These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 2.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 2
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | X |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 2 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 10 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 2 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time : 3 hrs
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions
- The question paper has 28 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Questions from serial number 1 to 7 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries one mark.
- Questions from serial number 8 to 18 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 wrods each.
- Questions from serial number 19 to 25 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question number 26 & 27 are map questions from History with 1 mark each.
- Question number 28 is map question of 3 marks from Geography.
- For Q. Nos. 26, 27 and 28 (map based questions) one outline political map of India is provided. After completion the work, attach the map inside your answer book.
Question 1.
Who wrote Hind Swaraj? (1 Mark)
OR
Why did french colonise Vietnam?
Question 2.
What was Agent orange? (1 Mark)
OR
What is Diamond sutra?
Question 3.
Which steel plant is located in Chattisgarh? (1 Mark)
Question 4.
What is a Coalition Government? (1 Mark)
Question 5.
Name the countries which have coming together federation and holding together federation (1 Mark)
Question 6.
What is overlapping differences? (1 Mark)
Question 7.
Which constitutional bodies suggest reforms in political parties? (1 Mark)
Question 8.
Explain three features of ‘Go East Movement’ in Vietnam. (3 Marks)
Question 9.
Print media popularized the ideas of enlightment thinkers – Explain. (3 Marks)
Question 10.
What are the uses of Manganese ore? (3 Marks)
Question 11.
Explain any four merits of pipeline transport in India? (3 Marks)
Question 12.
Examine the significance of Decentralisation. (3 Marks)
Question 13.
In what ways has the local government deepened our democracy? (3 Marks)
Question 14.
Differentiate between horizontal and vertical division of powers. (3 Marks)
Question 15.
What are the basis of communalism? (3 Marks)
Question 16.
Substitutes of cheap imports like Chinese toys is unethical – Discuss. (3 Marks)
Question 17.
Explain the process involved in the issuing of a cheque. (3 Marks)
Question 18.
Explain any three advantages of globalisation. (3 Marks)
Question 19.
What were the characteristics of ancient cities? (5 Marks)
OR
Explain any five sources of entertainment in London.
Question 20.
How did Civil Disobedience Movement differ from Non-cooperation Movement? (5 Marks)
OR
How did Non-cooperation Movement affect the people economically?
Question 21.
Distinguish between Red soil and laterite soil. (5 Marks)
Question 22.
Multipurpose river projects are referred to as the temples of modern India-Elucidate. (5 Marks)
OR
How has NTPC worked towards safer environment?
Question 23.
What are the various challenges faced by political parties? (5 Marks)
Question 24.
Differentiate between formal sector credit and informal sector credit. (5 Marks)
OR
What is the role of banks in India?
Question 25.
Explain any five rights of the consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 1986. (5 Marks)
OR
What are the lopsided of consumer movements?
Question 26.
Locate and label the following (1 Mark)
A place where Jallianwala Bagh incident took place.
Question 27.
Locate (1 Mark)
Place where violence erupted during Non-cooperation movement leading to its withdrawal.
Question 28.
Locate (3 Marks)
- Place where Cotton Textile Industry is located.
- Place where Software Technology Park is located.
- Iron and Steel Plant location.
Answers
Answer 1.
Gandhi (1)
OR
For economic exploitation.
Answer 2.
A poisonous chemical used by the US to destroy villages and forests in Vietnam. (1)
OR
Oldest Japanese book.
Answer 3.
Bhilai steel plant (1)
Answer 4.
When no single party gets majority and two or more political parties join together to form government is called coalition government (1)
Answer 5.
- U.SA, Switzerland, Australia (1/2)
- India, Spain, Belgium. (1/2)
Answer 6.
When one kind of social difference becomes more important than others is overlapping
difference. (1)
Answer 7.
The Constitution of India and the Election Commission of India. (1/2 + 1/2)
Answer 8.
- It attracted many Vietnamese students who went to Japan to study. (1)
- To overthrow the puppet emperor and re-establish the Nguyen dynasty. (1)
- To obtain foreign arms and help. (1)
Answer 9.
- The writings of thinkers provided a critical commentary on tradition and superstition. (1)
- Scholars argued for reason and rationality (1)
- They attacked the sacred authority of the church and despotic power of the ring. (1)
Answer 10.
- It is used in the manufacturing of steel. (1)
- It is used to make bleaching powder and insecticides. (1)
- It is used in manufacturing of batteries and paints. (1)
Answer 11.
- They are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas. (1)
- Solids can be transported when converted into slurry (1)
- Pipelines rule out trans-shipment losses and delays. (1)
Answer 12.
- It helps in the settlement of problems and issues at the local level. (1)
- It provides a platform for the direct participation of people in decision making. (1)
- It is the best way to realise principles of democracy i.e. democracy at the grass root level. (1)
Answer 13.
- It has increased women’s representation and voice in our democracy. (1)
- It has widened the scope of political participation. (1)
- Seats are reserved for the S.C, S.T and O.B.C which has increased their participation in decision making. (1)
Answer 14.
Horizontal | Vertical |
1.In this power is shared between legislature, executive and Judiciary. | 1. In this power is shared between union, state and local government. (1) |
2.It specifies the concept of checks and balances in order to check unlimited powers of the organs. | 2. There is no concept of check and balances because powers are given by the constitution from the higher to the lower level. (1) |
3. It ensures the concept of the expansion of democracy | 3. It promotes the concept of deepening of democracy. (1) |
Answer 15.
- The followers of a particular religion must belong to one community. (1)
- It follows that people who follow different religions cannot belong to the same community. (1)
- It believes that people belonging to different religions cannot live as equal citizens. (1)
Answer 16.
- It is unethical because it has contributed to the loss of Indianness. (1)
- The children are losing touch with the roots. (1)
- It leads to erosion of patriotism and Indian culture. (1)
Answer 17.
- The payer issues a cheque for a specific amount. (1)
- The cheque instructs the bank to pay the amount from the depositor’s account to whom it has been issued. (1)
- The amount is then transferred from one bank account to another bank account in a day or two. (1)
Answer 18.
- Rapid improvement in technology, especially in the development of information and communication technology (1)
- Competition among the producers is an advantage to the consumers. (1)
- It has also created new opportunities for companies producing services, especially in information technology, data entry and accounting. (1)
Answer 19.
- Ancient cities were a river valley civilisations like Harappa. (1)
- Cities developed only with the increase in food supply. (1)
- They were often centres of political power with administrative network. (1)
- They also emerged in the periphery of religious institutions (1)
- Cities were of different sizes and complexity. (1)
OR
- For the rich London season
- Pubs for working class
- Art galleries, libraries and museums
- Lower classes loved music halls
- Cinema for all
Answer 20.
Non – co-operation | Civil – disobedience |
Launching period 1920 -1922 | 1930-34. (1) |
Reason – Anger of Jallianwala Bagh Tragedy | Protest of the arrival of simon commission. (1) |
Methods – Surrender of tides, boycott of British institutions | Defying and breaking of colonial rules. (1) |
Aim – Swaraj or self-government | Puma Swaraj or complete independence (1) |
Participation -All sections of the society | Dalits, Muslims, industrial workers and businessmen did not join (1) |
OR
- Boost to Indian textile
- Indians used own made clothes
- Refusal to foreign goods
- Import of foreign cloth decreased
- foreign cloth was burnt
Answer 21.
Red soil | Laterite soil |
1. It is formed due to weathering of igneous and metamorphic rocks | 1.It is formed by leaching process in the tropical areas. |
2.Highly porous and less fertile but when deep, it is fertile. | 2.It is less fertile |
3.less crystalline | 3.Crystalline |
4.red in colour due to iron | 4.red in color due to little clay and much gravel of red sandstone |
5.found in Tamil Nadu, Karnataka Andhra, Orissa and Jharkhand | 5.found in the hills of Deccan, Kerala, Orissa, Assam and Meghalaya. |
Answer 22.
- They provide water to areas which suffer from water scarcity. (1)
- Flood control by regulating flow of water. (1)
- Fish breeding. (1)
- Recreational facilities. (1)
- Soil conservation through afforestation. (1)
OR
- Reducing environmental pollution
- Ecological monitering
- Green belts
- Minimizing waste generation
- Optimum use of equipment
Answer 23.
- Lack of internal democracy – As parties do not hold organizational meetings and do not conduct regular internal elections (2)
- Dynastic succession – The top post are always controlled by members of our family (1)
- Money and muscle power – parties support criminals who raise money and have muscle power (1)
- Absence of meaningful choice – There is not much ideological difference between political parties so voters never get any positive option. (1)
Answer 24.
Formal Sector | Informal Sector |
1.Credit is provided by banks and co-operative societies | 1.Credit is provided by traders and money- Lenders. (1) |
2.R.B.I supervises the sector | 2.No supervision (1) |
3.Proper terms of credit like documentation, rate of interest, collateral are followed | 3.Terms of credit are flexible (1) |
4.Rate of interest is low | 4.Rate of interest is high (1) |
OR
- Provides loans
- Money in safe custody
- Wave loans of the farmers
- Gives interest on savings
- Mediate between people who have surplus and those who need money.
Answer 25.
- Right to safety – Consumer has the right to be protected against goods and services which are Hazardous to life and health. (1)
- Right to be informed – Consumer has the right to have complete information of the product he buys. (1)
- Right to choose – Consumer has freedom to choose from a variety of products at competitive prices. (1)
- Right to be heard – Consumer has the right to file a complaint and to be heard in case of dissatisfaction of a good. (1)
- Right to seek Redressal – Consumer has the right to get relief in case product falls short of his expectation. (1)
OR
- Not well organized
- Rules often not followed
- No clarity on issue of compensation
- Most of the time no cash memos
- Redressal is expensive.
Answer 26.
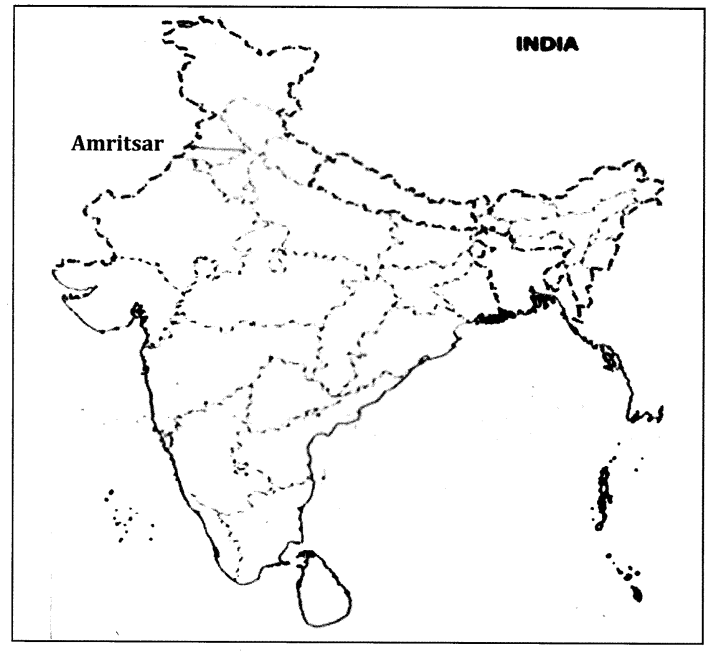
- A Place in Punjab where Jallianwala Bagh incident took place (1)
Answer 27.
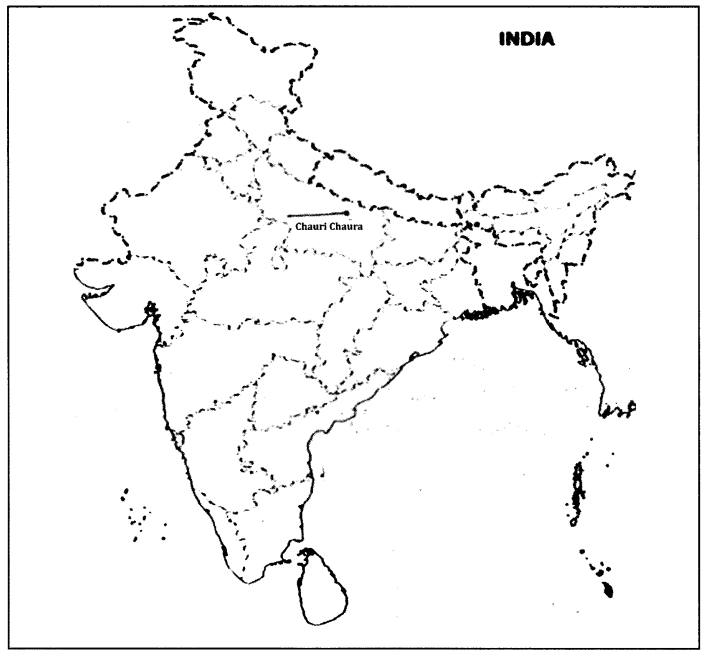
- place where violence erupted during Non-cooperation Movement leading to its withdrawl (1)
Answer 28.
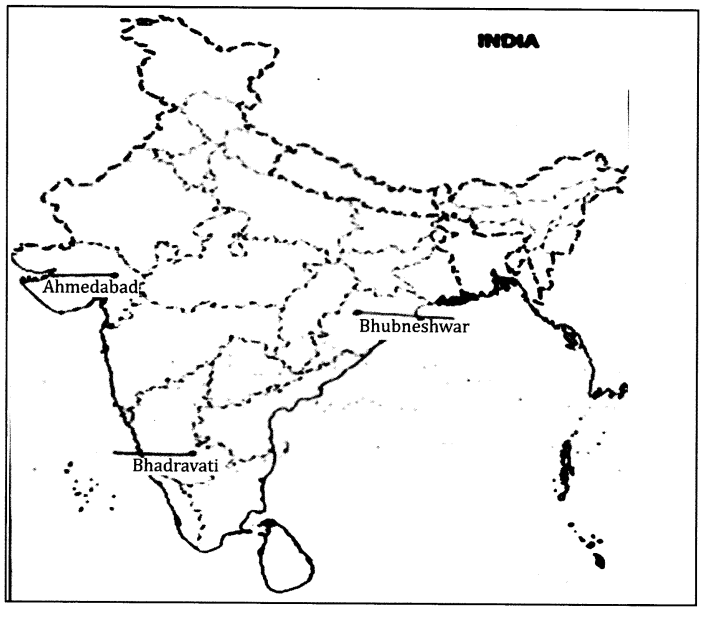
- A Place where cotton textile industry is located – Ahmedabad (1)
- A Place where software technology park is located – Bhubneshwar (1)
- Iron and steel plant location – Bhadravati (1)
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 2 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.