Hall Heroult’s Process the electrolyte is covered with powdered coke.
(b) During galvanization, iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
Answer:
(i)
(a) Cryolite lowers the melting point of alumina from 2050° to 950°C. This in turn increases the conductivity of electrolyte and saves on electricity, which is the main source of energy in the reduction of alumina.
(b) Sodium hydroxide dissolves the alumina (Al2O3), but not the impurities to form sodium aluminate. The impurities are filtered out and the sodium aluminate is treated with carbon dioxide to form pure aluminium hydroxide. Alumina is recovered from sodium hydroxide by strong heating.
(c) Graphite is used as cathode as it is a good conductor of electricity and is not attacked by the chemicals.
(ii)
(a) It prevents burning of carbon anodes and prevents heat loss from the molten electrolyte.
(b) Zinc forms a protecting coating on the surface of iron and hence prevents it from rusting. Zinc by itself form a protective layer of zinc oxide and hence does not tarnish.
Question 6.
Select from the following salts — AgCl, MgCl2, NaHSO4, PbCO3, ZnCO3, KNO3, Ca(NO3)2 — the salt which on heating gives a yellow residue when hot and white when cold.
Answer:
On heating, this salt gives a yellow residue when hot and a white residue when cold is ZnCO3
2016
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks from the choices given :
Metals are good _____ (oxidizing agents/reducing agents)
because they are electron _____ (acceptors / donors).
Answer:
Metals are good reducing agents because they are electron donors.
Question 2.
Select the correct answer from A, B, C and D :kThe two main metals in Bronze are :
(A) Copper and zinc
(B) Copper and lead
(C) Copper and nickel
(D) Copper and tin
Answer:
(D) Copper and tin
Question 3.
Identify the term in the following :
“The method used to separate ore from gangue by preferential wetting.”
Answer:
Froth flotation process
Question 4.
- Name the solution used to react with Bauxite-as a first step in obtaining pure aluminium oxide, in the Baeyer’s process.
- Write the equation for the reaction where the – aluminum oxide for the electrolytic extraction of aluminum is obtained by heating aluminum hydroxide.
- Name the compound added to – pure alumina to lower the fusion temperature during the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
- Write the equation for – the reaction that occurs at the cathode during the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis.
- Explain why – it is preferable to use a number of graphite electrodes as anode instead of a single electrode, during the abvoe electrolysis.
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide.
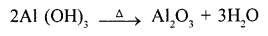
- Cryolite (Na3Al F6) acts as a solvent and lower the fusion temperature from 2050°C to 950°C.
- Cathode : (rich in electron)
AL3 + 3e– → Al - It is preferable to use a number of graphite electrodes as anode because anode gets oxidised by the oxygen evolved.
Hence, if large number of electrodes are used it will keep the process continuous for a longer time.
2017
Question 1.
From the list of terms given, choose the most appropriate term to match the given description: [calcination, roasting, pulverisation, smelting]
- Crushing of the ore into a fine powder.
- Heating of the ore in the absence of air to a high temperature.
Answer:
- Pulverisation
- Calcination
Question 2.
Name the following :
- An alloy of lead and tin that is used in electrical circuits.
- An ore of zinc containing its sulphide.
- A metal oxide that can be reduced by hydrogen.
Answer:
- Fusible alloy
- Zincite (ZnS)
- Copper oxide (CuO)
Question 3.
Answer the following questions with respect to the electrolytic process – in the extraction of aluminium.
- Identify the components of the electrolyte other than pure alumina and the role played by each.
- Explain why powdered coke is sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture.
Answer:
- Cryolite (Na3AlF4) : It increases the conductivity of mixture and lowers the m.p. of electrolyte from 2050°C to 950°C.
- Fluorspar (CaF2) : It increases mobility of ions in the mixture as it acts as solvent for alumina and cryolite.
Powdered coke prevents (a) heat loss from the electrolyte (b) burning of electrodes projecting out of electrolyte.
Question 4.
Complete the following by selecting the correct option from the choices given –
- The metal whose oxide, which is amphoteric, is reduced to metal by carbon reduction _____ [Fe / Mg / Pb / Al]
- The divalent metal whose oxide is reduced to metal by electrolysis of its fused salt is _____ [Al / Na / Mg / K]
Answer:
- The metal whose oxide, which is amphoteric, is reduced to metal by carbon reduction Pb (Lead).
- The divalent metal whose oxide is reduced to metal by electrolysis of its fused salt is Mg (Magnesium).
Additional Questions
Question 1.
State how the physical and chemical property differences between metals and non-metals are related to their basic atomic structure.
Define a metal with particular emphasis on (i) ionization (ii) valency (iii) formation of oxides.
State the position [group] in the periodic table to which the following metals belong (i) Na – alkali metal (ii) Mg – alkaline earth metal (iii) Fe and Zn transition elements (iv) inner transition elements (metals) (v) Al – post transition element.
Answer:
Atoms of Metallic elements, in general, have relatively larger atomic size. Hence, their valence electrons are held less tightly by the nucleus. As such, the valence electrons are mobile, leading to good electrical and thermal conductivity in case of metals. Further, with 1,2 or 3 valence electrons, metals can easily lose electrons to form cations. Thus, metal are electropositive in nature and are strong reducing agents.
On the other hand, non-metallic elements, in general, have relatively smaller atomic size. Hence their valence electrons are held tightly by the nucleus. As such their valence electrons are not mobile, thus making non-metals bad conductor of heat and electricity. Further, non-metals have 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons. As such, non-metals tend to gain electrons to form anions. Thus non-metals are electronegative in nature and strong oxidising agents.
Thus, we find that the physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals are related to their basic atomic structure.
Defination of Metals :
- Atoms of metals with 1, 2 or 3 electrons in their valence shell can easily lose their valence electrons to form cations e.g.
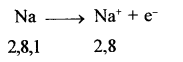
- As metals can easily lose electrons to form cations, metals are electropositive in nature.
- Metals on reacting with non-metals form ionic or electrovalent compounds, e.g.

- As metals tend to form cations, metals show a positive valency of 1,2 or 3.
Position of Metals in the periodic table :
- Na – alkali metal – Group I (IA)
- Mg – alkaline earth metal – Group 2 (IIA)
- Fe and Zn transition elements – Group 9 (VIII), Group 12 (IIB)
- Inner transition elements : zero group.
- Al-post transition element: Group 13 (III A)
Question 2.
Metals occur in the free state and in the combined state, name two metals which occur in the free or native state. In the combined state metals occur in the form of compounds. Name two different metallic compounds in each case which occur as
- halides
- oxides
- sulphides.
Answer:
Gold and Platinum are the two metals that occur in the free or native state.
The metallic compounds which occur in :
- Halides – Cryolite[Na3AlF6], Flurospar[CaF2], Rock Salt[NaCl]
- Oxides – Bauxite[Al2O3.2H2O], Zincite[ZnO], Cuprite[Cu2O]
- Sulphides – Iron Pyrite[FeS2], Zinc blende[ZnS], Gdlena[PbS]
Question 3.
Differentiate between
- mineral & ore
- matrix & flux.
Answer:
Differentiate between mineral & ore
Mineral :
- The compounds of various metal found in nature associated with their earthly impurities are called minerals.
Ore :
- The naturally occurring minerals from which metals can be extracted profitably and conveniently are called ores,
Differentiate between matrix & flux
- Matrix : The rocky impurities including silica [SiO2], mud etc. associated with the ore is called matrix or gangue.
- Flux : The substance added to the ore to get rid of the matrix resulting in the formation of a fusible compound slag.
Question 4.
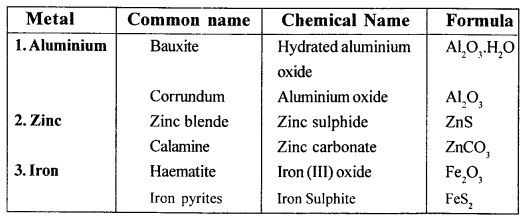
Give the (i) common (ii) chemical nadie (iii) formula of two common ores each of aluminium, zinc and iron.
Answer:
Question 5.
In the stages involved in the extraction of metals in general – give reasons for the following.
(i) Dressing of the ore is an essential process in the extraction of metal from its ore.
Answer:
The ores are found mixed with earthy impurities like sand, clay, lime stone etc. These unwanted impurities in the ore are called gangue or matrix.
The process of removal of gangue from powdered ore is called concentration or ore dressing.
Hence, it is the essential process in the extraction of metal from its ore because it convert’s the impure ore to pure concentrated ore
(ii) An electromagnetic wheel is used in the magnetic separation process of ore from gangue.
Answer:
An electromagnetic wheel is used in the magnetic separation process of ore from gangue as it seperate’s the magnetic particles from the non-magnetic particles. The magnetic particles get attracted to the magnetic wheel and thus get seperated from the gangue.
(iii) In the froth floatation process, the ore floats on the top & the gangue settles down.
Answer:
The impurities get wetted by water and remain behind in the tank. Since, the ore is lighter, it comes on the surface with the froth and the impurities(gatlgue) are left behind.
(iv) Magnetic separation is not used during the dressing of bauxite ore in the extraction of aluminium.
Answer:
Bauxite is concentrated by Leaching (Baeyer’s process). The impure bauxite is treated with concentrated NaOH, Al2O3 and SiO2 dissolve, but Fe2O3 and other basic materials remain insoluble and are removed by filtration.
Aluminium is highly reactive metal, belonging to the III A group of the periodic table. In nature, aluminium is found in the form of its oxide in its ore.
Hence, Magnetic separation is not used during the dressing of bauxite ore in the extraction of aluminium.
(v) Conversion of concentrated ore to its oxide is an essential step in the extraction of metals from the ore, even then the step is not necessary in the metallurgy of aluminium.
Answer:
Conversion of concentrated ore to its oxide is an essential step in the extraction of metals from the ore, even then the step is not necessary in the metallurgy of aluminium because in metallurgy of aluminium, the ore is already an oxide.
(vi) Roasting of the concentrated ore is carried out in the presence of excess air, while calcination of the concentrated ore in the absence or limited supply of air.
Answer:
Roasting is a process of converting an ore into its oxide by heating strongly in presence of excess air, so that oxygen gets added to form the corresponding oxide. It is done on sulphide ores in order to remove sulphur as sulphur gets escape in the form of gas.
![]()
Whereas in carbonates ores, one needs to drive out carbonate and moisture impurities. So, ore is heated to a high temperature in absence of air. This process is called calcination.
![]()
(vii) Roasting the ore generally results in evolution of sulphur dioxide gas, while calcination of the ore evolves carbon dioxide gas.
Answer:
Generally, sulphide ores are roasted, so SO2 is given off.
While carbonate and hydrated ores are calcined, so CO2 or water vapours are given off.
(viii) Reduction of metallic oxides to metal in the extraction of metals from the ores- is based on the position of the metal in the activity series.
Answer:
The method used to extract a metal from its ore depends on the position of the metal in the reactivity series.
(a) Metals higher up in the series need to be extracted using electricity.
(b) Metals lower in the series can be extracted by reduction with carbon.
(ix) Oxides or halides of highly electropositive metals e.g. K, Na, Ca, Al are reduced to metals by electrolysis and not by reduction with coke.
Answer:
Oxides are highly active metals like potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and aluminium have great affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by coke.
(x) Coke is not preferred as a reducing agent in the reduction of the oxide of mercury to its metal, but is preferred in the reduction of the oxide of zinc to its metal.
Answer:
Coke is not preferred as a reducing agent in the reduction of the oxide of mercury to its metal because metals low in the activity series are very reactive and the oxides of the metals can be reduced to metals by heating in air.
The reducing nature of carbon plays an important role in metallurgy and helps extract metals from their ores.
For example :
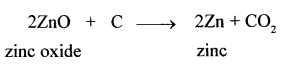
Question 6.
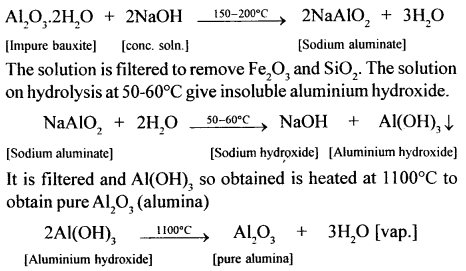
In the extraction of aluminium from bauxite, the first step is the dressing of the ore by Baeyer’s process. Give balanced equations for the conversion of impure bauxite to pure alumina using a concentrated solution of NaOH.
Answer:
Bauxite (red) contains Fe2O3. and SiO2 as the main impurities. It is crushed to a powder and is treated with a cone, solution of NaOH at 150-200°C (under pressure) when Al2O3 dissolves.
Question 7.
In the electrolytic reduction of pure alumina to pure aluminium – by Hall Herault’s process, give the electrolytic reactions involved in the same, resulting in formation of aluminium at the cathode.
Answer:
Aluminium is obtained from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolytic reduction. The electrolytic both consists of a mixture of cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) and alumina (Al2O3)
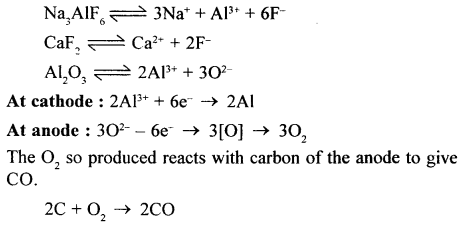
Question 8.
State the function of
- NaOH
- cryolite
- fluorspar in the metallurgy of aluminium.
Answer:
Functions of :
(i) NaOH : Crushed and powdered bauxite is heated with a cone, solution of NaOH at 150-200°C for 2 hours under pressure. The main impurities present in bauxite (Fe2O3 and SiO2) remain unaffected with cone. NaOH since these are not amphoteric. Bauxite, being amphoteric reacts with the base to form sodium aluminate, which is soluble in water. Thus NaOH helps in the purification of the ore.
(ii) Cryolite :
(a) To increase the mobility of the fused mixture.
(b) To lower the fusion point of the mixture.
(c) To increase the electrical conductivity of the mixture.
(iii) Fluorspar :
(a) To increase the mobility of the fused mixture.
(b) To lower the fusion point of the mixture.
Question 9.
Give reasons for the following – pertaining to Hall Herault’s process.
- The fusion temperature of the electrolyte has to be lowered before conducting the electrolytic reduction.
- The constituents of the electrolyte in addition to one part of fused alumina contains three parts of cryolite and one part of fluorspar.
- A layer of powdered coke sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture, protects the carbon electrodes.
- It is preferred to use a number of graphite electrodes as anode, instead of a single graphite electrode.
Answer:
(i) The liberated A1 metal [m.p. 660°C] may also tend to volatize out and get wasted. Hence the fusion temperature of the electrolytic mixture has to be – lowered.
(ii) The reasons for addition of mainly cryolite [in a higher ratio] and fluorspar to the electrolytic mixture are :
(a) They lowers the fusion point of the mixture i. e. the mixture fuses [melts] around 950°C instead of 2050°C.
(b) They enhances the mobility of the fused mixture by acting as a solvent for the electrolytic mixture.
Thus cryolite in the molten state of subdivision dissolves aluminium oxide.
(c) Addition of cryolite enhances the conductivity of the mixture.
Since pure alumina is almost a non-conductor of electricity
(iii) The layer of powdered coke is sprinkled over the electrolytic mixture because :
(a) It prevents burning of carbon electrodes in air at the emergence point from the bath.
(b) It minimizes or prevents heat loss by radiation.
(iv) The graphite[carbon] anodes are continously replaced during the electrolysis because :
(a) The oxygen evolved at the anode escapes as a gas or reacts with the carbon anode.
(b) The carbon anode is thus oxidised to carbon monoxide which either bums giving carbon dioxide or escapes out through an outlet.
2C + O2 → 2CO [2CO + O2 → 2CO2]
(c) The carbon anode is hence consumed and renewed periodically after a certain period of usage,
Question 10.
Define — (a) alloy, (b) amalgam
Answer:
- Alloy : An alloy is a homogenous mixture of two or more metals and non-metals, out of which at least one is a metal.
For example, brass (Zn + Cu), bronze (Cu + Sn), solder (Sn +Pb), stainless steel (Fe + Cr + Ni + C) etc. - Amalgam : An alloy in which mercury is an essential constituent is called an amalgam.
For example, Dental amalgam (Hg + Ag + Sn), it is used for filling dental cavities.
Question 11.
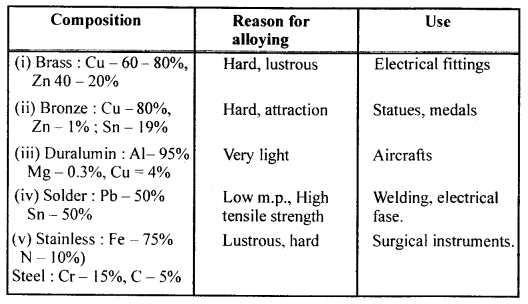
State (i) composition (ii) reason for alloying (iii) one use of each of the following alloys.
- Brass
- Bronze
- Duralumin
- Solder [fuse metal]
- Stainless steel
Answer:
Unit Test Paper 6 — Metallurgy
Q.1. Loss of electrons from an element ‘X’ is represented by : X – 3e– → X3+ (X → X3+ + 3e–)
1. X is a _____ (metal/non-metal) and will form _____ (electrovalent/covalent) compounds only.
Ans. X is a metal and will form electrovalent compounds only.
2. X3+ formed is a _____ (cation / anion) and element ‘X’ has a valency of _____ [+2 /+3 / -3].
Ans. X3+ formed is a cation and element ‘X’ has a valency of +3.
3. If X3+ combines with oxygen the formula of the product is _____ (X2O3 / XO / X3O2),
Ans. If X3+ combines with oxygen the formula of the product is X2O3.
4. If the above product in the _____ (solid/molten) state is electrolysed the ion X3+ will get discharged at the _____ (anode / cathode).
Ans. If the above product in the molten state is electrolysed the ion X3+ will get discharged at the cathode.
5. The ion X3+ _____ (accepts / loses) electrons and gets _____ (oxidised / reduced) to neutral _____ (ions / atoms / molecules).
Ans. The ion X3+ loses electrons and gets reduced to neutral atoms.
Q.2. Select the correct answer from the list A, B, C and D given in each statement.
1. The oxide of the metal which reacts with both acids and alkalis- to give salt & water.
A : MgO
B : CuO
C : Al2O3
D : K2O
2. The common name of the ore of iron – whose chemical formula is Fe3 O4.
A : Iron pyrites
B : Magnetite
C : Haematite
D : Spathic iron ore
3. The chemical name – of the main ore of aluminium.
A : Aluminium flouride
B : Aluminium oxide
C : Sodium aluminium flouride
D : Hydrated aluminium oxide
4. The process of dressing of the ore which involves separation of ore & gangue – due to preferential wetting.
A : Magnetic separation
B : Hydrolytic method
C : Froth flotation method
D : Chemical method
5. The metallic oxide reduced to metal generally by – thermal decomposition.
A : ZnO
B : MgO
C : HgO
D : Al2O3
Answer:
- C : Al2O3
- B : Magnetite
- D : Hydrated aluminium oxide
- C : Froth flotation method
- C : HgO
Q.3. Name the substance A to E, reacted with each reactant below to give the respective product/s.
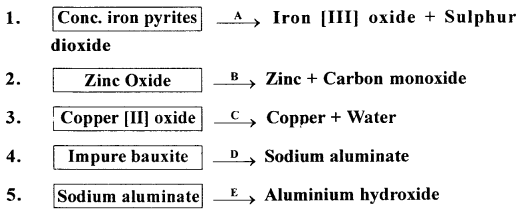
Answer:

Q.4. Name the following :
- A metallic ore converted to its oxide – iron [II] oxide on heating the concentrated ore.
- A black metallic oxide reduced to metal on heating with coke.
- The compound which on ignition at elevated temperatures gives pure alumina.
- The non-metal which forms the anode during electrolytic reduction of fused alumina in Hall Heroult’s process.
- A metal other than manganese, present in duralumin but not in magnalium.
Answer:
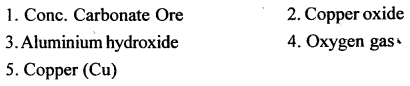
Q.5. Match the properties & uses of alloys in List 1 – with the correct answer from List 2.

Answer:

For More Resources