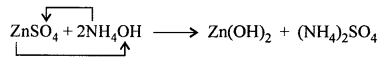
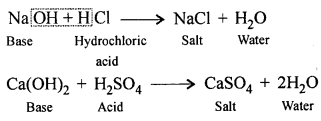
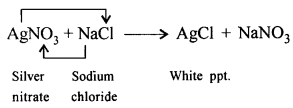
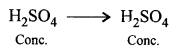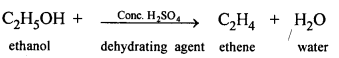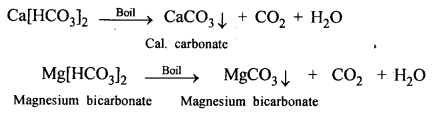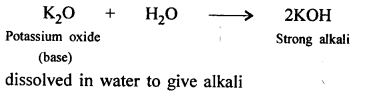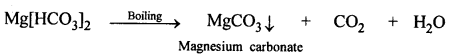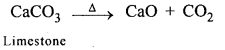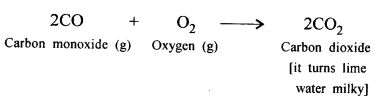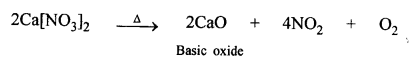New Simplified Chemistry Class 8 ICSE Solutions – Carbon & Its Compounds
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Simplified ChemistryChemistryPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
EXERCISE
Question 1.
Differentiate between the two branches of chemistry – organic chemistry & inorganic chemistry with suitable examples.
Answer:
- Organic chemistry : “A branch of science that deals with the study of specific compounds (of carbon) hydrogen and oxygen.”
e.g. methane CH4, ethane C2H6, CH3COOH, CH4OH methyl alcohol. - Inorganic chemsitry : “A branch of science that deals with the study of – oxides of carbon, carbonates, metallic carbides etc.”
e.g. H2C03 – carbonic acid, C02, CaC03 calcium carbonate.
Question 2.
State how carbon occurs in the free state and in the combined state.
Answer:
- Occurence of carbon : In free state – diamond, graphite, in impure form as coal.
- In combind state : C02 in atmosphere, hydro-carbon as natural gas, petroleum, cellulose in wood and limestone CaC03.
Question 3.
Define the term ‘allotropy’. Give a reason why carbon exhibits allotropy.
Answer:
Allotropy : “The phenomenon of occuring of an element in two or more forms having same chemical properties but different physical properties.”
Carbon shows allotropy as a result of – difference in atomic arrangement in the crystal structure.
Question 4.
Name two crystalline and four amorphous allotropes of carbon.
Answer:
Allotropes of carbon:
Crystalline :
- diamond
- graphite.
Amorphous :
- coal,
- coke
- lampblack
- wood charcoal.
Question 5.
Compare the structure of the crystal of diamond & graphite with special reference to the reason for diamond being the hardest natural substance while graphite one of the softest. Compare the electrical & thermal conductivity of the two crystalline allotropes of carbon.
Answer:
- Structure of crystal of diamond : Hardest natural substance is due to – strength and uniformity of the carbon – carbon covalent bond [tetrahadron structure].
It is bad conductor of electricity and heat due to abscence of free electrons in the crystal, i.e. no electron is free to move. - Structure of graphite : “Is soft and greasy due to parallel layers of C-atoms held together by weak VANDER WAAL – forces which slide over one another, i.e. hexagonal structure.
It is good conductor of heat and electricity due to – presence of mobile electrons in the crystal.
Question 6.
With reference to the structure of the two crystalline allotropes of carbon, state why diamond is inert or unreactive while graphite is comparably more reactive.
Answer:
Structure of diamond is compact and hence unreactive. Graphie has open structure and more prone to chemical attack.
Question 7.
State the reasons for (a) Use of diamond – as an. item of jewellery, (b) Use of graphite – (i) as a lubricant for heated machine parts, (ii) as a lining for crucibles used in manufacture of high grade steel, (iii) as an electrode in electroplating.
Answer:
(a) Use of diamond – as an item of jewellery as – diamond has sparkling brilliance due to high refractive index is cut and polished.
(b)
- Heavy machines which run very fast, when other lubricants are used catch fire, but graphite as lubricant when used parallel layers slide over one and other is non-volatile and non-sticky and reduces friction between rotating parts.
- Graphite is used in refractory crucibles as graphite can withstand high temperature is a good conductor of heat.
- Graphite as electrode in electroplating as graphite is good conductor of electricity relatively inert and almost does not react with acids.
Question 8.
State in brief the transformation of vegetable matter to different types of coal varying in carbon content. State two uses each of
(a) coal
(b) coke
(c) lampblack or soot.
Answer:
Transformation of vegetable matter to coal is due to slow bacterial decomposition of vegetable matter under the influence of heat from within the earth, high pressure of earth (soil) above it and in absence of oxygen over millions of year.
The different stages of transformation of vegetable matter results in different types of coal
- 60%C is peat
- 65%C is lignite
- 85%C is bituminous
- 90%C is anthracite
Question 9.
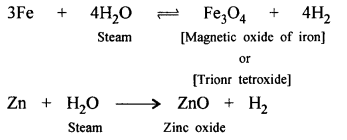
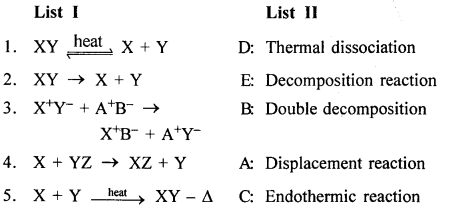
‘Wood charcoal – an amorphous aliotrope of carbon reduces heated metallic oxides to metals.’ Give a balanced equation to support the statement.
Answer:
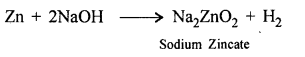
Wood charcoal reduces ZnO, Fe2O3 to metal.
Question 10.
Carbon dioxide occurs both in the free state and in the combined state.
State three methods how carbon dioxide is added to the atmosphere.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is added to the atmosphere by
- Burning of carbon compounds – wood petroleum.
- Death and decay of organic matter.
- Respiration in living organisms.
Question 11.
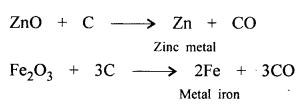
In the laboratory preparation of carbon dioxide by action of a dilute acid on a metallic carbonate give – (a) A balanced equation for the preparation (b) A reason for (i) use of a washer bottle containing cone. H2SO4 in the preparation (ii) Not collecting the prepared gas over water (iii) Not using dilute sulphuric acid as a reactant in the preparation.
Answer:
![]()
(b)
- Cone. H2SO4 used in washer bottle absorbs moisture from the gas.
- C02 is soluble in water and hence is not collected over water.
- Dil. sulphuric acid is not used as reactant. Since H2SO4 reacts with calcium carbonate forming- a coating of insoluble calcium sulphate [CaSO4]. The reaction slowly comes to a stop.
Question 12.
How would you prove experimentally that
(a) Carbon dioxide does not support combustion
(b) Is slightly acidic in nature.
Answer:
(a) Carbon dioxide does not support combustion.
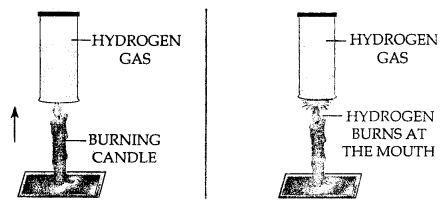
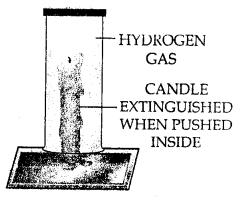
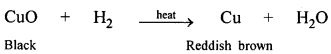
- Experiment : Bring a burning candle in a gas jar full of CO2 gas. The candle is extinguished. This shows that CO2 is non-supporter of combustion.
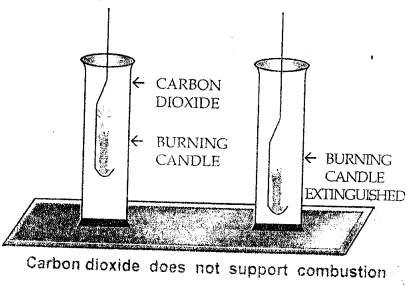
(b) CO2 gas is acidic in nature. Bring a moist blue; litmus paper in the mouth of gas jar full of CO2 gas. The blue colour of filter paper changes red. This shows that CO2 gas is acidic in nature.
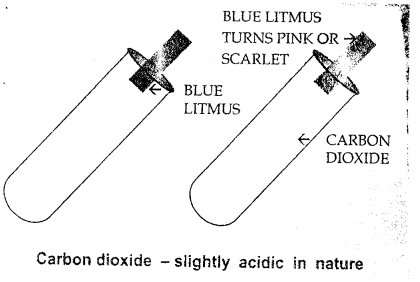
Question 13.
Starting from carbon dioxide how would you obtain
(a) A weak acid
(b) A fertilizer
(c) A highly poisonous gas
(d) Black particles of carbon.
[Give balanced equations for the same]
Answer:
(a) Carbonic acid from CO2 : when CO2 is dissolved in water, carbonic acid is formed.
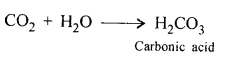
(b) CO2 reacts with ammonia gas to form urea (a nitrogenous fertilizers).
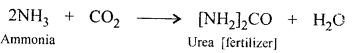
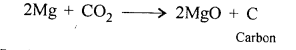
(c) CO2 is reduced to a highly poisonous gas CO by carbon (coke).
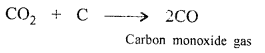
(d) Black particles of carbon : Burning magnesium burns in CO2 making use of oxygen of CO2 producing black carbon particles.
![]()
Question 14.
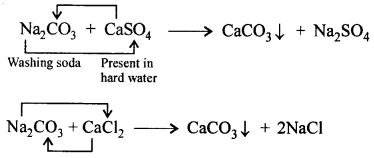
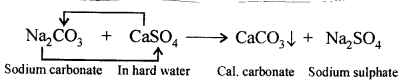
State how you would convert carbon dioxide to a metallic carbonate using a basic oxide e.g. sodium oxide. [Give a balanced equation]
Answer:
Basic oxide like Na2O by CO2 are converted into carbonate.
Na2O + CO2 → Na2CO3
Question 15.
‘When carbon dioxide is bubbled into lime water, the lime water turns milky and when bubbled in excess the milkiness disappears’. Give balanced equations to support the statement.
Answer:
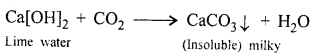
When CO2 is passed in excess, milkiness disappears due to formation of bicarbonate which is soluble in water.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the term ‘dry ice’. State its application. Give three reasons why carbon dioxide finds application in fire extinguishers.
Answer:
- Dry ice : Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice.
- Applications : Dry ice is used as refrigerant for preservation of foods as it freezes faster and lasts longer than ordinary ice.
Question 17.
Using a magnesium ribbon, how would you prove that a given gas jar contains carbon dioxide.
Answer:
It is a test to find gas in the jar is carbon dioxide. On burning magnesium ribbon in a jar of carbon dioxide.
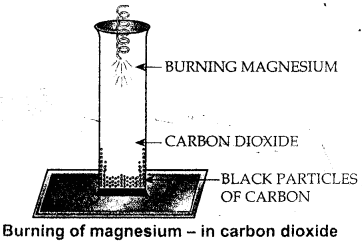
Mg bums in CO2 gas depositing – black particles of carbon on the walls of the jar. If black particles are found on the walls of jar, it is carbon dioxide gas.
CO2 + 2Mg → 2MgO + C
Question 18.
State the function of cone, sulphuric acid in the laboratory preparation of carbon monoxide from oxalic acid.
Answer:
Function of cone, sulphuric acid is to remove molecules of water from formic acid i.e. it acts as dehydrating agent.
Question 19.
Give reasons why carbon monoxide is considered a highly poisonous gas. State why it is dangerous
- To sleep in a closed room with a fuel burning
- To be in the vicinity of smokers.
Answer:
Carbon monoxide is highly Poisonous gas : Carbon-monoxide combines with haemoglobin oxygen cariying capacity of blood is decreased
- In a room which is closed and coal fire produces CO in limited supply of oxygen as room is closed. The haemoglobin combines with CO to form carboxy- -haemoglobin and oxygen carrying capacity decreases which causes death.
- To be in vacinity of smokers : The fumes of – burning tobacco contains traces of carbon monoxide.
Question 20.
Convert carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide using two different methods.
Answer:
Methods of converting CO to CO2.
- CO bums in oxygen and changes to C02.
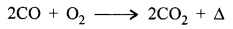
- By reducing metal oxide.
ZnO + CO → Zn + CO2
Question 21.
State how carbon monoxide finds application in
- The metallurgy of iron
- Preparation of an alcohol.
[Give balanced equations for the same]
Answer:
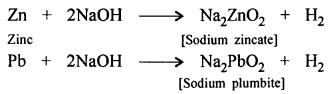
- CO is used to extract iron metal from its oxide as it reduces heated metal oxide.

- Preparation of alcohol :
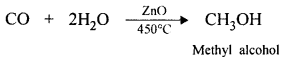
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name the following :
Question 1.
A crystalline allotrope of carbon built up from a hexagonal unit.
Answer:
Graphite.
Question 2.
An allotrope of carbon used for the manufacture of coke.
Answer:
Coal.
Question 3.
An amorphous allotrope of carbon which floats on water.
Answer:
Wood charcoal.
Question 4.
An acid formed when carbon dioxide is dissolved in water under pressure.
Answer:
Carbonic acid.
Question 5.
The gaseous product obtained when carbon monoxide is passed over heated iron (III] oxide.
Answer:
CO2 [Carbon dioxide].
Q.2. Select the correct answer from A, B, C, D & E for each statement given below :
A : Anthracite
B : Diamond
C : Carbogen
D : Urea
E: Lampblack
Question 1.
An allotrope of carbon used as a tip for deep boring drills.
Answer:
B : Diamond
Question 2.
The type of coal with the highest carbon conent.
Answer:
A : Anthracite
Question 3.
An allotrope of carbon obtained by burning kerosene oil in a limited supply of air.
Answer:
E : Lampblack
Question 4.
A nitrogenous fertilizer obtained from carbon dioxide.
Answer:
D : Urea
Question 5.
A compound which finds use for a victim of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Answer:
C : Carbogen
Q.3. Give a balanced equation for the following conversions : [In one or two steps]
Question 1.
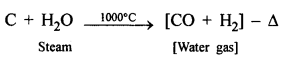
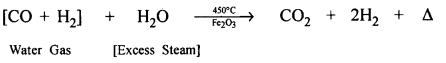
Coke to water gas.
Answer:
Steam is passed over white hot coke at 1000°C
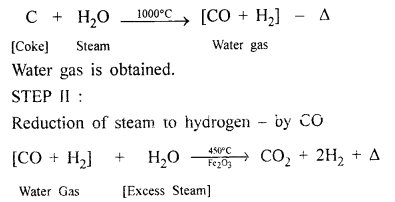
Question 2.
Calcium bicarbonate to calcium nitrate using a dilute acid.
Answer:
Calcium bicarbonate to calcium nitrate
![]()
Question 3.
Lime water [soln. of calcium hydroxide] to calcium bicarbonate.
Answer:
Lime water to calcium bicarbonate
When CO2 is passed it turns milky.
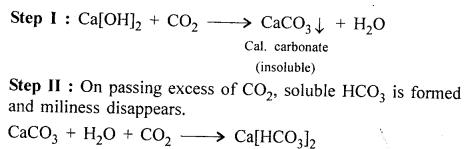
Question 4.
Carbon dioxide to carbon.
Answer:
CO2 to carbon
On burning magnesium in CO2
Question 5.
A metallic oxide to calcium carbonate.
Answer:
A metallic oxide to calcium carbonate
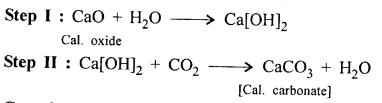
Q.4. Complete the statements by filling the blanks with the correct word from the bracket.
Question 1.
The crystal of ___ [diamond/graphite] is opaque to light and is a good conductor of heat.
Answer:
The crystal of graphite is opaque to light and is a good conductor of heat.
Question 2.
A graphite-clay mixture baked at high temperature is used in making ___ [lubricants/refractory cruscibles].
Answer:
A graphite-clay mixture baked at high temperature is used in making refractory cruscibles.
Question 3.
Adsorption capacity of wood charcoal is increased by passing ___ [carbon dioxide/steam] over wood charcoal, at high temperature.
Answer:
Adsorption capacity of wood charcoal is increased by passing steam over wood charcoal, at high temperature.
Question 4.
___ [organic/inorganic] Chemistry is the Chemistry of carbon compounds mainly of ‘Carbon’, ‘Hydrogen’ & ‘Oxygen’.
Answer:
Organic Chemistry is the Chemistry of carbon compounds mainly of ‘Carbon’, ‘Hydrogen’ & ‘Oxygen’.
Question 5.
Sodium oxide combines with carbon dioxide to give ___ (sodium carbonate/sodium bicarbonate].
Answer:
Sodium oxide combines with carbon dioxide to give sodium carbonate.
Q.5. Give reasons for the following :
Question 1.
Diamond & graphite are allotropic modifications of carbon.
Answer:
Both diamond and graphite are carbon element, differ only in physical state and properties. Both on burning form CO2 and nothing is left.
Question 2.
It is dangerous to stand behind a running engine of a vehicle.
Answer:
Running engine of a vehicle produces carbon monoxide which is dangerous for us.
Question 3.
Both CO2 & SO2 turn lime water milky. Moist potassium permanganate paper, helps in distinguishing the two gases.
Answer:
SO2 gas moist potassium permanganate paper turns purple to colourless when comes in contact with sulphur dioxide gas where as CO2 gas has no effect.
Question 4.
Carbon monoxide and not carbon dioxide is a highly poisonous gas.
Answer:
CO is highly poisonous combines with haemoglobin of R.B.C. and reduces the oxygen carrying capacity and death results.
Question 5.
Lime water finds application for testing both carbon dioxide & carbon monoxide gas individually.
Answer:
CO carbon-monoxide when passed through lime water, does not produce milkiness where as CO2 produces milkiness in lime water and hence is used to test CO and CO2.