What Are Sources Of Light
Any object that gives out light is called a source of light. Luminous objects are also called sources of light. Sources of light can be natural or artificial (man-made).
Examples of natural sources of light are ‘he sun and other stairs and insects like the firefly. Some artificial sources of light are candle, electric bulb, and laser.
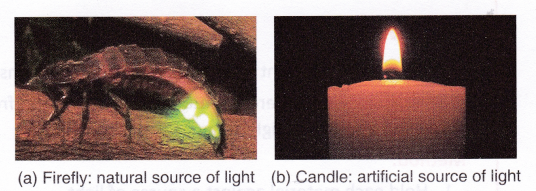
- The objects which emit (give) light are called luminous objects. It may be natural or man-made. Sun is a natural source of light and electric lamp, and oil lamp, etc. are man-made source of light.
- The Non-luminous objects do not emit light. However, such objects become visible due to the reflection of the light falling on them. Moon does not emit light. It becomes visible due to the reflection of the sunlight falling on it.
Transparent, Translucent and Opaque Materials
Different types of materials transmit light differently. Based on the way they transmit light, materials can be divided into transparent, translucent, and opaque materials.
Materials that allow light to pass through significant scattering or absorption are called transparent materials. We will be able to see through these materials very clearly. Examples of transparent materials are clear air, clear glass, clean water, some kinds of plastic, and cellophane paper.
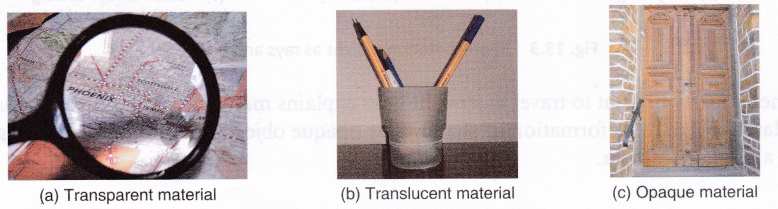
Materials that allow light to pass through them, but scatter or diffuse the light as it passes through, i.e., a parallel beam of light comes through in all directions are called translucent materials, that is why an object cannot be seen clearly through a translucent material. Examples of translucent materials are butter paper, a frosted glass, paper smeared with oil, and smoked glass.
Materials that completely block light are called opaque materials. We will not be able to see through these materials at all. Examples of an opaque materials are metal, mud, cement, coal, and wood. A mirror is a very good example of opaque material. An ideal mirror does not let any light pass through it.
Activity
Aim: To classify different materials as transparent, translucent or opaque.
Materials needed: Different materials like clear glass, frosted/smoked glass, paper, and wood and a source of light (e.g., a candle or torch).
Method:
- Hold each material against a source of light.
- See if the source of light can be seen clearly that is, its outlines etc.
- Classify them as transparent, translucent, or opaque. One has been done for you.
