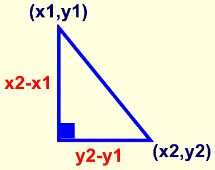
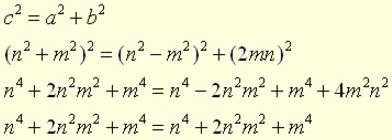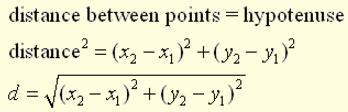Pythagorean Theorem in Algebra
Over 2,500 years ago, a Greek mathematician named Pythagoras popularized the concept that a relationship exists between the hypotenuse and the legs of right triangles and that this relationship is true for all right triangles. The Egyptians knew of this concept, as it related to 3, 4, 5 right triangles, long before the time of Pythagoras. It was Pythagoras, however, who generalized the concept and who is attributed with its first geometrical demonstration. Thus, it has become known as the Pythagorean Theorem.
“In any right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs.”

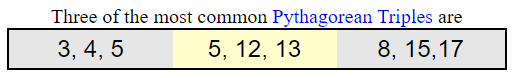
Pythagorean Triples:
There are specific sets of positive integer values that have a special connection to the Pythagorean Theorem. These sets not only satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem, but multiples of these integers also satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem.
For example, the numbers 3, 4, 5 satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem: 32 + 42 = 52.
If you multiply all of these numbers by 2, you get 6, 8, 10 which also statisfy the Pythagorean Theorem: 62 + 82 = 102. Multiplying 3, 4, 5 by the same positive integer value will create a new set of integers that will also satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem.
If a, b and c are positive integers that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem, then ka, kb and kc, where k is a positive integer, will also satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem.
The special sets of integers that possess this property are called “Pythagorean Triples”.
Interpretation:
The Pythagorean Theorem can be interpreted in relation to squares drawn to coincide with each of the sides of a right triangle, as shown at the right.
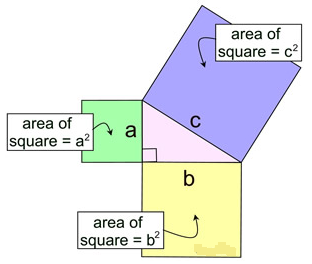
The theorem can be rephrased as, “The (area of the) square described upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equl to the sum of the (areas of the) squares described upon the other two sides.”
REMEMBER: The Pythagorean Theorem ONLY works in Right Triangles!
Example 1: A triangle has sides 6, 7 and 10. Is it a right triangle?
Let a = 6, b = 7 and c = 10. The longest side MUST be the hypotenuse, so c = 10. Now, check to see if the Pythagorean Theorem is true.
102 = 62 + 72
100 = 36 + 49
100 = 85
Since the Pythagorean Theorem is NOT true, this triangle is NOT a right triangle.
Example 2: A ramp was constructed to load a truck. If the ramp is 9 feet long and the horizontal distance from the bottom of the ramp to the truck is 7 feet, what is the vertical height of the ramp to the nearest tenth of a foot?
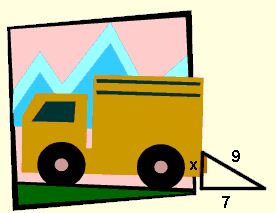 Since the ramp is described as having horizontal and vertical measurements, a right angle is implied. Solve using the Pythagorean Theorem:
Since the ramp is described as having horizontal and vertical measurements, a right angle is implied. Solve using the Pythagorean Theorem:
92 = x2 + 72
81 = x2 + 49
x2 = 81 -49
x2 = 32
x = 5.7
The height of the ramp is 5.7 feet. The ramp will allow packages to be loaded into an area of the truck that is too high to be reached from the ground.
 It was, however, Pythagoras who generalized the theorem to all right triangles and is credited with its first geometrical demonstration. Consequently, the theorem bears his name.
It was, however, Pythagoras who generalized the theorem to all right triangles and is credited with its first geometrical demonstration. Consequently, the theorem bears his name.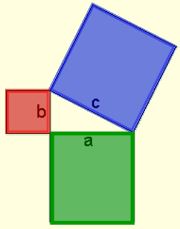 Geometrically, the Pythagorean Theorem can be interpreted as discussing the areas of squares whose sides are the sides of the triangle (as seen in the picture at the left). The theorem can be rephrased as, “The (area of the) square described upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the (areas of )the squares described upon the other two sides.”
Geometrically, the Pythagorean Theorem can be interpreted as discussing the areas of squares whose sides are the sides of the triangle (as seen in the picture at the left). The theorem can be rephrased as, “The (area of the) square described upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the (areas of )the squares described upon the other two sides.”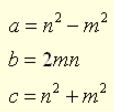 It can be shown that the results from these equations do, in fact, satisfy the Pythatorean Theorem:
It can be shown that the results from these equations do, in fact, satisfy the Pythatorean Theorem: