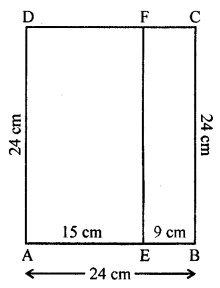
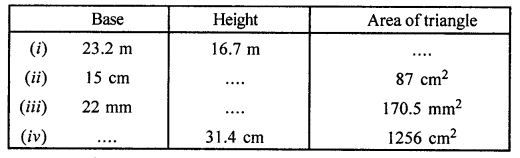
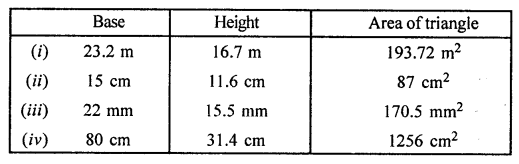
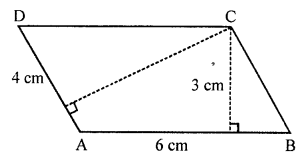
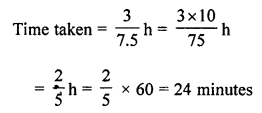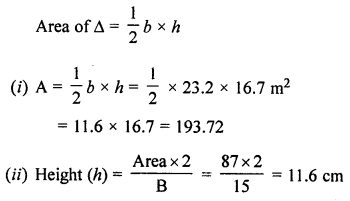ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 6 Ratio and Proportion Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) The simplest form of the ratio \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) : \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) is ………
(ii) 75 cm : 1.25 m = ……..
(iii) If two ratios are equivalent, then the four quantities are said to be in ………
(iv) If 8, x, 48 and 18 are in proportion then the value of x is ………
(v) If the cost of 10 pencils is ₹ 15, then the cost of 6 pencils is ……..
(vi) If a cyclist is travelling at a speed of 15 km/h, then the distance covered by him in 20 minutes is ……..
Solution:
(i) The simplest form of the ratio \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) : \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) is 2 : 3.
(ii) 75 cm : 1.25 m = 3 : 5
(iii) If two ratios are equivalent,
then the four quantities are said to be in proportion.
(iv) If 8, x, 48 and 18 are in proportion then the value of x is
8 : x :: 48 : 18
x = 3
(v) If the cost of 10 pencils is ₹ 15, then the cost of 6 pencils is
Cost of 10 pencils = ₹ 15
Let cot of 6 pencils = ₹ x
10 : 6 15 : x
10x = 6 × 5
x = 3
Cost of 6 pencils = ₹ 3
(vi) If a cyclist is travelling at a speed of 15 km/ h,
then the distance covered by him in 20 minutes is ……
Speed of a cyclist = 15 km/h
Distance travelled in 20 minutes = \(\frac { 20 }{ 60 }\) × 15 km = 5 km
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) A ratio is always greater than 1.
(ii) Ratio of half an hour to 20 seconds is 30 : 20.
(iii) The ratio 5 : 7 is greater than the ratio 5 : 6.
(iv) If the numbers 3, 5, 12 and x are in proportion then the value of x is 20.
(v) The ratio 3 : 2 and 4 : 5 are equivalent.
Solution:
(i) A ratio is always greater than 1. (False)
Correct:
Ratio can be less than 1 or equal to 1.
It is not necessary that it is greater than 1.
(ii) Ratio of half an hour to 20 seconds is 30 : 20. (False)
Correct:
= 30 × 60 : 20 = 1800 : 20 = 90 : 1
(iii) The ratio 5 : 7 is greater than the ratio 5 : 6. (False)
Correct:
\(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\), \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\)
\(\frac { 30:35 }{ 42 }\)
30 < 35
5 : 7 is not greater than the ratio 5 : 6
(iv) If the numbers 3, 5, 12 and x are in proportion
then the value of x is 20. (True)
3, 5, 12 and x are in proportion then
x × 3 = 5 × 12
x = 20
(v) The ratio 3 : 2 and 4 : 5 are equivalent. (False)
Correct:
\(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) ≠ \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) as 15 ≠ 8
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 14):
Question 3.
A ratio equivalent to 6 : 10 is
(a) 3 : 4
(b) 18 : 30
(c) 12 : 40
(d) 5 : 3
Solution:
6 : 10 = 3 : 5
18 : 30 = 3 : 5
6 : 40 is equivalent to 18 : 30 (b)
Question 4.
A ratio equivalent to the ratio \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) : \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) is
(a) 4 : 6
(b) 8 : 9
(c) 6 : 8
(d) 9 : 8
Solution:
\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) : \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
\(\frac { 8:9 }{ 12 }\)
= 8 : 9 (b)
Question 5.
The ratio of 75 mL to 3 litres is
(a) 25 : 1
(b) 40 : 1
(c) 1 : 40
(d) 3 : 200
Solution:
75 mL to 3 litres
= 75 : 3000
= 1 : 40 (c)
Question 6.
The ratio of the number of sides of a rectangle to the number of edges of a cuboid is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 3
(c) 2 : 3
(d) none of these
Solution:
Ratio of number of sides of a rectangle
to the number of edges of a cuboid = 4 : 12 = 1 : 3 (b)
Question 7.
In a class of 35 students, the number of girls is 20. The ratio of number of boys to the number of girls in the class is
(a) 3 : 4
(b) 4 : 3
(c) 7 : 4
(d) 7 : 3
Solution:
Total number of students = 35
No. of girls = 20
No. of boys = 35 – 20 = 15
Ratio in boys and girls = 15 : 20 = 3 : 4 (a)
Question 8.
The ratio of number of girls to the number of boys in a class is 6 : 7. If there are 21 boys in the class, then the number of girls in the class is
(a) 39
(b) 24
(c) 18
(d) 13
Solution:
Girls : boys = 6 : 7
No. of boys = 21
Let no. of girls = x
6 : 7 :: x : 21
7 × x = 6 × 21
x = 18
No. of boys = 18 (c)
Question 9.
Two numbers are in the ratio 3 : 5. If the sum of the numbers is 144, then the largest number is
(a) 48
(b) 54
(c) 72
(d) 90
Solution:
Ratio between two numbers = 3 : 5
Sum of numbers 144
Then larger number = \(\frac { 144 }{ 3+5 }\) × 5
= \(\frac { 144 }{ 8 }\) × 5 = 90 (d)
Question 10.
If x, 12, 8 and 32 are in proportion, then x is
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 2
Solution:
x, 12, 8 and 32 are in proportion, then
x × 32 = 12 × 8
x = 3 (c)
Question 11.
If 3, 12 and x are in continued proportion, then x is
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 16
(d) 48
Solution:
3, 12 and x are in continued proportion, then
3 : 12 :: 12 : x
3x = 12 × 12
x = 48 (d)
Question 12.
If the weight of 5 bags of sugar is 27 kg, then the weight of one bag of sugar is
(a) 5.4 kg
(b) 5.2 kg
(c) 5.4 kg
(d) 5.6 kg
Solution:
Weight of 5 bags of sugar = 27 kg
Weight of one bag of sugar
= 5 : 1 :: 27 : x
5x = 1 × 27
x = \(\frac { 27 }{ 5 }\) = 5.4 kg (c)
Question 13.
Sonali bought one dozen notebooks for ₹ 66. What did she pay for one notebook?
(a) ₹ 6.50
(b) ₹ 6.60
(c) ₹ 5.60
(d) ₹ 5.50
Solution:
Cost of 12 books = ₹ 66
Let cost of one book = x
12 : 1 = 66 : x
12 × x = 1 × 66
x = 5.5
Cost of 1 book = ₹ 5.50 (d)
Question 14.
The speed of 90 km/h is equal to
(a) 10 m/sec
(b) 18 m/sec
(c) 25 m/sec
(d) none of these
Solution:
Speed of 90 km/h = \(\frac { 90\times 5 }{ 18 }\) m/sec
= 25 m/sec (c)
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Sudhanshu divided his property into two parts in the ratio 8 : 5. If the first part is ₹ 1,60,000 and second part is donated to an orphanage, find the amount donated to the orphanage. What values are being promoted?
Solution:
Ratio in two parts of a property = 8 : 5
First part = ₹ 1,60,000
Second part = \(\frac { 160000\times 5 }{ 8 }\) = ₹ 10,00,000
It is a good to donate the needy people and support them.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
Present ages of Rohit and Mayank are in the ratio 11 : 8. 8 years hence the ratio of their ages will be 5 : 4. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Ratio in the present ages of Rohit and Mayank = 11 : 8
Let age of Rohit = 11x, then that of Mayank = 8x
8 years hence, their ages will be
Age of Rohit = 11x + 8 years
and age of Mayank = 8x + 8 years
and the ratio of their ages after 8 years = 5 : 4
\(\frac { 11x+8 }{ 8x+8 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 4 }\)
⇒ 44x + 32 = 40x + 40
⇒ 44x – 40x = 40 – 32
⇒ 4x = 8
⇒ x = 2
Present age of Rohit = 11x = 11 × 2 = 22 years
and age of Mayank = 8x = 8 × 2 = 16 years
Question 2.
Ratio of length and breadth of a rectangle is 3 : 2. If the length of the rectangle is 5 m more than the breadth, find the perimeter of the rectangle.
Solution
Ratio in length and breadth of a rectangle = 3 : 2
Let length = 3x m and Breadth = 2x
Also, l of rectangle is 5 m more than the breadth
i.e. 3x = 2x + 5
⇒ 3x – 2x = 5
⇒ x = 5
Length = 3x = 3 × 5 = 15m
Breadth = 2x = 2 × 5 = 10m
Perimeter = 2(Length + Breadth) = 2 (15 + 10) m = 2 × 25 = 50 m