Absolute Value
The absolute value of a number can be considered as the distance between 0 and that number on the real number line.
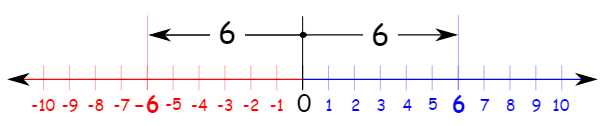
Remember that distance is always a positive quantity (or zero).
The distance in the diagram below from -3 to 0 is 3 units. These units are never negative values.
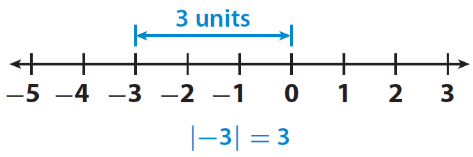
Read More:
- Absolute Value Equations
- Absolute Value Inequalities
- Absolute Value of Complex Numbers
- Integers and Examples
- Fundamental Operations on Integers
- Whole Numbers And Its Properties
- Hints for Remembering the Properties of Real Numbers
- What Are The Four Basic Operations In Mathematics
- Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions
Absolute Value of an Integer:
The absolute value of an integer is the numerical value (magnitude) of an integer regardless of its sign (direction). It is denoted by the symbol | |. The absolute value of an integer is either zero or positive. Also, the corresponding positive and negative integers have the same absolute value.
Examples:
The absolute value of -2 is | -2 | = 2.
The absolute value of 5 is | 5 | = 5.
The absolute value of 0 is | 0 | = 0
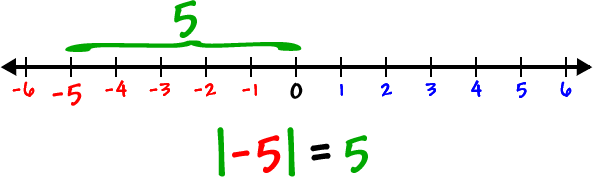
Absolute Value Inequality Graph
