What is the Area of a Right Circular Cone

If r, h and ℓ denote respectively the radius of base, height and slant height of a right circular cone, then-
- ℓ 2 = r2 + h2
- Area of base = πr2
- Curved (lateral) surface area = πrℓ
- Total surface area = πr (ℓ + r)
- Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\) πr2h
Read more about Radius of a Right Circular Cylinder
Right Circular Cone Example Problems with Solutions
Example 1: The height of a cone is 48 cm and the radius of its base is 36 cm. Find the curved surface
area and the total surface area of the cone.
(Take π = 3.14).
Solution: Given : h = 48 cm and r = 36 cm.
∴ ℓ2 = h2 + r2
⇒ ℓ2 = 482 + 362 = 2304 + 1296 = 3600
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {3600} \,\,cm\) = 60 cm
∴ The curved surface area = πrℓ
= 3.14 × 36 × 60 cm2 = 6782.4 cm2
And, the total surface area of the cone
= πrℓ + πr2 = πr (ℓ + r)
= 3.14 × 36 × (60 + 36)cm2
= 10851.84 cm2
Example 2: Curved surface area of a cone is 2200 cm2.
It its slant height is 50 cm, find :
(i) radius of the base.
(ii) total surface area.
(iii) height of the cone.
Solution: (i) Given : πrℓ = 2200 cm2 and ℓ = 50 cm
⇒ \(\frac{{22}}{7} \times r \times 50\) = 2200
i.e., r = \(\frac{{2200 \times 7}}{{22 \times 50}}cm\) = 14 cm
(ii) Total surface area = πrℓ (ℓ + r)
= \(\frac{{22}}{7}cm \times 14\) × (50 + 14) cm2
= 2816 cm2 Ans.
(iii) ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ h2 = ℓ2 – r2
= 502 – 142 = 2500 – 196 = 2304
∴ h = \(\sqrt {2304}\) cm = 48 cm
Example 3: A conical tent is 10 m high and radius of its base is 24 m. Find
(i) slant height of the tent.
(ii) cost of the canvas required to make the tent, if the cost of 1 m2 canvas is Rs. 70.
Solution: (i) Given : h = 10 m and r = 24 m
∴ ℓ2 = h2 + r2
⇒ ℓ2 = 102 + 242 = 100 + 576 = 676
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {676}\) m = 26 m
(ii) Area of canvas required
= Curved surface area of the tent
= πrℓ = \(\frac{{22}}{7} \times 24 \times 26m\) = \(\frac{{13728}}{7}{m^2}\)
∵ Cost of 1 m2 canvas is Rs. 70
∴ Total cost of canvas required
= \(\frac{{13728}}{7} \times Rs.70\)
= Rs. 1,37,280
Example 4: What length of tarpaulin 3 m wide will be required to make conical tent of height 8 m and base radius 6m? Assume that the extra length of material that will be required for stitching margins and wastage in cutting is approximately 20 cm (Use π = 3.14).
Solution: For the tent : h = 8 m and r = 6 m
ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ ℓ2 = 82 + 62
= 64 + 36 = 100 and ℓ = \(\sqrt {100} \,\,m\) = 10m
Curved surface area of the tent = πrℓ
= 3.14 × 6 × 10 m2 = 188.4 m2
⇒ Area of tarpaulin used = 188.4 m2
⇒ Length of tarpaulin × its width = 188.4 m2
⇒ Length of tarpaulin × 3 m = 188.4 m2
⇒ Length of tarpaulin = \(\frac{{188.4}}{3}m = 62.8m\)
∵ Extra length of tarpaulin required
= 20 cm = 0.2 m
∴ Total length of tarpaulin required
= 62.8 m + 0.2 m = 63 m
Example 5: A bus stop is barricaded from the remaining part of the road, by using 50 hollow cones made of recycled cardboard. Each cone has a base diameter of 40 cm and height 1 m. If the outer side of each of the cones is to be painted and the cost of painting is Rs. 12 per m2, what will be the cost of painting all these cones?
(Use π = 3.14 and take \(\sqrt {1.04}\) = 1.02)
Solution: For each cone :
r = \(\frac{{40}}{2}\) cm = 20 cm = 0.2 m and h = 1 m
∴ ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ ℓ2 = (1)2 + (0.2)2
= 1 + 0.04 = 1.04
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {1.04}\)m = 1.02 m
C.S.A of each cone = πrℓ
= 3.14 × 0.2 × 1.02 m2 = 0.64056 m2
⇒ C.S.A of 50 cones = 50 × 0.64056 m2
= 30.028 m2 = Area to be painted
∵ The cost of painting is Rs. 12 per m2
∴ The total cost of painting outer sides of 50 cones
= 30.028 × Rs. 12 = Rs. 384.34
Example 6: The radius and the slant height of a cone are in the ratio 3 : 5. If its curved surface area is 2310 cm2, find its height.
Solution: Given : r : ℓ = 3 : 5
⇒ if r = 3x cm, ℓ = 5x cm
C.S.A. = πrℓ ⇒ \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 3x × 5x = 2310
⇒ x2 = \(\frac{{2310 \times 7}}{{22 \times 3 \times 5}} = 49\) ⇒ x = 7
∴ r = 3x = 3 × 7 cm = 21 cm
and ℓ = 5x = 5 × 7 cm = 35 cm,
ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ h2 = 352 –212
= 1225 – 441 = 784
∴ Height (h) = \(\sqrt {784} cm\) = 28 cm
Example 7: A circus tent is in the shape of a cylinder, upto a height of 8 m, surmounted by a cone of the same radius 28 m. If the total height of the tent is 13 m, find:
(i) total inner curved surface area of the tent.
(ii) cost of painting its inner surface at the rate of Rs. 3.50 per m2.
Solution: According to the given statement, the rough sketch of the circus tent will be as shown:
(i) For the cylindrical portion :
r = 28 and h = 8 m
∴ Curved surface area = 2πrh
= 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 28 × 8 m2 = 1408 m2
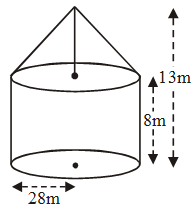 For conical portion :
For conical portion :
r = 28 m and h = 13 m – 8 m = 5 m
∴ ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ ℓ2 = 52 + 282 = 809
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {809}\)m = 28.4 m
∴ Curved surface area = πrℓ
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 28 × 28.4 m2 = 2499.2 m2
∴ Total inner curved surface area of the tent.
= C.S.A. of cylindrical portion + C.S.A. of the conical portion
1408 m2 + 2499.2 m2 = 3907.2 m2
(ii) Cost of painting the inner surface
= 3907.2 × Rs. 3.50 = Rs. 13675.20
Example 8: The height of a cone is 30 cm and its volume is 3140 cm3. Taking π = 3.14, find :
(i) radius of the base.
(ii) area of the base.
Solution: (i) Given : h = 30 cm and volume = 3140 cm3
Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\)
⇒ 3140 = \(\frac{1}{3} \times 3.14\) × r2 × 30
⇒ r2 = \(\frac{{3140 \times 3}}{{3.14 \times 30}} = 100\) and r = 10cm
(ii) Area of the base = πr2
= 3.14 × 102 cm2 = 314 cm2
Alternative Method :
\(\frac{1}{3}\) × area of base × height = volume
⇒ \(\frac{1}{3}\) × area of base × 30 = 3140
⇒ Area of base = \(\frac{{3140 \times 3}}{{30}}c{m^2}\)
= 314 cm2
Example 9: A right triangle ABC has sides 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm. Find the :
(i) volume of solid obtained by revolving ∆ ABC about the side 12 cm.
(ii) volume of solid obtained by revolving ∆ ABC about side 5 cm.
(iii) difference between the volumes of the solids obtained in step (i) and step (ii).
Solution: ∵ 52 + 122 = 132 ⇒ Angle opp. to 13 cm is right angle
(i) When the ∆ is revolved about the side of
12 cm, for the cone formed :
h = 12 cm and r = 5.
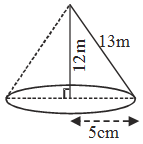 ∴ Volume of solid obtained = \(\frac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\)
∴ Volume of solid obtained = \(\frac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 5 × 5 × 12 cm3
= 314.29 cm3
(ii) When the ∆ is revolved about the side of 5 cm, for the cone formed :
h = 5 cm, and r = 12 cm.
∴ Volume of solid obtained = \(\frac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 12 × 12 × 5 cm3 = 754.29 cm3
(iii) Required difference
= 754.29 cm3 – 314.29 cm3 = 440 cm3
Example 10: The volume of a right circular cone is 9856 cm3. If the diameter of the base is 28 cm, find:
(i) height of the cone.
(ii) slant height of the cone
(iii) curved surface area of the cone.
Solution: Given : volume of cone = 9856 cm3
and radius (r) = \(\frac{28}{2}\) cm = 14cm
(i) Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h ⇒ 9856 = \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 14 × 14 × h
⇒ h = \(\frac{{9856 \times 3 \times 7}}{{22 \times 14 \times 14}}cm\) = 48 cm
(ii) ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ ℓ2 = 482 + 142
= 2304 + 196 = 2500
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {2500}\)cm = 50 cm
∴ Slant height = 50 cm
(iii) Curved surface area = πrℓ
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 14 × 50 cm2 = 2200 cm2
Example 11: A heap of wheat is in the form of a cone whose diameter is 10.5 m and height is 3 m. Find its volume. The heap is to be covered by canvas to protect it from rain. Find the area of the canvas required.
Solution: For the conical heap :
Radius (r) = \(\frac{{10.5}}{2}m\) = 5.25 m
and height (h) = 3m.
∴ Volume = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h
= \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{{22}}{7} \times 5.25\) × 3 m3 = 86.625 m3
Now, ℓ2 = h2 + r2 ⇒ ℓ2 = (3)2 + (5.25)2
= 9 + 27.5625 = 36.5625
⇒ ℓ = \(\sqrt {36.5625}\)m = 6.047 m
∴ Area of canvas required
= curved surface area of the conical heap
= πrℓ = \(\frac{{22}}{7} \times 5.25 \times 6.047{m^2}\) = 99.7755 m2
Example 12: A cylinder and a cone have same base area. But the volume of cylinder is twice the volume of cone. Find the ratio between their heights.
Solution: Since, the base areas of the cylinder and the cone are the same.
⇒ their radius are equal (same).
Let the radius of their base be r and their heights be h1 and h2 respectively.
Clearly, volume of the cylinder = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h1
and, volume of the cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr2h2
Given :
Volume of cylinder = 2 × \(\frac{1}{3}\) volume of cone
⇒ πr2h1 = 2 × πr2h2
⇒ h1 = \(\frac{2}{3}\)h2
⇒ \(\frac{{{h_1}}}{{{h_2}}} = \frac{2}{3}\)
i.e., h1 : h2 = 2 : 3