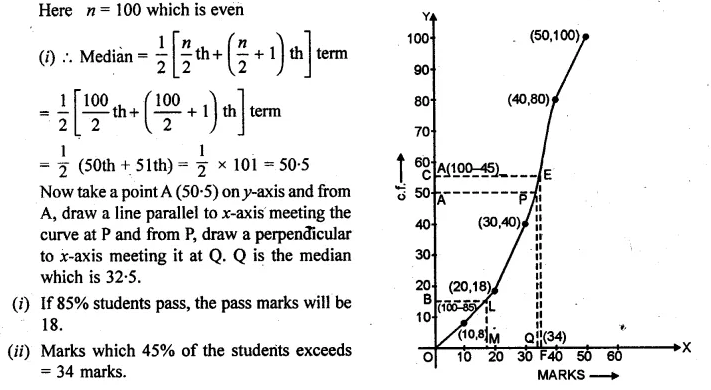
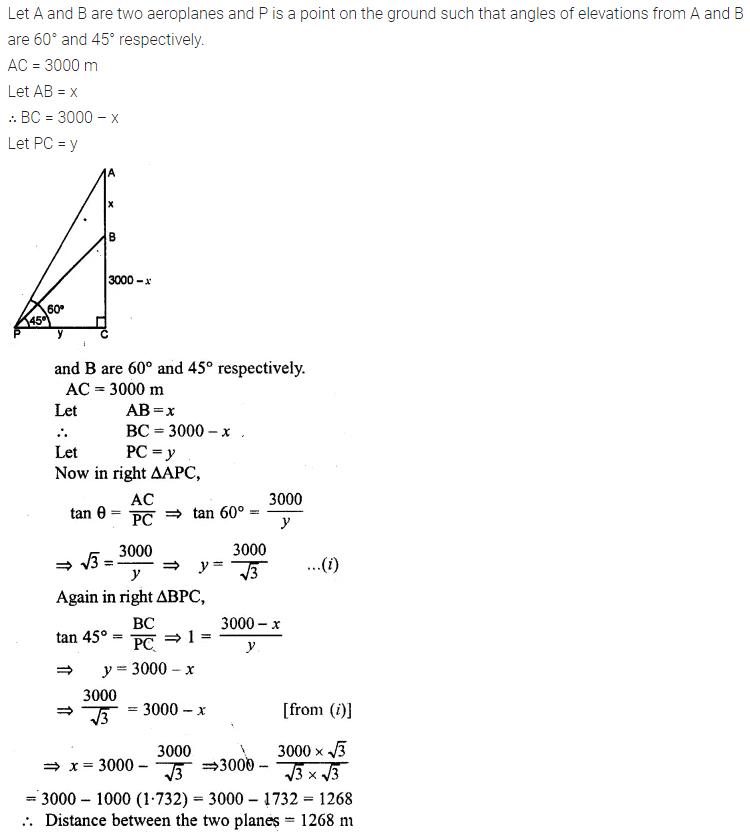
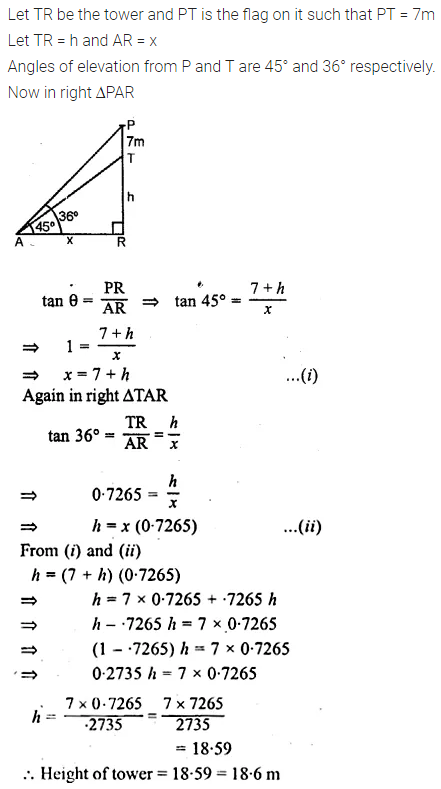
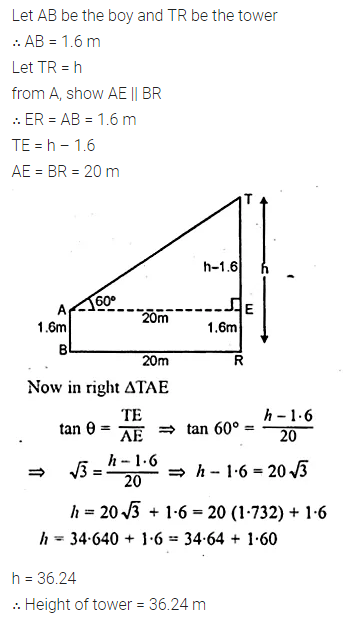
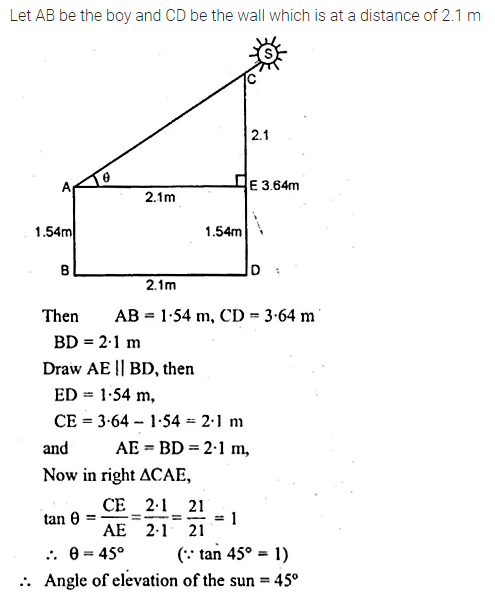
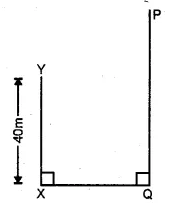
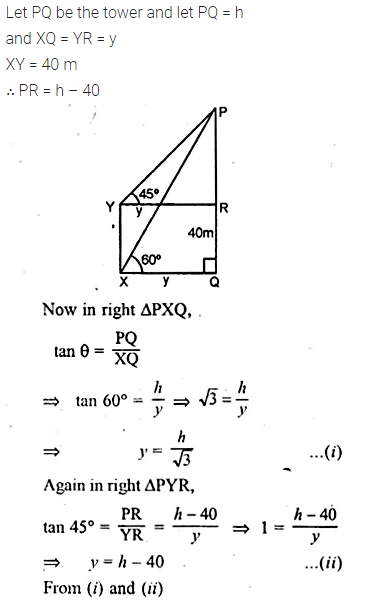
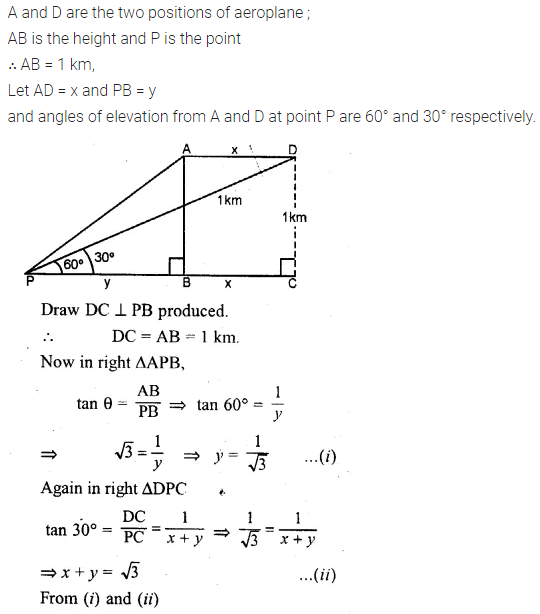
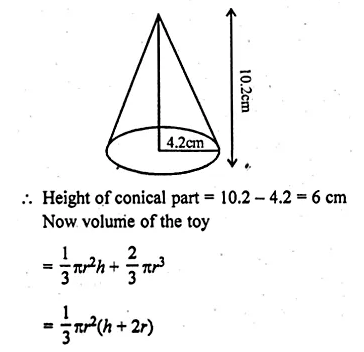
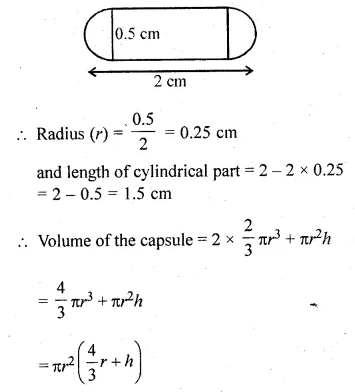
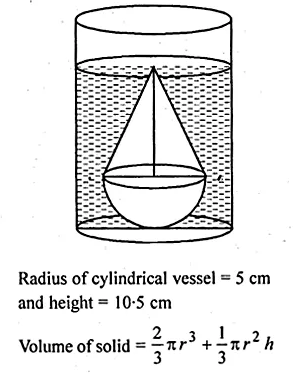
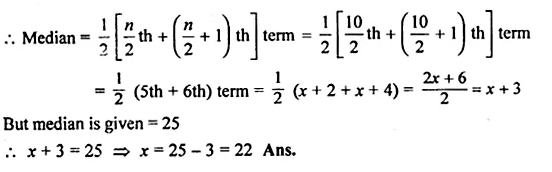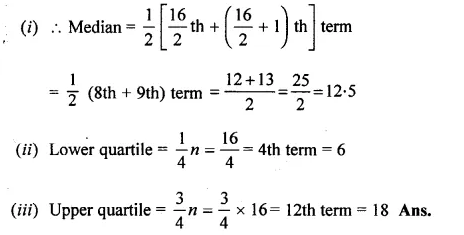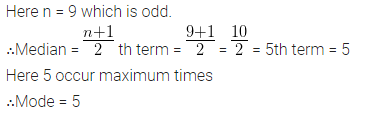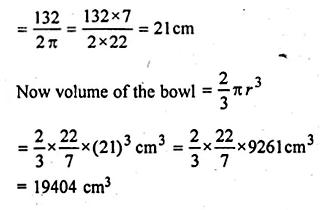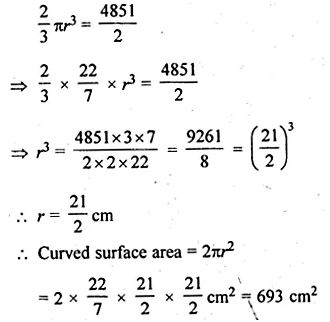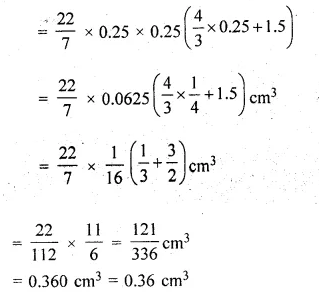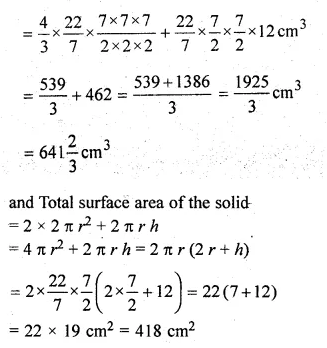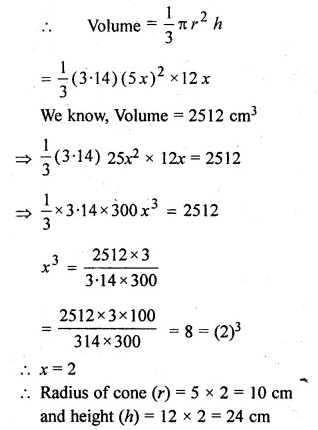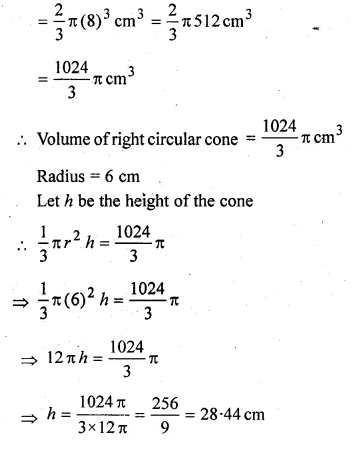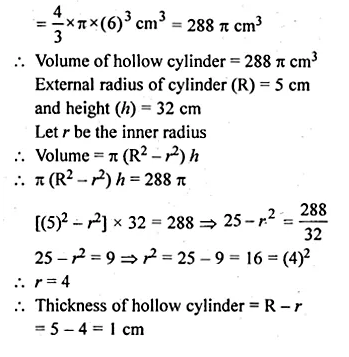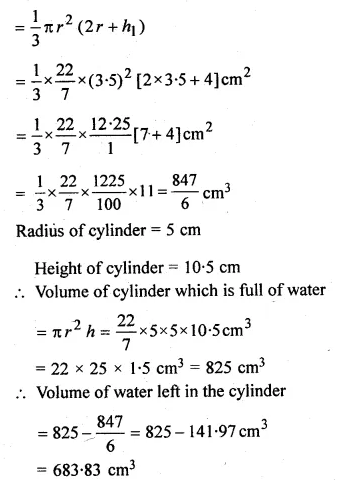ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 24 Probability Chapter Test
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 24 Probability Chapter Test.
ML Aggarwal SolutionsICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
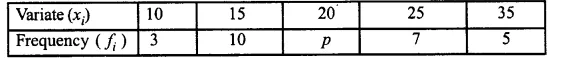
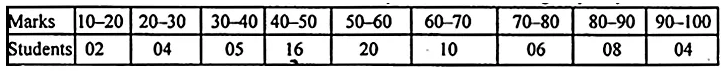
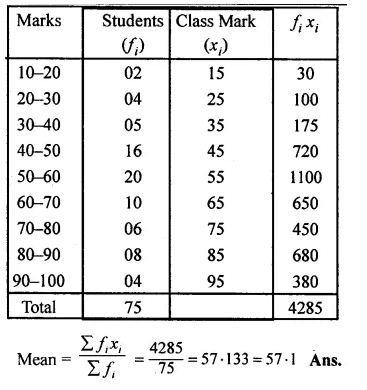
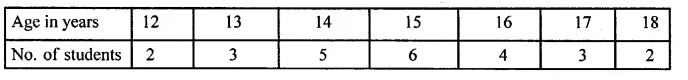
Question 1.
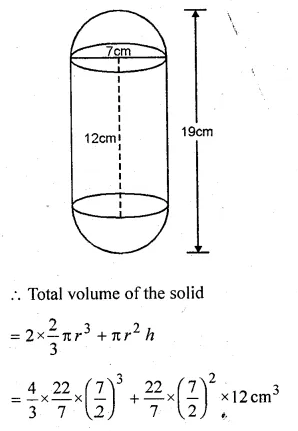
A game consists of spinning an arrow which comes to rest at one of the regions 1, 2 or 3 (shown in the given figure). Are the outcomes 1, 2 and 3 equally likely to occur? Give reasons.
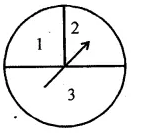
Solution:

Question 2.
In a single throw of a die, find the probability of getting
(i) a number greater than 5
(ii) an odd prime number
(iii) a number which is multiple of 3 or 4.
Solution:
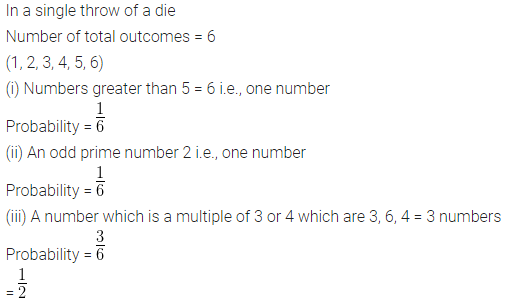
Question 3.
A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 are defective and the others are good. Rohana will buy a pen if it is good, but will not buy it if it is defective. The shopkeeper draws one pen at random and gives it to her. What is the probability that :
(i) She will buy it ?
(ii) She will not buy it ?
Solution:
In a lot, there are 144 ball pens in which defective ball pens are = 20
and good ball pens are = 144 – 20 = 124
Rohana buys a pen which is good only.
(i) Now the number of possible outcomes = 144
and the number of favourable outcomes = 124

Question 4.
A lot consists of 48 mobile phones of which 42 are good, 3 have only minor defects and 3 have major defects. Varnika will buy a phone if it is good but the trader will only buy a mobile if it has no major defect. One phone is selected at random from the lot. What is the probability that it is
(i) acceptable to Varnika?
(ii) acceptable to the trader?
Solution:

Question 5.
A bag contains 6 red, 5 black and 4 white balls. A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Find the probability that the ball drawn is
(i) white
(ii) red
(iii) not black
(iv) red or white.
Solution:

Question 6.
A bag contains 5 red, 8 white and 7 black balls. A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Find the probability that the drawn ball is:
(i) red or white
(ii) not black
(iii) neither white nor black
Solution:

Question 7.
A bag contains 5 white balls, 7 red balls, 4 black balls and 2 blue balls. One ball is drawn at random from the bag. What is the probability that the ball drawn is :
(i) white or blue
(ii) red or black
(iii) not white
(iv) neither white nor black ?
Solution:

Question 8.
A box contains 20 balls bearing numbers 1, 2, 3, 4,……, 20. A ball is drawn at random from the box. What is the probability that the number on the ball is
(i) an odd number
(ii) divisible by 2 or 3
(iii) prime number
(iv) not divisible by 10 ?
Solution:

Question 9.
Find the probability that a number selected at random from the numbers 1, 2, 3,……35 is a
(i) prime number
(ii) multiple of 7
(iii) multiple of 3 or 5.
Solution:

Question 10.
Cards marked with numbers 13, 14, 15,…..60 are placed in a box and mixed thoroughly. One card is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the number on the card is
(i) divisible by 5
(ii) a number which is a perfect square.
Solution:

Question 11.
The box has cards numbered 14 to 99. Cards are mixed thoroughly and a card is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the card drawn from the box has
(i) an odd number
(ii) a perfect square number.
Solution:

Question 12.
A bag contains 5 red balls and some blue balls. If the probability of drawing a blue ball is four times that of a red ball, find the number of balls in the bags.
Solution:
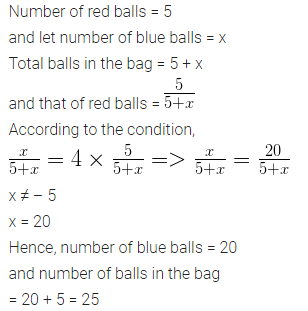
Question 13.
A bag contains 18 balls out of which x balls are white.
(i) If one ball is drawn at random from the bag, what is the probability that it is white ball?
(ii) If 2 more white balls are put in the bag, the probability of drawing a white ball will be \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \) times that of probability of white ball coming in part (i). Find the value of x.
Solution:
Total numbers of balls in a bag = 18
No. of white balls = x
(i) One ball is drawn a random
Probability of being a white ball = \(\\ \frac { x }{ 18 } \)
(ii) If 2 more white balls an put, then number of white balls = x + 2
and probability is \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \) times
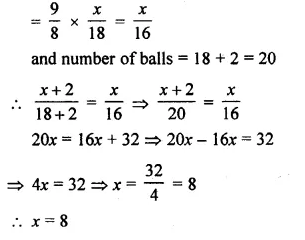
Question 14.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that the card drawn is :
(i) a red face card
(ii) neither a club nor a spade
(iii) neither an ace nor a king of red colour
(iv) neither a red card nor a queen
(v) neither a red card nor a black king.
Solution:


Question 15.
From pack of 52 playing cards, blackjacks, black kings and black aces are removed and then the remaining pack is well-shuffled. A card is drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting
(i) a red card
(ii) a face card
(iii) a diamond or a club
(iv) a queen or a spade.
Solution:

Question 16.
Two different dice are thrown simultaneously. Find the probability of getting:
(i) sum 7
(ii) sum ≤ 3
(iii) sum ≤ 10
Solution:

Question 17.
Two dice are thrown together. Find the probability that the product of the numbers on the top of two dice is
(i) 6
(ii) 12
(iii) 7
Solution:

We hope the ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 24 Probability Chapter Test help you. If you have any query regarding ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 24 Probability Chapter Test, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.