ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 18 Mensuration Chapter Test
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 18 Mensuration Chapter Test.
ML Aggarwal SolutionsICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
A cylindrical container is to be made of tin sheet. The height of the container is 1 m and its diameter is 70 cm. If the container is open at the top and the tin sheet costs Rs 300 per m2, find the cost of the tin for making the container.
Solution:
Height of container opened at the top (h) = 1 m = 100 cm
and diameter = 70 cm
∴Radius (r) = \(\\ \frac { 70 }{ 2 } \) = 35 cm
∴Total surface area = 2πrh + πr2

Question 2.
A cylinder of maximum volume is cut out from a wooden cuboid of length 30 cm and cross-section of square of side 14 cm. Find the volume of the cylinder and the volume of wood wasted.
Solution:
Dimensions of the wooden cuboid = 30 cm × 14 cm × 14 cm
Volume = 30 × 14 × 14 = 5880 cm3

Question 3.
Find the volume and the total surface area of a cone having slant height 17 cm and base diameter 30 cm. Take π = 3.14.
Solution:
Slant height of a cone (l) = 17 cm
Diameter of base = 30 cm
Radius (r) = \(\\ \frac { 30 }{ 2 } \) = 15 cm
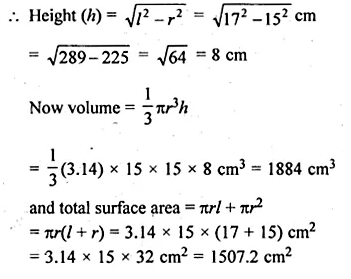
Question 4.
Find the volume of a cone given that its height is 8 cm and the area of base 156 cm2.
Solution:
Height of a cone = 8 cm
Area of base = 156 cm
.’. Volume = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) × area of base × height
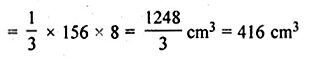
Question 5.
The circumference of the edge of a hemispherical bowl is 132 cm. Find the capacity of the bowl.
Solution:
Circumference of the edge of bowl = 132 cm
Radius of a hemispherical bowl
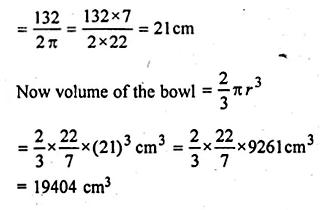
Question 6.
The volume of a hemisphere is \(2425 \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) cm2. Find the curved surface area.
Solution:
Volume of a hemisphere = \(2425 \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) cm3
= \(\\ \frac { 4851 }{ 2 } \) cm3
Let radius = r, then
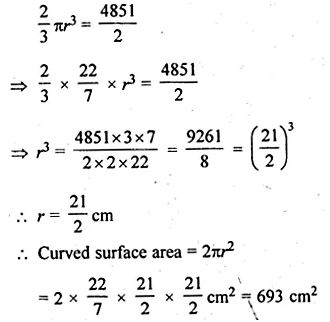
Question 7.
A solid wooden toy is in the shape of a right circular cone mounted on a hemisphere. If the radius of the hemisphere is 4.2 cm and the total height of the toy is 10.2 cm, find the volume of the toy
Solution:
A wooden solid toy is of a shape of a right circular cone
mounted on a hemisphere.
Radius of hemisphere (r) = 4.2 cm
Total height = 10.2 cm
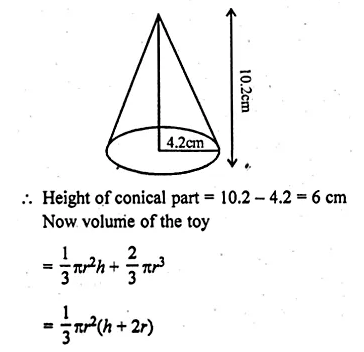
Question 8.
A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder of diameter 0.5 cm with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends. The length of the entire capsule is 2 cm. Find the capacity of the capsule.
Solution:
Diameter of cylindrical part = 0.5 cm
Total length of the capsule = 2 cm
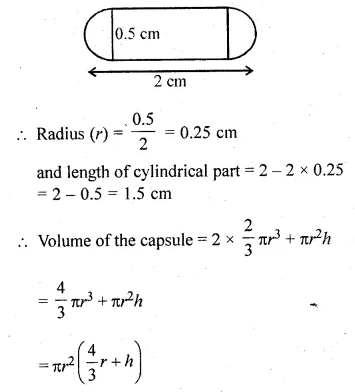
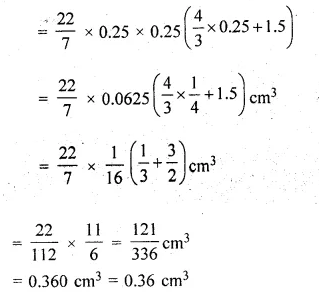
Question 9.
A solid is in the form of a cylinder with hemispherical ends. The total height of the solid is 19 cm and the diameter of the cylinder is 7 cm. Find the volume and the total surface area of the solid.
Solution:
Radius of cylinder = \(\\ \frac { 7 }{ 2 } \)cm
and height of cylinder = 19 – 2 × \(\\ \frac { 7 }{ 2 } \) cm
= 19 – 7 = 12 cm
and radius of hemisphere = \(\\ \frac { 7 }{ 2 } \) cm
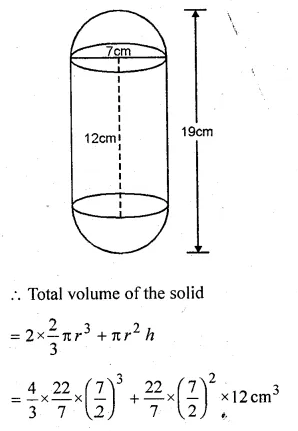
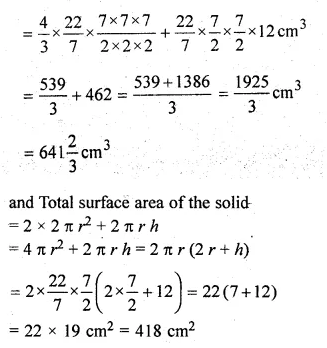
Question 10.
The radius and height of a right circular cone are in the ratio 5 : 12. If its volume is 2512 cm , find its slant height. (Take π = 3.14).
Solution:
Let radius of cone (r) = 5x
then height (h) = 12x
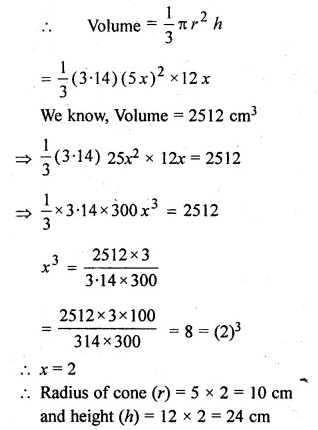
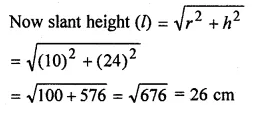
Question 11.
A cone and a cylinder are of the same height. If diameters of their bases are in the ratio 3 : 2, find the ratio of their volumes.
Solution:
Let height of cone and cylinder = h
Diameter of the base of cone = 3x
Diameter of base of cylinder = 2x
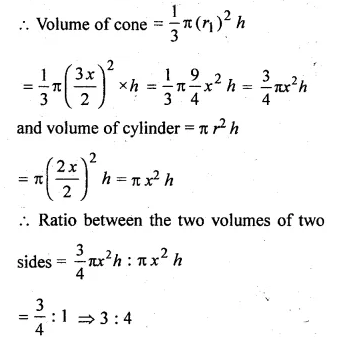
Question 12.
A solid cone of base radius 9 cm and height 10 cm is lowered into a cylindrical jar of radius 10 cm, which contains water sufficient to submerge the cone completely. Find the rise in water level in the jar.
Solution:
Radius of the cone (r) = 9 cm
Height of the cone (h) = 10 cm
Volume of water filled in cone

Question 13.
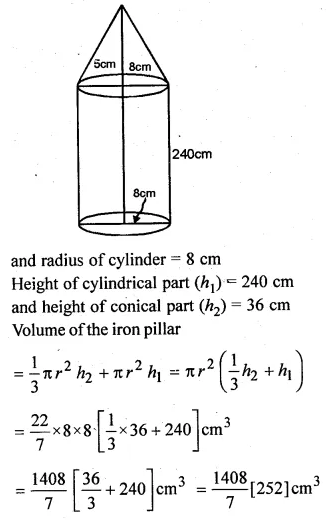
An iron pillar has some part in the form of a right circular cylinder and the remaining in the form of a right circular cone. The radius of the base of each of cone and cylinder is 8 cm. The cylindrical part is 240 cm high and the conical part is 36 cm high. Find the weight of the pillar if one cu. cm of iron weighs 7.8 grams.
Solution:
Radius of the base of cone = 8 cm
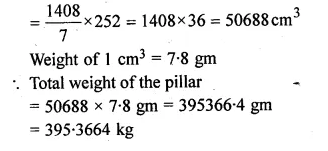
Question 14.
A circus tent is made of canvas and is in the form of right circular cylinder and a right circular cone above it. The diameter and height of the cylindrical part of the tent are 126 m and 5 m respectively. The total height of the tent is 21 m. Find the total cost of the tent if the canvas used costs Rs 36 per square metre.
Solution:
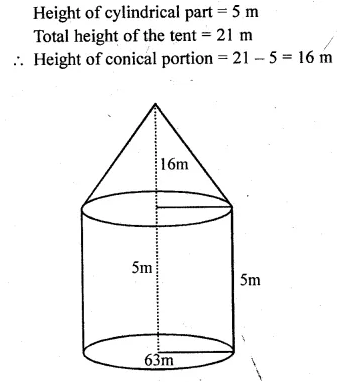
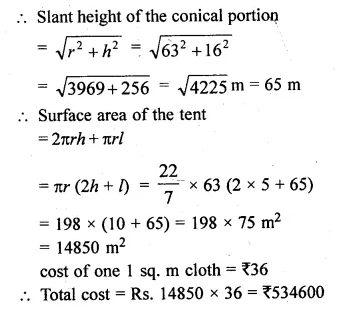
Question 15.
The entire surface of a solid cone of base radius 3 cm and height 4 cm is equal to the entire surface of a solid right circular cylinder of diameter 4 cm. Find the ratio of their
(i) curved surfaces
(ii) volumes.
Solution:
Radius of the base of a cone (r) = 3 cm
Height (h) = 4 cm

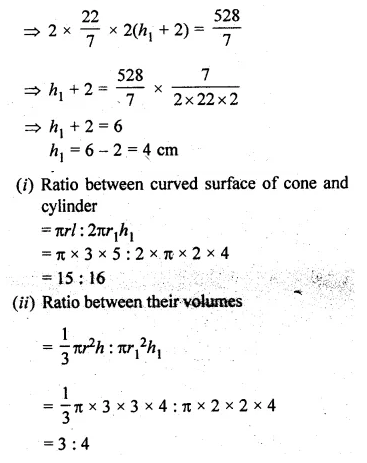
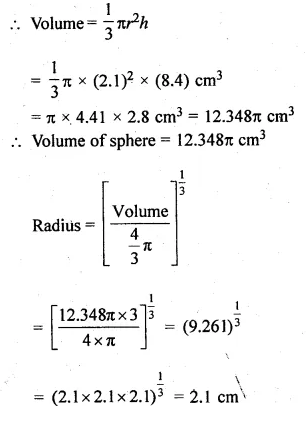
Question 16.
A cone is 8.4 cm high and the radius of its base is 2.1 cm. It is melted and recast into a sphere. Find the radius of the sphere.
Solution:
Radius of base of a cone (r) = 2. 1 cm
and height (h) = 8.4 cm
Question 17.
How many lead shots each of diameter 4.2 cm can be obtained from a solid rectangular lead piece with dimensions 66 cm, 42 cm and 21 cm.
Solution:
Dimensions of a solid rectangular lead piece
= 66 cm × 42 cm × 21 cm
.’. Volume = 66 × 42 × 21 cm3
Diameter of a lead shot = 4.2 cm

Question 18.
Find the least number of coins of diameter 2.5 cm and height 3 mm which are to be melted to form a solid cylinder of radius 3 cm and height 5 cm.
Solution:
Radius of a cylinder (r) = 3 cm
Height (h) = 5 cm

Question 19.
A hemisphere of lead of radius 8 cm is cast into a right circular cone of base radius 6 cm. Determine the height of the cone correct to 2 places of decimal.
Solution:
Radius of hemisphere = 8 cm
Volume = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \pi { r }^{ 3 }{ cm }^{ 3 }\)
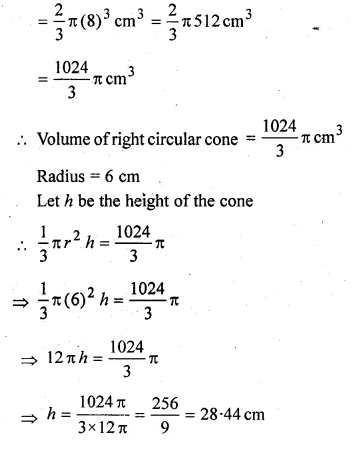
Question 20.
A vessel in the form of a hemispherical bowl is full of water. The contents are emptied into a cylinder. The internal radii of the bowl and cylinder are respectively 6 cm and 4 cm. Find the height of the water in the cylinder.
Solution:
Radius of hemispherical bowl = 6 cm
.’. Volume of the water in the bowl

Question 21.
The diameter of a metallic sphere is 42 cm. It is metled and drawn into a cylindrical wire of 28 cm diameter. Find the length of the wire.
Solution:
Diameter of sphere = 42 cm
Radius of sphere =\(\\ \frac { 42 }{ 2 } \) = 21 cm

Question 22.
A sphere of diameter 6 cm is dropped into a right circular cylindrical vessel partly filled with water. The diameter of the cylindrical vessel is 12 cm. If the sphere is completely submerged in water, by how much will the level of water rise in the cylindrical vessel?
Solution:
Radius of sphere = \(\\ \frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) = 3 cm

Question 23.
A solid sphere of radius 6 cm is metled into a hollow cylinder of uniform thickness. If the external radius of the base of the cylinder is 5 cm and its height is 32 cm, find the uniform thickness of the cylinder.
Solution:
Radius of solid sphere = 6 cm
Volume of solid sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \pi { r }^{ 3 }\)
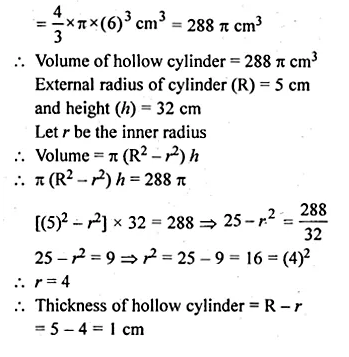
Question 24.
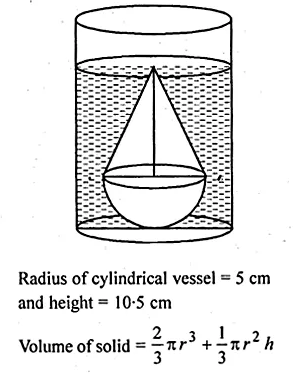
A solid is in the form of a right circular cone mounted on a hemisphere. The radius of the hemisphere is 3.5 cm and the height of the cone is 4 cm. The solid is placed in a cylindrical vessel, full of water, in such a Way that the whole solid is submerged in water. If the radius of the cylindrical vessel is 5 cm and its height is 10.5 cm, find the volume of water left in the cylindrical vessel.
Solution:
Radius of hemisphere (r) = 3.5 cm
Height of cone (h1) = 4 cm
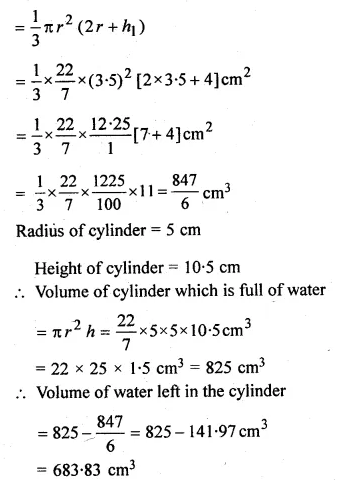
We hope the ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 18 Mensuration Chapter Test help you. If you have any query regarding ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 18 Mensuration Chapter Test, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.