Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations is part of Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Botany Chapter wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 |
| Chapter Name | Organisms and Populations |
| Number of Questions Solved | 77 |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations
Plus Two Botany Organisms and Populations One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Zero growth means
(a) Natality balance mortality
(b) Natality is more than mortality
(c) Natality is less than mortality
(d) Natality is zero
Answer:
(a) Natality balance mortality
Question 2.
Different types of interactions and the nature of interactions between species A and B are given in column I and II respectively. Choose the correct answer key where they are matched.
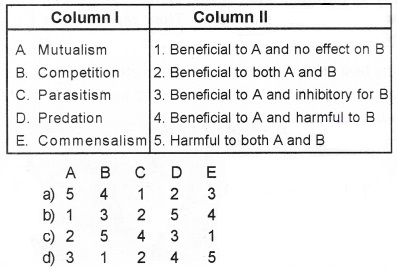
Answer:
(c) 2 5 4 3 1
Question 3.
Which one of the following is not used for the construction of ecological pyramids?
(a) Dry weight
(b) Number of individuals
(c) Rate of energy flow
(d) Fresh weight
Answer:
(d) Fresh weight
Question 4.
In a pond there were 200 frogs, 40 more were born in a year. Calculate the birth rate of population.
Answer:
Birth rate = 40/200 = 0.2 offspring per year.
Question 5.
What is the cause of altitude sickness at high altitudes?
Answer:
Is due to the low atmospheric pressure of high altitudes that the body is unable to get enough oxygen.
Question 6.
Amensalism is an association between two species where:
(a) One species is harmed and other is benefitted
(b) One species is harmed and other is unaffected
(c) One species is benefitted and other is unaffected
(d) Both the species are harmed
Answer:
(c) One species is benefitted and other is unaffected.
Question 7.
According to Allen’s Rule, the mammals from colder climates have:
(a) Shorter ears and longer limbs
(b) longer ears and shorter limbs
(c) longer ears and longer limbs
(d) shorter ears and shorter limbs
Answer:
(c) longer ears and longer limbs
Question 8.
Lichens are the association of:
(a) bacteria and fungus
(b) algae and bacterium
(c) fungus and algae
(d) fungus and virus
Answer:
(c) fungus and algae
Question 9.
Salt concentration (Salinity) of the sea measured in parts per thousand is:
(a) 10-15
(b) 30-75
(c) 0-5
(d) 30-35
Answer:
(d) 30-35
Question 10.
Formation of tropical forests needs mean annual temperature and mean annual precipitation as:
(a) 18-25°C and 150-400 cm
(b) 5-15°C and 50-100 cm
(c) 30-50°C and 100-150 cm
(d) 5-15°C and 100-200 cm
Answer:
(a) 18-25°C and 150 – 400 cm
Question 11.
Observe the following statements. Select the correct one.
(a) Temperature increases progressively from equator towards the poles and from plain to mountain tops.
(b) Temperature is sub-zero level in polar areas and high altitude and increases to above 50°c in tropical desert in summer.
(c) In unique habitats such as thermal springs and deep sea hydrothermal vents average temperatures exceed 20°c.
(d) Mango trees grow in temperate countries like Canada and Germany.
Answer:
(a) Temperature is sub-zero level in polar areas and high altitude and increases to above 50°c in tropical desert in summer.
Question 12.
Cuscuta and vanda are growing on a mango tree. Which plant makes harm to the mango tree. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Cuscuta makes harm, it is a parasite that derives its nutrition from the host plant.
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not related to competition.
(a) Competition occurs when closely related species compete for the same resources that are limiting.
(b) Unrelated species also compete for same resources.
(c) Even if resources are abundant, the feeding effect of one species might be reduced due to the interfering and inhibitory presence of other species.
(d) Calotropis. growing in abandoned fields is an example of competition.
Answer:
(d) Calotropis growing in abandoned fields is an example of competition.
Question 14.
Parasitic mode of life ensures free lodging and meals. Identify the correct statements related to parasites.
(a) Parasites are not host specific and co-evolved.
(b) Parasites have special adaptations like loss of unnecessary sense organs, presence of suckers, loss of digestive systems, high reproductive capacity.
(c) Lice is an endoparasite.
(d) The female mosquito is a parasite.
Answer:
a, b.
Question 15.
Observe the relationship between the first two terms and fill in the blanks. Hibernation: Bear;……….: Snail
Answer:
Aestivation.
Question 16.
Read the statements properly and choose the correct one.
(a) Many desert plants have CAM pathway that enables their stomata to remain open during day time.
(b) In Opuntia, leaf reduced into green flattened structure.
(c) Kangaroo rat in North American deserts is capable of meeting all water requirements through the protein oxidation.
(d) Mammals from colder climate generally have shorter ears and limbs.
Answer:
(d) Mammals from colder climate generally have shorter ears and limbs.
Plus Two Botany Organisms and Populations Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In a biotic community initially the population size was 250 during the year 2005 after a period of time 130 animals died of forest fire 20 were nearly born. During the next winter season 20 animals immigrated. Find out the change in population size.
Answer:
Nt = No + B + I – D + E
Therefore Nt = 250+ 20+ 20- 130 + 40
= 290- 170= 120
Question 2.
Some organism are different intheirtoleration level to temperature fluctuations
- Name the type of organism that can tolerate wide range of temperature variation especially in increased global temperature?
- Name the other type organisms restricted to narrow range.
Answer:
- Eurythermal species,
- Stenothermal.
Question 3.
In desert condition water availability very low hence normal plants cannot withstand. What are the adaptations are desert plants.
Answer:
- Thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces
- Stomata arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss through transpiration.
- They show CAM pathway (they open stomata during night and closed during day time)
- Opuntia, their leaves are reduced to spines and the flattened stems do photosynthesis.
Question 4.
In extreme summer and winter certain animals like frogs and lizard abandon their active life. This is popularly known as summer sleep and winter sleep respectively. Write down the technical term for summer sleep and winter sleep.
Answer:
- Summer sleep – Aestivation
- Winter sleep – Hibernation
Question 5.
What you meant by resource partitioning in an ecosystem.
Answer:
If two species compete for the same resource, they avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding or different foraging patterns.This is called resource partitioning.
Question 6.
Camouflaging is a method adopted by prey to lessen effect of predatien in animals. List out some mechanisms seen in plant species.
Answer:
Plants have evolved a variety of morphological and chemical defences against their predators (herbi-vores).
- Thorns in plants are morphological means of defence.
- Plants produce and store chemicals that make the herbivore sick. Eg: Glycosides, Quinine, Caf¬feine, Opuim etc.
Question 7.
Gause proposed the Competitive Exclusion Principle in 1934.
- Define it
- Give an example.
Answer:
1. Competitive Exclusion Principle states that the closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely The competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually.
2. Abingdon tortoise compete with goats in galapagos island for same food source and tortoise became extinct.
Question 8.
Many tribes living in high altitudes of Himalayas have higher red blood cell count.
- Do you agree?
- Give reason
Answer:
1. Yes.
2. In high altitudes there is low oxygen availability. The tribes having high RBC production since the binding capacity of RBC with 02 decreases and ultimately results in high breathing rate.
Question 9.
Tribalsin high altitude are difficult to live in the initial phase of colonization but after few days they are adapted to live.
- Write down 2 adaptations they developed
- Name two disease symptoms in low 02 and atmospheric pressure conditions
Answer:
1. 2 adaptations they developed:
- increase RBC production
- increase breathing rate
2. nausea, fatigue.
Question 10.
The relationship between cattle egret and grazing cattle is considered as commensalism. Justify.
Answer:
Cattle egret gets food in the form of insects when the grazing cattle flushes out insects from the vegetation as it moves during grazing. The egret is benefited but there is no harm for the cattle.
Question 11.
Abingdon tortoise and goats are compete with each other in Galapagos Islands for common food finally one of them is eliminated.
- Name the principle proposed by Gause to explain the elimination of one species due to other
- Suggest one important method to reduce competition
Answer:
- competitive exclusion principle
- resource partitioning
Question 12.
Thermoregulation is expensive to small animals like Shrews and Hummingbirds live in colder climates. Do you agree? Give reason.
Answer:
Yes
Their body surface area is large compared to body volume, hence they have to spend more energy to increase metabolic rate when cold outside for producing more heat.
Question 13.
Ophrys is a Mediterranean orchid it’s petals shows resemblance to female be in colour size and markings but a male bee come into the flower and pollinate
- Name the sexual deciet between male bees and orchid
- Which is the interaction used to explain pollination method mentioned above
Answer:
- pseudocopulation
- mutualism
Question 14.
In sample A population growth under abandoned food supply violin sample B population growth under reduced food supply.
- Name the two types of growth occurs in sample A and sample B
- What will be the shape of curve get in sample A and sample B population
Answer:
- In sample A exponential growth, in sample B Logistic growth
- In sample A- J shaped, In sample B- S shaped
Question 15.
dN/dt = (b-d) × N
Let (b-d) = r, then
dN/dt = rN
- What does r indicate in the above equation?
- Which parameter is chosen for assessing impact of any biotic or abiotic factor on population growth?
Answer:
- Intrinsic rate of natural increase
- r parameter
Question 16.
Use proper terms of the statement given below.
- Few organisms can tolerate and thrive in wide range of temperature.
- Some organisms are tolerant to a narrow range of salinities.
- The organism should try to maintain the constancy of its internal environment.
- The organism may move temporarily from the stressful habitats to more hospitable area and return when stressful period is over.
Answer:
- Eurythermal
- Stenothermal
- Homeostasis
- Migrate
Question 17.
The integral form of the exponential growth equation is Nt = N0ert. Expand the symbols in this equation.
Answer:
- Nt – Population density at time t
- No – Population density at time 0
- r – Intrinsic rate of natural increase
- e – base of natural logarithms.
Question 18.
In rocky intertidal communities of the American Pacific Coast the starfish Pisasterwere removed for an experimental purpose.
- How did this affect the invertebrates in that region?
- List out the important role of predators in nature.
Answer:
1. Pisaster is an important predator in the intertidal area. When Pisasters were removed, more than 10 invertebrate species became extinct because of interspecific competition.
2. important role of predators in nature:
- Predation helps to transfer energy to higher trohpic level from plants,
- Agricultural pest control or biological control is based on the ability of predator that important in regulating prey population.
Question 19.
Match A with B based on mutualism.
| A | B |
| Lichen | Wasp |
| Mycorrhiza | Ophrys |
| Fig tree | Cyanobacteria |
| Sexual deceit | Fungi |
Answer:
- Lichen – cyanobacteria
- Mycorrhiza – fungi
- Fig tree – Wasp
- Sexual deceit – Ophrys
Question 20.
Define commensalism and write any two examples.
Answer:
Interaction in which one species benefited and the other is neither harmed nor benefited.
Example – Cattle egret and grazing cattle Sea anemone and clownfish.
Question 21.
Adaptations may be morphological, physiological or behavioural. Write the behavioural adaptations in desert lizard.
Answer:
Desert lizards bask in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone They move into shade when the temperature starts increasing.
Question 22.
Interaction between sea anemone and clown fish is termed as commensalism. Substantiate this statement.
Answer:
Sea anemone has stining tentacles and the clown fish lives among them, In this interaction the fish get protection from predators which stay away from the stinging tentacles but sea anemone does not derive any benefit or harm by hosting the clown fish.
Question 23.
Competition causes extinction of species. Substantiate this statement based on the extinction of Abingdon tortoise.
Answer:
A bingdon tortoise in Galapagos islands became extinct due to the introduction of goat on the island because goats have greater browsing efficiency than tortoise. Due to the lack of food tortoise became extinct.
Plus Two Botany Organisms and Populations Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Given below is the bar diagram showing the age structure of three countries. Answer the following questions by analyzing the diagram.
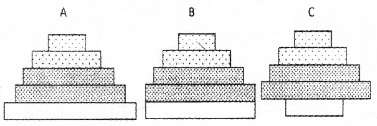
- Which country has the highest population?
- Which country has declining population?
- One of the countries has a stable population. Explain.
Answer:
- A has the highest population
- C has declining population
- B has stable population. In this population reproductive and pre-reproductive individuals are more or less same. Hence it is stable.
Question 2.
Population growth curves (two types are given: observing the graph answer the following questions).
- Identify the curves a & b.
- Explain the signficance of K.
- Which population growth has limited food supply?
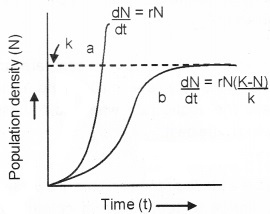
Answer:
- Curve ‘a’ is exponential growth curve and b is logistic growth curve.
- K is the carrying capacity. Beyond K no further growth of population is possible.
- Logistic growth
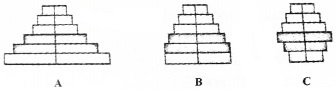
- Name A, B and C pyramids.
- Which one is ideal for a population. Suggest reason.
- How does such age pyramids help policy makers of the country.
Answer:
1. Name A, B and C pyramids:
- Expaning
- Stable
- Declining
2. Expanding
Pre reproductive individuals are more in number than reproductive and post-reproductive.
3. It reflects the growth status
Question 4.
Scientist paul Ehrlich and Peter Raven developed the concept of co-evolution.
- Give an example for co-evolution.
- How did they show mutualistic association.
- Name the mutualistic relationship shown by male bee and ophrys petal.
Answer:
1. Wasp and fig tree.
2. The female wasp lays its egg in the ovary locule and uses the developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae. The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg laying sites.
3. Pseudocopulation
Question 5.
Analyze the given graph which represents the population growth curve.
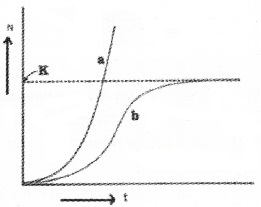
- Which growth curves do ‘a’ and ‘b’ indicate?
- Suggest an equation for ‘b’.
- What parameters are required for calculating current r-value?
Answer:
1. growth curves do ‘a’ and ‘b’ indicate
- Exponential growth curve
- logistic growth curve
2. \(\frac{\mathrm{d}\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{dt}}=\mathrm{rN}\left(\frac{\mathrm{K}-\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right)\)
3. Current birth rate and death rate.
Question 6.
Observe the flow chart given below and answer the following questions.
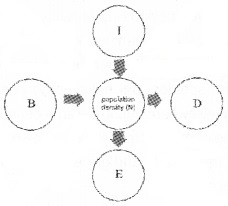
- Identify I, B, D and E.
- Write the equation for population density.
- B and I are positive, D and E are negative about population. Suggest reason.
Answer:
1. Identify I, B, D and E:
- l-Immigration
- D-Mortality
- B-Natality
- E-Emigration
2. Nt+1 = Nt + [(B+1)-(D + E)]
3. N and I are natality and immigration – Both contribute an increase in population density. D and E are mortality and emigration – Both contribute to decrease in population.
Question 7.
Analyse the given graph and answer the following questions.
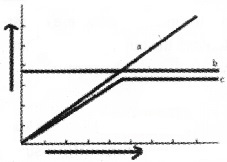
- Label a, b, c.
- How a differs from b?
Answer:
1.
- Conformers
- Regulators
- Partial regulators
2.
- Organism Cannot maintain constant internal environment.
- Organism can maintain constant internal environment through thermoregulation and osmoregulation.
Question 8.
Fill in the blanks.
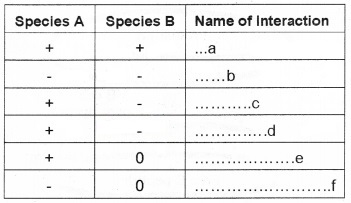
Answer:
(a) Mutualism
(b) Competition
(c) Predation
(d) Parasitism
(e) Commensalism
(f) Amensalism
Plus Two Botany Organisms and Populations NCERT Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define phenotypic adaption. Give one example.
Answer:
Phenotypic adaptions are acquired non-genetic changes in individuals such as physiological modification, acclimatization or behavioural changes.
For examples, if a person has ever been to any high altitude, on visiting such as place he or she must have altitude sickness because body does not get enough oxygen. But gradually he or she gets acclimatized and stop experiencing altitude sickness.
Question 2.
Most living organisms cannot survive at temperature above 45°C. How are some microbes able to live in habitats with temperature exceeding 100°C?
Answer:
The microbes of high temperature area are known as thermo-acidophiles. They are able to survive at high temperature through.
- Reduction in amount of free water.
- Occurrence of branched chain lipids that reduce fluidity of cell membranes.
Question 3.
List the attributes that populations but not individuals possess.
Answer:
- Population density.
- Natality or birth rate.
- Mortality or death rate.
- Population growth.
- Sex ratio.
- Age distribution.
Question 4.
If a population growing exponentially double in size in 3 years, what is the intrinsic rate of increase (r) of the population?
Answer:
Nt = N0 ert
Since Nt = 2; N0 = 1, e = 2.71828 ; t = 3
2 = (1 × 2.71828)3r
Log 2 = 3 r log (2.71828)
0.3010 = 3 r × 0.4343
r= 0.2310
Intrinsic rate of increase=23.1 %.
Question 5.
Name important defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory?
Answer:
Leaves modified into thorns, development of spiny margins on the leaves. Many plants produce and store chemicals that make the herbivore sick.
eg: calotropis produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides. Some other chemical substances like nicotine, quinine, opium etc are produced by plants and provide defence against grazing animals.
Question 6.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction?
Answer:
It is an example of commensalism, where the or-chid gets space (benefitted) but the mango tree is neither benefited nor harmed.
Question 7.
What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
Answer:
The ecological principle behind the biological control of pest insects is based on the ability of predator to regulate prey population in that habitat. For example Gambusia fish prey upon the larvae of mosquito and acts as biological controller of malaria.
Plus Two Botany Organisms and Populations Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The niche of a population is defined as
(a) set of condition that interacts
(b) place where it lives
(c) set of conditions and resources it uses
(d) geographical’ area that it covers
Answer:
(c) set of conditions and resources it uses
Question 2.
Competition for food, light and space is most severe between two
(a) closely related species growing in different niches
(b) distantly related species growing in different niches
(c) closely related species growing in same niches
(d) distantly related species growing in same niches
Answer:
(c) closely related species growing in same niches
Question 3.
An ecosystem, which can be easily damaged but can recover after some time if damaging effect stops, will be having
(a) low stability and high resilience
(b) high stability and low resilience
(c) low stability and low resilience
(d) high stability and high resilience
Answer:
(a) low stability and high resilience
Question 4.
Assertion: Predaton is an interspecific ineraction with I a feeding strategy.
Reason: Predation and their prey maintain fairly stable population become abundant or scarce.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true but Reason is false
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 5.
The assemblage of all the populations of different species that function as an Integrated unit through coevolved metabolic transformation in a specific area is Called
(a) biome
(b) biotic community
(c) population
(d) ecosystem
Answer:
(b) biotic community
Question 6.
A lake near a village suffered heavy mortality of fishes within a few days. Consider the following reasons for this
I) Lots of urea and phosphate fertilizers were used in the crops in the vicinity.
II) The area was sprayed with DDT by an aircraft
III) The lake water turned green and stinky.
IV Phytoplankton populations in the lake declined initially thereby greatly reducing photosynthesis. Which two of the above were the main causes of fish mortality in the lake?
(a) II, III
(b) III, IV
(c) I, III
(d) I, II
Answer:
(d) I, II
Question 7.
In commensalism
(a) both partners are harmed
(b) weaker partner is benefitted
(c) both partners are benefitted
(d) None of the partners is benefited
Answer:
(b) weaker partner is benefitted
Question 8.
If the strong partner is benefitted and the weak partner is damaged. It is known as
(a) predation
(b) alleloathy
(c) symbiosis
(d) commensalisms
Answer:
(a) predation
Question 9.
Competition of species leads to
(a) extinction
(b) mutation
(c) greater number of niches are formed
(d) symbiosis
Answer:
(a) extinction
Question 10.
Which of the following statement regarding species interdependence are true?
I. An association of two species where one is benefitted and other remain unaffected is called mutualism.
II. An interspecific association where both partners derive benefit from each other is called commensalism.
III. A direct food relation between two species of animals in which one animals kills and feeds on another is referred as predation.
IV. A relationship between two of organisms where both the partners are benefitted from each other is called symbiosis.
(a) I and II only
(b) III and IV only
(c) I and III only
(d) II and III only
Answer:
(b) III and IV only
Question 11.
In India, human population is heavily weighed towards the younger age group as a result of
(a) Short life span of many individuals and low birth rate
(b) Short life span of many individuals and high birth rate
(c) long life span of many individuals and high birth rate
(d) long life span of many individuals and low birth rate
Answer:
(b) Short life span of many individuals and high birth rate
Question 12.
Ratio between mortality and natality is
(a) population ratio
(b) census proportion
(c) vital index
(d) density coefficient
Answer:
(c) vital index
Question 13.
The population of an insect species shows an explosive increase in number during rainy season followed by its disappearance at the end of the season. What does this show?
(a) S-shaped or sigmoid growth of this insect
(b) The food plants mature and die at the end of the rainy season
(c) Its population growth curve is of type
(d) The population of its predators increases enormously
Answer:
(c) Its population growth curve is of type
Question 14.
The annual variations in temperature results distinct seasons, these variations together with annual variation in precipitation leads to
(a) rain forest
(b) deserts ,
(c) lake
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(d) both a and b
Question 15.
Few organisms can tolerate and thrive in a wide range of temperatures they are called as
(a) eurythermal
(b) stenothermal
(c) euryhaline
(d) stenohaline
Answer:
(a) eurythermal
Question 16.
The type of benthic animals in ocean is determined by
(a) pH of water
(b) mineral composition
(c) sediment characteristics
(d) dissolved CO„ level
Answer:
(c) sediment characteristics
Question 17.
Important characteristics of mammals live in Antarctica or in the Sahara desert have
(a) osmoregulation
(b) thermoregulation
(c) thermoperiodicity
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(d) both a and b
Question 18.
The Smaller animals have a larger surface area, so they tend to lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside. This result in spending
(a) much energy for catabolism
(b) much energy for catabolism and anabolism
(c) low energy for catabolism
(d) much energy for anabolism
Answer:
(b) much energy for catabolism and anabolism
Question 19.
The Keolado National Park in Rajasthan host many
(a) bat population from warmer countries
(b) bird population from warmer countries
(c) bird population from winter countries
(d) bat population from winter countries
Answer:
(c) bird population from winter countries
Question 20.
Mammals of colder climates have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss. This is come under
(a) Allen’s Rule
(b) bergmans rule
(c) jordans rule
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) Allen’s Rule
Question 21.
The number of births plus the number of immigrants is the major component in determining the
(a) density of population
(b) sex ratio
(c) age distribution
(d) species composition
Answer:
(a) density of population
Question 22.
If the resources in the habitat are unlimited, this results in the population have
(a) s- shaped curve
(b) j shaped curve
(c) parabolic curvature
(d) linear curve
Answer:
(b) j shaped curve
Question 23.
The equation dN/dt = rN(K-N/K) is represented as
(a) logistic population growth
(b) exponential population growth K
(c) Verhulst-Pearl Logistic Growth
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(d) both a and c
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations help you. If you have any query regarding the Kerala Plus Two Botany Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 6 Organisms and Populations, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.