New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions – Study Of Compounds: Hydrogen Chloride
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Viraf J Dalal Chemistry Class 10 Solutions and Answers
Simplified ChemistryEnglishMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
Questions
2005
Question 1.
Write balanced equations for the following reactions :
- Copper oxide and dilute Hydrochloric acid.
- Manganese (IV) oxide and concentrated Hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 2.
- Name the experiment illustrated aside.
- Which property of hydrogeii chloride is demonstrated by this experiment.
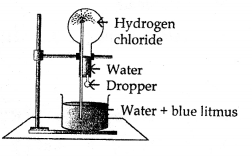
- State the colour of the water that has entered the round-bottomed flask.
Answer:
- Fountain experiment.
- Hydrogen chloride is soluble in water.
- Red.
2006
Question 1.
From the list — Ammonia, Copper oxide, Copper sulphate, Hydrogen chloride, Hydrogen sulphide, Lead bromide — select the compound which can be oxidized to chlorine.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride
Question 2.
Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction of zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Question 3.
State what is observed when hydrochloric acid is added to silver nitrate solution.
Answer:
A white ppt. of silver chloride is formed.
Question 4.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of calcium bicarbonate and dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Ca(HCO3)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + 2CO2 + 2H2O.
2007
Question 1.
Write a balanced equation for the following reaction :
Sodium chloride from sodium carbonate solution and dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Question 2.
Of the two gases, NH3 and HCl, which is more dense.
Name the method of collection of this gas.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride gas ; by upward displacement of air.
Question 3.
Give one example of a reaction between the above two gases which produces a solid.
Answer:
NH3 (g) + HCl (g) → NH4 Cl (s-solid)
Question 4.
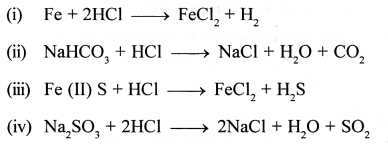
Write equations for the reaction of dil. HCl with each of the following :
- iron
- sodium hydrogen carbonate
- iron [II] sulphide
- sodium sulphite
Answer:
2008
Question 1.
What property of hydrogen chloride is demonstrated when it is collected by downward delivery (upward displacement)? Why is hydrogen chloride not collected over water.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride is heavier than air.
Hydrogen chloride cannot be collected over water because hydrogen chloride is highly soluble in water.
Question 2.
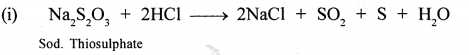
Write the equations for the following reactions :
- dil. HCl and sodium thiosulphate.
- dil. HCl and lead nitrate solution.
Answer:
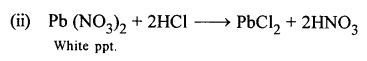
2009
Question 1.
Name the gas evolved (formula is not acceptable). The gas produced by the action of concentrated sulphuric acid on sodium chloride.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
Question 2.
Match each substance A to E listed below with the appropriate description given below :
(A) Sulphur
(B) Silver chloride
(C) Hydrogen chloride
(D) Copper (II) sulphate
(E) Graphite.
(i) A Covalent compound which behaves like an ionic compound in aqueous solution.
(ii) A compound which is insoluble in cold water but soluble in excess of ammonia solution.
Answer:
- (C) Hydrogen chloride
- (B) Silver chloride
Question 3.
Write a fully balanced equation for each of the following :
- Red lead is warmed with concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- Magnesium metal is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
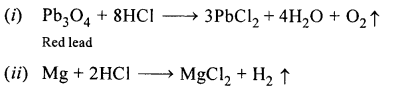
Question 4.
Correct the following statements.
HCl is prepared in the laboratory by passing hydrogen chloride directly through water.
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid is prepared in the laboratory by passing hydrogen chloride gas through inverted funnel arrangement in water.
2010
Question 1.
Select the correct answer from A, B, C and D.
(i) Aqua regia is a mixture of :
A : Dilute hydrochloric and cone, nitric acid
B : Cone, hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid
C : One part of cone, hydrochloric acid 3 parts of cone, nitric acid.
D : 3 parts of Cone, hydrochloric acid and 1 part of cone, nitric acid
Answer:
D : 3 parts of Cone, hydrochloric acid and 1 part of cone, nitric acid
Question 2.
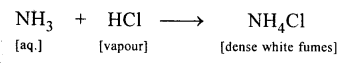
State your observation when :
A glass rod dipped in NH4OH soln. is brought near an open bottle containing cone. HCl
Answer:
Dense white fumes of – ammonium chloride are formed.
Question 3.
- State the salt and the acid, used in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride.
- Give the equation for the preparation.
- State a method to prove that the gas jar used for collection of HC1 gas is filled with hydrogen chloride?
- Observing the method of collection of the gas, state what you can tell about the density of hydrogen chloride ?
Answer:
- Sodium chloride and Sulphuric acid

- In order to know that the jar is filled with the gas, bring a glass rod dipped in ammonium hydroxide solution near its mouth. If dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are produced, it indicates that the gas jar is full of HCl gas.

- The method used to collect HCl is “Upward displacement of air”. This clearly indicates that HCl gas is heavier than air.
Question 4.
How would you distinguish between dilute HCl and dilute HNO3, by addition of only one solution.
Answer:
HCl (dilute)

Question 5.
Name two gases which can be used in the study of the fountain experiment.
State the common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment ?
Answer:
- Hydrogen chloride gas (HCl)
- Ammonia (NH3)
Solubility of gases is the common property demonstrated by the fountain experiment.
2011
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer from the choices given :
Hydrogen chloride gas being highly soluble in water is dried by :
(A) Anhydrous calcium chloride
(B) Phosphorous pentaoxide
(C) Quick lime
(D) Concentrated sulphuric acid.
Answer:
(D) Concentrated sulphuric acid.
Question 2.
Write balanced equations of dil. HCl with – Calcium bicarbonate.
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrochloric acid, Hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved in water.
(i) Draw a diagram to show the arrangement used for the absorption of HCl in water.
(ii) State why such an arrangement is necessary? Give two reasons for the same.
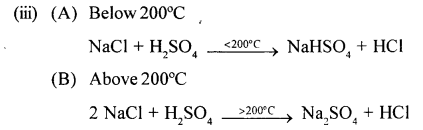
(iii) Write balanced chemical equations for the laboratory preparation of HCl gas when the reactants are :
(A) below 200°C
(B) above 200° C
Answer:
(i) Refer to page 335 of this book.
(ii) Two reasons for the use of funnel arrangement are :
(A) Prevents back suction of water into the flask.
(B) Provides a large surface area for the absorption of the gas (HCl).
2012
Question 1.
Rewrite the correct statement with the missing word/s :
Aqua regia contains one part by volume of nitric acid and three parts by volume of hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Aqua regia contains one part by volume of cone, nitric acid and three parts by volume of cone, hydrochloric acid.
Question 2.
Give reasons : Hydrogen chloride gas cannot be dried over quick lime.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride is acidic while quick lime is basic, so they react.
Question 3.
Concentrated hydrochloric acid and Potassium permanganate solution.
Answer:
Question 4.
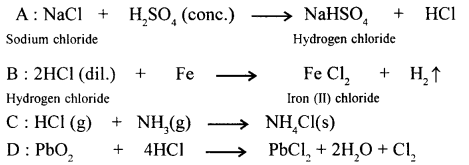
Give balanced equations with conditions, if any, for the following conversions A to D.
A : Sodium Chloride → Hydrogen Chloride
B : Hydrogen Chloride → Iron (II) chloride
C : Hydrogen Chloride → Ammonium chloride
D : Hydrogen Chloride → Lead chloride.
Answer:
2013
Question 1.
Identify the gas evolved when :
- Potassium sulphite is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
- concentrated hydrochloric acid is made to react with manganese dioxide.
Answer:
- Sulphur dioxide gas
- Chlorine gas
Question 2.
State one appropriate observation for
- Copper sulphide is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
- A few drops of dil. HCl are added to AgNO3 soln, followed by addition of NH4OH soln.
Answer:
- A colourless gas with a smell of rotten eggs is given off and a green coloured solution is formed.
- White ppt is formed which dissolves in ammonium hydroxide.
2014
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks from the choices in the bracket : Quicklime is not used to dry HCl gas because _____ (CaO is alkaline, CaO is acidic, CaO is neutral)
Answer:
Quicklime is not used to dry HCl gas because CaO is alkaline.
Question 2.
Write the balanced equation for : Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium sulphide.
Answer:
Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on sodium sulphide.
Na2S + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2S
Question 3.
State your observation : Dilute HC1 is added to sodium carbonate crystals.
Answer:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
effervescence of CO2 seen which turns lime water milky
Question 4.
Study the figure given below and answer the questions that follow :
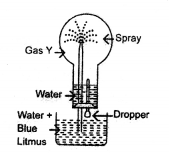
- Identify the gas Y.
- What property of gas Y does this experiment demonstrate?
- Name another gas which has the same property and can be demonstrated through this experiment.
Answer:
- Identify the gas Y — It is HCl (Hydrogen chloride)
- Property of Y —Highly solubility in water
- The another gas has same property — NH3 (Ammonia)
2015
Question 1.
Select from the gases — ammonia, ethane, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulphide, ethyne — The gas which produces dense white fumes with ammonia gas.
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride
Question 2.
Identify the acid which on mixing with silver nitrate solution produces a white precipitate which is soluble in excess ammonium hydroxide.
Answer:
Dilute hydrochloric acid
Question 3.
The following questions are pertaining to the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas:
- Write the equation for its preparation mentioning the condition required.
- Name the drying agent used in the above preparation and give a reason for the choice.
- State a safety precaution you would take during the preparation of hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
- The equation for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas :
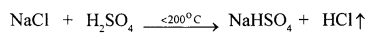
Although it is a reversible reaction, it goes to completion as hydrogen chloride continuously escapes as a gas.
The reaction can occur up to the stage of the formation of sodium sulphate on heating above 200°C.
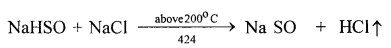
- The drying agent used in the laboratory preparation of hydrochloric acid is conc.sulphuric acid.
The other drying agents such as phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) and quick lime
(CaO) cannot be used because they react with hydrogen chloride.
- A safety precaution which should be taken during the preparation of hydrochloric acid :
Always wear chemical splash goggles, chemical-resistant gloves and a chemical resistant apron in the laboratory during the preparation of hydrochloric acid.
2016
Question 1.
Select the correct answer from A, B, C and D : The aim of the Fountain experiment is to prove that :
(A) HCl turns blue litmus red
(B) HCl is denser than air
(C) HCl is highly soluble in water
(D) HCl fumes in moist air.
Answer:
(C) HCl is highly soluble in water
Question 2.
Fill in the blank : _____ (AgCl / PbCl2), a white precipitate is soluble in excess NH4OH.
Answer:
AgCl (because of formation of diammine silver chloride), a white precipitate is soluble in excess NH4OH.
Question 3.
Write balanced chemical equation for : Action of hydrochloric acid on sodium bicarbonate.
Answer:
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2 ↑
Question 4.
State your observations when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to :
- Lead nitrate soln. and the mixture is heated.
- Copper carbonate.
- Sodium thiosulphate.
Answer:
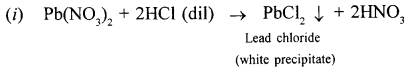
When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to lead nitrate white precipitates of lead chloride is formed.
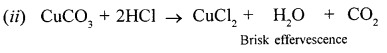
When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper carbonate brisk effervescence due to the liberation of carbon dioxide is observed.
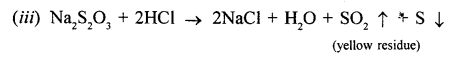
When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium thiosulphate pale yellow residue (due to formation of sulphur) is formed and a gas with choking odour is formed.
Question 5.
Identify the gas evolved and give the chemical test in when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with :
- Sodium sulphite.
- Iron (II) sulphide.
Answer:
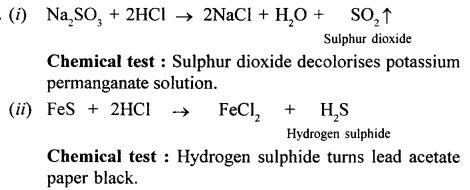
2017
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks from the choices given – Potassium sulphite on reacting with hydrochloric acid, releases gas. _____ [Cl2, SO2, H2S]
Answer:
Potassium sulphite on reacting with hydrochloric acid, releases SO2 gas.
Question 2.
Identify the substance underlined – A solid formed by the reaction of two gases, one of which is acidic and the other basic in nature.
Answer:
Ammonium chloride.
Question 3.
State one relevant observation – Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on iron [II] sulphide.
Answer:
A foul smelling gas like rotten eggs is given off.
Question 4.
Certain blanks spaces are left in the following tables as A & 8. Identify each of them.
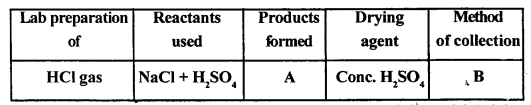
Answer:
A : The products are sodium hydrogen sulphate (NaHSO4) and HCl gas.
B : HCl gas as collected by the upward displacement of air.
Q. Complete the statements given below pertaining to hydrogen chloride gas or hydrochloric acid.
- Hydrogen chloride gas is not dried using _____ (cone.H2SO4, CaO).
- Hydrogen chloride gas on heating above 500°C gives hydrogen and chlorine.
The reaction is an example of _____ (thermal decomposition, thermal dissociation). - Iron reacts with hydrogen chloride gas forming [iron (II) chloride, iron (III) chloride) and hydrogen. The reaction is an example of _____ (double decomposition, synthesis, simple displacement).
- Hydrogen chloride and water are examples of (polar covalent compounds, non-polar covalent compounds) and a solution of hydrogen chloride in water _____ (contains, does not contain) free ions.
- Addition of _____ (sodium nitrate, zinc nitrate, silver nitrate) to hydrochloric acid, gives an insoluble precipitate of the respective chloride. This precipitate is _____ (soluble,insoluble) in ammonium hydroxide and _____ (soluble, insoluble) in dilute taitric add.
- Addition of _____ [iron (III) sulphide, iron (II) sulphide, iron pyrites] to dilute hydrochloric acid results in liberation of hydrogen sulphide gas.
- Aqua regia is a mixture of _____ (one, two, three) part/s of concentrated nitric acid and )_____ (one, two, three) part/s of concentrated hydrochloric acid by _____ (weight, volume). In aqua regia, nitric acid _____ (oxidises, reduces) hydrochloric acid to chlorine.
- Hydrochloric acid can be converted into chlorine by heating with _____ [calcium oxide, lead (H) oxide, lead (IV) oxide] which acts as a / an _____ (oxidising, reducing) agent.
Answer:
- CaO
- Thermal dissociation
- Iron (II) chloride ; simple displacement
- polar covalent compounds ; contains
- silver nitrate ; soluble ; insoluble
- iron (II) sulphide
- one, three, volume, oxidises
- Lead (II) oxide ; oxidisirig.
Additional Questions
Question 1.
Give a reason why
(a) gastric juices of luammals are acidic
(b) HCl is considered a polar covalent compound.
Answer:
(a) HCI gas occurs in free state in gastric juices of mammals.
(b) Due to difference in electronegativities of H and Cl ; The bond in HCl is a polar covalent.
Question 2.
Give the equation for preparation of HCI gas by Synthesis. State two conditions involved in the synthesis.
Answer:
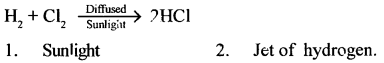
Question 3.
Give a balanced equation for preparation of HCl gas in the laboratory from sodium chloride.
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
In the laboratory preparation of HCl frem sodium chloride, state why the following are preferred –
- Cone. H2SO4 as a reactant
- Temp, below 200°C
- Cone. H2SO4 as a drying agent.
Answer:
- Since it is non-volatile and has a high boiling point.
- The glass apparatus does not crack, no hard crust is formed, fuel is not wasted.
- It only removes moisture content of the gas but not react with it.
Question 5.
State with reasons the method of collection of HCl gas in the laboratory.
Answer:
HCl gas is collected by upward displacement of air because it is 1.28 times heavier than air. It is not collected in water because it is highly soluble in water.
Question 6.
Compare the density of HCl gas with air and state the solubility of HCl gas in water.
Answer:
V.D of HCl = 18.25, V.D of air = 14.4. It is highly soluble in water.
Question 7.
State why HCl gas forms a mist of droplets of HCl acid in moist air.
Answer:
Due to high solubility, HCl gas fumes in moist air and forms a mist of droplets of HCl acid.
Question 8.
State what the fountain experiment demonstrates with reference to HCl gas.
Answer:
Fountain experiment demonstrates the solubility of HCI gas in water and its acidic nature.
Question 9.
State the colour change in three different indicators in presence of HCl gas.
Answer:
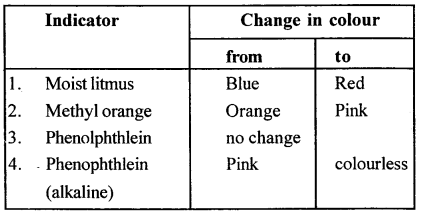
Question 10.
Give a balanced equation for the thermal dissociation of
- a gas
- a solid (both containing the chloride ion).
Answer:
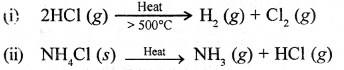
Question 11.
Give the equation and state the observation seen when HCl gas reacts with ammonia.
Answer:
When a gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas is inverted over ajar full of ammonia gas, dense white fumes are formed.
![]()
Question 12.
Convert iron to iron (II) chloride using HCl gas.
Answer:
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the arrangement (i) not used (ii) used – for converting HCl gas into HCl acid.
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid is prepared by dissolving hydrogen chloride gas in water usi ig a special funnel arrangement.
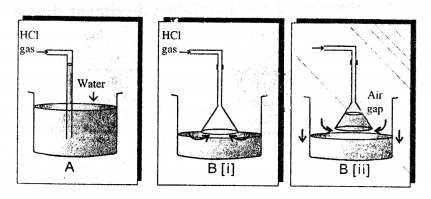
1. Direct absorption of HCl gas in water using a delivery tube i.e., arrangement (i) causes back suction.
Hydrogen chloride gas is extremely soluble in water. If a delivery tube through which HCl gas is passed is directly immersed in water, the rate of absorption of HCl gas is high and hence a partial vacuum is created in the tube. The pressure outside being higher causes the water to be pushed up into the delivery tube and damages the apparatus. This is called back-suction.
2. Special funnel arrangement, i.e., arrangement (ii) is used for avoiding back suction.
The funnel arrangement :
(a) Prevents or minimizes back-suction of water.
(b) Provides a large surface area for absorption of HCl gas.
The rim of the funnel is placed so that it just touches the trough containing water. If back-suction occurs, the water rises up the funnel and the level outside the funnel falls, thus creating an air gap between the rim of the funnel and the surface of water. The pressure outside and inside equalize and the water which had risen in the funnel falls down again. This process continues till the water in the trough is saturated with hydrogen chloride gas resulting information of hydrochloric acid.
Hence hydrochloric acid is not prepared in the laboratory by passing hydrogen chloride gas directly through water, but prepared using a special funnel arrangement.
Question 14.
Explain the term ‘constant boiling mixture’.
Answer:
A solution of HCl in water forms a constant boiling mixture with water.
Question 15.
State why dilute HCl cannot be concentrated beyond a certain concentration by boiling.
Answer:
On boiling the mixture evolves out the vapours of both acid and water in the same proportion as in the liquid. Hence dil HCl cannot be concentrated beyond a certain concentration.
Question 16.
Name the ions obtained when HCl dissociates in aqueous solution.
Answer:
Hydronium ions.
Question 17.
Name the ion responsible for acidic nature of HCl acid.
Answer:
The presence of hydrogen ions |H+| imparts acidic nature to HCl.
Question 18.
State which of two – a solution of HCl in water or in toluene is an electrolyte, giving reasons.
Answer:
A solution of hydrogen chloride in water; water being a covalent solvent ionizes aqueous solution of HCl shows acidic properties and is an electrolyte, whereas toluene is not; being not a polar solvent.
Question 19.
Give four different word equations relating to acidic properties of an aq. soln. of HCl gas.
Answer:
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen
Sodium hydroxide + Hydrochloric acid → Sodium chloride + Water
Sodium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Sodium chloride + Carbon dioxide + Water
Calcium oxide + Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Water
Question 20.
Give balanced equations to obtain
- H2
- CO2
- SO2
- H2S from dil. HCl.
Answer:
- Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
- Na2CO2 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
- Na2SO3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H20 + SO2
- FeS + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2S
Question 21.
Convert two soluble metallic nitrates to insoluble metallic chlorides using dil. HCl.
Answer:
Question 22.
State how you would prove that HCl contains
- hydrogen – using an active metal below magnesium
- chlorine – using an oxidising agent not containing lead.
Answer:
Question 23.
State the composition of aqua regia. State which component is the oxidising agent in aqua regia.
Answer:
Question 24.
Convert hydrochloric acid to nascent chlorine.
Answer:
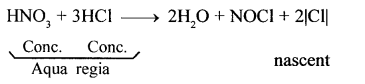
Question 25.
State why aqua regia dissolves gold, which is insoluble in all other acids.
Answer:
In aqua regia (a mixture of 1 part cone. HNO3 and 3 parts cone. HCl by volume), nitric acid oxidises hydrochloric acid to give nascent chlorine. This nascent chlorine is very reactive. It reacts with gold to give gold (III) chloride, which is soluble in water.
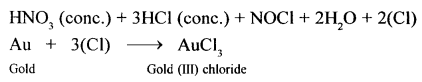
Question 26.
Give three tests for hydrochloric acid. Convert silver nitrate to a soluble salt of silver using hydrochloric acid and an alkali.
Answer:
- If glass rod dipped in ammonia soln. (NH4OH) brought near vapours of hydrochloric acid.
Dense white fumes of – ammonium chloride are formed. - Addition of silver nitrate soln. to dil. HCl (acidified with dil. HNO3)
Curdly white precipitate – of silver chloride obtained.
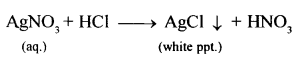
- Action of heat on a mixture of manganes dioxide and cone. HCl Greenish yellow gas (chlorine).
Question 27.
State two industrial products manufactured from hydrochloric acid, which are also manufactured from nitric and sulphuric acid. Give two general uses of hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Industrial products manufactured from HCl acid are : Dyes, paints, drugs.
General uses of hydrochloric acid are :
- Hydrochloric acid dissolves the calcium phosphate present in bones.
- Hydrochloric acid dissolves the metallic oxides coating on the surface of metals. Thereby cleans the metallic surface.
Unit Test Paper 7A — Hydrogen Chloride
Q.1. Give balanced equations for the conversions A, B, C, D and E given below :
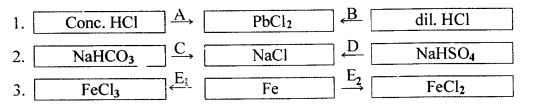
Answer:
Q.2. Give reasons for the following :
Question 1.
In the laboratory preparation of HCl acid from NaCl and cone. H2SO4, the residual salt formed at temperatures above 200°C forms a hard crust and sticks
to the glass.
Answer:
When sodium chloride and cone, sulphuric acid is heated above 200°C ; sodium sulphate forms a hard crust, sticks to the glass and is difficult to remove.
Question 2.
Dense white fumes are obtained when a jar of HCl gas is inverted over a jar of ammonia gas.
Answer:
When a gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas is inverted over of jar full of ammonia gas dense white fumes are formed. These fumes consists of particles of solid ammonium chloride suspended in air.
Question 3.
In the fountain experiment to demonstrated the high solubility of HCl gas in water, dry HCl gas is filled in the round bottom flask.
Answer:
HCl gas present in the flask dissolves in water due to high solubility, creating a partial vacuum in the flask. The outside pressure being higher pushes the water up the jet tube which emerges as fountain.
Question 4.
Iron sheets are cleaned with hydrochloric acid before dipping into molten zinc for galvanizing.
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid dissolves the metallic oxide coating on the surface of the metal, thereby cleans the metallic surface.
Question 5.
Hydrogen chloride gas fumes in moist air but hydrogen sulphide gas does not.
Answer:
HCl gas fumes in moist air due to its high solubility and forms a mist of droplets of HCl acid while H2S does not.
Q.3. Complete the statements given below using the correct word/s
- An aqueous solution of HCl gas is named _____ (aqua fortis/muriatic acid/oil of vitriol)
- The salt obtained when rock salt reacts with cone. H2SO4 at temperatures below 200°C is a/an _____ (acid/normal) salt.
- In the preparation of HCl acid from HCl gas, a funnel arrangement provides _____ (less/more) surface area for absorption of the gas.
- The ions which impart acidic properties to an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride are _____ (chloride/hydrogen/hydronium)
- The indicator which does not change colour on passage of hydrogen chloride gas is _____ (moist blue litmus/phenolphthalein/methyl orange)
Answer:
- mutriatic acid
- normal
- more
- hydrogen
- phenolphthalein
Q.4. Choose from the letters A, B, C, D and E, to match the descriptions 1 to 5 given below.
A : NH4 Cl
B : AgCl
C : PbCl2
D : FeCl2
E : Ag(NH3)2 Cl
- A solubl salt obtained on reaction of a metallic chloride with liquor ammonia.
- A salt which is insoluble in dilute nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide.
- A salt obtained on reaction of an active metal with hydrogen chloride gas.
- A salt obtained when a basic gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas.
- A salt soluble in hot water but not in cold, obtained on heating an oxidising agent with cone. HCl.
Answer:
- E [Ag (NH3)2 Cl]
- B (AgCl)
- D (FeCl2)
- A (NH4Cl)
- C (PbCl2)
Q.5. Select the correct word or formula from the same given in bracket :
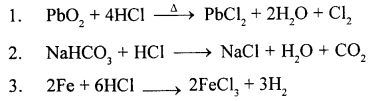
- The substance reacted with cone. HCl and heated to prove that cone. HCl contains Cl2. (PbCl2/PbO2/Pb0)
- The metal reacted with dil. HCl to prove that dil. HCl contains hydrogen. (Cu/Fe/Ag/Pb)
- The gas/es which is / are heavier than air and highly soluble in water. (NH3 / HCl/CO2/H2S)
- The acid which is not an oxidising agent. (Cone. HNO3/ Cone. HCl/Conc. H2SO4)
- The acid which is not a monobasic acid. (Acetic/ Sulphurous/Hydrochloric/Nitric/Formic acid)
Answer:
1. PbO2
2. Fe
3. HCl(g)
4. Cone. HNO3
5. Sulphurous acid
Q.6. Select the correct words from the list given below to complete the following word equations :
Metallic oxide, active metal, metallic carbonate, metallic bisulphite, active metal, metallic hydroxide, metallic bicarbonate, metallic sulphate, metallic sulphide.
- _____ + hydrochloric acid (dil) → salt + hydrogen
- _____ + hydrochloric acid (dil) → salt + water
- _____ + hydrochloric acid (dil) → salt + water + carbon dioxide
- _____ + hydrochloric acid (dil) → salt + water + sulphur dioxide
- _____ + hydrochloric acid (dil) → salt + hydrogen sulphide
Answer:
- active metal
- metallic hydroxide
- metallic carbonate / bicarbonate
- metallic sulphite
- metallic sulphide
For More Resources