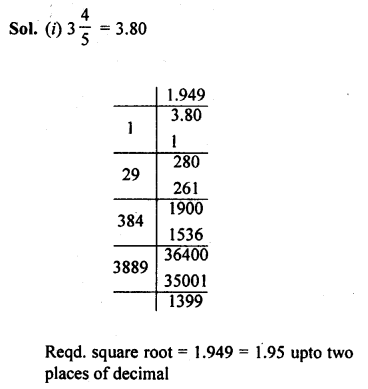
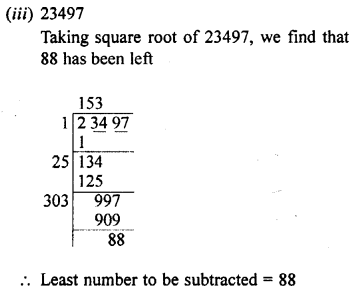
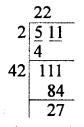
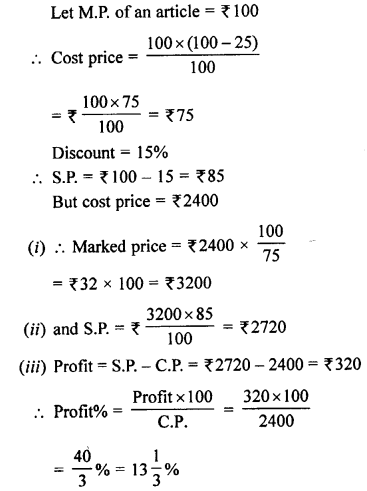
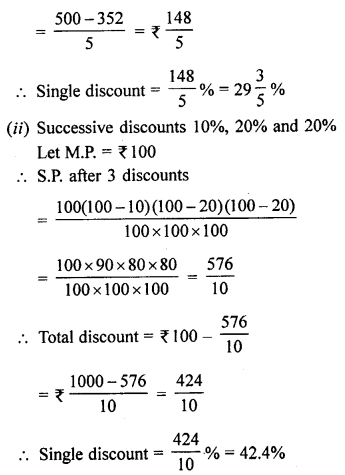
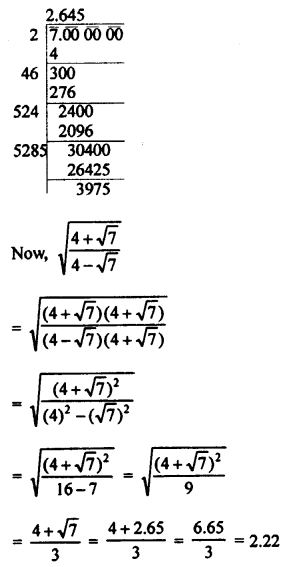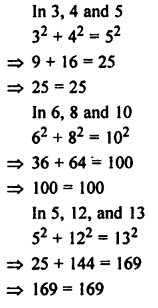Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 18 Constructions (Using ruler and compass only)
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 18 Constructions (Using ruler and compass only)
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 18 Constructions (Using ruler and compass only). You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Maths SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
Constructions Exercise 18A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
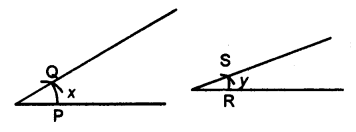
Given below are the angles x and y.
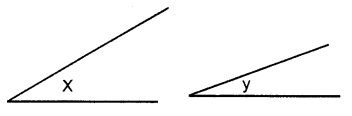
Without measuring these angles, construct :
(i) ∠ABC = x + y
(ii) ∠ABC = 2x + y
(iii) ∠ABC = x + 2y
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction :
- Draw a line segment BC of any suitable length.
- With B as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius. With the same radius, draw arcs with the vertices of given angles as centres. Let these arcs cut arms of the arc x at points P and Q and arms of angle y at points R and S.
- From the arc, with centre B, cut DE = PQ arc of x and EF = RS arc of y
- Join BF and produce upto point A.
Thus ∠ABC = x + y
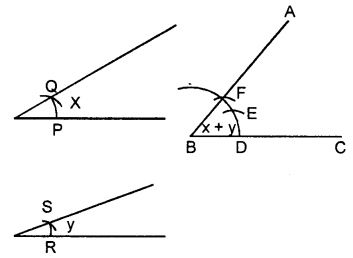
(ii) Steps of Construction :
Proceed in exactly the same way as in part(i)
takes DE = PQ = arc of x.
EF = PQ = arc of x and FG = RS = arc of y.
Join BG and produce it upto A.
Thus ∠ABC = x + x+ y = 2x + y
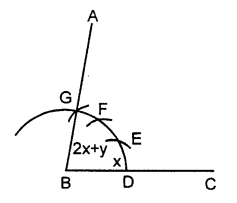
(iii) Steps of Construction :
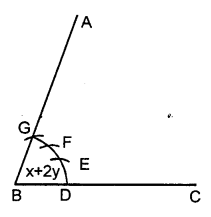
Proceed in exactly the same way as in (ii)
taking DE = PQ = arc of x. and EF = RS = arc of y and FG = RS = arc of y.
4. Join BF and produce upto point A.
Thus ∠ABC = x + y + y = x + 2y
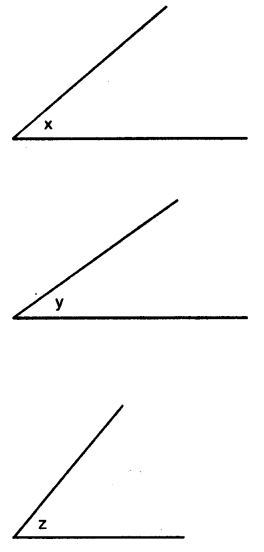
Question 2.
Given below are the angles x, y and z.
Without measuring these angles construct :
(i) ∠ABC = x + y + z
(ii) ∠ABC = 2x + y + z
(iii) ∠ABC = x + 2y + z
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction :
- Draw line segment BC of any suitable length.
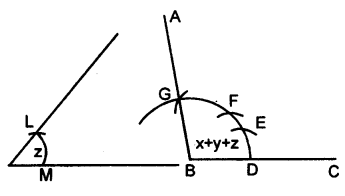
- With B as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius. With the same radius, draw arcs with the vertices of given angles as centres. Let these arcs cut arms of the anlge x at the points P and Q and arms of the angle y at points R and S and arms of the angle z at the points L and M.
- From the arc, with centre B, cut
DE = PQ = arc of x, EF = RS = arc of y and FG = LM = arc of z. - Join BG and produce it upto A.
Then ∠ABC = x + y + z
(ii) Proceed as in part (i) upto step 2.
3. From the arc, with centre B, cut
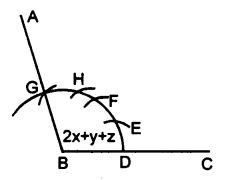
DE = 2PQ = 2 arc of x
EF = RS = arc of y
FG = LM = arc of z
4. Join BG and produce it upto point A
Then ∠ABC = 2x + y + z
(iii) proceed as in (i) upto step 2
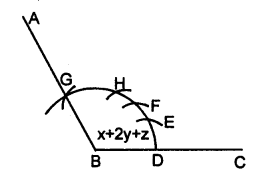
3. Here cut arc DE = arc PQ = arc of x arc EF = 2 arc RS = 2 arc of y arc FG = arc LM = arc of z.
4. Join BG and produce it upto A
5. Then ∠ABC = x + 2y + z
Question 3.
Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm. Construct angle ABC = 60°.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
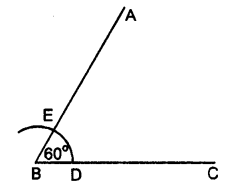
- Draw a line segment BC = 4 cm
- With B as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius which cuts BC at the point D.
- With D as centre, and the same radius as in step 2, draw one more arc which cuts the previous arc at the point E.
- Join BE and produce it to the point A.
Thus ∠ABC = 60°
Question 4.
Construct angle ABC = 45° in which BC = 5 cm and AB = 4.6 cm.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
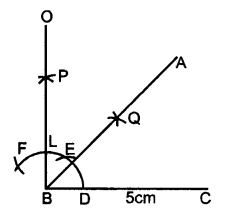
- Draw a line segment BC = 5 cm
- Taking B as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius, which cuts BC at the point D.
- With D as centre and the same radius, as taken in step 2, draw an arc which cuts the previous arc at point E.
- With E as centre and the same radius, draw one more arc which cuts the first arc at point F.
- With E and F as centres and radii equal to more than half the distance between E at F, draw arc which cut each other at point P.
- Join BP to meet EF at L and produce to point O. Then ∠OBC = 90°
- Draw BA, the bisector of angle OBC. [With D, L as centres and suitable radius draw two arc meeting each other at Q produced it to R]
=> ∠ABC = 45° [∴ BA is bisector of ∠OBC ∴ ∠ABC = = 45°] - From BR cut arc AB = 4.6 cm
Question 5.
Construct angle ABC = 90°. Draw BP, the bisector of angle ABC. State the measure of angle PBC.
Solution:
- Draw ∠ABC = 90° (as in Ques. 4)
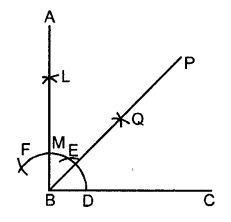
- Draw bisector of ∠ABC
Then ∠PBC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (90°) = 45°
Question 6.
6. Draw angle ABC of any suitable measure.
(i) Draw BP, the bisector of angle ABC.
(ii) Draw BR, the bisector of angle PBC and draw BQ, the bisector of angle ABP.
(iii) Are the angles ABQ, QBP, PBR and RBC equal?
(iv) Are the angles ABR and QBC equal ?
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
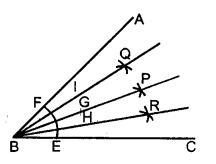
- Construct any angle ABC
- With B as centre, draw an arc EF meeting BC at E and AB at F.
- With E, F as centres draw two arc of equal radii meeting each other at the point P.
- Join BP. Then BP is the bisector of ∠ABC
∠ABP = ∠PBC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ∠ABC - Similarly draw BR, the bisector of ∠PBC and draw BQ as the bisector of ∠ABP [With the same method as in steps 2, 3]
- Then ∠ABQ = ∠QBP = ∠PBR = ∠RBC
- ∠ABR = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) ∠ABC and ∠QBC = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) ∠ABC
∠ABR = ∠QBC.
Constructions Exercise 18B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Draw a line segment AB of length 5.3 cm. Using two different methods bisect AB.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
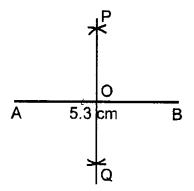
- Draw a line segment AB = 5.3 cm
- With A as centre and radius equal to more than half of AB, draw arcs on both sides of AB.
- With B as centre and with the same radius as taken in step 2, draw arcs on both the sides of AB.
- Let the arcs intersect each other at points P and Q.
- Join P and Q.
- The line PQ cuts the given line segment AB at the point O.
Thus, PQ is a bisector of AB such that
OA = OB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) AB
Second Method
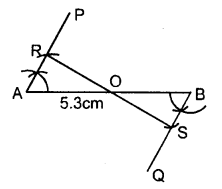
Steps of Construction :
- Draw the given line segment AB = 5.3 cm.
- At A, construct ∠PAB of any suitable measure. Then ∠PAB = 60° construct ∠QBA = 60°
- 3.From AP, cut AR of any suitable length and from BQ ; cut BS = AR.
- Join R and S
- Let RS cut the given line segment AB at the point O.
Thus RS is a bisector of AB such that OA = OB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) AB
Question 2.
Draw a line segment PQ = 4.8 cm. Construct the perpendicular bisector of PQ.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
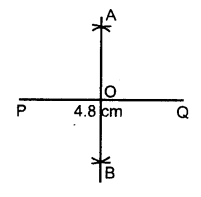
- Draw a line segment PQ = 4.8 cm.
- With P as centre and radius equal than half of PQ, draw arc on both the PQ.
- With Q as centre and the same radius as taken in step 2, draw arcs on both sides of PQ.
- Let the arcs intersect each other at point A and B
- Join A and B.
- The line AB cuts the line segment PQ at the point O. Here OP = OQ and ∠AOQ = 90°. Then the line AB is perpendicular bisector of PQ.
Question 3.
In each of the following, draw perpendicular through point P to the line segment AB :
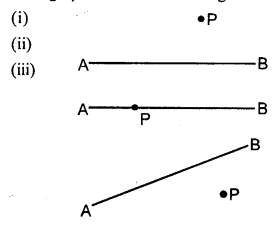
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction :
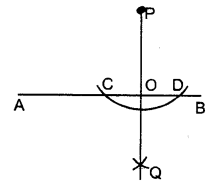
- With P as centre, draw an arc of a suitable radius which cuts AB at points C and D.
- With C and D as centres, draw arcs of equal radii and let these arcs intersect each other at the point Q.
[The radius of these arcs must be more than half of CD and both the arcs must be drawn on the other side] - Join P and Q
- Let PQ cut AB at the point O.
Thus, OP is the required perpendicular clearly, ∠AOP = ∠BOP = 90°
(ii) Steps of Construction :
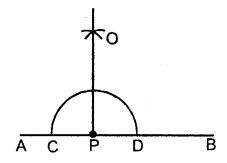
- With P as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius which cuts AB at points C and D.
- With C and D as centres, draw arcs of equal radii. Which intersect each other at point A.
[This radius must be more than half of CD and let these arc intersect each other at the point 0] - Join P and O. Then OP is the required perpendicular.
∠OPA = ∠OPB = 90°
(iii) Steps of Construction :
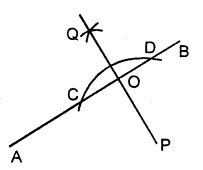
- With P as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius which cuts AB at points C and D.
- With C and D as centre, draw arcs of equal radii
[The radius of these arcs must be more than half of CD and both the arcs must be drawn on the other side.]
and let these arcs intersect each other at the point Q. - Join Q and P. Let QP cut AB at the point O. Then OP is the required perpendicular.
Clearly, ∠AOP = ∠BOP = 90°
Question 4.
Draw a line segment AB = 5.5 cm. Mark a point P, such that PA = 6 cm and PB = 4.8 cm. From the point P, draw perpendicular to AB.
Solution:
Step of Construction :
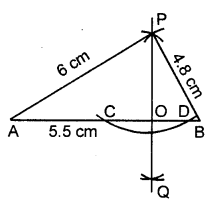
- Draw a line segment AB = 5.5 cm
- With A as centre and radius = 6 cm, draw an arc.
- With B as centre and radius = 4.8 cm draw another arc.
- Let these arcs meet each other at the point P.
PA = 6 cm, PB = 4.8 - With P as centre and some suitable radius draw an arc meeting AB at the points C and D.
- With C as centre and radius more than half of CD, draw an arc.
- With D as centre and same radius as in step 6, draw an arc.
- Let these arcs meet each other at the point Q.
- Join PQ.
- The PQ meet AB at point O.
Then PO ⊥ AB i.e; ∠AOP = 90° = ∠POB.
Question 5.
Draw a line segment AB = 6.2 cm. Mark a point P in AB such that BP = 4 cm. Through point P draw perpendicular to AB.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
- Draw a line segment AB = 6.2 cm
- Cut off BP = 4 cm
- With P as centre and some radius draw arc meeting AB at the points C, D.
- With C, D as centres and equal radii [each is more than half of CD] draw two arcs, meeting each other at the point O.
- Join OP. Then OP is perpendicular for AB.
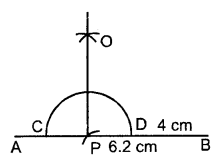
Constructions Exercise 18C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Draw a line AB = 6 cm. Mark a point P any where outside the line AB. Through the point P, construct a line parallel to AB.
Solution:
Steps of construction :
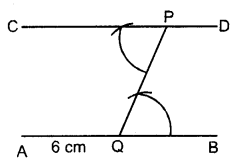
- Draw a line AB = 6 cm
- Take any point Q on the line AB and join it with the given point P.
- At point P, construct ∠CPQ = ∠PQB
- Produce CP upto any point D.
Thus, CPD is the required parallel line.
Question 2.
Draw a line MN = 5.8 cm. Locate a point A which is 4.5 cm from M and 5 cm from N. Through A draw a line parallel to line MN.
Solution:
Steps of construction :
- Draw a line MN = 5.8 cm
- With M as centre and radius = 4.5 cm, draw an arc.
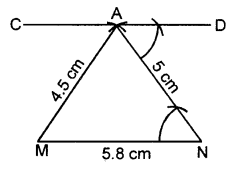
- With N as centre draw another arc of radius 5 cm. These arcs intersect each other at A.
- Join AM and AN.
- At point A, draw ∠DAN = ∠ANM
- Produce DA to any point C.
Thus CAD is the required parallel line.
Question 3.
Draw a straight line AB = 6.5 cm. Draw another line which is parallel to AB at a distance of 2.8 cm from it.
Solution:
Steps of construction :
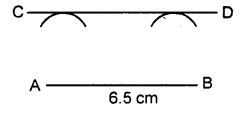
- Draw a straight line AB = 6.5 cm
- Taking point A as centre, draw an arc of radius 2.8 cm.
- Taking B as centre, drawn another arc of radius 2.8 cm.
- Draw a line CD which touches the two arcs drawn.
Thus CD is the required parallel line.
Question 4.
Construct an angle PQR = 80°. Draw a line parallel to PQ at a distance of 3 cm from it and another line parallel to QR at a distance of 3.5 cm from it. Mark the point of intersection of these parallel lines as A.
Solution:
Steps of construction :
- Draw ∠PQR = 80°
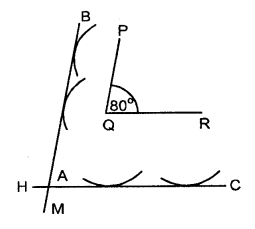
- With P as centre draw an arc of radius 2 cm.
- Again with Q as centre, draw another arc of radius 2 cm. Then BM is a line which touches the two arcs. Then BM is a line parallel to PQ.
- With Q as centre, draw an arc of radius 3.5 cm. With R as centre draw another arc of radius 3.5 cm. Draw a line HC which touches these two arcs. Let these two parallel line intersect at A.
Question 5.
Draw an angle ABC = 60°. Draw the bisector of it. Also draw a line parallel to BC a distance of 2.5 cm from it.
Let this parallel line meet AB at point P and angle bisector at point Q. Measure the length of BP and PQ. Is BP = PQ ?
Solution:
Steps of construction :
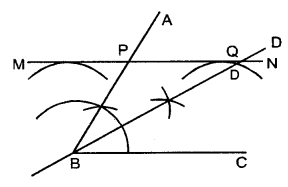
- Draw, ∠ABC = 60°
- Draw BD, the bisector of ∠ABC.
- Taking B as centre, draw an arc of radius 2.5 cm.
- Taking C as centre, draw another arc of radius 2.5 cm.
- Draw a line MN which touches these two arcs drawn. Then MN is the required line parallel to BC.
- Let this line MN meets AB at P and bisector BD at Q.
- Measure BP and PQ.
By measurement we see BP = PQ.
Question 6.
Construct an angle ABC = 90°. Locate a point P which is 2.5 cm from AB and 3.2 cm from BC.
Solution:
Steps of construction :
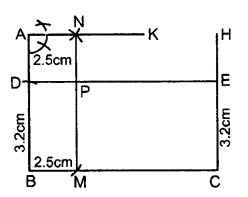
- Draw ∠ABC = 90°
- From AB, cut BD = 3.2 cm.
- Through point C, draw CH⊥BC. From CH, cut CE = 3.2. Join DE. Now DE is a line parallel to BC and at a distance of 3.2 cm from BC.
- From BC cut BM = 2.5 cm.
- Through point A, draw AK ⊥ AB. From AK cut AN = 2.5 cm. Join NM. Therefore NM is parallel to AB and at a distance of 2.5 cm from AB.
- DE and MN intersect each other at P. Thus P is the required point which is 2.5 cm from AB and 3.2 cm from BC.
Constructions Exercise 18D – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD; if:
(i) AB = 4.3 cm, BC = 5.4, CD = 5 cm, DA = 4.8 cm and angle ABC = 75°.
(ii) AB = 6 cm, CD = 4.5 cm, BC = AD = 5 cm and ∠BCD = 60°.
(iii) AB = 8 cm, BC = 5.4 cm, AD = 6 cm, ∠A = 60° and ∠B = 75°.
(iv) AB = 5 cm, BC = 6.5 cm, CD =4.8 cm, ∠B = 75° and ∠C = 120°.
(v) AB = 6 cm = AC, BC = 4 cm, CD = 5 cm and AD = 4.5 cm.
(vi) AB = AD = 5cm, BD = 7 cm and BC = DC = 5.5 cm
Solution:
(i) Rough figure is as follow :
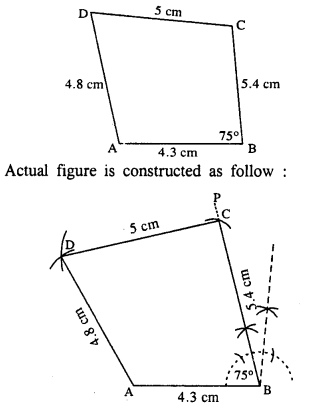
Steps :
- Draw AB = 4.3 cm.
- At B, draw ∠PBA = 75°
- Cut BC = 5.4 cm.
- From C & A, draw arcs of radii 5 cm and 4.8 cm respectively which intersect at D.
- Join AD and DC.
ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(ii) Rough figure is as follow :
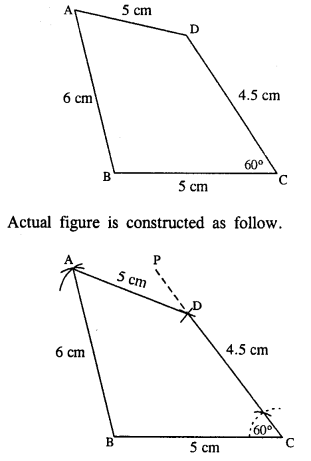
Steps :
- Draw BC = 5 cm.
- Draw ∠PCB = 60° and cut CD = 4.5 cm.
- From B and D, draw arcs of radii 6 cm and 5 cm respectively which intersect at A.
- Join AB and AD.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(iii) Rough figure is as follow :
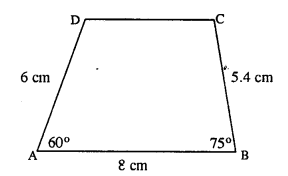
Actual quadrilateral is constructed with the help of above rough figure.
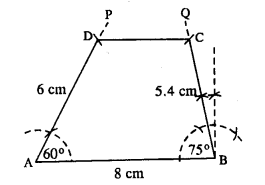
Steps :
- Draw AB = 8 cm.
- At A, draw ∠PAB = 60° and cut DA = 6 cm.
- At B, draw ∠QBA = 75° and cut BC = 5.4 cm.
- Join DC.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(iv) Rough figure is as shown below.
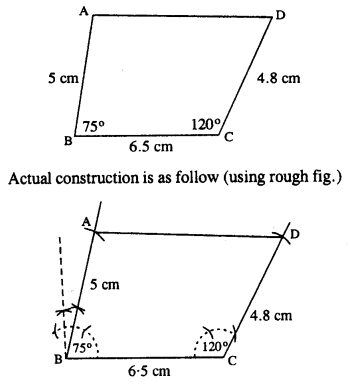
Steps :
- Draw BC = 6-5 cm.
- Draw ∠B = 75° and cut BA = 5 cm.
- Draw ∠C = 120° and cut CD = 4.8 cm.
- Join AD.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(v) Rough figure is as shown below.
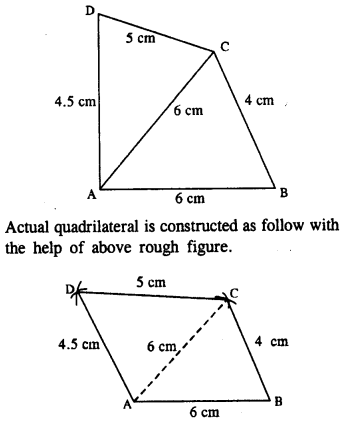
Steps :
- Draw AB = 6 cm.
- From A and B, draw arcs of radii 6 cm and 4 cm which cut at C.
- From A and C, draw arcs of radii 4.5 cm and 5 cm respectively which intersect at D.
- Join BC, CD and DA. Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(vi) Rough figure is as follow :
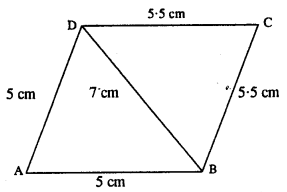
Actual construction is as follow (using above rough fig.)
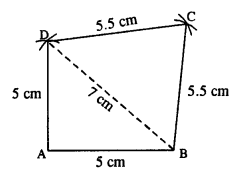
Steps :
- Draw AB = 5 cm.
- From A & B draw arcs of radii 5 cm and 7cm which intersect at D.
- From B & D draw arcs of radii 5.5 cm each which intersect at C.
- Join AD, BD, DC and BC.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 2.
Construct a parallelogram ABCD, if :
(i) AB = 3.6 cm, BC = 4.5 cm and ∠ABC = 120°.
(ii) BC = 4.5 cm, CD = 5.2 cm and ∠ADC = 75°.
(iii) AD = 4 cm, DC = 5 cm and diagonal BD = 7 cm.
(iv) AB = 5.8 cm, AD = 4.6 cm and diagonal AC = 7.5 cm.
(v) diagonal AC = 6.4 cm, diagonal BD = 5.6 cm and angle between the diagonals is 75°.
(vi) lengths of diagonals AC and BD are 6.3 cm and 7.0 cm respectively, and the angle between them is 45°.
(vii) lengths of diagonals AC and BD are 5.4 cm and 6.7 cm respectively and the angle between them is 60°.
Solution:
(i) Rough figure is as follow :
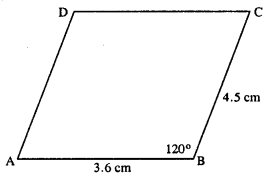
The above rough figure is used to construct the actual ||gm as follow :
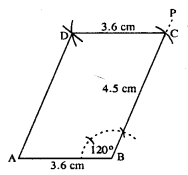
Steps :
- Draw AB = 3.6 cm.
- Draw BP such that ∠B = 120°.
- Cut BC = 4.5 cm.
- From A, draw arc of radius 4.5 cm.
- From C, draw arc of radius 3.6 cm. Which interescts first arc at D.
- Join AD and CD.
Hence ABCD is the required ||gm.
(ii) Rough figure is as follow :
Steps :
- Draw CD = 5.2 cm.
- Draw ZCDP = 75°
- Cut DA = 4.5 cm.
- From A draw arc of radius 5.2 cm.
- From C, draw arc of radius 4.5 cm which meets first arc at B.
- Join AB and CB.
Thus ABCD is the required ||gm.
(iii) Rough figure is as follow :
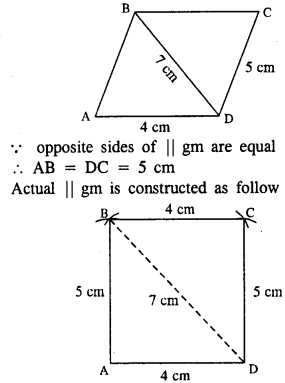
Steps :
- Draw AD = 4 cm.
- From A, draw an arc of radius 5 cm.
- From B, draw an arc of radius 4 cm.
- From D, draw an arc of ardius 5 cm which intersect first arc at C.
- Join AB, BD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required || gm.
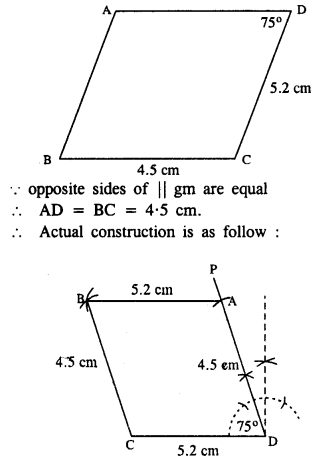
(iv) Rough figure is as follow :
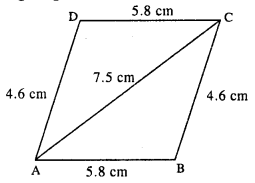
opposite sides of ||gm are equal
BC = AD = 4.6 cm.
Actual figure is constructed as follow :
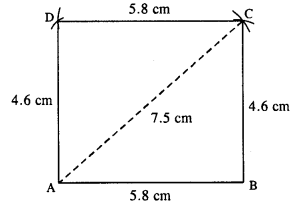
Steps:
- Draw AB = 5.8 cm.
- Draw an arc of radius 4.6 cm with centre B.
- Draw an arc of radius 7.5 cm from A which intersects first arc at C.
- From A, draw an arc of radius 4.6 cm.
- From C, draw an arc of radius 5.8 cm which intersects first arc at D.
- Join AD, CD, BC and AC.
Thus ABCD is the required //gm.
(v) Rough figure is as follow.
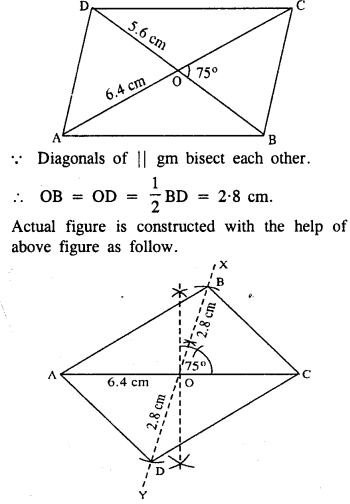
Steps :
- Draw AC = 6.4 cm.
- Bisect AC at O.
- Draw ∠XOC = 75° and produce XO to Y.
- Cut OB = OD = 2 8 cm.
- Join AB, BC, AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required ||gm.
(vi)
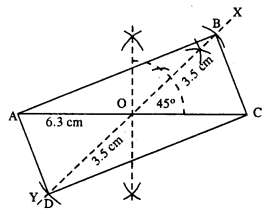
Steps :
- Draw AC = 6.3 cm.
- Bisect AC at O.
- At O, draw ∠XOC = 45° and produce XO to Y.
- Cut OB = OD = 3.5 cm (half the diagonal 7 cm.)
- Join AB, CB, AD and CD. Thus ABCD is the required || gm.
(vii)
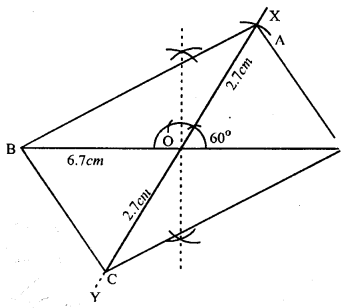
Steps :
- Draw BD 6.7 cm.
- Bisect BD at O.
- At O, draw ∠XOD = 60° and produce XO to Y.
- Cut OA = OC = 2.7 cm (half the diagonals 5.4 cm)
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required ||gm.
Question 3.
Construct a rectangle ABCD ; if :
(i) AB = 4.5 cm and BC = 5.5 cm.
(ii) BC = 61 cm and CD = 6.8 cm.
(iii) AB = 5.0 cm and diagonal AC = 6.7 cm.
(iv) AD = 4.8 cm and diagonal AC = 6.4 cm.
(v) each diagonal is 6 cm and the angle between them is 45°.
(vi) each diagonal is 5.5 cm and the angle between them is 60°.
Solution:
(i)
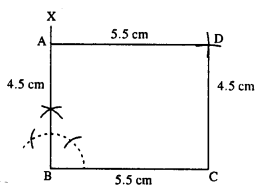
Steps :
- Draw BC = 5.5 cm.
- At B, draw ∠XBC = 90°
- Cut BA = 4.5 cm.
- From A, draw an arc of radius 5.5 cm.
- From C, draw an arc of radius 4 5 cm which meets first arc at D.
- Join AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
(ii)
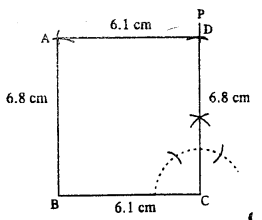
Steps:
- Draw BC = 6.1 cm.
- At C, draw ∠PCB = 90°.
- Cut CD = 6.8 cm.
- Draw an arc of radius 6.8 cm from B.
- From D, draw an arc of radius 6.1 cm which meets the first arc at A.
- Join AB and AD.
Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
(iii)
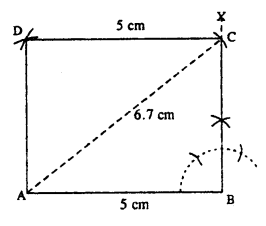
Steps :
- Draw AB = 5 cm.
- At B, draw ∠XBA = 90°.
- From A, draw an arc of radius 6.7 cm which meets XB at C.
- From C, draw an arc of a radius 5 cm.
- From A, draw an arc of radius equal to BC which meets first arc at D.
- Join AD and CD. Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
(iv)
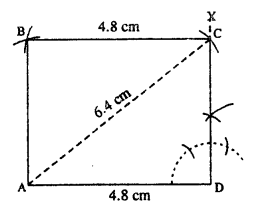
Steps :
- Draw AD = 4.8 cm.
- At D, draw ∠XDA = 90°.
- From A, draw an arc of radius 6-4 cm which meets DX at C.
- From A, draw an arc of radius equal to DC.
- From C, draw an arc of radius 4.8 cm which meets first arc at B.
- Join AB and CB. Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
(v)
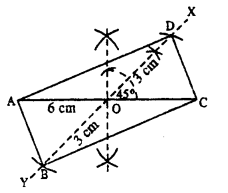
Steps :
- Draw AC = 6 cm.
- Bisect AC at O.
- At O, draw ∠XOC = 45° and produce XO to Y.
- Cut OB = OD = 3 cm (half the diagonal 6 cm)
- Join AB, CB, AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
(vi)
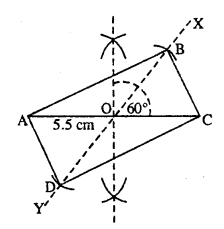
Steps :
- Draw AC = 5.5 cm.
- Bisect AC at O.
- At O, draw ∠XOC = 60° and produce XO to Y.
- Cut OB = OA and OD = OA (half the diagonal AC).
- Join AB, BC, AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rectangle.
Question 4.
Construct a rhombus ABCD, if ;
(i) AB = 4 cm and ∠B = 120°.
(ii) BC = 4.7 cm and ∠B = 75°.
(iii) CD = 5 cm and diagonal BD = 8.5 cm.
(iv) BC = 4.8cm, and diagonal AC = 7cm.
(v) diagonal AC = 6 cm and diagonal BD = 5.8 cm.
(vi) diagonal AC = 4.9 cm and diagonal BD = 6 cm.
(vii) diagonal AC = 6.6 cm and diagonal BD = 5.3 cm.
Solution:
(i)
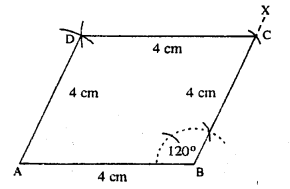
Steps :
- Draw AB = 4 cm.
- At B, draw ∠XBA = 120°
- Cut BC = 4 cm.
- Draw arcs of radii 4 cm each from A and C which intersect at D.
- Join CD and AD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
(ii)
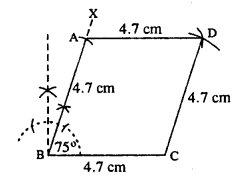
Steps :
- Draw BC = 4.7 cm.
- At B, draw ∠XBC = 75°
- Cut BA = 4.7 cm.
- From A and C, draw arcs of radii 4.7 cm each which intersect at D.
- Join AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the rhombus.
(iii)
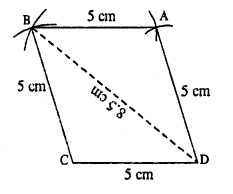
Steps :
- Draw CD = 5 cm.
- From C & D draw arcs of radii 5 cm and 8.5 cm respectively which intersect at B.
- From B and D, draw arcs of radii 5 cm each which intersect at A.
- Join AB and AD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
(iv)
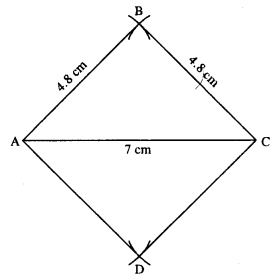
Steps :
- Draw AC = 7 cm.
- Draw arcs of radii 4.8 cm each from A and C which intersect at B.
- From A & C again draw arcs of radii 4.8 cm each which intersect at D.
- Join AB, BC, AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
(v)
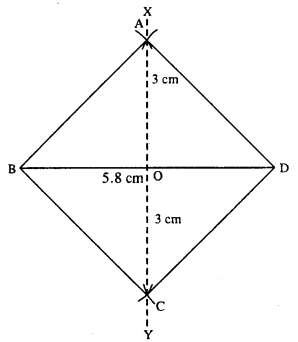
Steps :
- Draw BD = 5.8 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector XY of BD.
- Cut OA = OC = 3 cm (half the diagonal 6 cm)
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
(vi)
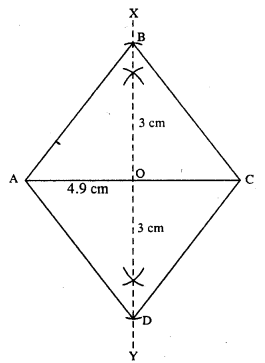
Steps :
- Draw AC = 4.9 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector XY of AC.
- Cut OB = OD = 3 cm (half the diagonal 6 cm)
- Join AB, BC, AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
(vii)
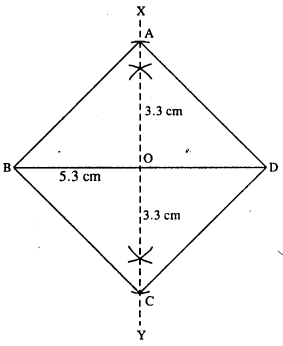
Steps :
- Draw BD = 5.3 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector XY of BD.
- Cut OA = OC = 3.3 cm (half the diagonal 6.6 cm)
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.
Question 5.
Construct a square, if :
(i) its one side is 3.8 cm.
(ii) its each side is 4.3 cm.
(iii) one diagonal is 6.2 cm.
(iv) each diagonal is 5.7 cm.
Solution:
(i)
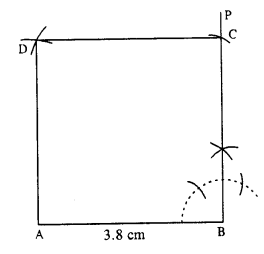
Steps :
- Draw AB = 3.8 cm.
- At B, draw ∠PBA = 90°.
- Cut BC = 3.8 cm.
- From A and C, draw arcs of radii 3.8 cm each which intersect at D.
- Join AD and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required square.
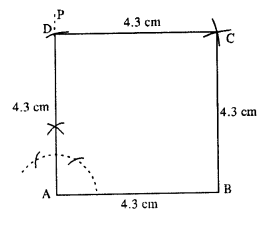
(ii)
Steps :
- Draw AB = 4.3 cm.
- Draw ∠PAB = 90° at A.
- Cut AD = 4.3 cm.
- From B and D, draw arcs of radii 4.3 cm each which intersect at C.
- Join AD, BC and CD.
Hence ABCD is the required square.
(iii)
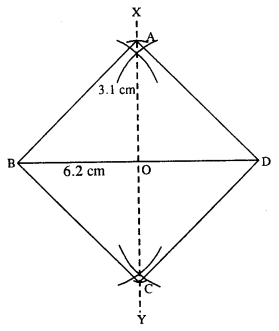
Steps :
- Draw BD = 6.2 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector XY of BD.
- Cut OA = OC = 3.1 cm (half the diagonal)
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required square.
(iv)
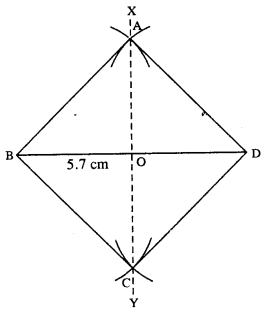
Steps :
- Draw BD = 5.7 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector XY of BD.
- From 0, draw arcs of radii equal to OB which cuts XY at A and C.
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
Thus ABCD is the required square.
Question 6.
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which ; ∠A = 120°, ∠B = 60°, AB = 4 cm, BC = 4.5 cm and CD = 5 cm.
Solution:
Rough figure is as follow :
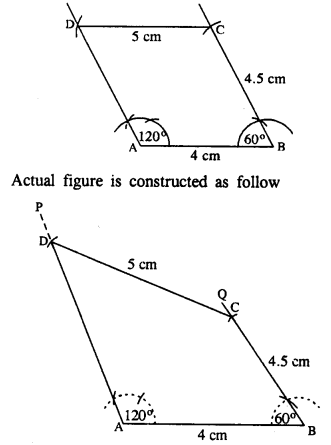
Steps :
- Draw AB = 4 cm.
- At A, draw ∠PAB = 120°.
- At B, draw ∠QBA = 60°.
- From BQ, cut BC = 4.5 cm.
- From C, draw an arc of radius 5 cm which meets AP at D.
- Join CD.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 7.
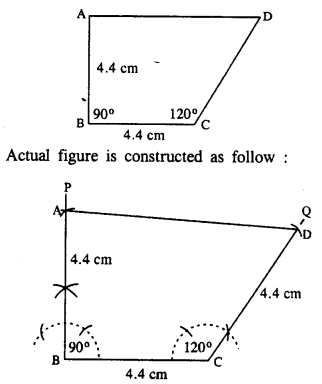
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, such that AB = BC = CD = 4.4 cm, ∠B = 90° and ∠C = 120°.
Solution:
Rough figure is as follow
Steps :
- Draw BC = 4.4 cm.
- At B, draw ∠PBC = 90°.
- Cut BA = 4.4 cm.
- At C, draw ∠QCB = 120°.
- Cut CD = 4.4 cm.
- Join AD.
Thus ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
Question 8.
Using ruler and compasses only, construct a parallelogram ABCD, in which : AB = 6 cm, AD = 3 cm and ∠DAB = 60°. In the same figure draw the bisector of angle DAB and let it meet DC at point P. Measure angle APB.
Solution:
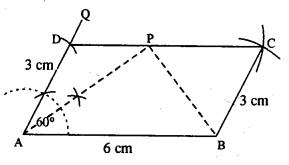
Steps :
- Draw AB = 6 cm.
- At A draw ∠QAB = 60°.
- From AQ cut AD = 3 cm.
- From D, draw an arc of radius 6 cm.
- From B, draw an arc of radius 3 cm which meets first arc at C.
- Join CD and BC.
Thus ABCD is the required ||gm. - Bisect ∠DAB, so that bisector meets CD at P.
- Join PB and measure ZAPB.
∴ ∠APB = 90°.
Question 9.
Draw a parallelogram ABCD, with AB = 6 cm, AD = 4.8 cm and ∠DAB = 45°. Draw the perpendicular bisector of side AD and let it meet AD at point P. Also draw the diagonals AC and BD ; and let they intersect at point O. Join O and P. Measure OP.
Solution:
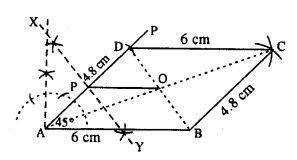
Steps :
- Draw AB = 6 cm.
- Draw ∠PAB = 45°.
- Cut AD = 4.8 cm.
- From D, draw an arc of radius 6 cm.
- From B, draw an arc of radius 4.8 cm which meets first arc at C.
- Join BC, CD, AD.
Thus ABCD is the required ||gm. - Draw perpendicular bisector XY of AD which cuts AD at P.
- Join AC and BD which intersect at O.
- Join OP and measure it.
OP = 3 cm.
Question 10.
Using ruler and compasses only, construct a rhombus whose diagonals are 8 cm and 6 cm. Measure the length of its one side.
Solution:
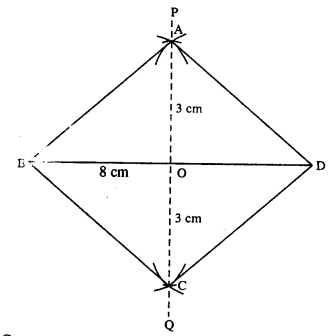
Steps :
- Draw BD = 8 cm.
- Draw perpendicular bisector PQ of BD.
- Cut OA = OC = 3 cm [half the diagonal 6 cm]
- Join AB, AD, BC and CD.
- Measure side AB which is 5 cm.
Thus ABCD is the required rhombus.


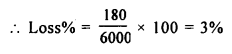

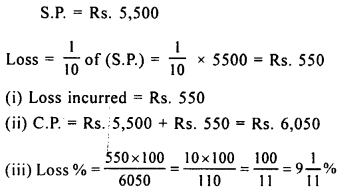
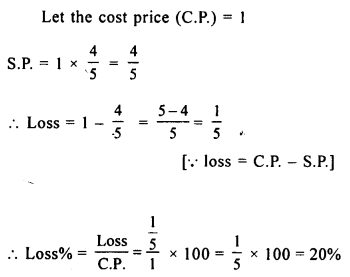
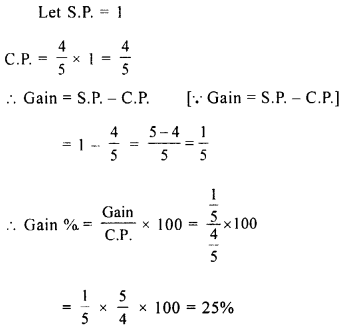










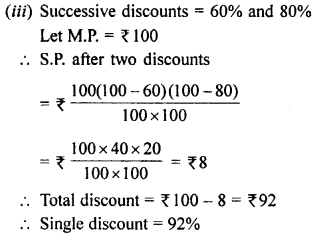

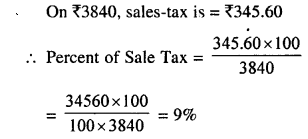








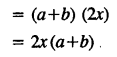
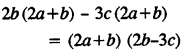
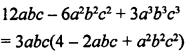
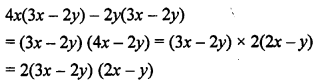
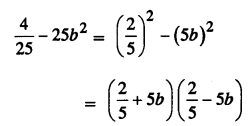
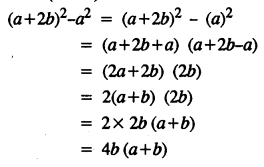
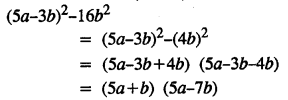
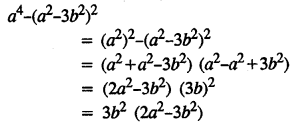
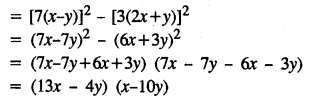
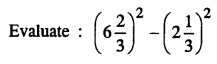
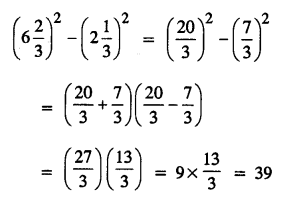
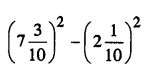
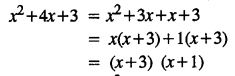
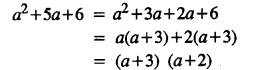
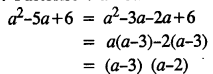
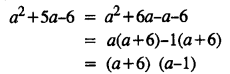


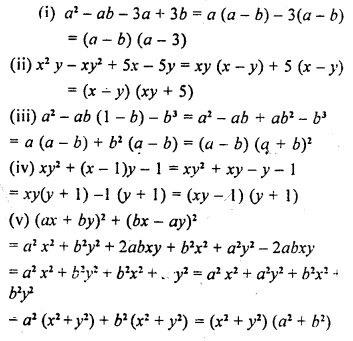
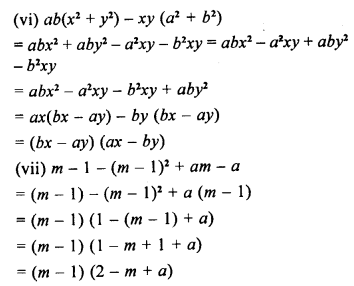
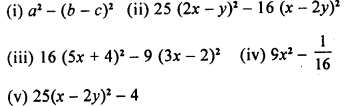
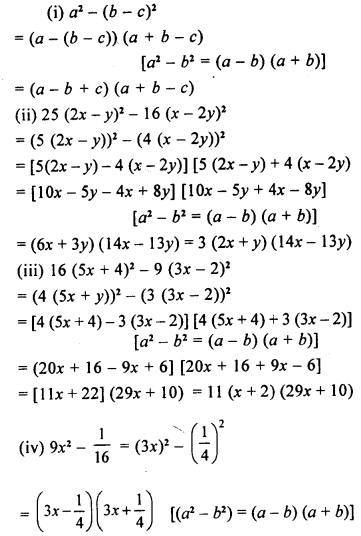

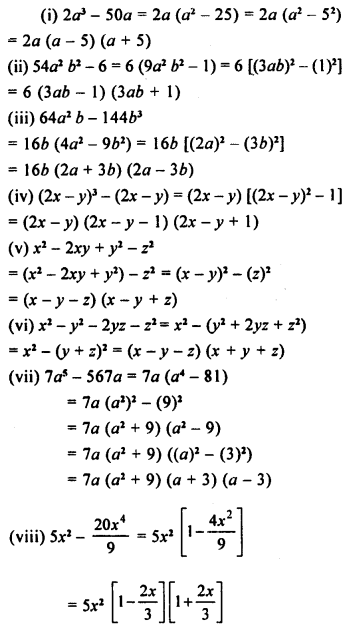
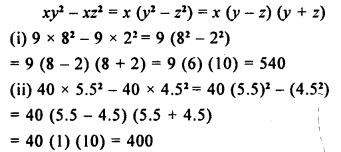
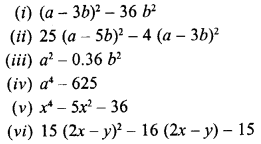
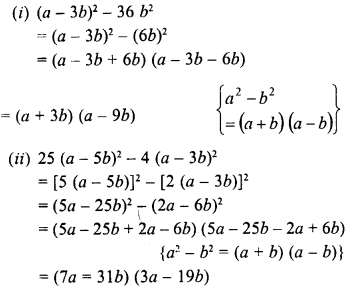
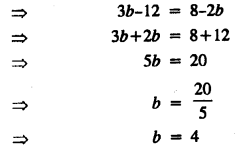
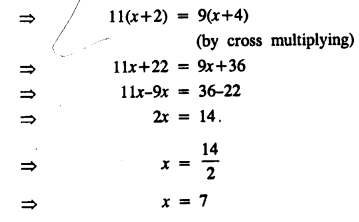
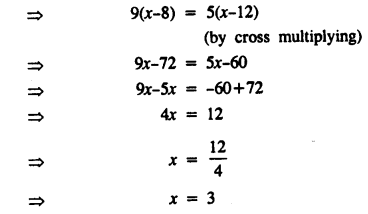
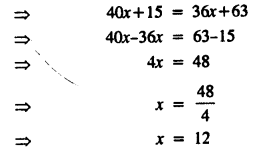



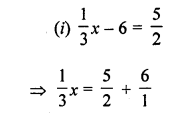
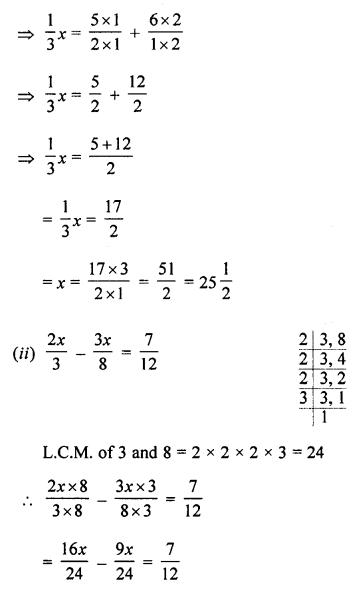
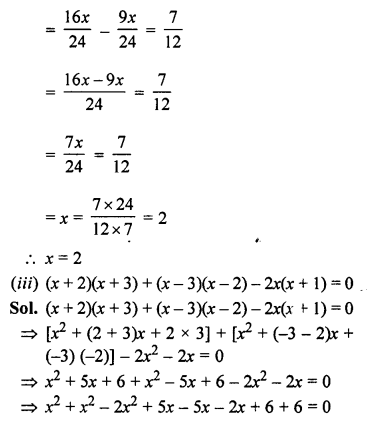

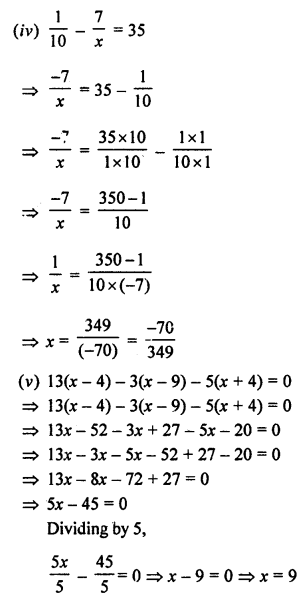
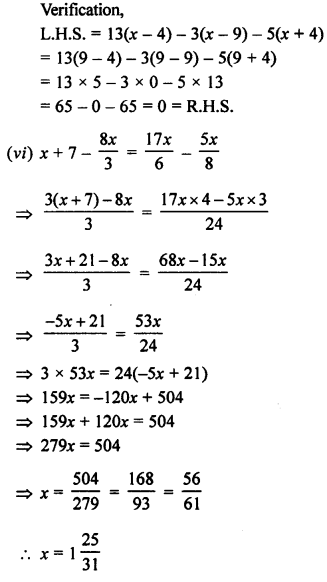
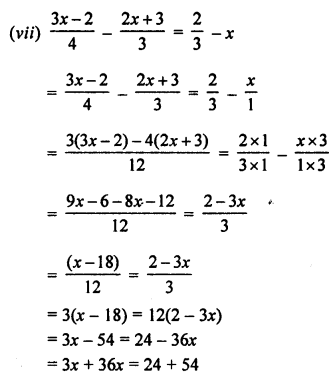
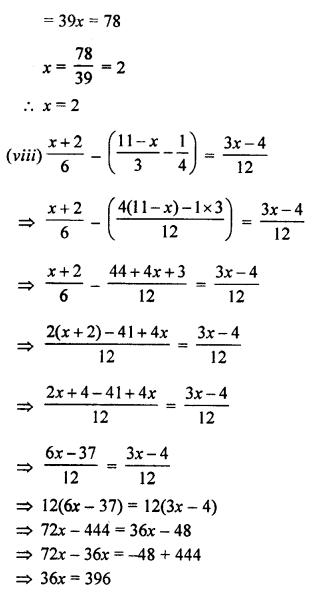
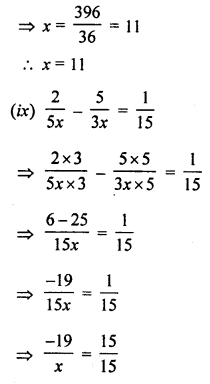
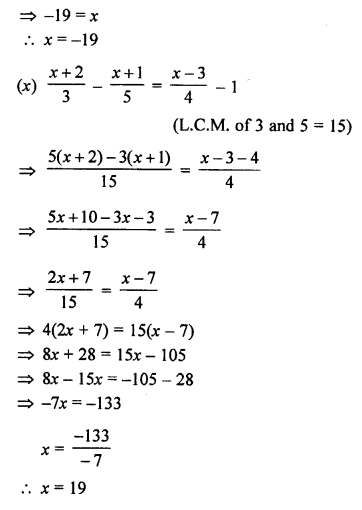
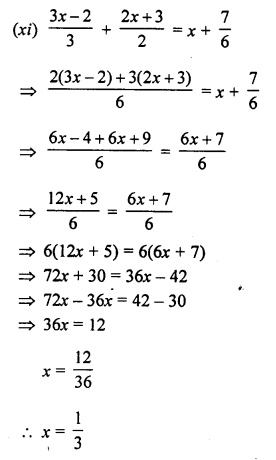
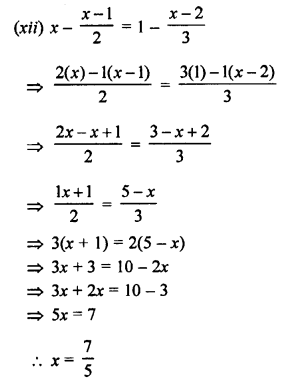
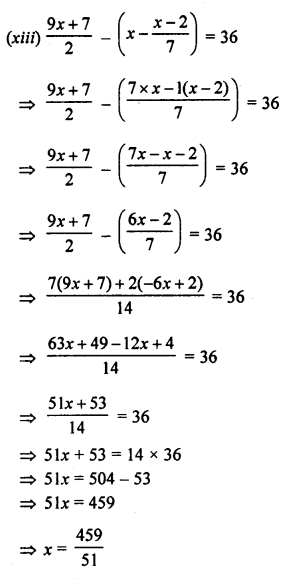
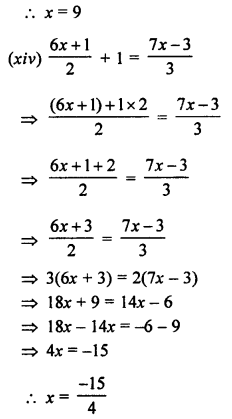
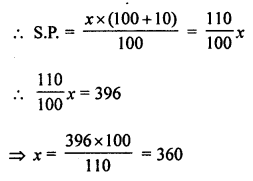

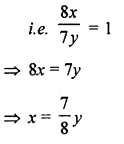
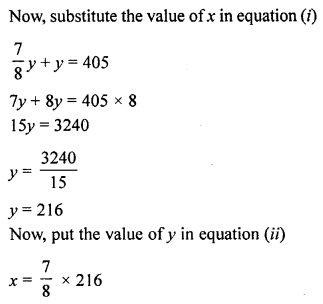
 .
.