Physics Symbols: All Physics Symbols and Their Names Pdf are covered in this page, we are also providing Greek Symbols in Physics and there units and quantity.
Physics Symbols and Their Names
List of Physics Symbols and Their Names
Symbols used to denote physical quantities related to space and time:
| Symbol | Quantity/ Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| r | Radius, the radius of curvature | Meter |
| s | Displacement | Meter |
| d | Distance | Radian |
| θ, φ | Angular displacement, angular separation, the rotational angle | Meter |
| x, y, z | Cartesian coordinates | Unitless |
| î, ĵ, k̂ | Cartesian unit vectors | Unitless |
| r, θ, φ | Spherical coordinates | Meter/Radian |
| r̂, θ̂, φ̂ | Spherical unit vectors | Unitless |
| r, θ, z | Cylindrical coordinates | Meter/Radian |
| r̂, θ̂, ẑ | Cylindrical unit vectors | Unitless |
| n̂ | Normal unit vector | Unitless |
| t̂ | Tangential unit vector | Unitless |
| h | Height, depth | Meter |
| ℓ, L | Length | Meter |
| t | Time | Second |
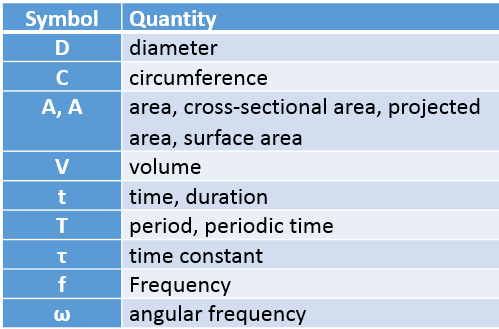
| D | Diameter | Meter |
| C | Circumference | Meter |
| A, A | Area | Square meter |
| V | Volume | Cubic meter |
| t | Time, duration | Second |
| T | Periodic time | Second |
| τ | Time Constant | Second |
| f | Frequency | Hertz |
| ω | Angular frequency | Radian per second |
Symbols used to denote physical quantities related to Mechanics:
| Symbol | Quantity/ Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| v | Velocity, speed | meter per second |
| a | Acceleration | meter per second squared |
| ac | Centripetal/Centrifugal acceleration | meter per second squared |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity | meter per second squared |
| m | Mass | Kilogram |
| F | Force | Newton |
| Fg /W | Force due to gravity/Weight | Newton |
| Fn, N | Normal force, normal | Newton |
| Ff | Force of friction | Newton |
| µ | Coefficient of friction | Unitless |
| p | Momentum | Kilogram meter per second |
| J | Impulse | Newton second |
| E | Energy | Joule |
| K | Kinetic energy | Joule |
| U | Potential energy | Joule |
| Vg | Gravitational potential | Joule per kilogram |
| η | Efficiency | Unitless |
| P | Power | Watt |
| ω | Rotational speed, rotational velocity | Radian per second |
| α | Rotational acceleration | Radian per second squared |
| τ | Torque | Newton meter |
| I | Moment of inertia | Kilogram meter squared |
| L | Angular momentum | Kilogram meter squared per second |
| H | Angular impulse | Newton meter second |
| k | Spring constant | Newton per meter |
| p | Pressure | Pascal |
| σ | Stress | Pascal |
| τ | Shear stress | Pascal |
| ρ | Density, volume mass density | Kilogram per cubic meter |
| σ | Area mass density | Kilogram per square meter |
| λ | Linear mass density | Kilogram per meter |
| FB, B | Buoyancy | Newton |
| qm | Mass flow rate | Kilogram per second |
| qV | Volume flow rate | Cubic meter per second |
| FD, R | Drag or air resistance | Newton |
| CD | Drag coefficient | Unitless |
| η | Viscosi | Pascal-second |
| ν | Kinematic viscosity | Square meter per second |
| Ma | Mach number | Unitless |
| Re | Reynolds number | Unitless |
| Fr | Froude number | Unitless |
| E | Young’s modulus of elasticity | Pascal |
| G | Shear modulus of rigidity | Pascal |
| K | Bulk modulus of compression | Pascal |
| ε | Linear strain | Unitless |
| γ | Shear strain | Unitless |
| θ | Volume strain | Unitless |
| γ | Surface tension | Newton per meter |
Symbols used to denote physical quantities related to thermal physics:
| Symbol | Quantity/Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| COP | Coefficient of performance | Unitless |
| w | Ways, number of identical microstates | Unitless |
| S | Entropy | Joule per kelvin |
| U | Internal energy | Joule |
| ε | Emissivity | Unitless |
| k | Thermal conductivity | Watt per meter Kelvin |
| P | Heat flow rate | Watt |
| N | Number of particles | Unitless |
| n | Amount of substance | Mole |
| L | Latent heat/specific latent heat | Joule per kilogram |
| c | Specific heat capacity | Joule per kilogram Kelvin |
| Q | Heat | Joule |
| Β | Volume expansivity, coefficient of volume thermal expansion | Inverse kelvin |
| α | Linear expansivity, coefficient of thermal expansion | Inverse kelvin |
| T | Temperature | Kelvin |
Symbols used to denote physical quantities related to Waves and Optics:
| Symbol | Quantity/Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| M | Magnification | Unitless |
| f | Focal length | Meter |
| n | Index of refraction | Unitless |
| L | Level | Decibel, decineper |
| I | Intensity | Watt per square meter |
| v, c | Wave speed | Meter per second |
| λ | Wavelength | Meter |
| P | Power of a lens | Dioptre |
Symbols used to denote physical quantities related to Electricity and Magnetism:
| Symbol | Quantity/Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| S | Poynting vector, intensity | Watt per square meter |
| η | Energy density | Joule per cubic meter |
| n | Turns per unit length | Inverse meter |
| N | Number of turns | Unitless |
| ΦB | Magnetic flux | Weber |
| B | Magnetic field | Tesla |
| FB | Magnetic force | Newton |
| σ | Conductivity | Siemens per meter |
| G | Conductance | Siemens |
| ρ | Resistivity | Ohm-meter |
| R, r | Electric resistance/internal resistance | Ohm |
| I | Electric current | Ampere |
| ϵ | Dielectric constant | Unitless |
| C | Capacitance | Farad |
| ℰ | Electromotive force (emf) | Volt |
| V | voltage, electric potential | Volt |
| UE | Electric potential energy | Joule |
| ΦE | Electric flux | Newton meter squared per coulomb |
| E | Electric field | Newton per coulomb/volt per meter |
| FE | Electrostatic force | Newton |
| λ | Linear charge density | Kilogram per meter |
| σ | Area charge density | Kilogram per square meter |
| ρ | Volume charge density | Kilogram per cubic meter |
| q, Q | Electric charge | Coulomb |
Symbols used in modern physics:
| Symbol | Quantity/Coefficients | S.I Unit |
| D | Dose/ dose absorbed | gray |
| Half-life | Second | |
| ψ(r,t), ψ(r)φ(t) | Wave function | Unitless |
| Φ | Work function | Joule |
| H | Effective dose | Sievert |
| Γ | Lorentz factor/Lorentz gamma | Unitless |