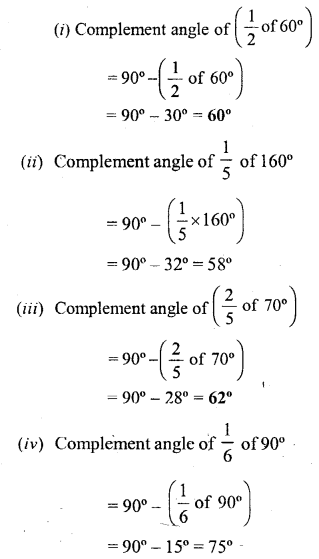
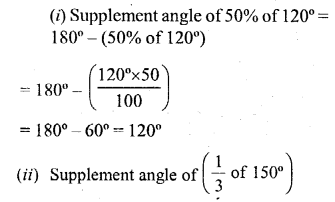
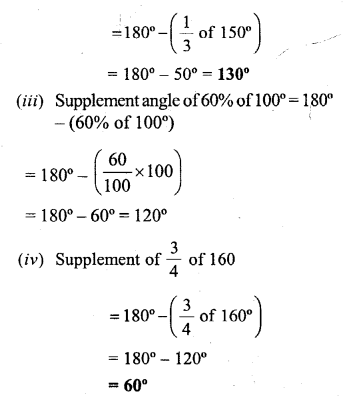
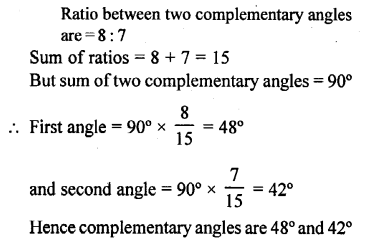
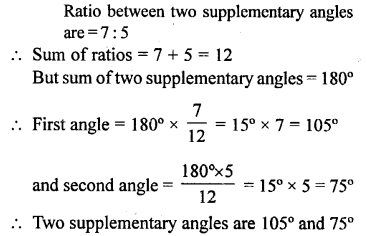
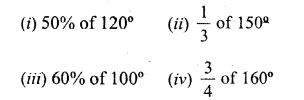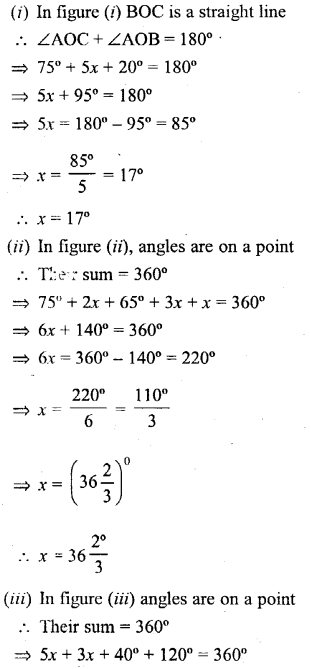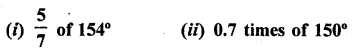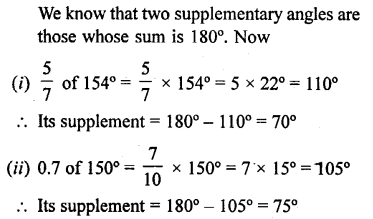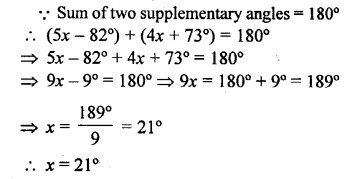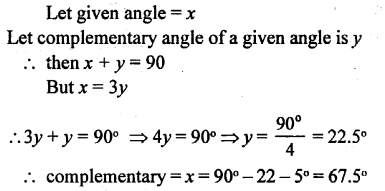Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions Chapter 25 Properties of Angles and Lines (Including Parallel Lines)
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions Chapter 25 Properties of Angles and Lines (Including Parallel Lines)
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Maths ICSE SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
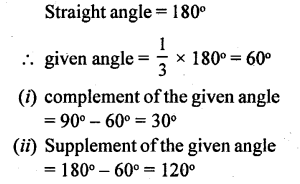
IMPORTANT POINTS
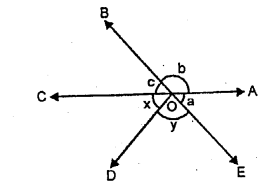
1. Property : When two straight lines intersect:
(i) sum of each pair of adjacent angles is always 180°.
(ii) vertically opposite angles are always equal. .
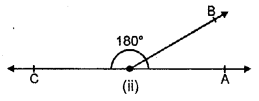
2. Property : If the sum of two adjacent angles is 180°, their exterior arms are always in the same straight line.
Conversely, if the exterior arms of two adjacent angles are in the same straight line ; the sum of angles is always 180°
3. Parallel Lines : Two straight lines are said to be parallel, if they do not meet anywhere, no matter how much they are produced in either direction.
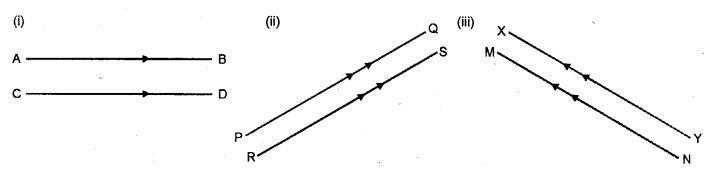
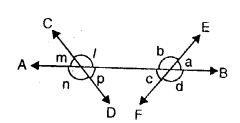
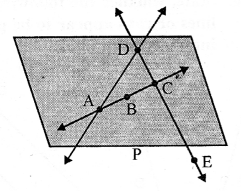
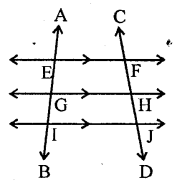
4. Concepts of Transversal Lines : When a line cuts two or more lines (parallel or non-parallel); it is called a transversal line or simply, a transversal. In each of the following figures : PQ is a transversal line.
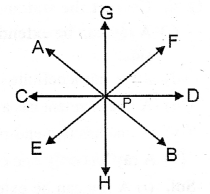
5. Angles formed by two lines and their transversal line : When a transversal cuts two parallel or nonparallel lines; eight (8) angles are formed which are marked 1 to 8 in the adjoining diagram.
These angles can further he distinguished, as given below:
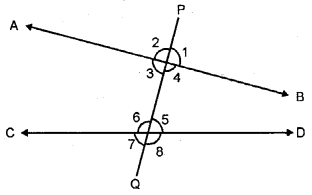
(i) Exterior Angles : Angles marked 1, 2, 7 and 8 are exterior angles.
(ii) Interior Angles : Angles marked 3, 4, 5 and 6 are interior angles.
(iii) Exterior Alternates Angles : Two pairs of exterior alternate angles are marked as : 2 and 8 ; and, 1 and 7.
(iv) Interior Alternate Angles : Two pairs of interior alternate are marked as : 3 and 5 ; and 4 and 6. In general, interior alternate angles are simply called as alternate angles only.
(v) Corresponding Angles : Four pairs of corresponding angles are marked as : 1 and 5 ; 2 and 6 ; 3 and 7 ; and 4 and 8.
(vi) Co-interior or Conjoined or Allied Angles : Two pairs of co-interior or allied angles are marked as : 3 and 6 ; and 4 and 5.
(vii) Exterior Allied Angles : Two pairs of exterior allied angles are marked as : 2 and 7 ; and 1 and 8.
Properties of Angles and Lines Exercise 25A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Two straight lines AB and CD intersect each other at a point O and angle AOC = 50° ; find :
(i) angle BOD
(ii) ∠AOD
(iii) ∠BOC
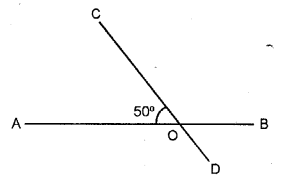
Solution:
(i)∠BOD = ∠AOC
(Vertically opposite angles are equal)
∴ ∠BOD =50°
(ii) ∠AOD
∠AOD + ∠BOD = 180°
∠AOD + 50° = 180° [From (i)]
∠AOD = 180°-50°
∠AOD = 130°
(iii) ∠BOC = ∠AOD
(Vertically opposite angles are equal)
∴ ∠BOC =130°
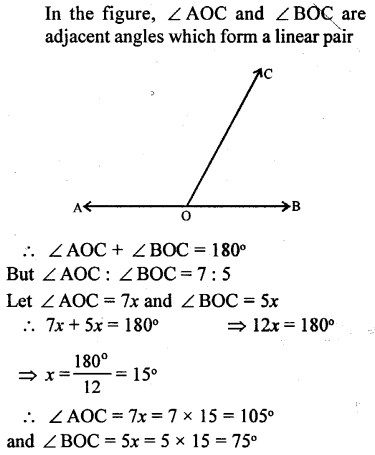
Question 2.
The adjoining figure, shows two straight lines AB and CD intersecting at point P. If ∠BPC = 4x – 5° and ∠APD = 3x + 15° ; find :
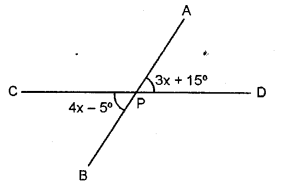
(i) the value of x.
(ii) ∠APD
(iii) ∠BPD
(iv) ∠BPC
Solution:
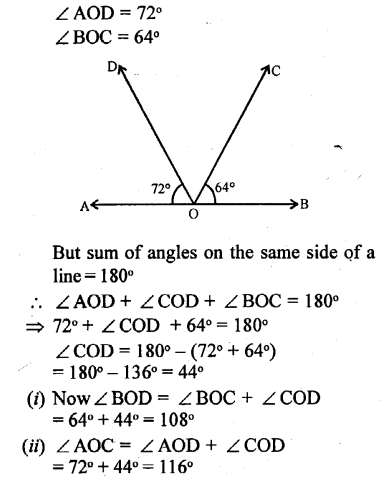
Question 3.
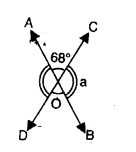
The given diagram, shows two adjacent angles AOB and AOC, whose exterior sides are along the same straight line. Find the value of x.
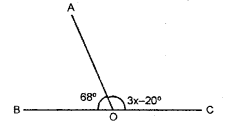
Solution:
Since, the exterior arms of the adjacent angles are in a straight line ; the adjacent angles are supplementary
∴ ∠AOB + ∠AOC = 180°
⇒ 68° + 3x – 20° = 180°
⇒ 3x = 180° + 20° – 68°
⇒ 3x = 200° – 68° ⇒ 3x =132°
x = \(\frac { 132 }{ 3 }\)° = 44°
Question 4.
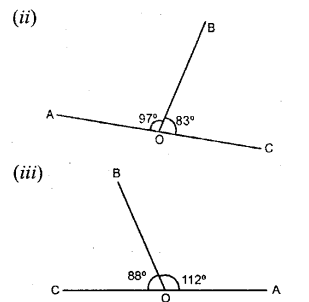
Each figure given below shows a pair of adjacent angles AOB and BOC. Find whether or not the exterior arms OA and OC are in the same straight line.
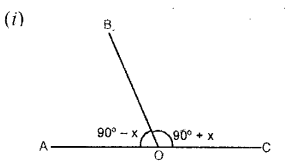
Solution:
(i) ∠AOB + ∠COB = 180°
Since, the sum of adjacent angles AOB and COB = 180°
(90° -x) + (90°+ x) = 180°
⇒ 90°-x + 90° + x = 180°
⇒ 180° =180°
The exterior arms. OA and OC are in the same straight line.
(ii) ∠AOB + ∠BOC = 97° + 83° = 180°
⇒ The sum of adjacent angles AOB and BOC is 180°.
∴ The exterior arms OA and OC are in the same straight line.
(iii)∠COB + ∠AOB = 88° + 112° = 200° ; which is not 180°.
⇒ The exterior amis OA and OC are not in the same straight line.
Question 5.
A line segment AP stands at point P of a straight line BC such that ∠APB = 5x – 40° and ∠APC = .x+ 10°; find the value of x and angle APB.
Solution:
AP stands on BC at P and
∠APB = 5x – 40°, ∠APC = x + 10°
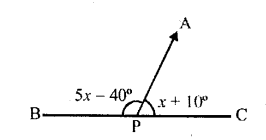
(i) ∵APE is a straight line
∠APB + ∠APC = 180°
⇒ 5x – 40° + x + 10° = 180°
⇒ 6x-30°= 180°
⇒6x= 180° + 30° = 210°
x = \(\frac { 210 }{ 6 }\)° = 35°
(ii) and ∠APB = 5x – 40° = 5 x 35° – 40°
= 175 ° – 140° = 135°
Properties of Angles and Lines Exercise 25B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
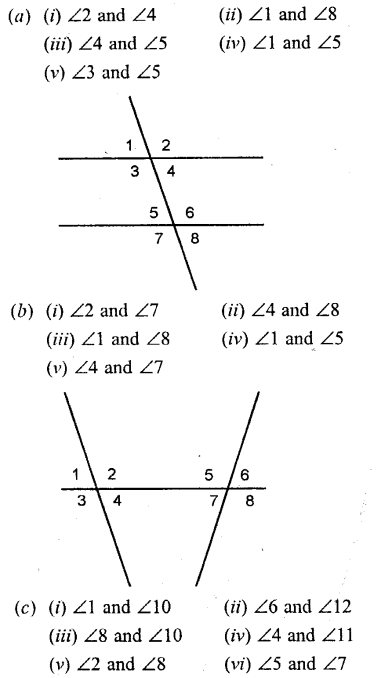
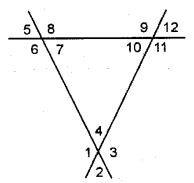
Identify the pair of angles in each of the figure given below :
adjacent angles, vertically opposite angles, interior alternate angles, corresponding angles or exterior alternate angles.
Solution:
(a) (i) Adjacent angles
(ii) Alternate exterior angles
(iii) Interior alternate angles
(iv) Corresponding angles
(v) Allied angles
(b) (i) Alternate interior angles
(ii) Corresponding angles
(iii) Alternate exterior angles
(iv) Corresponding angles
(v) Allied angles.
(c) (i) Corresponding
(ii) Alternate exterior
(iii) Alternate interior
(iv) Alternate interior
(v) Alternate exterior
(vi) Vertically opposite
Question 2.
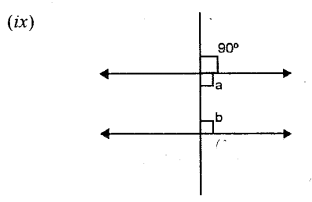
Each figure given below shows a pair of parallel lines cut by a transversal For each case, find a and b, giving reasons.
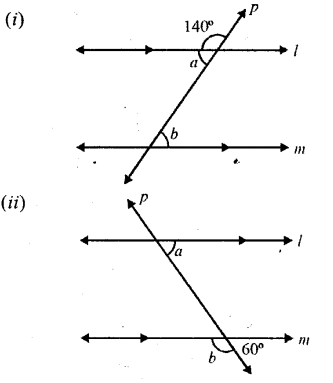
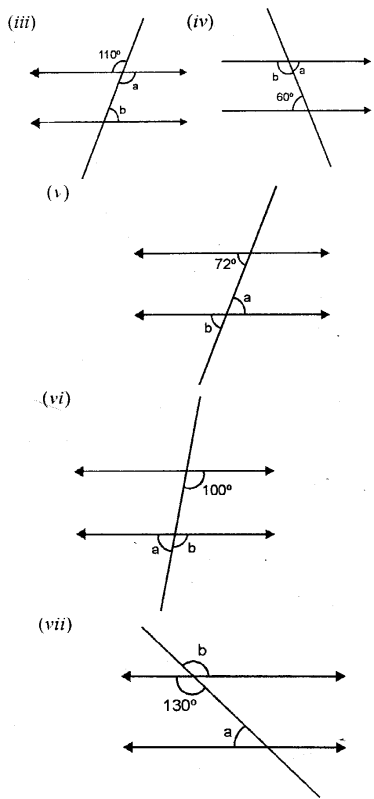
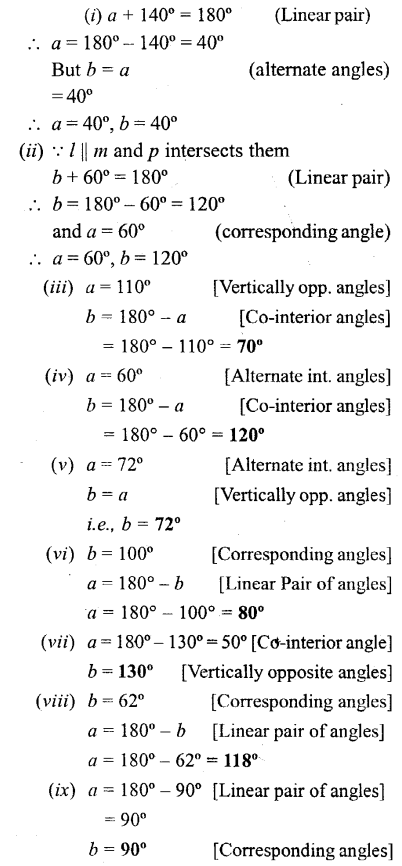
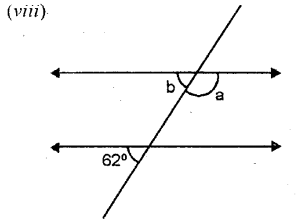
Solution:
Question 3.
If ∠1 = 120°, find the measures of : ∠2, ∠3, ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 and ∠8. Give reasons.
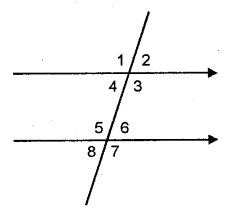
Solution:
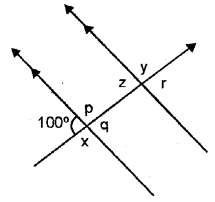
Question 4.
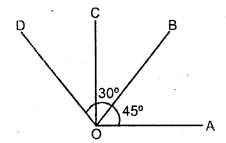
In the figure given below, find the measure of the angles denoted by x,y, z,p,q and r.
Solution:
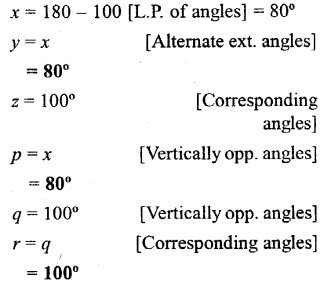
Question 5.
Using the given figure, fill in the blanks.
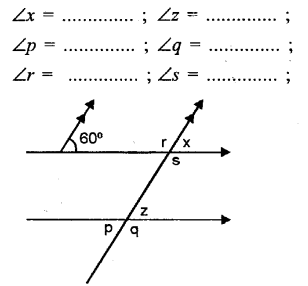
Solution:
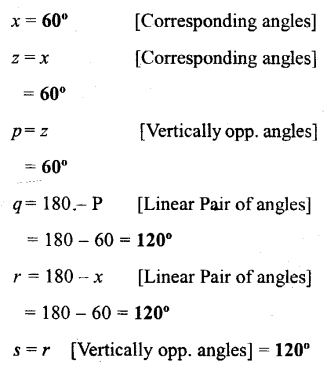
Question 6.
In the given figure, find the anlges shown by x,y, z and w. Give reasons.
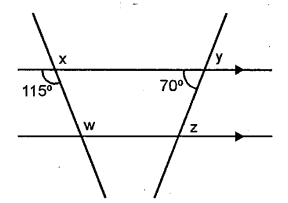
Solution:

Question 7.
Find a, b, c and d in the figure given below :
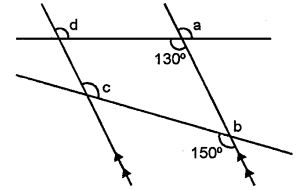
Solution:

Question 8.
Find x, y and z in the figure given below :
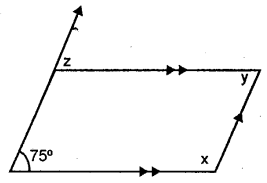
Solution:

Properties of Angles and Lines Exercise 25C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
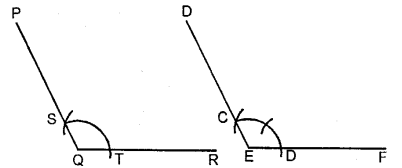
In your note-book copy the following angles using ruler and a pair compass only.
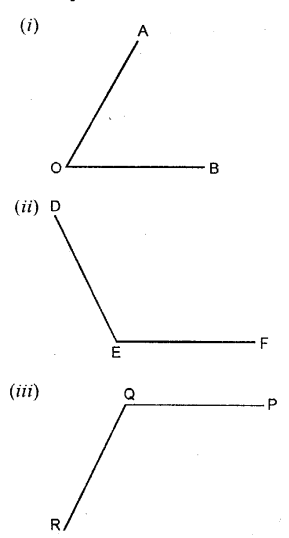
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction :
1. At point Q, draw line QR = OB.
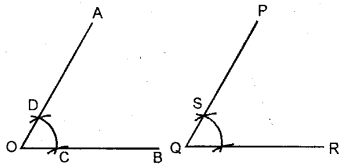
2. With O as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius, to cut the arms of the angle at C and D.
3. With Q as centre, draw the arc of the same size as drawn for C and D. Let this arc cuts line QR at point T.
4. In your compasses, take the distance equal to distance between C and D; and then with T as centre, draw an arc which cuts the earlier arc at S.
5. Join QS and produce upto a suitable point P. ∠PQR so obtained, is the angle equal to the given ∠AOB.
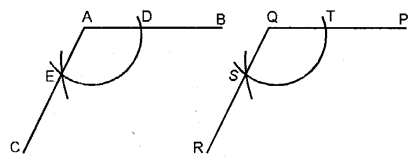
(ii) Steps of Construction :
1. A t point E, draw line EF.
2. With E as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius, to cut the amis of the angle at C and D.
3. With Q as centre, draw the arc of the same size as drawn for C and D. Let this arc cuts line QR at point T.
4. In your compasses, take the distance equal to distance between C and D ; and then with T as centre, draw an arc which cuts the earlier arc at S.
5. Join QS and produce upto a suitable point R ∠PQR, so obtained, is the angle equal to the given ∠DEE
(iii) Steps of Construction :
1. At point A draw line AB = QP
2. With Q as centre, draw an arc of any suitable radius, to cut the arms of the angle A + C and D.
3. With A as centre, draw the arc of the same size as drawn for C and D. Let this arc cuts line AB at D.
4. In your compasses, take the distance equal to distance between 7 and 5 ; and then with D as centre, draw an arc which cuts the earlier arc at E.
5. Join AE and produced upto a suitable point C. ∠BAC, so obtained is the angle equal to the given ∠PQR.
Question 2.
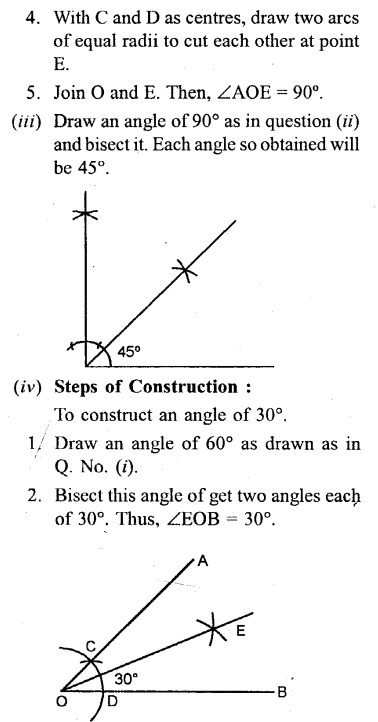
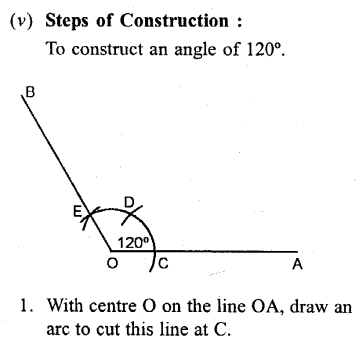
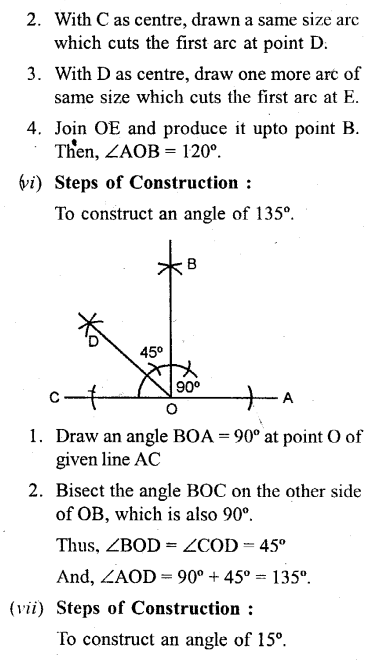
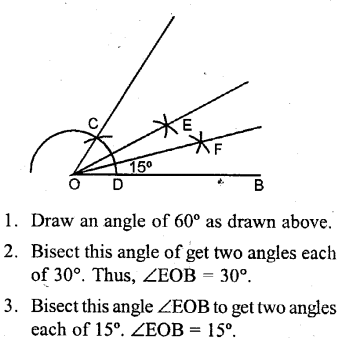
Construct the following angles, using ruler and a pair of compass only
(i) 60°
(ii) 90°
(iii) 45°
(iv) 30°
(v) 120°
(vi) 135°
(vii) 15°
Solution:


Question 3.
Draw line AB = 6cm. Construct angle ABC = 60°. Then draw the bisector of angle ABC.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
1. Draw a line segment AB = 6 cm.
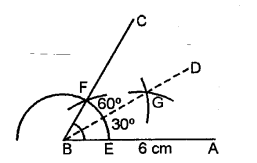
2. With the help of compass construct ∠CBA = 60°.
3. Bisect ∠CBA, with the help of compass, take any radius which meet line AB and BC at point E and F.
4. Now, with the help of compass take
radius more than \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) of EF and draw two arcs from point E and F, which intersect both arcs at G, proceed BG toward D ∠DBA is bisector of ∠CBA.
Question 4.
Draw a line segment PQ = 8cm. Construct the perpendicular bisector of the line segment PQ. Let the perpendicular bisector drawn meet PQ at point R. Measure the lengths of PR and QR. Is PR = QR ?
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
1. With P and Q as centres, draw arcs on both sides of PQ with equal radii. The radius should be more than half the length of PQ.
2. Let these arcs cut each other at points R and RS
3. Join RS which cuts PQ at D.
Then RS = PQ Also ∠POR = 90°.
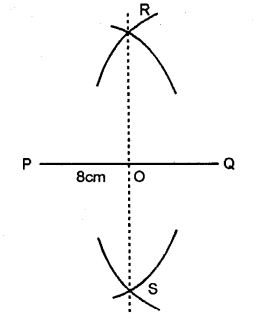
Hence, the line segment RS is the perpendicular bisector of PQ as it bisects PQ at P and is also perpendicular to PQ. On measuring the lengths of PR = 4cm, QR = 4 cm
Since PR = QR, both are 4cm each
∴PR = QR.
Question 5.
Draw a line segment AB = 7cm. Mark a point Pon AB such that AP=3 cm. Draw perpendicular on to AB at point P.
Solution:
1. Draw a line segment AB = 7 cm.
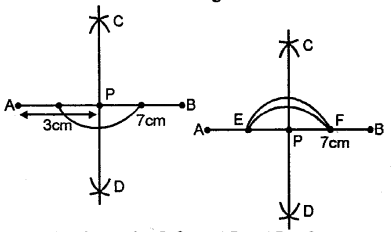
2. Out point from AB – AP =3cm
3. From point P, cut arc on out side of AB, E and F.
4. From pont E & F cut arcs on both side intersection each other at C & D.
5. Join point P, CD.
6. Which is the required perpendicular.
Question 6.
Draw a line segment AB = 6.5 cm. Locate a point P that is 5 cm from A and 4.6 cm from B. Through the point P, draw a perpendicular on to the line segment AB.
Solution:
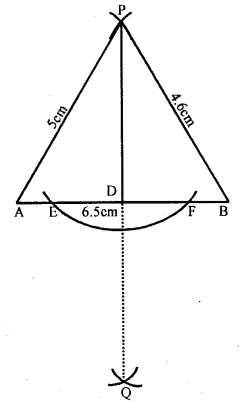
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment AB =6.5cm
(ii) With centre A and radius 5 cm, draw an arc and with centre B and radius 4.6 cm, draw another arc which intersects the first arc at P.
Then P is the required point.
(iii) With centre A and a suitable radius, draw an arc which intersect AB at E and F.
(iv) With centres E and F and radius greater than half of EF, draw the arcs which intersect each other at Q.
(v) Join PQ which intersect AB at D.
Then PD is perpendicular to AB.
Properties of Angles and Lines Exercise 25D – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Draw a line segment OA = 5 cm. Use set-square to construct angle AOB = 60°, such that OB = 3 cm. Join A and B ; then measure the length ofAB.
Solution:
Measuring the length of AB = 4.4cm. (approximately)
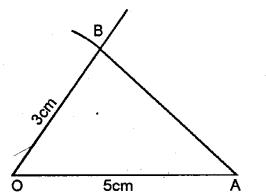
Question 2.
Draw a line segment OP = 8cm. Use set-square to construct ∠POQ = 90°; such that OQ = 6 cm. Join P and Q; then measure the length of PQ.
Solution:
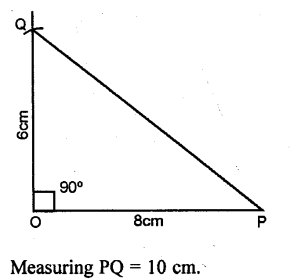
Question 3.
Draw ∠ABC = 120°. Bisect the angle using ruler and compasses. Measure each angle so obtained and check whether or not the new angles obtained on bisecting ∠ABC are equal.
Solution:
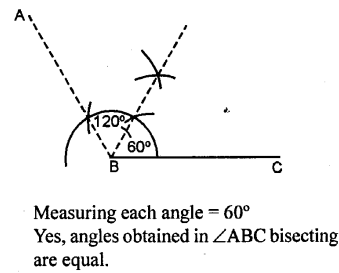
Question 4.
Draw ∠PQR = 75° by using set- squares. On PQ mark a point M such that MQ = 3 cm. On QR mark a point N such that QN = 4 cm. Join M and N. Measure the length of MN.
Solution:
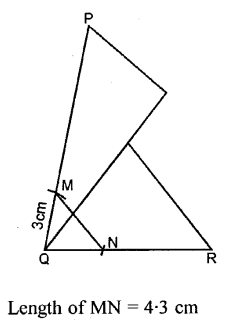
Properties of Angles and Lines Revision Exercise – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
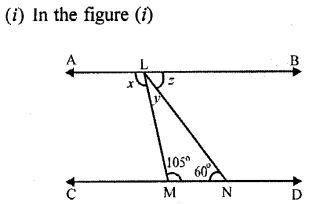
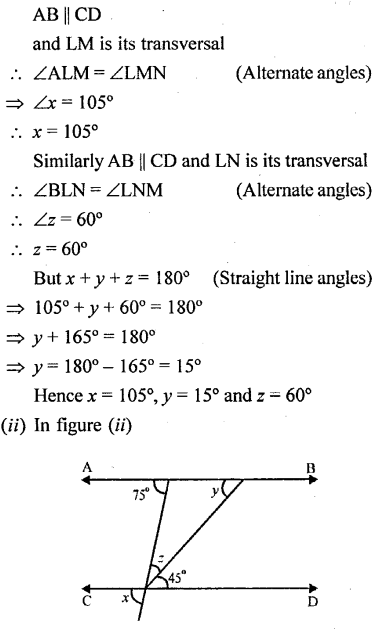
Question 1.
In the following figures, AB is parallel to CD; find the values of angles x, y and z :
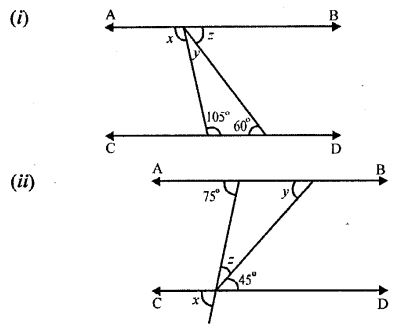
Solution:
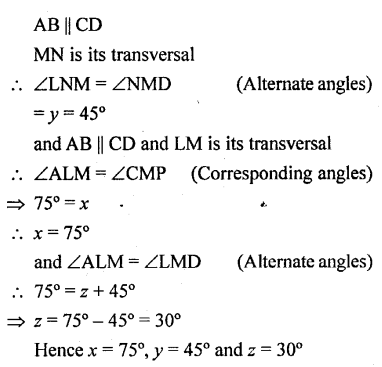
Question 2.
In each of the following figures, BA is parallel to CD. Find the angles a, b and c:
Solution:
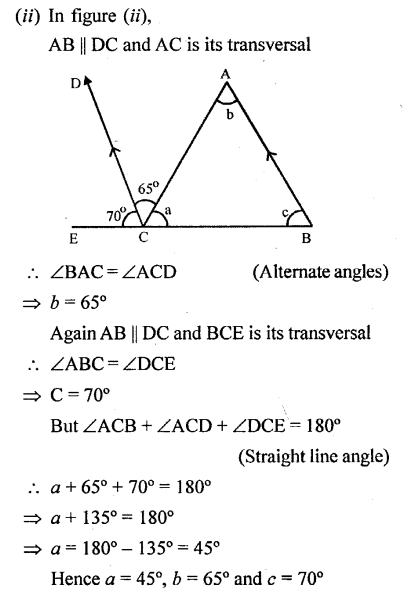
Question 3.
In each of the following figures, PQ is parallel to RS. Find the angles a, b and c:
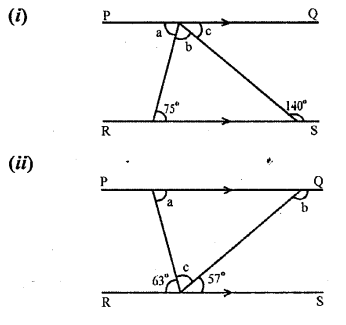
Solution:
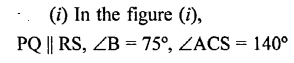
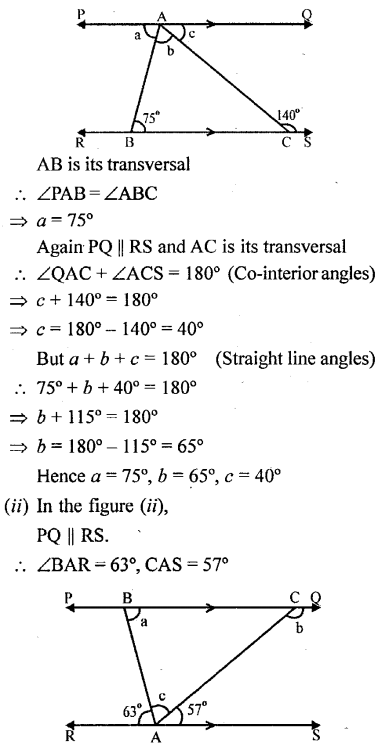
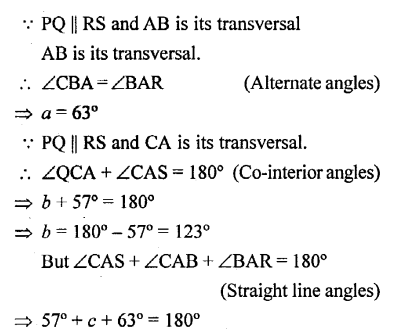
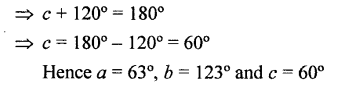
Question 4.
Two straight lines are cut by a transversal. Are the corresponding angles always equal?
Solution:
If a transversal cuts two straight lines, their the corresponding angles are not equal unless the lines are not parallel. One in case of parallel lines, the corresponding angles are equal.
Question 5.
Two straight lines are cut by a transversal so that the co-interior angles are supplementary. Are the straight lines parallel ?
Solution:
A transversal intersects two straight lines and co-interior angles are supplementary
∴ By deflations, the lines will be parallel.
Question 6.
Two straight lines are cut by a transversal so that the co-interior angles are equal. What must be the measure of each interior angle to make the straight lines parallel to each other ?
Solution:
A transveral intersects two straight lines and co-interior angles are equal to each other,
∵ The two straight lines are parallel Their sum of co-interior angles = 180°
But both angles are equal
∴ Each angle will be \(\frac { 180 }{ 2 }\)° = 90°
Question 7.
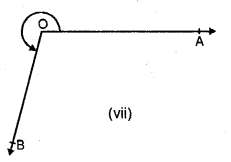
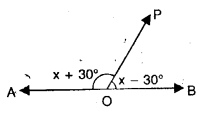
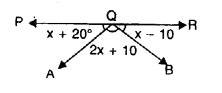
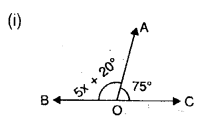
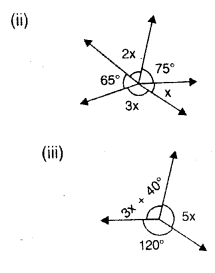
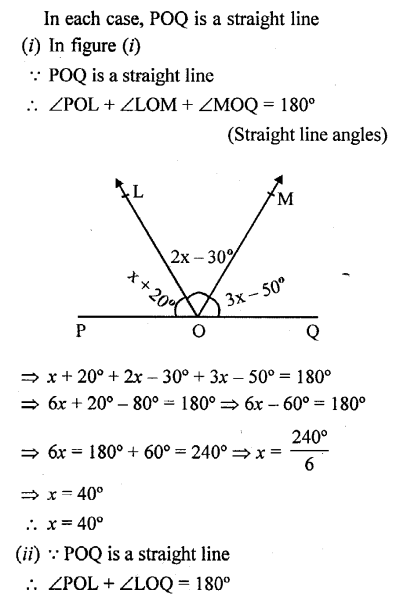
In each case given below, find the value of x so that POQ is straight line
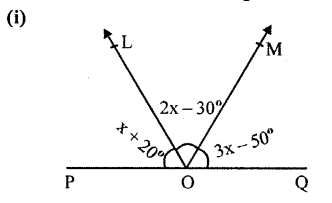
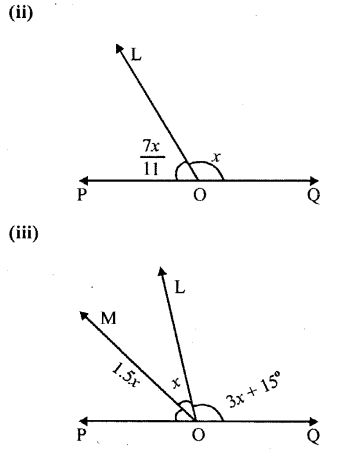
Solution:

Question 8.
in each case, given below, draw perpendicular to AB from an exterior point P
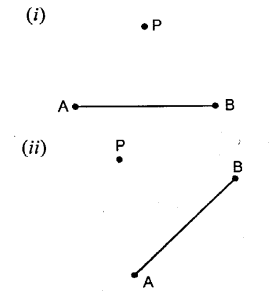
Solution:
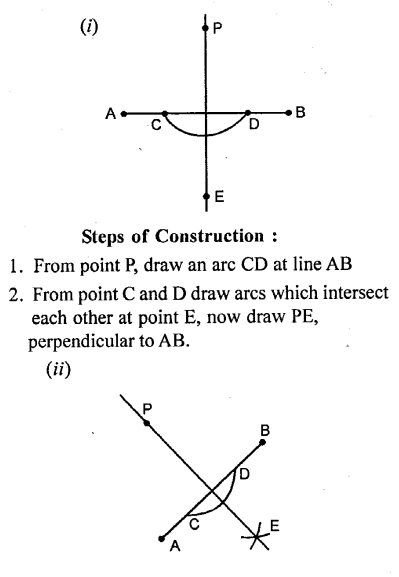


Question 9.
Draw a line segment BC = 8 cm. Using set-squares, draw ∠CBA = 60° and ∠BCA = 75°. Measure the angle BAC. Also measure the lengths of AB and AC.
Solution:
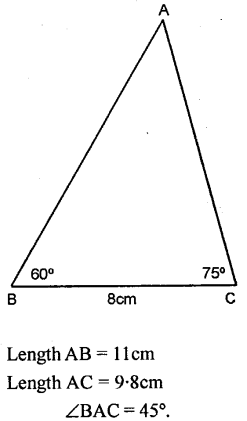
Question 10.
Draw a line AB = 9 cm. Mark a point P in AB such that AP=5 cm. Through P draw (using set-square) perpendicular PQ = 3 cm. Measure BQ.
Solution:
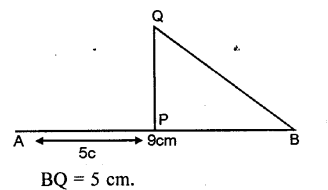
Question 11.
Draw a line segment AB = 6 cm. Without using set squares, draw angle OAB = 60° and angle OBA = 90°. Measure angle AOB and write this measurement.
Solution:
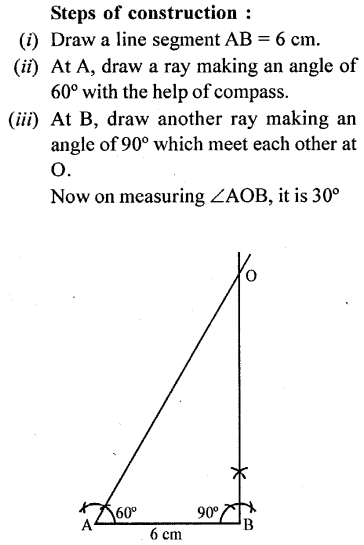
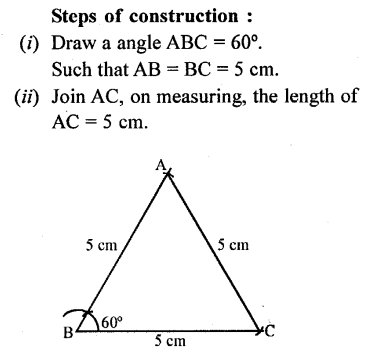
Question 12.
Without using set squares, construct angle ABC = 60° in which AB = BC = 5 cm. Join A and C and measure the length of AC.
Solution: