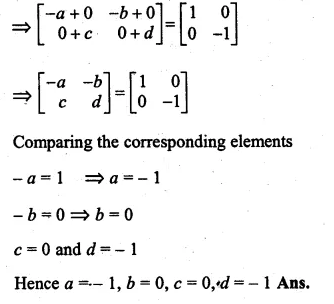
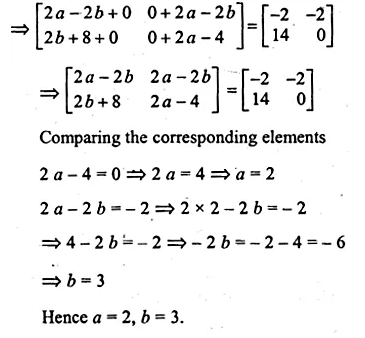
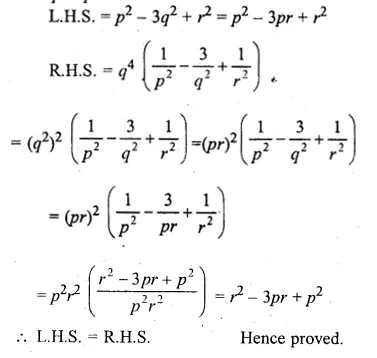
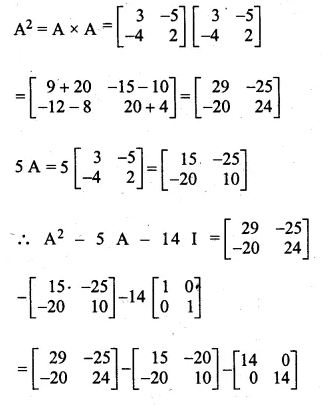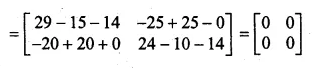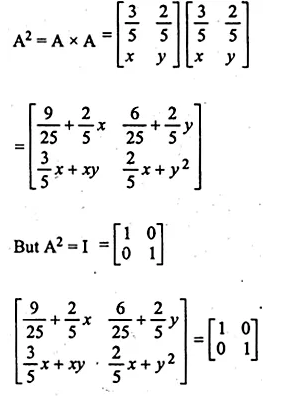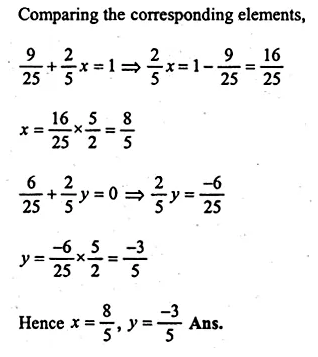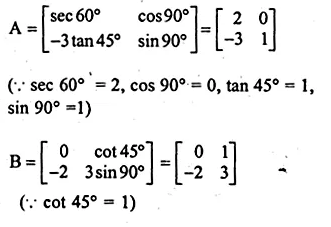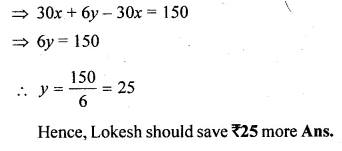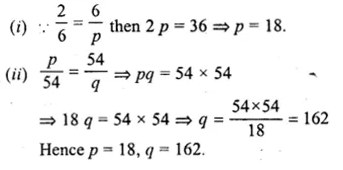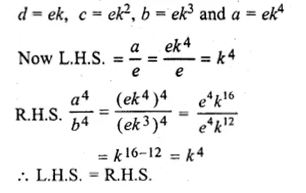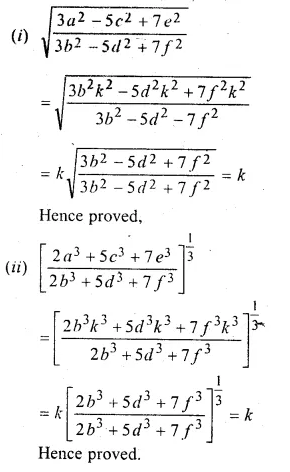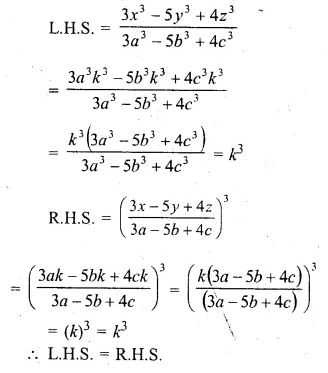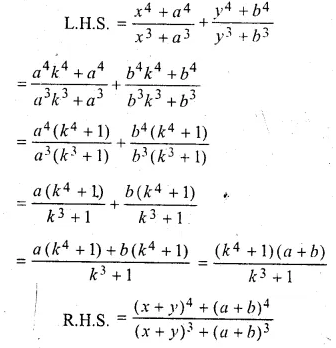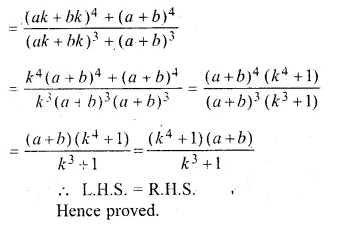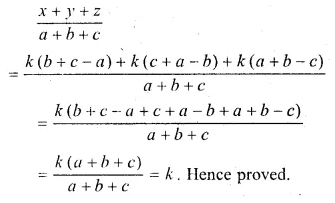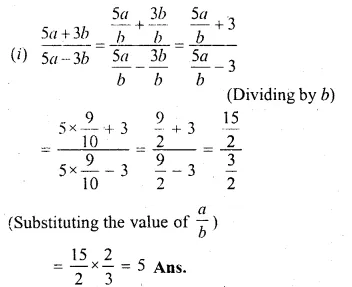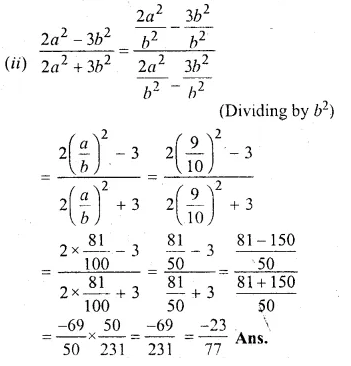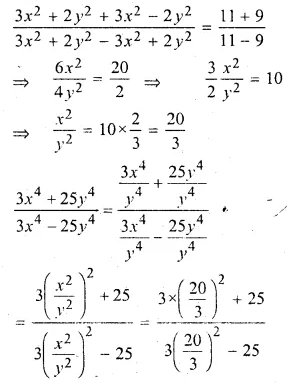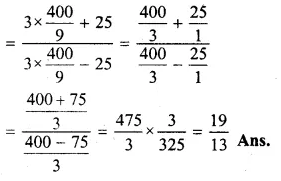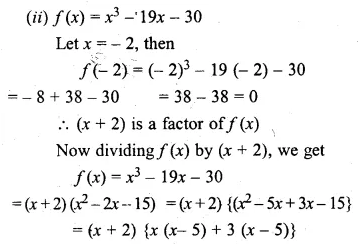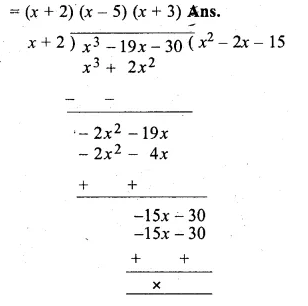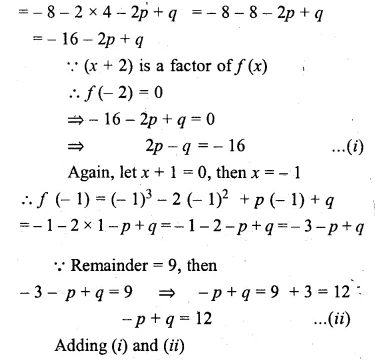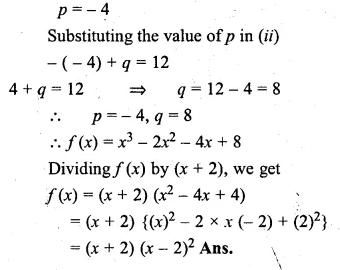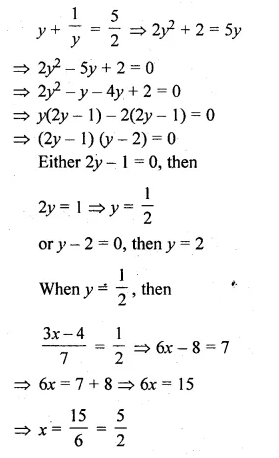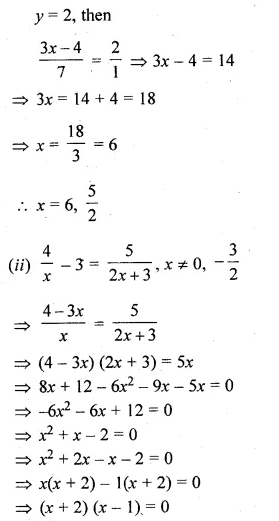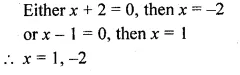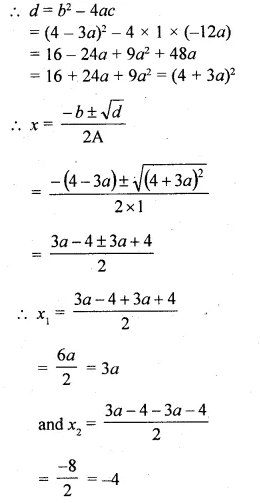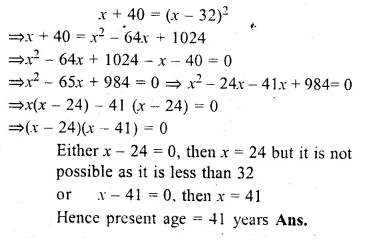ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 11 Section Formula Chapter Test
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 11 Section Formula Chapter Test.
ML Aggarwal SolutionsICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
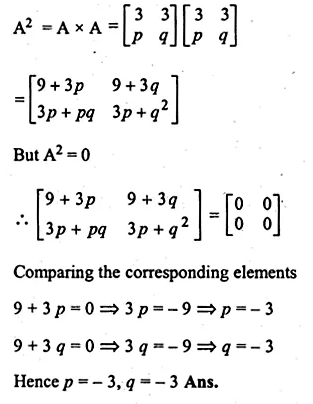
Question 1.
The base BC of an equilateral triangle ABC lies on y-axis. The coordinates of the point C are (0, – 3). If origin is the mid-point of the base BC, find the coordinates of the points A and B
Solution:
Base BC of an equilateral ∆ABC lies on y-axis co-ordinates of point C are (0, – 3), origin (0, 0) is the mid-point of BC.

Question 2.
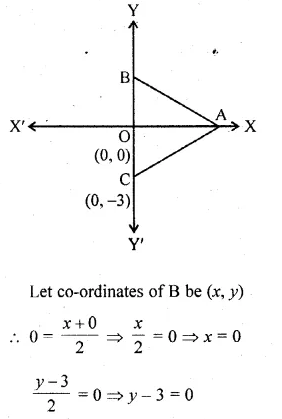
A and B have co-ordinates (4, 3) and (0, 1), Find
(i) the image A’ of A under reflection in the y – axis.
(ii) the image of B’ of B under reflection in the lineAA’.
(iii) the length of A’B’.
Solution:
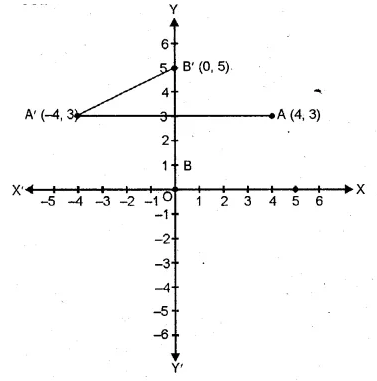
(i) Co-ordinates of A’, the image of A (4, 3) reflected in y-axis will be ( – 4, 3).
(ii) Co-ordinates of B’ the image of B (0, 1) reflected in the line AA’ will be (0, 5).
(iii) Length A’B’
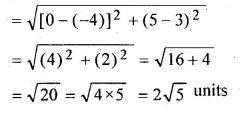
Question 3.
Find the co-ordinates of the point that divides the line segment joining the points P (5, – 2) and Q (9, 6) internally in the ratio of 3 : 1.
Solution:
Let R be the point whose co-ordinates are (x, y) which divides PQ in the ratio of 3:1.
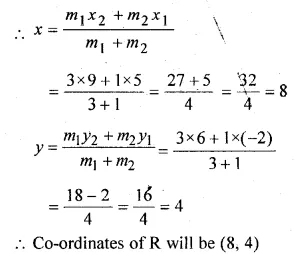
Question 4.
Find the coordinates of the point P which is three-fourth of the way from A (3, 1) to B ( – 2, 5).
Solution:
Co-ordinates of A (3, 1) and B ( – 2, 5)
P lies on AB such that
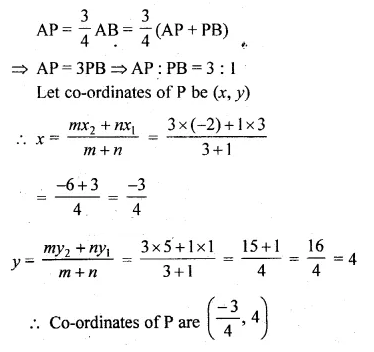
Question 5.
P and Q are the points on the line segment joining the points A (3, – 1) and B ( – 6, 5) such that AP = PQ = QB. Find the co-ordinates of P and Q.
Solution:
Given
AP = PQ = QB
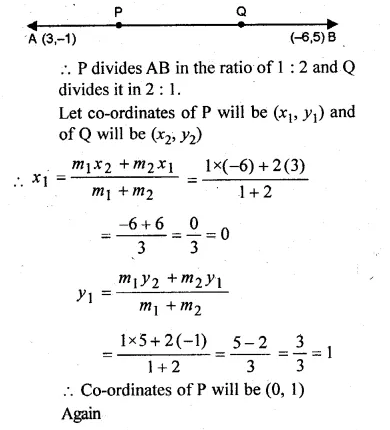
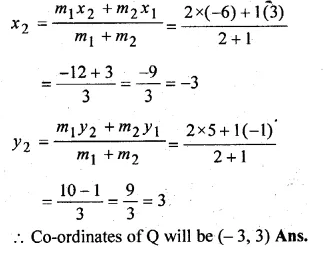
Question 6.
The centre of a circle is (α + 2, α – 5). Find the value of a given that the circle passes through the points (2, – 2) and (8, – 2).
Solution:
Let A (2, – 2), B (8, – 2) and centre of the circle be
O (α + 2, α – 5)
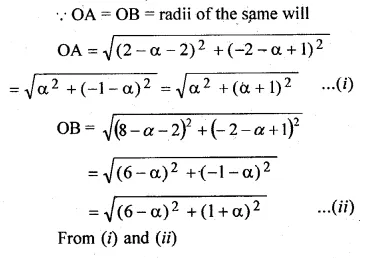
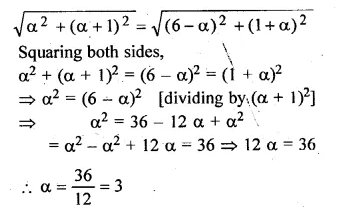
Question 7.
The mid-point of the line joining A (2, p) and B (q, 4) is (3, 5). Calculate the numerical values of p and q.
Solution:
Given
(3, 5) is the mid-point of A (2, p) and B (q, 4)
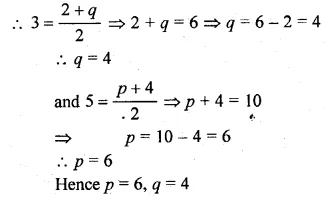
Question 8.
The ends of a diameter of a circle have the co-ordinates (3, 0) and ( – 5, 6). PQ is another diameter where Q has the coordinates ( – 1, – 2). Find the co-ordinates of P and the radius of the circle.
Solution:
Let AB be the diameter where co-ordinates of A are (3, 0) and of B are ( – 5, 6).
Co-ordinates of its origin O will be
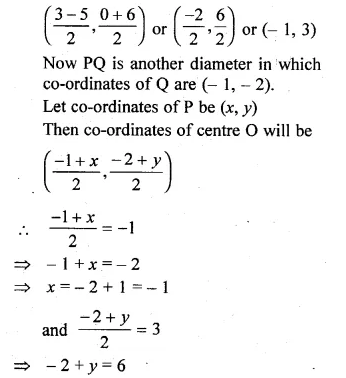

Question 9.
In what ratio does the point ( – 4, 6) divide the line segment joining the points A( – 6, 10) and B (3, – 8) ?
Solution:
Let the point ( – 4, 6) divides the line segment joining the points
A ( – 6, 10) and B (3, – 8), in the ratio m : n
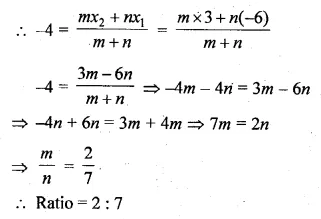
Question 10.
Find the ratio in which the point P ( – 3, p) divides the line segment joining the points ( – 5, – 4) and ( – 2, 3). Hence find the value of p.
Solution:
Let P ( – 3, p) divides AB in the ratio of m1 : m2 coordinates of
A ( – 5, – 4) and B ( – 2, 3)
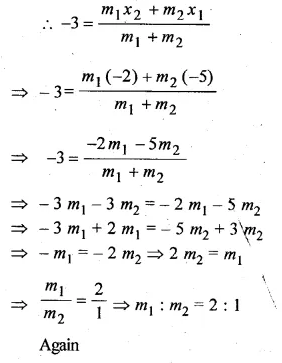
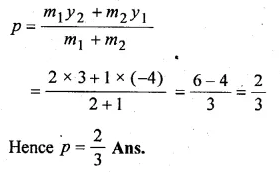
Question 11.
In what ratio is the line joining the points (4, 2) and (3, – 5) divided by the x-axis? Also find the co-ordinates of the point of division.
Solution:
Let the point P which is on x-axis, divides the line segment joining the points A (4, 2) and B (3, – 5) in the ratio of m1 : m2.
and let co-ordinates of P be (x, 0)
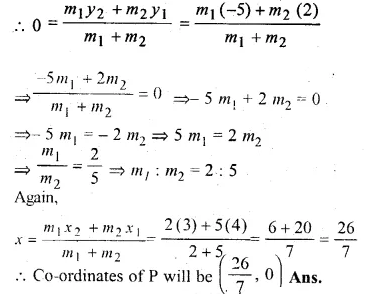
Question 12.
If the abscissa of a point P is 2, find the ratio in which it divides the line segment joining the points ( – 4 – 3) and (6, 3). Hence, find the co-ordinates of P.
Solution:
Let co-ordinates of A be ( – 4, 3) and of B (6, 3) and of P be (2, y)
Let the ratio in which the P divides AB be m1 : m2
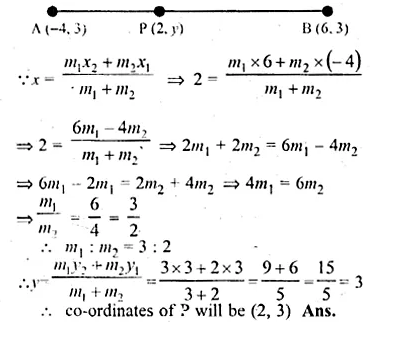
Question 13.
Determine the ratio in which the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divide the line segment joining the points A (2, – 2) and B (3, 7). Also find the co-ordinates of the point of division.
Solution:
Points are given A (2, – 2), B (3, 7)
and let the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divides AB in the ratio m1 : m2 at P and let co-ordinates of

Question 14.
The point A(2, – 3) is reflected in the v-axis onto the point A’. Then the point A’ is reflected in the line x = 4 onto the:point A”.
(i) Write the coordinates of A’ and A”.
(ii) Find the ratio in which the line segment AA” is divided by the x-axis. Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Solution:
A’ is the reflection of A(2, – 3) in the x-axis
(i) ∴ Co-ordinates of A’ will be (2, 3)
Draw a line x = 4 which is parallel to y-axis
A” is the reflection of A’ (2, 3)
∴Co-ordinates OA” will be (6, 3)
(ii) Join AA” which intersects x-axis at P whose
co-ordinate are (4, 0)
Let P divide AA” in the ratio in m1 : m2
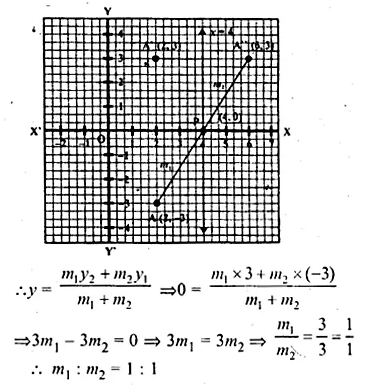
Hence P(4, 0) divides AA” in the ratio 1 : 1
Question 15.
ABCD is a parallelogram. If the coordinates of A, B and D are (10, – 6), (2, – 6) and (4, – 2) respectively, find the co-ordinates of C.
Solution:
Let the co-ordinates of C be (x, y) and other three vertices of the given parallelogram are A (10, – 6), B, (2, – 6) and D (4, – 2)
∴ ABCD is a parallelogram
Its diagonals bisect each other.
Let AC and BD intersect each other at O.
∴O is mid-points of BD
∴ Co-ordinates of O will be
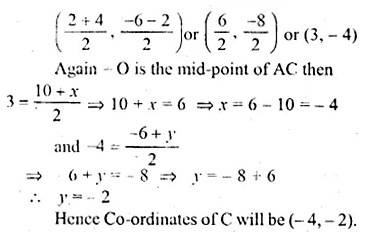
Question 16.
ABCD is a parallelogram whose vertices A and B have co-ordinates (2, – 3) and ( – 1, – 1) respectively. If the diagonals of the parallelogram meet at the point M(1, – 4), find the co-ordinates of C and D. Hence, find the perimeter of the parallelogram. find the perimeter of the parallelogram.
Solution:
ABCD is a || gm , m which co-ordinates of A are (2, – 3) and B (-1, -1)
Its diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at M (1, – 4)
∴ M is mid point of AC and BD Let co-ordinates of C be (x1, y1) and of D be (x2, y2) when M is mid point of AC then
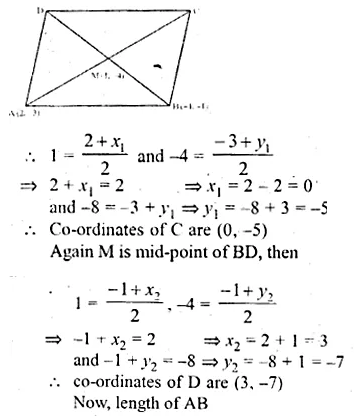
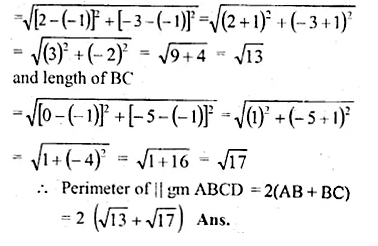
Question 17.
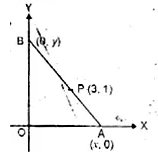
In the adjoining figure, P (3, 1) is the point on the line segment AB such that AP : PB = 2 : 3. Find the co-ordinates of A and B.
Solution:
A lies on x-axis and
B lies on y-axis
Let co-ordinates of A be (x, 0) and B be (0, y) and P (3, 1) divides it in the ratio of 2 : 3.
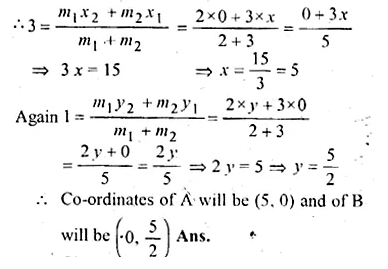
Question 18.
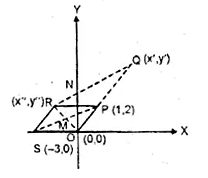
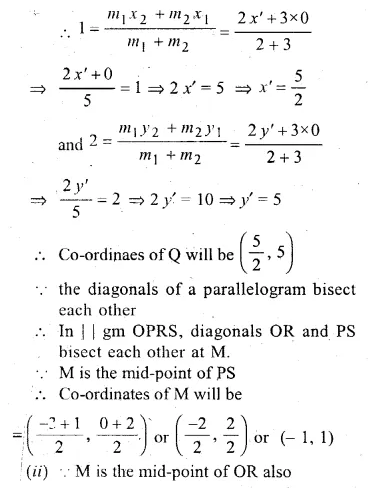
Given, O, (0, 0), P(1, 2), S( – 3, 0) P divides OQ in the ratio of 2 : 3 and OPRS is a parallelogram.
Find : (i) the co-ordinates of Q.
(ii)the co-ordinates of R.
(iii) the ratio in which RQ is divided by y-axis.
Solution:
(i) Let co-ordinates of Q be (x’, y’) and of R (x”,y”)
Point P (1, 2) divides OQ in the ratio of 2 : 3
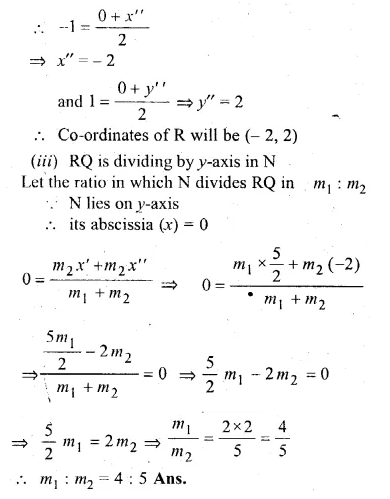
Question 19.
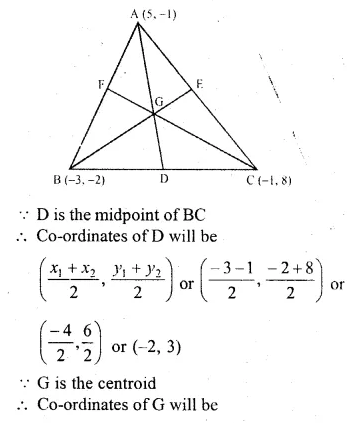
If A (5, – 1), B ( – 3, – 2) and C ( – 1, 8) are the vertices of a triangle ABC, find the length of the median through A and the co-ordinates of the centroid of triangle ABC.
Solution:
A (5, – 1), B ( – 3, – 2) and C ( – 1, 8) are the vertices of ∆ABC
D, E and F are the midpoints of sides BC, CA and AB respectively and G is the centroid of the ∆ABC
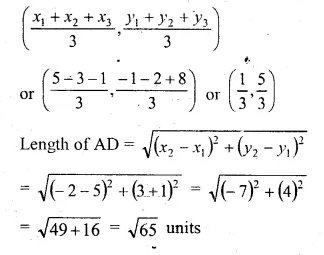
Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 11 Section Formula Chapter Test are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. APlusTopper try to provide online math tutoring for you.