The Trail History and Civics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Life under the Delhi Sultanate
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Trail HistoryCivics Focus on HistoryCivicsGeographyMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
EXERCISE
A. Fill in the blanks :
- The rule of the Delhi Sultans lasted for over three centuries.
- Society during the Sultanate period was divided into four major groups.
- The Turks introduced Arabic and Persian architectural styles.
- New musical instruments such as the tabla, sitar and sarangi were developed during the Sultanate period.
- The establishment of the Turkish rule in India led to the replacement of Sanskrit by Persian as the official language in many regions.
B. Match the following :


Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer :
1. Under the Delhi Sultanate, the aristocrats/the priests/ the peasants were the most powerful class in society.
Ans. Under the Delhi Sultanate, the aristocrats were the most powerful class in society.
2. The brahmanas/the ulema/the merchants were the chief advisors to the sultans.
Ans. The ulema were the chief advisors to the sultans.
3. The life of the peasants/the nobles/the priests was one of drudgery and poverty.
Ans. The life of the peasants was one of drudgery and poverty.
4. The caste system was followed strictly/sometimes followed/ignored by Hindus.
Ans. The caste system was followed strictly by Hindus.
5. Amir Khusrau is believed to have invented the harmonium/sitar/veena.
Ans. Amir Khusrau is believed to have invented the sitar.
D. State whether the following are true or false :
1. The ruling class in the Delhi Sultanate enjoyed a lavish lifestyle.
Ans. True.
2. The Delhi sultans always allowed the ulema to influence their policies.
Ans. False.
Correct : The Delhi sultans sometime does not allow the ulema to influence their policies.
3. The purdah system was strictly observed by- Muslim women.
Ans. True.
4. The Rajput style of miniature painting continued in the Sultanate period.
Ans. True.
5. New types of food, such as bread and wine, became a part of Indian cuisine during the Sultanate period.
Ans. True.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/sentences :
Question 1.
Why was the aristocracy the most powerful social group during the Sultanate period?
Answer:
Aristocracy was the most powerful social group because they had wealth and power.
Question 2.
During whose reign did the life and conditions of the peasants improve?
Answer:
During Firoze Shah’s reign peasants condition improved and they enjoyed many benefits.
Question 3.
What was the chief source of revenue for the government?
Answer:
The tax paid by the peasants was the chief source of revenue for the government.
Question 4.
Why did some Hindus convert to Islam?
Answer:
“Many Hindus, especially those belonging to the lower classes, were attracted to the Islamic principles of equality and converted to Islam. Some did the same to escape the jaziya tax, which was imposed only on non-Muslims.
Question 5.
How do we know that women during the Sultanate period were oppressed?
Answer:
Sati, child marriage and the purdah system became widely prevalent. The purdah system was strictly observed by Muslim women.
Question 6.
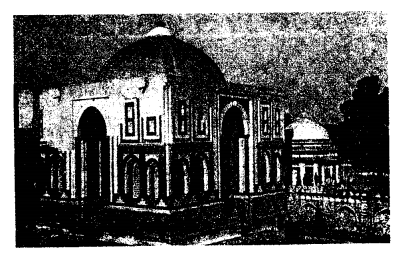
What is the characteristic feature of Sultanate architecture?
Answer:
The characteristic feature of Sultanate architecture is the extensive use of bricks, arches, domes, beams and balconies.
Question 7.
Which two styles of music influenced the development of Hindustani music?
Answer:
Hindustani music was the outcome of the fusion of the Perso- Arabic and Indian classical music styles.
Question 8.
By whom were qawwalis popularized?
Answer:
Qawwali is the Persian style of chorus singing which was popularized by Sufi saints.
Question 9.
Which style of painting was patronized by the Lodi sultans?
Answer:
Persian style of miniature paintings was patronized by the later Lodi sultans and used to illustrate books.
Question 10.
How did the Turkish rulers gradually become Indianized?
Answer:
When Turkish rulers married Indian Muslims, they assimilated many of their local cultural traits and gradually became Indianized.
F. Answer the following questions briefly :
Question 1.
What effect did several centuries of interaction between traditional Indian culture and Islamic culture have on the Indian society?
Answer:
The interaction between traditional Indian culture and Islamic culture had a deep impact on Indian society. This fusion resulted in a new pattern called Indo-Islamic culture.
Question 2.
Describe the main features of society during the Sultanate period with reference to (a) the aristocracy and (b) the peasants.
Answer:
(a) Aristocracy : This was the ruling class. It consisted of the Sultan, the nobles, the Hindu rajas and princes and landlords. This was the most powerful social group because they had wealth and power.
(b) Peasants : The peasants during that time were very poor and they had to lead a very hard life. They had to do all kind of small jobs and had to pay heavy taxes to government.
Question 3.
Discuss the distinctive features of Sultanate architecture.
Answer:
The characteristic feature of Sultanate architecture is the extensive use of bricks, arches, domes, beams and balconies. The Turkish monuments were plain. There was liberal use of floral and geometric designs. The use of red sandstone added colour to their buildings. Verses from the Koran were engraved on the walls of some buildings. Some of the important monuments of the Sultanate period are the Qutb Minar complex, the Alai Darwaza, the tomb of Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq, Firoz Shah Kotla, the Tughlaqabad for and the tombs of the Lodi kings.
Question 4.
Music and dance during the Sultanate period was the outcome of the fusion of Indo-Islamic culture. Explain.
Answer:
Indian or Hindustani music was the outcome of the fusion of the Perso-Arabic and Indian classical music styles. New musical instruments such as the tabla, sitar and sarangi were developed during this time.
The famous Persian poet, Amir Khusrau, is believed to have inveted the sitar by combining the South Indian veena with the Persian tanpura. The South Indian drum was probably altered to create the table.
The Persian style of chorus singing, known as qawwali, was popularized by the Sufi saints, a group of Muslim mystics, who became popular during this period. They sang devotional songs at their religious meetings.
Kathak, a new dance form that also developed during this time, combines Hindu themes with Persian customes.
Question 5.
Explain how new customs and practices changed the traditional lifestyle of the Indians.
Answer:
New customs and practices changed the traditional lifestyle of the Indians. Hindus and Muslims wore pyjama-kurtas, kaftans and salwar-kameez and continue doing so to this day. New types of foods such as biryani, bread and wine became a part of Indian cuisine.
G. Picture study :
This is a picture of a musical instrument used in Hindustani classical music. The name is derived from the Persian words—‘sell’ (meaning ‘three’) and ‘tar’ (meaning ‘strings’).

Question 1.
Identify the muscial instrument.
Answer:
Sitar.
Question 2.
During which period in medieval Indian history’ was this instrument invented?
Answer:
During Delhi Sultanate.
Question 3.
By whom and how was it invented?
Answer:
Amir Khusrau.
Question 4.
Name two other musical instruments that were developed during this period.
Answer:
Tabla, Sarangi.
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Into how many groups was society divided during the Sultanate period? Discuss the functions of each group.
Answer:
The society during the Sultanate was divided into four groups, namely
(a) Aristocracy
(b) Priests
(c) Town Dwellers
(d) Peasants
Functions of each group are :
(a) Aristocracy : This was the ruling class. It consisted of the Sultan, the nobles, the Hindu rajas and princes and landlords. This was the most powerful social group because they had wealth and power.
(b) Priests : This group included the ulemas, maulvis, qazis and brahmanas. The Ulemas were the chief advisors of the Sultans. The brahmanas were generally honoured in the Hindu society. They both played an active role in the administration.
(c) Town Dwellers : It consists of officials, artisans, craftsmen, merchants, slaves and domestic servants. Among these the merchants were quite prosperous.
(d) Peasants : The peasants during that time were very poor and they had to lead a very hard life. They had to do all kind of small jobs and had to pay heavy taxes to government
Question 2.
The Persian and Arabic styles blended harmoniously with the classical Hindu style to make a distinctive Indo-Islamic style. Discuss.
Answer:
The turks brought with them Arabic and Persian architectural styles. They liked the classical style of Hindu architecture also, when these two styles were blended by them, a distinctive Indo-Islamic style came out.
The Turkish monuments were plain whereas Hindu styles include use of floral and geometric designs. When both were combined, it gave a unique touch. Some of the important monuments of that time are Qutb Minar, Alai Darwaza, Firoz Shah Kotla etc.
Question 3.
Discuss the development during the Sultanate period in the following fields :
(a) Music
(b) Dance
(c) Painting
(d) Medicine
(e) Dress
Answer:
(a) Music : During this time fusion of Perso-Arabic and Indian classical music styles were done and outcome of it was Hindustani Music. New musical instruments like the tabla, sitar and sarangi were also developed during this time. The Persian style of chorus qawwali was also popularized during this time.
(b) Dance : Kathak a dance form, originated during the Delhi Sultanate period. It combines Hindu themes with Persian costumes.
(c) Painting : The Turkish rulers were not much interested in Painting but the Rajput style of miniature painting continued in the Sultanate period.
(d) Medicine : A Turkish style of medicine known as Yunani became famous during that time.
(e) Dress : Due to new customs and practices the traditional life style of the Indians changed. Hindu and Muslims started wearing pyjama-kurtas. kaftans and Salwar- kameez.