Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry is part of Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answer . Here we have given Plus One Chemistry Previous Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry.
Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
Question 1.
‘Use of DDT pollutes the environment.” Justify. (February – 2008)
Answer:
DDT is very harmful to human beings. It may cause mutation in our body.
Question 2.
a) What is meant by the green house effect? (March – 2009)
b) Explain what is meant by green house gases.
Answer:
a) Green house is the phenomenon in which earth’s atmosphere traps the heat from the sun and prevents it from escaping into outer space resulting in the rise of atmospheric temperature.
b) The gases which can trap infrared radiation leading to green house effect are called green house gases,
Question 3.
When the pH of the rain water drops below 5.6 it is called acid rain. (Say – 2o1o)
a) What are the major compounds responsible for acid rain?
b) What are the harmful effects of acid rain?
Answer:
a) SO2 and NO2 present in polluted air are the major content tutors of acid rains.
b) Acid rain is toxic to vegetation and aquatic life, It destroys statues, buildings and dissolve heavy metals from soil, rocks and sediments. Metals such as copper, lead, aluminium and mercury are washed out of the soil by acid rain, which enter wells and ponds. Leather, paper, fabrics etc. are disintegrated by the acid rain.
Question 4.
Two important oxides of carbon are carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. (March – 2o11)
a) How is CO2 responsible for global warming?
Organic matter such as leaves, grass, trash etc. are major pollutants in water.
b) How do organic pollutants affect aquatic life?
c) What is biological oxygen demand (BOD)?
Answer:
a) Due to the absorption of IR radiation, temperature increases.
b) Organic pollutants decrease the amount of dissolved oxygen and, it causes harmful effects to aquatic life.
c) It is the amount of dissolved oxygen required by micro-organisms to oxidise organic and inorganic matter present in polluted water.
Question 5.
Ozone in the stratosphere is produced by the help of ultraviolet radiations. It protects us from harmful ultraviolet radiations. (Say – 2011)
a) Write equation forthe formation of ozone in strato sphere.
b) Explain with chemical equatiion, the destruction of ozone by chlorofluro carbons causing ozone hole.
Answer:
a) Ozone in the stratosphere is a product of UV radiation acting on dioxygen (O2) molecules. The UV radiations split apart molecular oxygen into free oxygen (O) atoms. These oxygen atoms combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone.
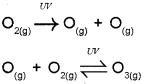
b) The chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released in the atmosphere mix with the normal atmospheric gases and eventually reach the stratosphere. In the stratosphere, they get broken down by powerful Uy radiations, releasing chlorine free radical.
![]()
The chlorine radical then react with stratospheric ozone to form chlorine monoxide radicals and molecular oxygen.
![]()
Reaction of chlorine monoxide radical with atomic oxygen produces more chlorine radicals.
![]()
The net process is O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g)
The chlorine radicals are continuously regener ated and cause the breakdown of ozone. Thus, CFCs are transporting agents for continuously generating chlorine radicalsinto the stratosphere and damaging the ozone layer.
Question 6.
Particulate pollutants are the minute solid particles or liquid droplets in air. (March – 2012)
a) Suggest two examples for non-viable particulate pollutants.
b) Write any two adverse effects of photochemical smog.
Answer:
a) Mists, Smoke, Fumes & Dust.
b) The effects of photochemical smog : The compounds present in the smog cause irritation to the eyes, nose throat and cause respiratory problems like coughing wheezing and bronchial asthma. O3 present in the smog reacts with materials made of rubber. PAN adversely affects green plants.
Question 7.
a) Write any two differences between classical smog and photochemical smog. (Say – 2012)
b) How the Green Chemistry is useful in bleaching of paper?
Classical smog
1) Occurs in cool humid climate.
2) Main constituents are ‘C’ partcIe & gaseous oxides of sulphur.
Photochemical smoa
1) Occur in warm, dry and sunny climate.
2) O3 and oxides of nitrogen (mainly NO2)
Question 8.
Pollution of water originates mainly from human activities. (March – 2013)
a) What do you mean by the term, PCB?
b) Howdo chemical pollutants cause eutrophication?
c) Mention the adverse effects of high fluoride concentration in drinking water.
Answer:
a) Poly chlorinated biphenyl is PCB
b) Fertilizers may contain phosphates or nitrates. The presence of the fertilizers in the polluted water in creases the growth of algae & other aquatic plants which, later on, under go decomposition and produce disagreeable odour. These plants deplete the amount of dissolved oxygen in water. This process is called eutrophication.
c) The soluble F ions make the enamel on teeth much harder by converting hydroxyapatite, the enamel on the surface of the teeth in to much hander fluorapatite.
Question 9.
Suppose that your teacher asks you to conduct a seminar on ozone depletion. Give any three harmful effects of ozone depletion that you would present in the seminar. (Say – 2013)
Answer:
1) More U.V radiation filters into the troposphere which leads to ageing of skin, skin cancer etc.
2) Plant proteins get easily affected by UV radiation which leads to the harmful mutation of cells.
3) It increases evaporation of surface water through the stomata of the leaves and decreases the moisture content of the soil.
Question 10.
There are international standards regarding drinking water. Write any three among them. (March – 2014)
Answer:
- Drinking water should contain only sufficient amount of fluoride (up to 1 ppm).
- The prescribed upper limit concentration of lead in drinking water is about 50 ppb.
- The presence of sulphate in drinking water should be in moderate levels (below 50 ppm).
- The maximum limit of nitrate in drinking water is 50 ppm.
Question 11.
a) Carbon monoxide is one of the most serious air pollutants. How does it pollute the atmosphere? (August – 2014)
b) Give any two applications of green chemistry in day-to-day life.
Answer:
a) It binds to haemoglobin to form carboxy haemo-globin, which is about 300 times more stable than the ozygen-haemoglobin complex. In blood, when the concentration of carboxyhaemoglobin reaches about 3-4 per cent, the oxygen carrying capacity of blood is greatly reduced. This oxygen deficiency, results into headache, weak eyesight, nervousness and cardiovascular disorder. In pregnant women who have the habit of smoking the increased CO level in blood may induce premature birth, spontaneous abortions and deformed babies.
b) 1) Dry cleaning of clothes – The process using tetra chloroethene in dry cleaning of clothes is now being replaced by a process, where liquefied CO2, with a suitable detergent is used. Replacement of halogenated solvent by liquid CO2 will result in less harm to ground water. These days H2O2 is used for the pur-pose of bleaching clothes in the process of laundary, which gives better results and makes use of lesser amount of water.
2) Synthesis of chemicals – Ethanal is now com-mercially prepared by one step oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium with an yield of 90%.
![]()
Question 12.
The Taj Mahal in India has been affected by ‘acid rain’. Explain the causes and harmful effects of acid rain. (March – 2015)
Answer:
Acid rain is the phenomenon in which the pH of rain water drops below 5.6 due to the presence of H+ ions formed by the reaction of rain water with acidic oxides present in atmosphere.
Causes : Acid rain is a byproduct of a variety of human activities that emit the oxides of sulphur and nitrogen in the atmosphere during burning of fossil fuels such as coal and oil in power stations and furnaces or petrol and diesel in motor engines. These contain S02and N02 which react with water and contribute to acid rain.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2SO4(aq)
4NO2(g) + O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 4HNO3(aq)
Aerosol particles of oxides or ammonium salts in rain drops result in wet-deposition. SO2 is also absorbed directly on both solid and liquid ground surfaces and is thus deposited as dry-deposition. Harmful effects:
- It is harmful for agriculture, trees, and plants as it dissolves and washes away nutrients needed for their growth.
- It causes respiratory ailments in human beings and animals.
- It affects plants and animal life in the aquatic eco-system when acid rain falls and flows as ground water to reach rivers, lakes etc.
- It corrodes water pipes resulting in the leaching of heavy metals such as iron, lead and copper into the drinking water.
- It damages buildings and other structures made of stone or metal.
Question 13.
‘Smog’ is the most common example of air pollution. (Say – 2015)
a) The smog that occurs in cool humid climate is called smog.
b) Explain the cause of the greenhouse effect’.
Answer:
a) Classical smog.
b) Atmosphere traps the sun’s heat near the earth’s surface and keep it warm just as the glass in a greenhouse. The sunlight passes through the atmosphere and heats upthe earth’s surface. The warm surface of earth emits infrared radiations which is partly reflected and partly absorbed by the greenhouse gases present in atmosphere. Greenhouse gases like CO2, methane, water vapour, nitrous oxide, CFCs and ozone are responsible fortrapping heat.
Question 14.
a) Write any two contributions of green chemistry in day to day life. (March – 2016)
b) Match the fol lowing :
| A | B |
| a) CFC’s b) Oxides of Nitrogen c) Cadmium d) Nitrates | i) Blue baby syndrome ii) Kidney damage iii) Eutrophication iv) Ozone depletion v) Red haze in the traffic |
Answer:
a) 1) Dry cleaning of clothes – the process of using tetrachloroethene for dry cleaning is now replaced by a process, where liquefied carbon dioxide, with a suitable detergent is used. Replacement of halogenated solvent by liquid CO2 will result in less harm to ground water.
2) Bleaching of Paper – Instead of chlorine gas, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with suitable catalyst, which promotes the bleaching action of hydrogen peroxide is used for bleaching paper.
3) Synthesis of Chemicals – Ethanal (CH3CHO) is commercially prepared by one step oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium with an yield of 90 %.
![]()
b) a) iv
b) v
c) ii
d) i
Question 15.
The phenomenon of global warming is due to greenhouse effect. (Say – 2016)
a) What is greenhouse effect?
b) What are the consequences of greenhouse effect?
Answer:
a) Just as the glass in a greenhouse holds the sun’s warmth inside, atmosphere traps the sun’s heat near the earth’s surface and keeps it warm. This is called natural greenhouse effect because it maintains the temperature and makes the earth perfect for life. The heating of the atmosphere due to absorption of infra-red radiations by CO2 and other greenhouse gases is called greenhouse effect.
b)
- Excessive heating of the earth’s atmosphere and increase in average global temperature (Global warming).
- Melting of polar ice cap and flooding of low-lying areas all over the earth.
- Increase in the incidence of infectious diseases like dengue, malaria, yellow fever, sleeping sickness, etc.
Question 16
Environmental pollution is the effect of undesirable changes in surroundings that have a harmful effect on plants, animals and human beings. (March – 2017)
a) Explain the adverse effect of global warming.
b) Choose the one which is not a component of photochemical smog.
i) NO2
ii) O3
iii) SO2
Answer:
a) As a result of golbal warming the average global temperature will increase to a level which may lead to melting of polar ice caps and flooding of low lying areas all over the earth. Increase in the global temperature increases the incidence of infectious diseases like dengue, malaria, yellow fever, sleeping sickness, etc.
b) ii) SO2
We hope the Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus One Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.