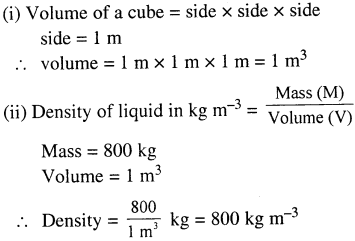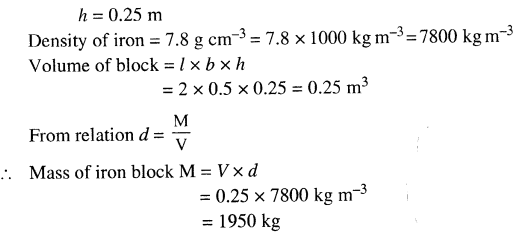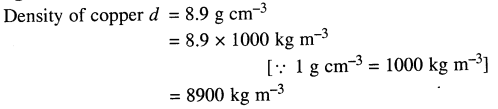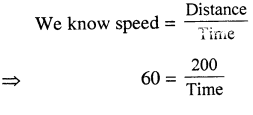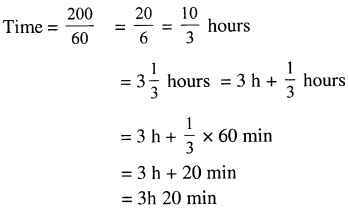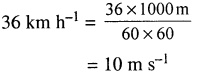Selina Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Light Energy
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics Chapter 4 Light Energy
- Points to Remember
- Light is a form of energy which helps us to see objects.
- Light always travels in a straight line in the form of rays.
- Light sources are either natural or artificial.
- The sun and stars are natural sources of light.
- A bulb, a candle etc. are artificial sources of light.
- The bodies which emit light themsleves are called Luminous Bodies, e.g. sun, star.
- The bodies which do not emit light are called non-luminous bodies, e.g. wood, brick etc.
- Objects are of three types, transparent, translucent or opaque.
- The pinhole camera is a simple application of the rectilinear propagation of light.
- When an object blocks light, it casts a shadow.
- Eclipses are formed due to formation of shadows.
- Solar and lunar eclipses are the examples of formation of shadow in nature.
- An eclipse is the partial or complete hiding of one heavenly body by shadow of another.
- When light strikes a polished surface it comes back in the same medium, is called reflection of light.
- A straight highly polished, smooth and reflecting surface is known as a plane mirror.
- Mirrors are of two types (a) plane mirrors (b) spherical mirrors.
- Smooth and polished surface like a mirror causes reflection and is called a regular reflection.
- Rough or diffused surface causes an irregular reflection.
- According to first law of reflection. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
- According to the second law of reflection, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
- The phenomenon due to which the left side of an object appears to be the right side of the object and right side appears left. This is known as lateral inversion.
- Image is of two types (a) Real image (b) Virtual image.
Test Yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) The image formed by a plane mirror is real.
Answer. False.
The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual.
(b) When a light ray is reflected from a wall, the angle of incidence is not equal to the angle of reflection.
Answer. False.
When a light ray is reflected from a wall, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(c) The image of the right hand in a plane mirror looks like that of a left hand.
Answer. True.
(d) The image formed by a plane mirror is upright.
Answer. True.
(c) The image formed by a plane mirror can be obtained on a screen.
Answer. False.
The image formed by a plane mirror cannot be obtained on a screen.
(f) The objects are seen around us due to irregular reflection of light.
Answer. True.
(g) The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 ms-1.
Answer. True.
(h) A rose appears red in light of all the colours.
Answer. False. A rose appears red in white light.
(i) A black paper absorbs light of all the colours and reflects none.
Answer. True.
(j) The primary colours are red, blue and green.
Answer. True.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
(b) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal lie in one plane
(c) The image formed by a plane mirror is at a distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
(d) The image formed by a plane mirror is erect and virtual.
(e) We are able to see the objects around us due to irregular reflection.
(f) A virtual image cannot be obtained on a screen.
(g) One surface of mirror is made opaque by silvering it followed by a thin coating of paint of lead oxide. .
(h) A plane mirror does not reflect 100 percent light falling on it.
(i) The colour of an opaque object is the colour of light which it reflects.
(j) Magenta, cyan and yellow are the secondary colours.
3. Match the following

4. Select the correct alternative
(a) A man standing in front of a plane mirror finds his image to be at a distance of 6 metre from himself. The distance of man from the mirror is
- 6 m
- 3 m
- 2 m
- 12 m
(b) The angle between the incident ray and the ray reflected from the plane mirror is 70°. The angle of incidence will be :
- 70°
- 30°
- 35°
- 90°
(c) The image formed by a plane mirror is
- virtual and inverted
- virtual and of same size
- real and inverted
- real and of same size
(d) The angle of incidence on a plane mirror is 30°.The angle of reflection will be:
- 30°
- 60°
- 15°
- 0°
(e) The angle of incidence on a plane mirror is 30°. The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is
- 30°
- 15°
- 60°
- 90°
(f) The property due to which a light ray striking a surface is returned back into the same medium is called
- refraction
- reflex action
- reflection
- regression
(g) A ray of light after reflection from a mirror is known as
- reflected ray
- normal
- incident ray
- refracted ray
(h) The speed of light is maximum in
- glass
- water
- air
- wood
(i) A red rose is seen in green light. It will appear.
- red
- blue
- yellow
- black
(j) The primary colours are
- Red, Blue and Yellow
- Magenta, Yellow and Cyan
- Red, Blue and Cyan
- Blue, Green and Red
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by the term reflection of light ?
Answer:
Reflection of light— When light strikes a polished surface it comes back in the same medium, is called reflection of light.
Question 2.
How is a plane mirror made ?
Answer:
To make a plane mirror, a thin piece of glass is taken. One surface of the mirror is made opaque by silvering it. On the top of that, another thin coating of red lead oxide is given which protects the silvering of the mirror.
Question 3.
Explain the following terms:
Incident ray, Reflected ray, Angle of incidence, Angle of reflection, Normal.
Answer:
Incident ray— The ray of light falling on the surface AB is called the incident ray. In figure PN is the incident ray.
Reflected ray— The incident ray bouncing back in the same medium after striking the reflecting ourface is called reflected ray. In figure NQ is the reflected ray.
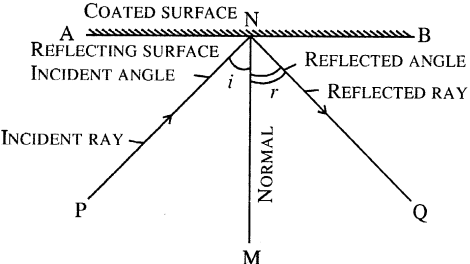
Angle of incidence— The angle formed between the incident ray and the normal is the angle of incidence. (PNM is the angle of incidence.)
Angle of reflection— The angle formed between the normal and the reflected ray is called angle of reflection (MNQ is the angle of reflection)
Normal— It is the line drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence. MN is the normal.
Question 4.
Draw a diagram showing the reflection of a light ray from a plane mirror. Label on it the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence i and the angle of reflection r.
Answer:
AO is the incident ray
OB is the reflected ray
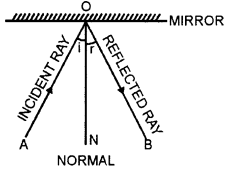
ON is the normal
∠AON is the angle of incidence
∠NOB is the angle of reflection.
Question 5.
State the two laws of reflection of light.
Answer:
Laws of reflection—
(i) The incident ray, normal and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Question 6.
Describe an experiment to verify the laws of reflection of light. Ans. Laws of reflection.
Answer:
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal i.e. ∠i = ∠r.
Verification
Take a wooden drawing board and fix a white sheet of paper on it. In the middle of paper draw a straight line KK\ Mark a point B on it. Draw a perpendicular BN. Place a mirror XX’ on line KK’ such that polished side of mirror is along the line. Hold-the mirror in the mirror holder.
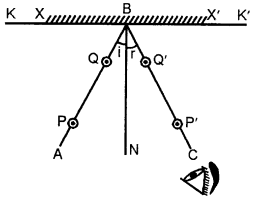
Fix two steel pins P and Q on the straight line AB atleast 10 cm apart. Look for the images of the pins P and Q and fix two pins P Q’ such that P’, Q’ and images of P and Q are all in the same straight line. Remove the pins and draw small circles around the pin pricks.
Remove the mirror also. Join P’Q’ and produce the straight line to meet at B.
Measure ∠ABN = i and ∠CBN = r.
It is found that ∠i = ∠r. This proves that Angle of Incidence is equal to Angle of Reflection.
As the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal lie in the plane of paper, therefore, they lie in the same plane.
Question 7.
A ray of light falls normally on a plane mirror. What is the angle of incidence ?
Answer:
Angle of incidence is 0°. Since angle of incidence is’the angle between incident ray and normal. Direction of reflected ray is along BA opposite to the direction of incident ray.
Question 8.
Draw a diagram to show the reflection of a light ray incident normally on a plane mirror.
Answer:
AO is the incident ray
OB is the reflected ray
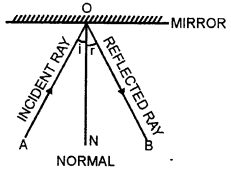
ON is the normal
∠AON is the angle of incidence
∠NOB is the angle of reflection.
Question 9.
The diagram in Fig. shows an incident ray AO and the reflected ray OB from a plane mirror. The angle AOB is 30°. Draw normal on the plane mirror at the point O and find :
Answer:
(i) the angle of incidence
(ii) the angle of reflection
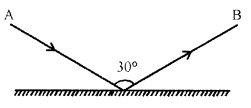
ON is normal on the plane mirror at point O
ON is perpendicular on a plane mirror
Angle of incidence ∠i = ∠AON
and angle of reflection ∠r = ∠BON
Since, ∠i – ∠r
∠AOB = 30°
⇒ ∠AON + ∠BON = 30°
⇒∠i + ∠i – 30°
⇒ 2 ∠i =30°
⇒ ∠i = 30 / 2 = 15°
∴Angle of incidence = ∠i = 15°
and Angle of reflection ∠i = 15°
Question 10.
In the following diagrams, measure and write the angle of incidence and draw the reflected ray in each case.
Answer:
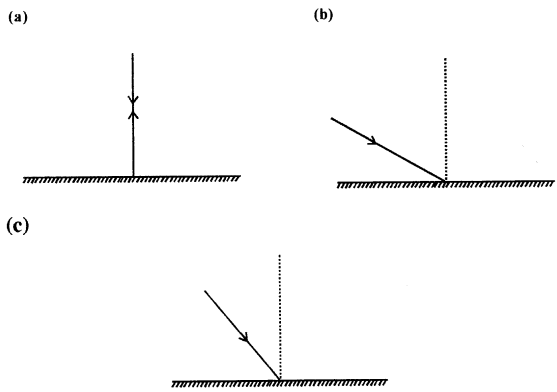
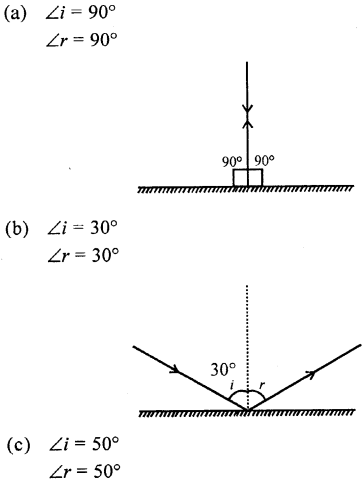
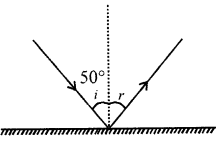
Question 11.
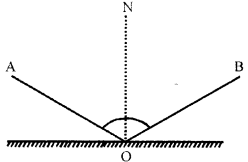
The diagram in fig. shows an incident ray AO and the normal ON on a plane mirror. Draw the reflected ray. State the law you use to draw the direction of the reflected ray.
Answer:
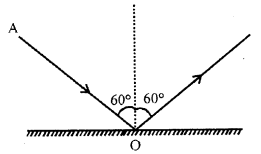
Law of reflection of light is used to draw the direction of the reflected ray.
This law states that angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
∠i = ∠r
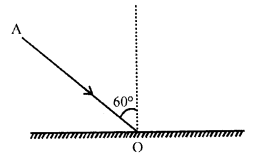
Question 12.
The following diagram shows an incident ray AO and the normal ON on a plane mirror. Find the angle of incidence and angle of reflection.
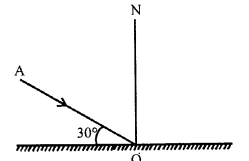
Answer:
ON is perpendicular on a plane mirror
Angle of incidence ∠i (∠AON) i.e.
Angle between incident ray and normal ray = 90° – 30° = 60°
Angle of Reflection = 60°
∴ ∠i = ∠r
∴ Angle between incident and reflected ray i.e. ∠AOB
= 60 + 60 = 120°
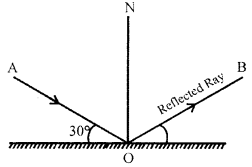
Question 13.
State in words, how do you find the location of image of an object formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
The location of image of a point object is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
Question 14.
Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of image of a point object by a plane mirror.
Answer:
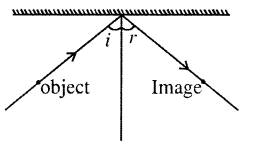
Question 15.
The following diagram shows a point object O placed in front of a plane mirror. Take two rays from the point O and show how the image of O is formed and seen by the eye.

Answer:
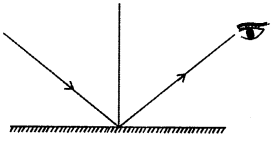
Question 16.
State four characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
(i) The image formed is erect.
(ii) The image is of the same size as that of the object.
(iii) The image is laterally inverted. Right side appears to be left and left side appeared to be right.
Question 17.
How is the position of image formed by a plane mirror related to the position of the object ?
Answer:
The image formed by a plane mirror is laterally inverted, upright, of the same size and is formed far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
Question 18.
You are standing at a distance 2 metre from a plane mirror.
(a) What is the distance of your image from the mirror ?
(b) What is the distance between you and your image ?
Answer:
(a) Distance of image from the mirror is also 2 metre.
(b) Distance between me and my image is 4 metre.
Question 19.
What is meant by lateral inversion of an image in a plane mirror ? Explain it with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Lateral Inversion : Inter change of sides between the object and its image is called Lateral Inversion.
Example :
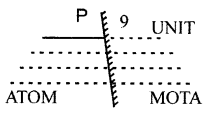
It means image formed behind the mirror is as far behind the mirror as object is in front of it.
i.e. distance of M = dist of M in distance of O in front of mirror = distance of O image, and so on.
Question 20.
Wirte down the letter C and I as seen in a plane mirror.
Answer:
![]()
Question 21.
What is irregular reflection ? Give an example.
Answer:
Irregular reflection – When a beam of light falls on such a surface which is not perfectly smooth and polished such as wall, wood, paper etc. the different portions of the surface reflect light in different directions. Such a reflection of light in different directions. Such a reflection of light from an uneven surface is called the irregular or diffused reflection.
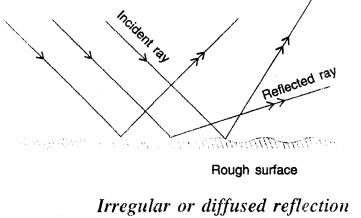
Question 22.
How do we see objects around us ?
Answer:
Objects are seen when light after striking them, returns in the same medium and reach our eyes.
Question 23.
State two uses of a plane mirror.
Answer:
It is used as :
(i) Looking glass
(ii) In periscopes.
Question 24.
Can light travel in vacuum ?
Answer:
Yes, light can travels in vacuum or air, a distance of nearly 299, 792, 458 metre (or nearly 3 x 108 metre) in one second. Thus, the speed of light in vacuum (or air) is 3 x 108 m s’1 nearly.
Question 25.
State the speed of light in (a) air, (b) glass.
Answer:
(a) Air — 3 × 108
(b) Glass — 2 × 108
Question 26.
State whether light slows down or speeds up in the following cases :
(a) Light going from air to glass.
(b) Light going from glass to water.
(c) Light going from water to air.
Answer:
(a) Slows down
(b) Speeds up
(c) Speeds up
Question 27.
What are the primary colours ? Name the three primary colours.
Answer:
Primary colours are the colours of light by mixing which white light is obtained. They are : (i) red (ii) green and (iii) blue.
Red + Green + Blue = White
Question 28.
What are the secondary colours ? Name the three secondary colours.
Answer:
Secondary colours are the colours of light which are obtained by mixing the two primary colours. They are (i) yellow, (ii) cyan, and (iii) magenta.
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate colour
(a) Blue + ………… = Cyan
(b) Red + Blue + …………. = Vhite
(c) Red + Blue = …………
(d) Green + Red = …………
Answer:
(a) Blue + Green = Cyan
(b) Red + Blue + Green = White
(e) Red + Blue = Magenta
(d) Green + Red = Yellow
Question 30.
The leaves appear green when seen in white light. Give a reason.
Answer:
Leaves appear green in white light because they reflect only the green light and absorb the light of all the other colours.
Question 31.
A rose appears red in white light. How will it appear in
(i) green light, (ii) red light ? Give a reason for your answer for each.
Answer:
(i) If a red rose is seen in green light, it appears black. The reason is that the rose absorbs the green light falling on it and reflect none.
(ii) If a red rose is seen in red light, it appears bright red. This is because the rose reflects the red light falling on it and absorbs none of it.
Question 32.
Why does a piece of paper appear white in sunlight ? How would you expect it to appear when viewed in red light?
Answer:
A piece of paper appears white in sunlight because it reflects light of all the colours. It would appear red when viewed in red light.
Question 33.
A piece of paper appears black in sunlight. What will be it£ colour when seen in red light ?
Answer:
A piece of paper appear black in sunlight. It would appear black when seen in red light because it absorbs light of all the colours.