Understanding Scalar and Vector Quantities
- Physical quantities can be grouped into scalar quantities and vector quantities.
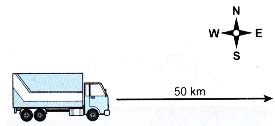
- Above Figure shows a truck travelling a distance of 50 km in the eastward direction. We describe the journey of the truck by stating the magnitude and the direction of its travel:
(a) The magnitude is 50 km.
(b) The direction is East. - Scalar quantities are physical quantities that have magnitude only.
- Vector quantities are physical quantities that have magnitude and direction.
- Some examples of scalar and vector quantities are listed in Table.
Scalar quantities Vector quantities Length Displacement Time Velocity Temperature Acceleration Mass Momentum Speed Force
Example 1
Mei is putting up a night at a campsite during her training program. It is a warm night with a temperature of 30°C and she will have only 3 hours of sleep before hiking to the base camp of the mountain located 2 km away.
 From the above description, determine whether each of the quantities involved is a scalar or a vector quantity and explain your answer.
From the above description, determine whether each of the quantities involved is a scalar or a vector quantity and explain your answer.
Solution:
| Event | Quantity | Explanation |
| A warm night with a temperature of 30°C | Scalar quantity | Temperature has magnitude only. |
| 3 hours of sleep | Scalar quantity | Time has magnitude only. |
| Hiking to the base camp 2 km away | Vector quantity | The magnitude of the distance and the direction of the hike are involved. |