Healthcare Vocabulary English: Vocabulary for the Health Professions! Learn important health and healthcare vocabulary in English, including common diseases, medical supplies and equipment, drug names, and other helpful vocabulary terms that you may encounter in the doctor’s office or in the hospital. This is also crucial in everyday discussion, for example, when expressing how you are feeling when someone asks or when discussing current health-related concerns.
In order to learn health-related terms in English that are demonstrated with images and examples to help you expand your English vocabulary skills and to help you get started with important health and healthcare vocabulary in English, we’ve put up a hand-picked health words a-z list of health vocabulary just for you.
List of Health Vocabulary Words in English
Name of Health Vocabulary Words
Speaking about one’s health is highly essential when communicating in any language , and it should be one of your primary emphasis points while learning English.
This is essential because if you ever become unwell while travelling in an English-speaking nation, you will be far more readily able to communicate what the problem related to good health is to those around you, so learning health vocabulary exercises is quite important in today’s time.
List of Health Vocabulary
- Common Diseases
- Common Illnesses
- Common Treatments
- Types of Doctors
- Medicine Names
- Medical Supplies and Equipment
Description of the Health Vocabulary Words
Common Diseases
Learn few common names of diseases and illnesses in English, i.e. asthma, a backache, a broken leg, an earache, a cold, a cough, a fever, the flu, a headache.
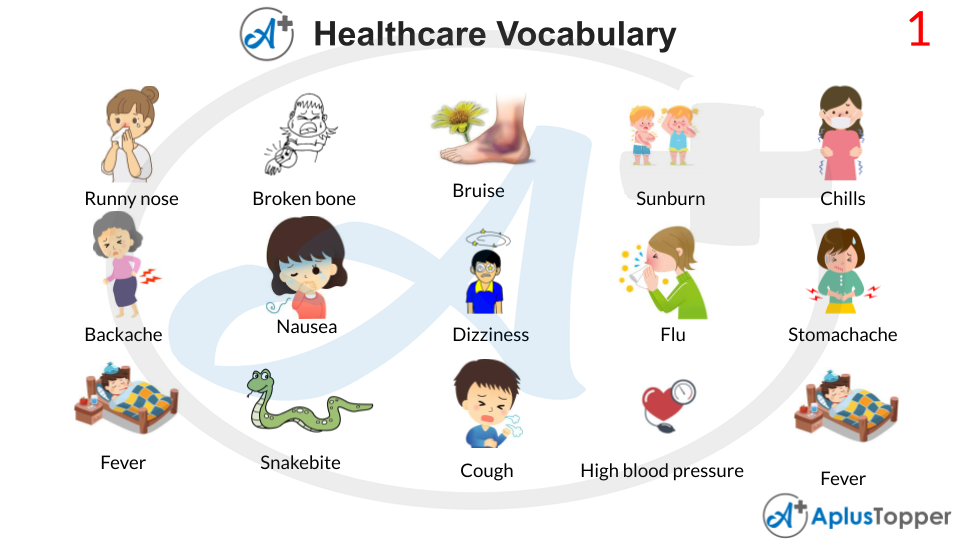
Excessive outflow from the nose and nasal passageways, ranging from clear fluid to thick mucus. A runny nose might have a variety of reasons that aren’t related to an illness. Cold exposure, high temperatures, and exercise are all examples.
A broken bone, either completely or partially. Trauma, misuse, and illnesses that weaken bones are all causes of bone fractures. Pain is the most common symptom. Depending on the region impacted, there may also be a loss of functionality. Resetting the bone in the original place and immobilising it in a splint or cast to allow it to recover are common treatments. Surgery with plates, screws and rods may be necessary in some cases.
Blood or bleeding under the skin as a result of any type of damage, usually black and blue at first, changing colour as healing continues. Bruising can occur for reasons other than an underlying illness. Blunt trauma, injury, recent IV usage, and blood draws are all examples.
Overexposure to sunshine or sunlamps causes this form of skin burn. Exposure to the sun or its harmful ray on a regular basis raises the risk of wrinkles, black spots, and skin cancer. Skin that is red, uncomfortable, itchy, and heated to the touch is one of the symptoms. It’s also possible for the skin to blister. Pain medications and itching treatments are used to treat the condition.
Shivering or shaking commonly accompany the sensation of being cold, even if it is not in a chilly environment. Shivering or shaking might have a variety of causes that aren’t related to an illness. Exposure to the cold, fear, or stress is all examples.
Physical discomfort ranging from moderate to debilitating anywhere on the spine or back. Back pain might have a variety of causes that aren’t related to an illness. Excessive exercise or lifting, extended sitting and lying down, sleeping in an awkward posture, or wearing a poorly fitted backpack are all examples of overuse.
A feeling of being sick, with a want to vomit. Nausea can have a variety of reasons that aren’t related to an illness. Motion from a car or plane, taking medicines on an empty stomach, eating too much or too little, or drinking too much alcohol are all examples.
Lightheaded, faint, or as if the head is spinning, with a distorted sense of balance and location. Dizziness might have a variety of reasons that aren’t related to an illness. Spinning in circles, drunkenness, pharmaceutical side effects, and standing up too rapidly are all examples.
A frequent viral illness can be fatal, especially in people who are at high risk. The flu is considered a respiratory illness that affects the lungs, nose, and throat. Young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with chronic illnesses or weakened immune systems are all in danger. Fever, chills, muscular pains, cough, congestion, runny nose, headaches, and tiredness are some of the symptoms.
Pain originating from the inside of the abdomen or the outside muscular wall, ranging from moderate and transient to severe and require immediate medical attention. Abdominal discomfort might have a variety of causes that aren’t related to an illness. Constipation, wind, overeating, stress, and muscle tension are all examples.
Fever is basically a rise in average body temperature of 98.6°F (37°C) during a short period of time. Medications like paracetamol and ibuprofen can help relieve pain. Giving aspirin to youngsters can lead to an uncommon but deadly illness.
An injury or bruise produced by a snake’s bite. If the snake is poisonous, a bite from it might be fatal. Pain, swelling, redness, and bleeding at the bite site are all possible symptoms. If an individual gets bitten by a snake, it is critical that he or she maintains cool, immobilises the bite region, and removes any jewellery or restrictive clothes. As quickly as possible, seek emergency medical attention.
To expel air and remove irritation in the throat or airway, make a quick, powerful hacking sound. Coughing can have a variety of causes that aren’t related to an illness. Normal airway clearance, irritants such as smoke and gas, cigarette use, or incorrectly swallowing food and beverages are all examples.
Common Illnesses
Fever is basically a rise in average body temperature of 98.6°F (37°C) during a short period of time. Medications like paracetamol and ibuprofen can help relieve pain. Giving aspirin to youngsters can lead to an uncommon but deadly illness.
A condition in which the blood present inside one’s body exerts too much pressure against the arterial walls. Hypertension is often described as a blood pressure reading of 140/90 or above, with a reading of 180/120 being considered critical. Symptoms related to high blood pressure are often absent. If left untreated, it can lead to health problems like heart disease and stroke. Lowering blood pressure to normal may be as simple as eating a better diet with less salt, exercising frequently, and taking medication.
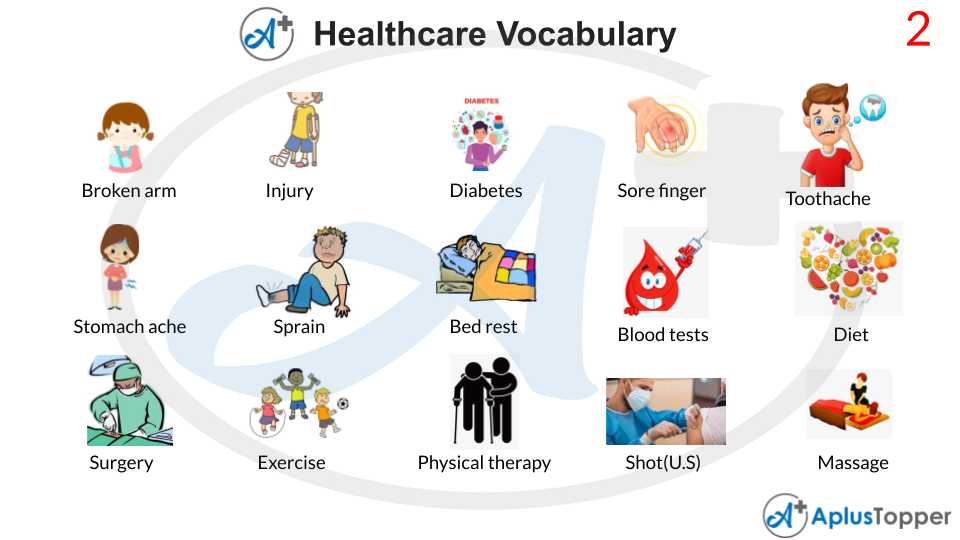
A fracture in any of these bones is referred to as a “broken arm.” A broken arm affects one or more of your arm’s three bones: the ulna, radius, and humerus. Falling into an outstretched hand is one of the most prevalent causes of a fractured arm.
An injury occurs when your body is damaged. It is a broad word that encompasses injuries caused by accidents, falls, strikes, weapons, and other factors. Every year, millions of individuals hurt themselves in the United States. These injuries can vary from mild to fatal. Injuries can occur at work or at play, inside or outdoors, while driving a car or crossing the street.
Diabetes is a particular disease in which the body’s ability to digest food for energy is impaired. The majority of the food one eats is converted to glucose, or sugar, which our bodies utilise as fuel. The pancreas, an organ which is located near the stomach, produces the hormone insulin, which aids glucose absorption into our bodies cells.
Inflammation is defined in one or more joints, resulting in pain and stiffness that can get worse as you get older. There are numerous forms of arthritis, each with its own set of causes, such as wear and tear, infections, and underlying illnesses. Pain, oedema, a restricted range of motion, and stiffness are some of the symptoms. Medication, physiotherapy, and, in rare cases, surgery is used to alleviate symptoms and enhance the quality of life.
Tooth decay or infection can cause pain or inflammation in or around the tooth. Toothache can be caused by a variety of factors other than an underlying illness. Biting onto anything hard, flossing, getting something caught between the teeth, or wearing braces are all examples. It’s a normal component of the developing process for youngsters.
Pain originating from the inside of the abdomen or the outside muscular wall, ranging from moderate and transient to severe and require immediate medical attention. Abdominal discomfort might have a variety of causes that aren’t related to an illness. Constipation, wind, overeating, stress, and muscle tension are all examples.
A sprain occurs when ligaments, the strong bands of fibrous tissue that link two bones in your joints, strain or break. An ankle sprain is the most frequent type of injury. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation are used as part of the first therapy. Mild sprains can be treated effectively at home.
Common Treatments
Bed rest, often known as the rest cure, is a medical therapy in which a person spends most of their time in bed in order to recover from an illness. Bed rest is defined as deliberately lying in bed as a therapy rather than being confined to bed due to a health condition that prohibits you from leaving the bed.
A blood test is a laboratory examination of blood taken from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle or a fingerprick. Multiple tests for particular blood components, such as a glucose or cholesterol test, are sometimes bundled into a single test panel known as a blood panel or blood work.
Diet refers to the cumulative amount of food consumed by a human or other creature. Diet frequently connotes the utilisation of a certain nutritional intake for health or weight-loss purposes (with the two often being related).
Surgery is a medical or dental speciality that employs operational manual and instrumental methods on a patient to treat a pathological condition after examining such as a disease or injury, as well as to assist and enhance body function, appearance, or to repair undesired ruptured regions.
Any physiological action that maintains or improves general health and physical fitness and wellness is considered exercise. It is done for a variety of purposes, including to help grow and increase strength, to avoid ageing, to strengthen muscles and the cardiovascular system, to hone sports abilities, to lose or maintain weight, to promote health, or just for fun.
One of the allied health professions is physical therapy, often known as physiotherapy. It is given by physical therapists who use physical examination, diagnosis, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, illness prevention, and health promotion to promote, maintain, or restore health.
The manipulation of the body’s soft tissues is known as massage. Hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet, or a device are often used in massage methods. Massage is most commonly used to relieve tension or discomfort in the body.
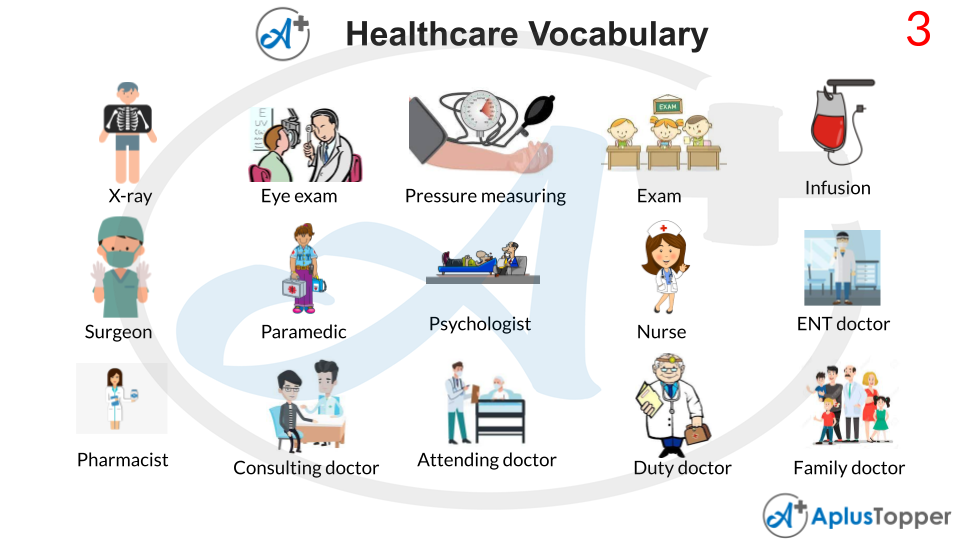
An X-ray, often known as X-radiation, is a type of penetrating high-energy electromagnetic radiation. The wavelength of most X-rays is in the range of 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies of 124 eV to 124 keV.
An eye exam is a set of examinations used to evaluate eyesight and the ability to concentrate on and distinguish things. Other eye-related tests and exams are also included. Optometrists, ophthalmologists, orthoptists, and opticians are the most common providers of eye exams.
A medical practitioner checks a patient for any probable medical signs or symptoms of a medical ailment during a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination. It usually entails a series of inquiries regarding the patient’s medical history, followed by a physical examination based on the symptoms described.
Infusion treatment is a medical term that refers to the administration of fluids and medications through an intravenous or subcutaneous route. This can positively be accomplished with the use of a specialised infusion pump. In most cases, a fenestrated catheter is introduced into the specific region to be treated.
Types of Doctors
Here are different types of specialists and doctors and in various areas in the healthcare profession.
A surgeon is a practitioner or person who specialises in assessing and treating diseases that may necessitate surgery or other physical changes to the human body. Surgical procedures can be used to diagnose or treat illness or injuries. Surgeons lead a team of other physicians and nurses in the operating room to ensure that surgery goes smoothly.
A paramedic is basically a health care worker whose primary responsibility is to offer advanced emergency medical care to severely injured or ill patients who seek treatment in an emergency room. Not all paramedics work in ambulances.
A psychologist investigates normal and aberrant mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behaviour through experimenting with, as well as observing, analysing, and recording how people interact with one another and their surroundings.
A registered nurse is normally a person who has completed a nursing programme and satisfied the conditions for obtaining a nursing licence set out by a nation, state, province, or other government-authorised licencing organisation. A person who is competent in maintaining and promoting health who practises independently or under the supervision of a physician, surgeon, or dentist – compare licenced practical nurse, a registered nurse.
Otorhinolaryngology is a surgical speciality of medicine that focuses on the surgical and medicinal treatment of head and neck disorders. Otorhinolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, otolaryngologists, or ENT surgeons or physicians are doctors who specialise in this field.
A pharmacist, often known as a druggist or a chemist who is a health practitioner who understands the characteristics, interactions, composition, and correct use of drugs. At the same time, the pharmacist offers the general public pharmacological information and guidance, as well as basic health care services.
Senior doctors who have finished comprehensive medical training in a specialised area of medicine and are registered on the GMC’s specialist register are referred to as consultants. Every patient who has been admitted to the hospital will be assigned to a specific consultant.
An attending physician has finished their training and is now working in their chosen speciality on their own. This phrase is commonly used at teaching facilities to distinguish fully qualified senior-level physicians from junior physicians still pursuing their higher education.
This service provides you with rapid access to your primary care physician’s office, where they are familiar with you and have your complete medical record. We advocate using this service instead of travelling to the hospital’s A&E department. Reception can then add you to the roster of Duty Doctors.
A primary care physician (PCP), sometimes known as a primary care provider, is a doctor who specialises in general medicine. Our primary care physicians (PCPs) are our first port of call for medical attention. PCPs are usually physicians, although they can also be nurse practitioners or physician assistants.
A veterinarian (vet), sometimes known as a veterinary surgeon or veterinary physician, is a medical practitioner who treats illnesses, injuries and problems in animals other than humans.
A dentist, also recognised as a dental surgeon, is a doctor who specialises in dentistry, which includes the diagnosis, treatment of illnesses and disorders of the mouth and provides prevention. The dentist’s support staff assists in the delivery of oral health care. Dental assistants, dental technicians, dental hygienists and occasionally dental therapists make up the dental team.
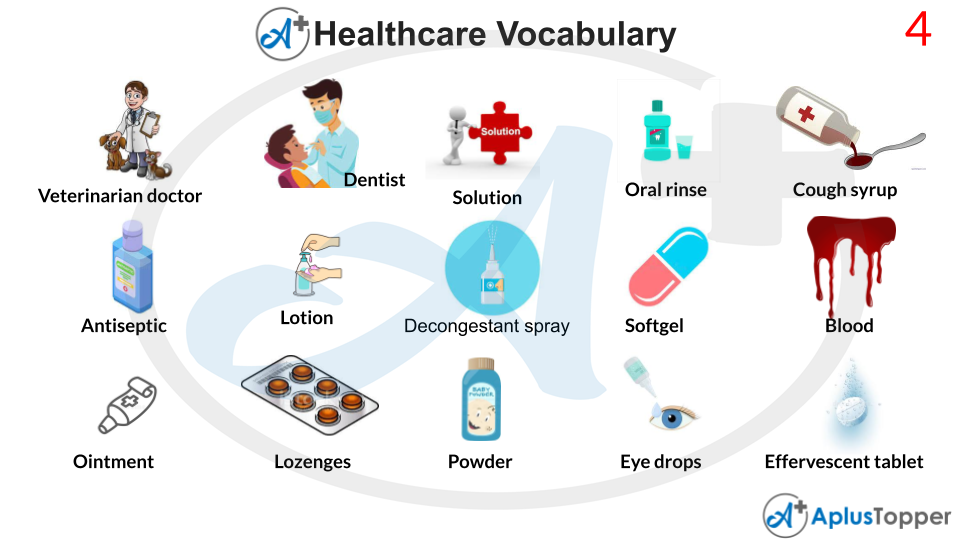
Medicine Names
Medicine is the practice and science of the treatment, prevention and diagnosis of disease.
A solution is a sort of homogenous combination constituting two or more chemical components in chemistry. A solute is basically a material that is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent, in such a combination. A solution is mixed at a scale that includes the effects of chemical polarity, resulting in solvation-specific interactions.
Gingivitis can be treated with chlorhexidine gluconate mouth rinse, although not all forms of gingivitis. Only use the medicine to treat the problem for which your dentist has recommended it. The mouthwash chlorhexidine gluconate is a germicidal mouthwash that kills germs in the mouth. Gingivitis is treated with chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse (swelling, bleeding gums, redness). A dentist will generally prescribe chlorhexidine gluconate.
Sneezing, coughing, or a runny nose caused by a common cold, hay fever, or other upper respiratory allergens can be temporarily relieved with this combo solution. This medication comprises a cough suppressant that is non-opioid (such as chlophedianol, dextromethorphan). It works by affecting a specific area of the brain (the cough centre) in order to assist you to stop coughing.
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances or compounds that are administered to living tissue or skin to prevent infection, sepsis, and putrefaction. Antiseptics are distinguished from antibiotics by their capacity to safely eliminate germs inside the body, as opposed to disinfectants, which kill microbes on non-living things.
A lotion is a topical treatment with a low viscosity that is applied to the skin. Creams and gels, on the other hand, have a higher viscosity due to their reduced water content. External skin lotions are applied with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.
This medicine is utilised to treat nasal congestion caused by a variety of diseases such as the common cold, hay fever, allergies and sinusitis. It reduces oedema and congestion by restricting the blood vessels in the nose.
A soft gel is a specialised capsule that serves as an oral dosage form for medication. They have a gelatin-based shell that surrounds a liquid filling. Gelatin, water, an opacifier, and a plasticiser like glycerin or sorbitol make up softgel shells.
Blood is a bodily fluid found in humans and other animals that carries metabolic waste products away from cells while also delivering essential chemicals such as nutrition and oxygen. It consists of blood cells suspended in blood plasma in vertebrates.
A cream that is applied to the skin and is based on oil. An ointment holds an oil base, whereas a cream has a water base. A smooth, oily material is applied to the skin for medical or aesthetic purposes. Ointments can be applied to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes to treat everything from dry skin to wounds, burns, bites, haemorrhoids, and scrapes.
A throat lozenge is a tiny, usually pharmaceutical pill that is dissolved gently in the mouth to halt coughing, lubricate, and soothe inflamed tissues of the throat, which may be caused by the common cold or influenza. Because of their original diamond form, cough pills have been given the term lozenge.
Talc (or talcum) is a hydrated magnesium silicate clay mineral having the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Baby powder is made from talc powder, which is commonly mixed with corn starch.
Eye drops, often known as eye drops, are saline-based drops used as an ocular method of administration. They may comprise steroids, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetics, antihistamines, sympathomimetics, parasympatholytics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), antibiotics, antifungals, topical anaesthetics, or prostaglandins, depending on the disease being treated. Eye drops are sometimes just lubricating and tear-replacing solutions and may not include any medicines.
Carbon tablets, often known as effervescent tablets, are tablets that dissolve in water to release carbon dioxide. They are formed out of compressing powdered component materials into a dense mass, which is then packed in a blister pack or a hermetically sealed packaging with a desiccant in the cap.
A tablet is a solid oral dosage form (OSD) or solid unit dosage form used in pharmaceuticals. Tablets may be described as a solid unit dosage form of a medication or a combination of medications with appropriate excipients. It is made up of a powdered combination of active ingredients and excipients that is pressed or compressed into a solid dosage.
Toothpaste is a gel or pastes dentifrice that is applied to teeth with a toothbrush to clean and preserve their appearance and health. Toothpaste is abrasive that facilitates the removal of dental plaque, and food from the teeth supplies active chemicals (most frequently fluoride) to help prevent tooth decay (dental caries), helps to reduce halitosis and gum disease (gingivitis).
Aspirin, also scientifically known as acetylsalicylic acid, is a pain reliever, fever reducer, and inflammation reducer. Aspirin is used to treat inflammatory diseases such as Kawasaki illness, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. When taken soon after a heart attack, aspirin lowers the chance of death.
A caplet is a compressed combination of substances that is shaped into a capsule shape, similar to a tablet. To conceal the flavour and make it easier to swallow, it frequently includes a film or gelatin coating. A capsule is a flexible technique to deliver medicines orally in general.
Encapsulation is a term used in the pharmaceutical industry to describe a variety of dosage forms—techniques for enclosing medications in a reasonably stable shell known as a capsule, allowing them to be taken orally or used as suppositories.
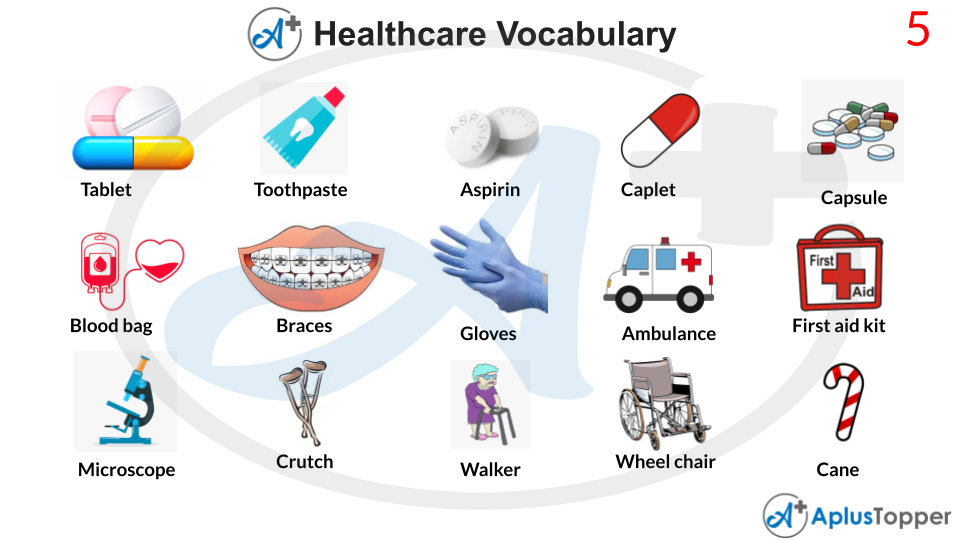
Medical Supplies and Equipment
Blood bags are used to collect, store, transport and separate blood in a safe and dependable manner. Blood coagulation is prevented by the rounded blood bag shape, which guarantees that blood and anticoagulants are adequately mixed during separation and transfusion.
Dental braces are orthodontic devices that straighten and align teeth, as well as help place them in relation to a person’s bite, with the goal of improving dental health. Braces can also close gaps. They are frequently used to treat underbites, malocclusions, overbites, open bites, deep bites, crossbites, crooked teeth, and other dental and jaw defects. Braces are available in two types: aesthetic and structural. Dental braces are frequently used in conjunction with other orthodontic tools to expand the palate or jaws, as well as to help shape the teeth and jaws in other ways.
A rubber glove is one that is composed of either natural or synthetic rubber. Rubber gloves can be either unsupported (rubber only) or supported (rubber and other materials) (rubber coating of textile gloves). Its major use is to protect the hands when conducting chemical-related jobs. Rubber gloves can be used to shield hands from detergent and allow for the use of hotter water when dishwashing.
A medically equipped vehicle that carries patients to treatment facilities such as hospitals is known as an ambulance. The patient is usually given medical care outside of the hospital. Emergency medical services employ ambulances to react to medical crises.
A first-aid kit is a collection of goods and equipment for administering medical care. The contents of first aid kits vary widely depending on the expertise and experience of people who put them together, the different first aid requirements of the region where they may be used, and differences in legislation or regulation in that area.
A microscope is a scientific device that is used to study items that are too tiny for the naked eye to perceive. Microscopy is considered the science of using a microscope to study tiny objects and structures. Unless assisted by a microscope, microscopic means undetectable to the naked sight.
A crutch is a mobility device that helps you shift your weight from your legs to your upper body. It is frequently used by persons who are unable to support their weight with their legs due to a mixture of problems ranging from temporary injuries to permanent impairments.
A walker, sometimes known as a walking frame, is a device used by handicapped or frail persons who require extra assistance to maintain balance or stability when walking, usually owing to age-related physical limitations. The basic design has a lightweight frame that is roughly waist height, 12 inches (30 cm) deep, and somewhat broader than the user.
A wheelchair is a wheeled chair that is used when walking is difficult or impossible due to disease, accident, or age-related difficulties. Spinal cord injuries (paraplegia, hemiplegia, and quadriplegia), cerebral palsy, brain damage, osteogenesis imperfecta, motor neuron disease, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, spina bifida, and other conditions can all cause these symptoms.
An assistive cane is a crutch or mobility device that looks like a walking stick. A cane can assist transfer weight from a weak or sore lower leg, increase stability by expanding the base of support and enhance balance by providing tactile information about the ground.
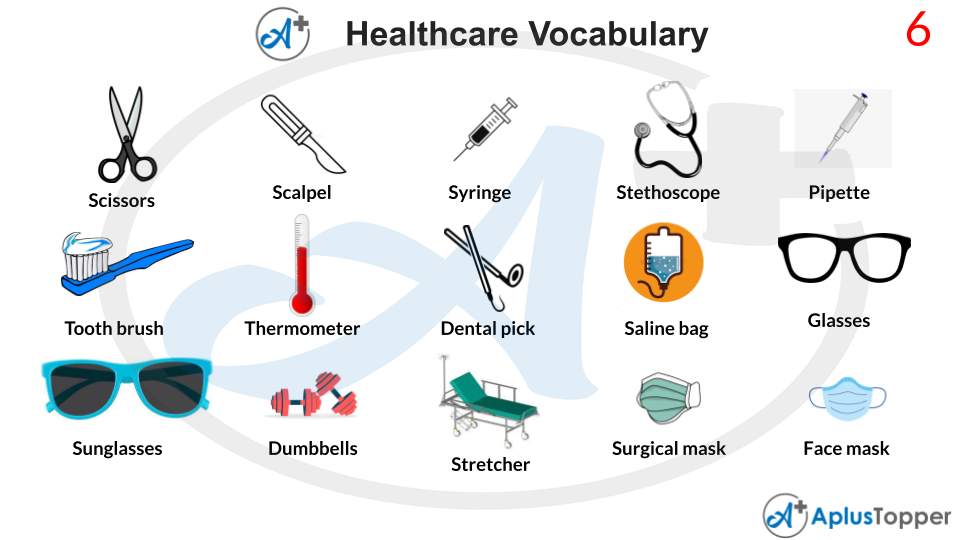
Scissors are shearing instruments that are operated by hand. When the handles opposite the pivot are closed, the sharpened edges of the metal blades glide against each other, forming a pair of scissors.
A scalpel, sometimes known as a lancet or bistoury, is a tiny bladed device used in surgery, anatomical dissection, podiatry, and a variety of arts and crafts. Scalpels are available in both single-use and reusable varieties.
A syringe is a basic reciprocating pump with a plunger that fits snugly inside a cylindrical tube known as a barrel. The syringe may take in and expel liquid or gas via a discharge hole at the front end of the tube by pulling and pushing the plunger linearly down the interior of the tube.
The stethoscope is basically an acoustic medical instrument used for auscultation or listening to an animal’s or person’s interior noises. A tiny disc-shaped resonator is generally placed against the skin, and one or two tubes are linked to two earpieces. A stethoscope is utilised to listen to the heart, lungs, and intestines, as well as blood flow in arteries and veins.
A pipette (sometimes spelt pipet) is a laboratory tool used to transfer a measured volume of liquid and is frequently used as a media dispenser in chemistry, biology, and medicine. From single-piece glass pipettes to more sophisticated adjustable or electronic pipettes, pipettes come in a variety of designs for diverse applications with varying levels of accuracy and precision.
A toothbrush is a tool for cleaning the teeth, gums, and tongue. It comprises a handle with tightly clustered bristles on top of which toothpaste may be applied and a head of tightly clustered bristles on top of which toothpaste can be applied to clean hard-to-reach parts of the mouth.
A thermometer is a device that monitors temperature or temperature differences. A thermometer consists of two key components: a temperature sensor that detects changes in temperature and a mechanism of translating those changes into numerical values.
Saline is used to replacing lost fluids, flush wounds, provide medicines, and keep patients alive during surgery, dialysis, and chemotherapy. Twenty snack-sized bags of potato chips have the same amount of sodium as a bag of saline solution.
Glasses, often known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are a type of visual eyewear that consists of a frame that supports glass or hard plastic lenses in front of a person’s eyes. Glasses are generally used for vision correction, such as reading glasses and near-sightedness glasses; but, without the specific lenses, they are occasionally used for aesthetic reasons.
Sunglasses or sunglasses (also known as shades or sunnies; see below for other names) are a type of protective eyewear that is used to shield the eyes from intense sunshine and high-energy visible light. Spectacles or glasses with coloured, polarised, or darkened lenses, often known as spectacles or glasses, can occasionally serve as visual assistance.
A dumbbell, which is a form of free weight, is a piece of weight-lifting equipment. It may be used alone or in pairs (one in each hand). They help to increase muscular development by activating a variety of muscles. Both muscular power and flexibility can be improved using them. They can help muscles and joints to coordinate and be more stable.
The frames, wheels, and racks of a wheeled stretcher are all distinct. They’re utilised by emergency medical workers, rescuers, and military people. In ambulances, EMS stretchers have wheels that allow them to move around on the pavement.
During medical operations, health workers use a surgical mask, often known as a medical face mask. By preventing the passage of pathogens (mainly bacteria and viruses) shed in respiratory droplets and aerosols from the wearer’s mouth and nose inhibits airborne transmission of diseases between patients and/or treatment workers when worn appropriately.
A cloth face mask is a mask worn over the mouth and nose made of ordinary fabrics, generally cotton. Cloth face masks are suggested by public health organisations for disease “source management” in epidemic conditions to protect people from virus-laden droplets in infected mask wearers’ breath, coughs, and sneezes when more effective masks are not available, and physical separation is impractical.
Surgical tape, also known as medical tape, is a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape that is used in medicine and first aid to secure a bandage or other dressing to a lesion. These tapes often feature a hypoallergenic adhesive that is meant to adhere strongly to skin, dressing materials, and underlying layers of tape while also being easy to remove without causing damage to the skin.
A bandage is a piece of cloth that can be used to support a medical device such as a dressing or splint, or it can be used on its own to support or limit the mobility of a bodily component. When used in conjunction with a dressing, the dressing is placed directly to the wound and held in place by a bandage.