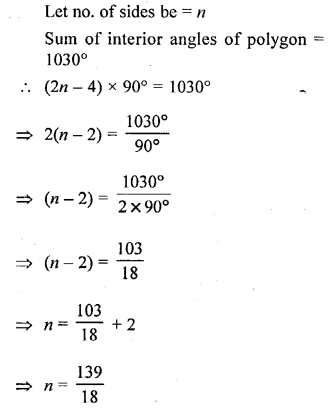
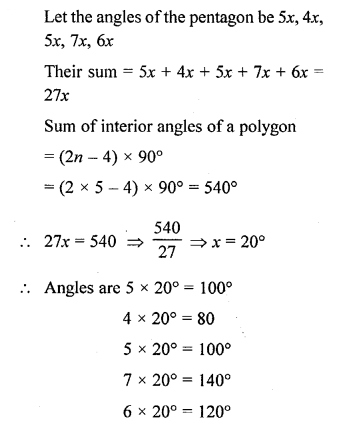
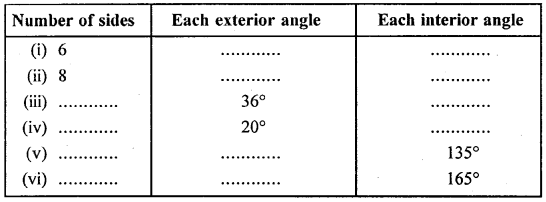
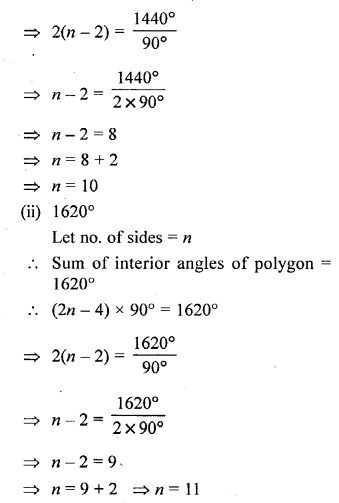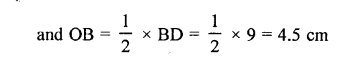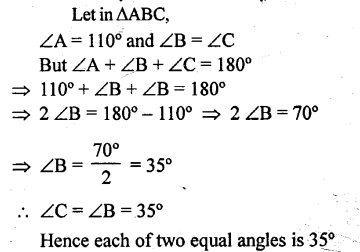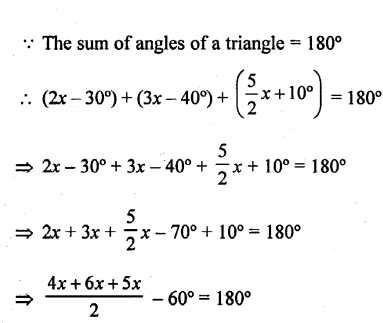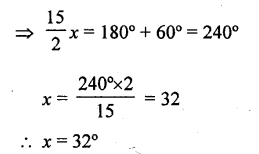Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions Chapter 26 Triangles (Including Types, Properties and Constructions)
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions Chapter 26 Triangles (Including Types, Properties and Constructions)
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Maths ICSE SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
IMPORTANT POINTS
1. Collinear Points: Three or more points which lie on the same straight line, are called collinear points.
2. Non-Collinear Points: Three or more points which do not lie on the same line, are called non- col linear points.
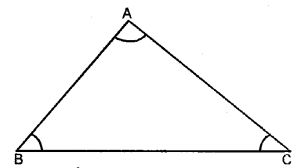
3. Triangle: By joining the three non-collinear points, a triangle is formed or A triangle is a figure which is enclosed by three lines segments. In the figure, ABC is a triangle.
4. Parts of triangle: A triangle has six parts, three sides and three angles which are on the vertices of the triangle.
5. Sum of angles of a triangle: The sum of the three angles of a triangle is 180°.
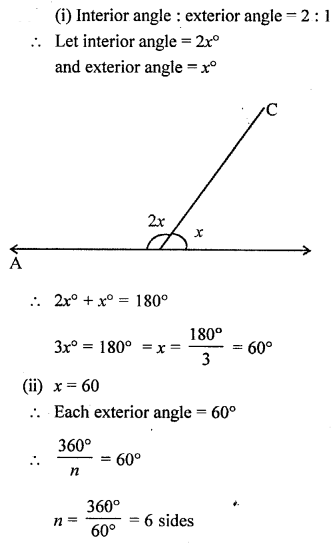
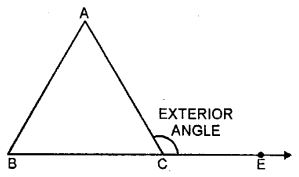
6. Exterior angle of a triangle: If one side of a triangle is produced then the exterior angle is formed. Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to sum of its interior opposite angles. In other words, we can say that exterior angle of a triangle is greater than each of its interior opposite angles. In the figure.
∠ACE is exterior angle and ∠ACE = ∠A + ∠B and also ∠ACE > ∠A and ∠ACF > ∠B.
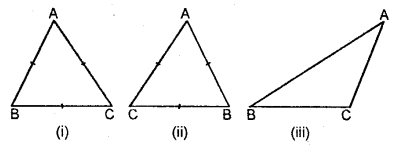
7. Classification of triangles :
(A) According to their sides.
(i) Equilateral Triangle: If three sides of a triangle are equal, it is called an equilateral triangle.
(ii) Isosceles Triangle: If any two sides of a triangle are equal, then it is called an isosceles triangle.
(iii) Scalene Triangle: If no two sides of the triangle are equal. Then it is called a scalene triangle.
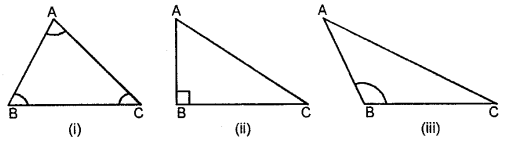
(B) According to Angles :
(i) Acute-angled Triangle: A triangle whose each angle is acute, is called an acute angled triangle.
(ii) Right-angled Triangle: A triangle whose one angle is a right angle i.e. 90°, is called a right angled triangle.
(iii) Obtused-angled Triangle: A triangle whose one angle is an obtused angle, is called an obtused-angled triangle.
8. Some special properties of a triangle:
(i) If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of other two cycles, the angle is a right angled.
(ii) If the acute angles of a right angled triangle are equal, then the triangle is a right angled isosceles triangle and its each acute angle will be of 45°.
(iii) Sum of two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
(iv) There can be only one right angle in a triangle.
(v) There can be only one obtuse angle in a triangle.
(vi) Side opposite to greater angle is greater.
(vii) Angle opposite to shorter side is shorter.
Triangles Exercise 26A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
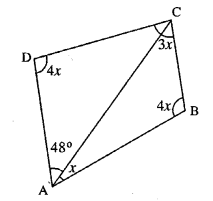
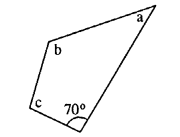
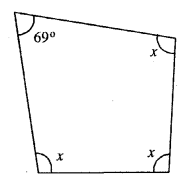
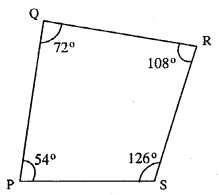
Question 1.
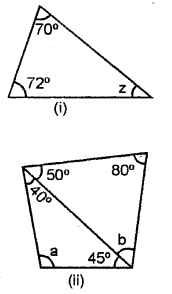
In each of the following, find the marked unknown angles :
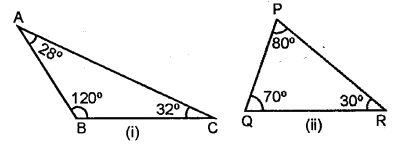
Solution:
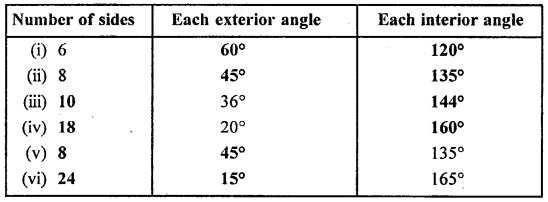
(i) Since, sum of all angles of triangle = 180°
Hence, 70° + 72° + z = 180°
⇒ 142°+ z = 180° ”
⇒ z= 180°-142°
z = 38°
(ii) Since, sum of all angles of a triangle = 180°
1st Triangle 50° + 80° + b = 180°
⇒ 130°+ &= 180°
⇒b= 180° – 130°
b = 50°
IInd Triangle 40° + 45° + a = 180°
⇒ 85° + a = 180°
⇒ a = 180° -85
a = 95°
(iii) 60° + 45° + 20° + x = 180°
⇒ 125° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 125° => x = 55°
Question 2.
Can a triangle together have the following angles ?
(i) 55°, 55° and 80°
(ii) 33°, 74° and 73°
(iii) 85°, 95° and 22°.
Solution:
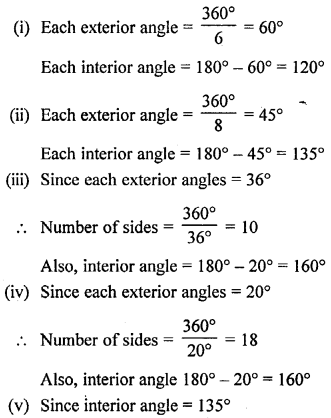
(i) Sum of all angles of a triangle = 180° Here, 55° + 55° + 80° = 180°
190° ≠ 180°
No.
(ii) 33°+ 74°+ 73°= 180°
180°= 180°
Yes.
(iii) 85° + 95° + 22° = 180°
202° ≠ 180°
No.
Question 3.
Find x, if the angles of a triangle are:
(i) x°, x°, x°
(ii) x°, 2x°, 2x°
(iii) 2x°, 4x°, 6x°
Solution:
(i) Since, sum of all the angles of a triangle =180
x° + x° + x° = 180
⇒ 3x° = 180
⇒ x° = \(\frac { 180 }{ 3 }\)
x = 60
(ii) x° + 2x° + 2x° = 180
5x° = 180
x° = \(\frac { 180 }{ 5 }\)
x° = 36
(iii) 2x° + 4x° + 6x° =180
12x° = 180
x° = \(\frac { 180 }{ 12 }\)
x° = 15
Question 4.
One angle of a right-angled triangle is 70°. Find the other acute angle.
Solution:
We know that, sum of angles of a triangle = 180°.
Let, the acute angle be ‘x’
∴ x + 90° + 70° = 180°
⇒ x+ 160° = 180°
⇒ x= 180°-160°
⇒ x = 20°
∴The acute angle is 20°.
Question 5.
In ∆ABC, ∠A = ∠B = 62° ; find ∠C.
Solution:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C= 180°
⇒ 62° + 62° + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 124° + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠C = 180° – 124°
⇒∠C = 56°
Question 6.
In ∆ABC, C = 56°C = 56° ∠B = ∠C and ∠A = 100° ; find ∠B.
Solution:
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 100° + ∠B + ∠B = 180°
⇒ 2∠B = 180° 100°
∠B = \(\frac { 80 }{ 2 }\)°
∠B = 40°
∠C = ∠B = 40°
Question 7.
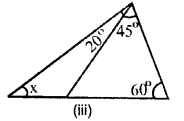
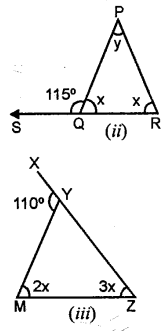
Find, giving reasons, the unknown marked angles, in each triangle drawn below:
Solution:
We know that,
Exterior angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of its two interior opposite angles (property)
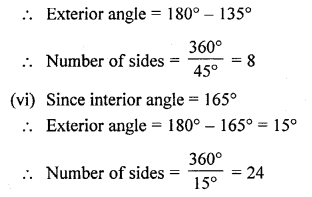
(i) ∴ 110° = x + 30° (by property)
⇒x=110°-30° x = 80°
(ii) x+115° = 180°
(linear property of angles)
⇒x = 180°- 115° ⇒x = 65°
∴115° = x + y
⇒ 115° = 65° + _y ⇒ y= 115° – 65° =50°
y = 50°
(iii) 110° = 2x + 3x
5x – 110°
x = \(\frac { 110 }{ 5 }\)°
x = 22°
∴2x = 2 x 22 = 44°
3x = 3 x 22 = 66°
Question 8.
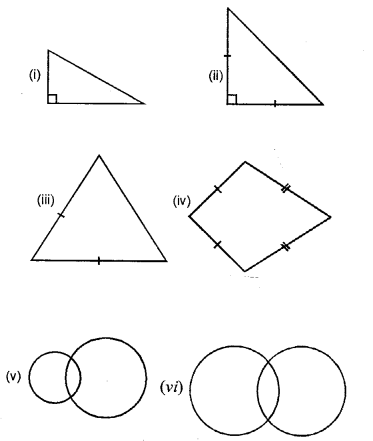
Classify the following triangles according to angle :
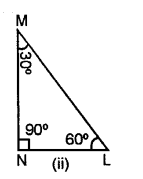
Solution:
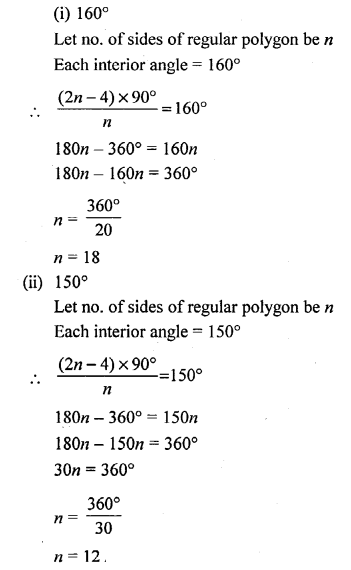
(i) Since, it has an obtuse angle of 120° Hence, it is obtuse angled triangle.
(ii) Since, all the angle of triangle is less than 90°.
Hence, it is an acute angled triangle.
(iii) Since ∠MNL = 90°, and sum of two acute angle ∠M + ∠N = 30° + 60° = 90°.
Hence, it is a right angled triangle.
Question 9.
Classify the following triangles according to sides :
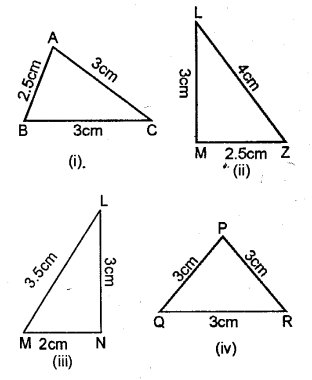
Solution:
(i) Since, two sides-are equal.
Hence, Isosceles triangle.
(ii) Since, all the three sides are unequal.
Hence, Scalene, triangle.
(iii) Since, all the three sides are unequal Hence, Scalene triangle.
(iv) All the three sides are equal.
Hence, equilateral triangle.
Triangles Exercise 26B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Construct traingle ABC, when :
Question 1.
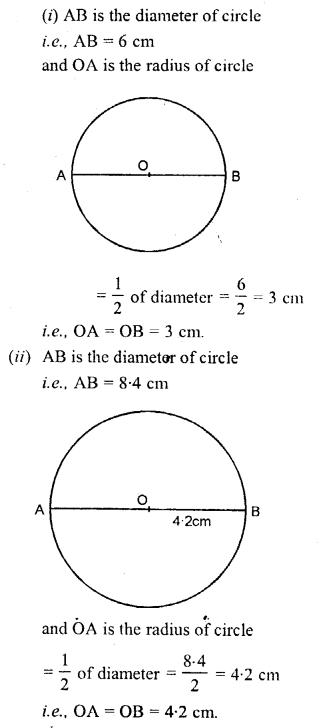
AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm and AC = 4 cm.
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
(1) Draw a line AB = 6 cm.
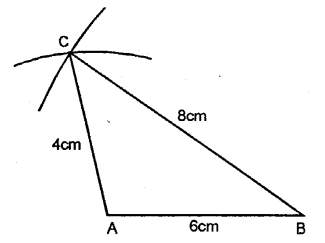
(2) compasses and taking B as centre, draw an arc of 8 cm radius.
(3) With A as centre, draw an arc of 4 cm radius, which cuts the previous arc at C.
(4) Join AC and BC.
Triangle ABC, obtained, is the required triangle.
Question 2.
AB = 3.5 cm, AC = 4.8 cm and BC = 5.2 cm.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line AB = 3.5 cm.
(2) Using compasses and taking B as centre, draw an arc of 5.2 cm radius.
(3) With A as centre, draw an arc of 4.8
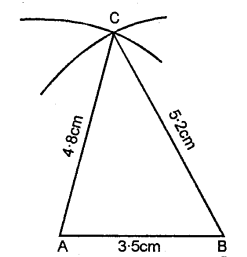
(4) Join AC and BC
Question 3.
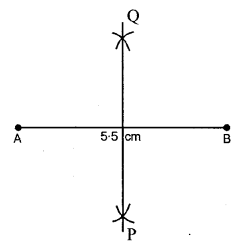
AB = BC = 5 cm and AC = 3 cm. Mea¬sure angles A and C. Is ∠A = ∠C?
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line AB = 5 cm.
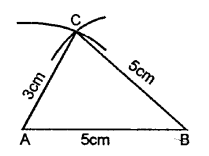
(2) Using compasses and taking B as cen¬tre, draw an arc of 5 cm radius.
(3) With A as centre, draw an arc of 3 cm radius, which cuts the previous arc at C.
(4) Join AC and BC.
Question 4.
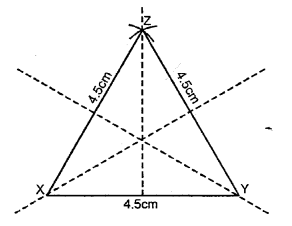
AB = BC = CA = 4.5 cm. Measure all the angles of the triangle. Are they equal ?
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a a line AB =4.5
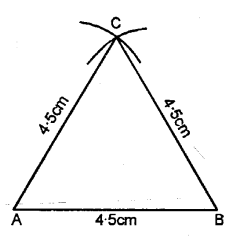
(2) Using compasses and taking BC as centre, draw an arc of 4.5 cm radius.
(3) With AC as centre, draw an arc of 4-5 cm radius, which cuts the previous arc at C.
(4) Join AC and BC.
(5) Measurement, ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°.
Question 5.
AB = 3 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠B = 90°.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AB = 3 cm.
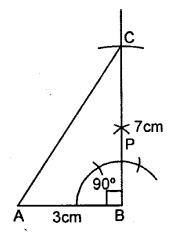
(2) With the help of compasses, construct ∠ABC = 90°.
(3) With B as centre, draw an arc of 7 cm length which cuts BP at C.
(4) Join A and C.
(5) Triangle ABC, so obtained, is the required triangle.
Question 6.
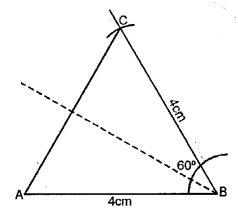
AC = 4.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠C = 60°.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line AC = 4.5 cm.

(2) With the help of compasses, construct ∠ACB = 60°.
(3) With C as centre, draw an arc of 6 cm radius, which cuts CB at C.
(4) Join B and A.
Question 7.
AC = 6 cm, ∠A = 60“ and ∠C = 45°. Measure AB and BC.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AC = 6 cm.
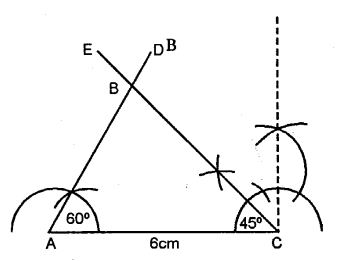
(2) At A construct an angle ∠A = 60°.
(3) At C construct an angle ∠C = 45°.
(4) AD and CE intersect each other at B.
(5) ∴ ∆ABC is the required triangle.
(6) On measuring AB = 4-4 cm, BC = 5.4 cm.
Question 8.
AB = 5.4 cm, ∠A = 30° and ∠B = 90°. Measure ∠C and side BC.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AB = 5.4 cm.
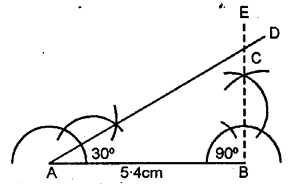
(2) At A construct an angle ∠A = 30°.
(3) At B construct an angle ∠B = 90°.
(4) AD and BE intersect each other at C.
(5) ∴ ∆ABC is the required triangle.
(6) On measuring ∠C = 60° side BC = 31 cm.
Question 9.
AB = 7 cm, ∠B = 120° and ∠A = 30°. Measure AC and BC.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AB = 7 cm
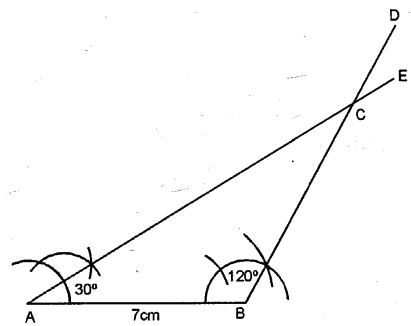
(2) At A construct an angle ∠A = 30°.
(3) At C construct an angle ∠C = 45°.
(4) AE and BD intersect each other at C.
(5) ∴ ∆ABC is the required triangle.
(6) On measuring length of AC = 12cm and BC = 7 cm respectively.
Question 10.
BC = 3 cm, AC = 4 cm and AB = 5 cm. Measure angle ACB. Give a special name to this triangle.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line segment AB = 5 cm

(2) From A, with the help of compass cut arc AC = 4cm
(3) From point B cut an arc BC = 3 cm.
(4) Join AC and BC.
(5) AABC is required right-angled triangle.
Measuring ∠ACB = 90°
Triangles Revision Exercise – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 6 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
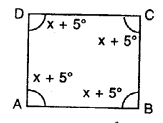
If each of the two equal angles of an isosceles triangle is 68°, find the third angle.
Solution:
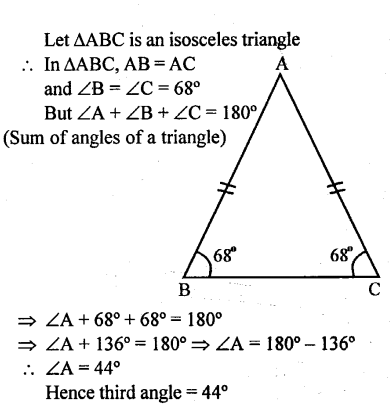
Question 2.
One of the angles of a triangle is 110°, the two other angles are equal. Find their value.
Solution:
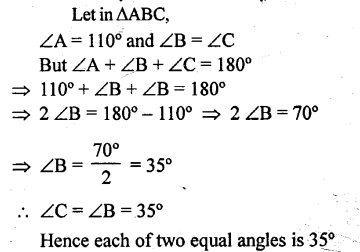

Question 3.
The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 3:5: 7. Find each angle.
Solution:
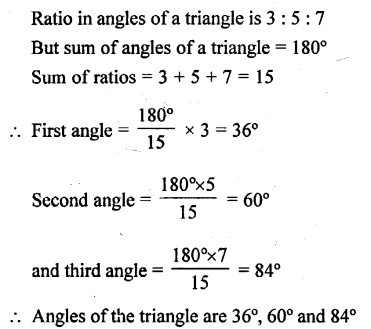
Question 4.
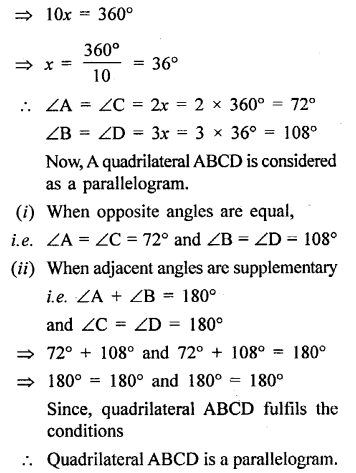
The angles of a triangle are (2x – 30°),(3x – 40°) and (\(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\)x + 10°) Find the value of x .
Solution:
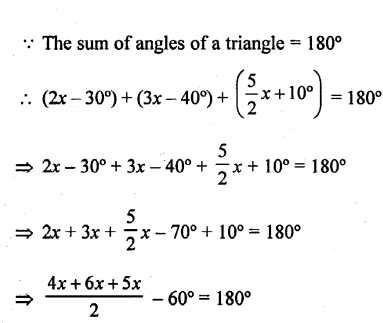
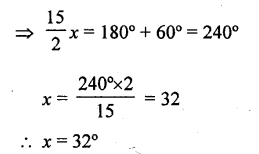
Question 5.
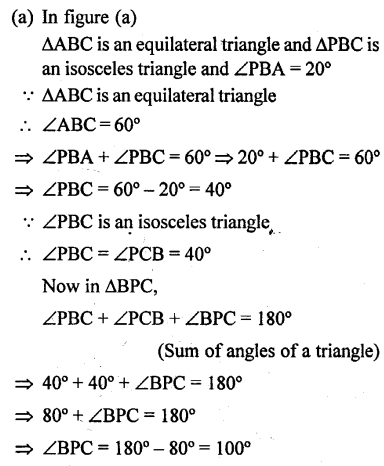
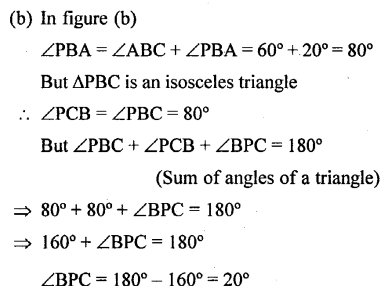
In each of the following figures, triangle ABC is equilateral and triangle PBC is isosceles. If PBA = 20°; find in each case:
(a) angle PBC.
(b) angle BPC.

Solution:
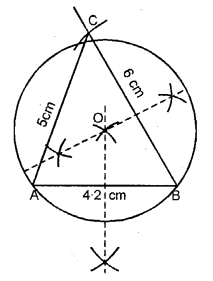
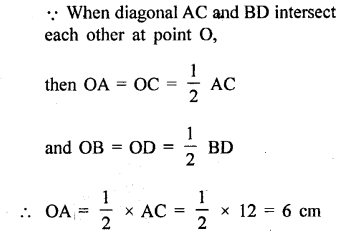
Question 6.
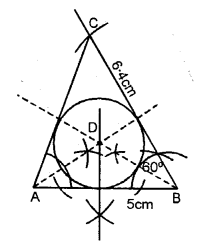
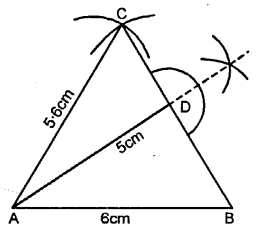
Construct a triangle ABC given AB = 6 cm, BC = 5 cm and CA = 5.6 cm. From vertex A draw a perpendicular on to side BC. Measure the length of this perpendicular.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line AB = 6 cm.
(2) Using compass, taking A and B as centre draw arcs of 5 cm and 5.6 cm respectively, which cut each other at C.
(3) Join AC and BC.
(4) Now, from vertex A draw a bisector AD towards BC.
On measuring length AD = 5 cm.
Question 7.
Construct a triangle PQR, given PQ = 6 cm, ∠P = 60° and ∠Q = 30°. Measure angle R and the length of PR.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line PQ = 6 cm.
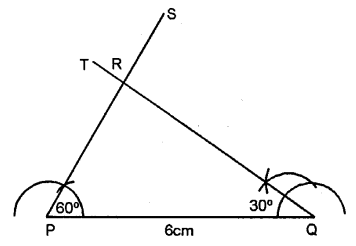
(2) Using compass taking P as centre draw an angle ∠P = 60°.
(3) Using compass taking Q as a centre draw an angle ∠Q = 30°.
(4) PS and QT intersect each other R.
(5) ∆RPQ is the required triangle.
On measuring; ∠R = 90°, length of PR = 3 cm.
Question 8.
Construct a triangle ABC given BC = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm and ∠C = 75°. Draw the bisector of the interior angle at A. Let this bisector meet BC at P ; measure BP.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw BC = 5 cm.
(2) With the help of compass from centre C. Draw an angle ∠C = 75°.
(3) From CD, cut an arc AC = 6 cm.
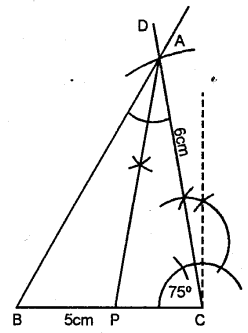
(4) JoinAB.
(5) From A draw an bisector AP.
(6) On measuring BP = 2.6 cm.
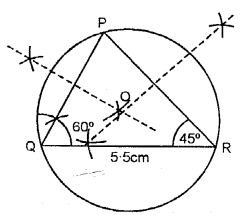
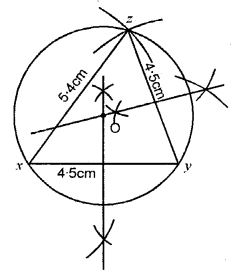
Question 9.
Using ruler and a pair compass only, construct a triangle XYZ given YZ = 7 cm, ∠XYZ = 60° and ∠XZY = 45°. Draw the bisectors of angles X and Y.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line YZ = 7 cm.
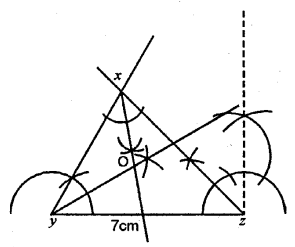
(2) Y as a centre draw an ∠XYZ = 60°.
(3) Z as a centre draw an ∠XZY = 45°.
(4) From X and Y as centre draw bisector of ∠X and ∠Y, which meet at point O.
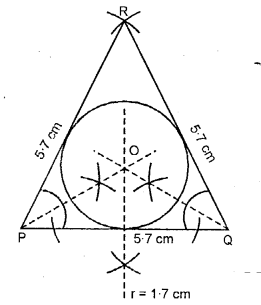
Question 10.
Using ruler and a pair compass only, construct a triangle PQR, given PQ = 5.5 cm, QR = 7.5 cm and RP = 6 cm. Draw the bisectors of the interior angles at P, Q and R. Do these bisectors meet at the same point ?
Solution:
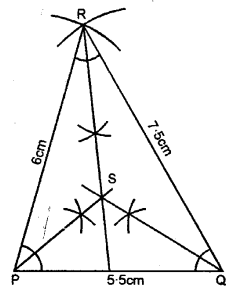
Steps of Construction :
(1) Draw a line PQ = 5.5 cm.
(2) From Q as a centre draw an arc QR = 7.5 cm.
(3) From P as a centre draw an arc PR = 6 m, which intersects previous arc at R.
(4) Join PR and QR.
(5) Now, draw interior bisectors of ∠P, ∠QR ∠R which meets each other at point S.
Question 11.
One angle of a triangle is 80° and the other two are in the ratio 3 : 2. Find the unknown angles of the triangle.
Solution:
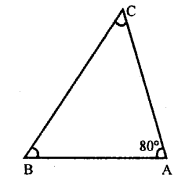
Let angle ∠A of a triangle ABC = 80°
But sum of three angles of a triangle = 180°
Sum of remaining two angles = 180° – 80° = 100°
Ratio in their two angles = 3:2
Let second angle = 3x
and third angle = 2x
3x + 2x = 100°
5x = 100 x = \(\frac { 100 }{ 5 }\) = 20°
second angle ∠B = 3x = 3 x 20° = 60°
and third angle ∠C = 2x = 2 x 20° = 40°
Hence other two angles are 60° and 40°.
Question 12.
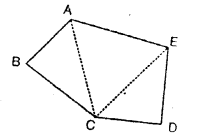
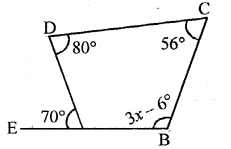
Find the value of x if ∠A = 32°, ∠B = 55° and obtuse angle AED = 115°.
Solution:
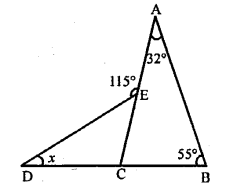
In the figure, ∠A = 32, ∠B = 55°
∠AED =115°
In ∆ABC
Exterior ∠ACD = ∠A + ∠B = 32° + 55° = 87°
Similarly in ∆CDE
Ext. ∠AED = ∠D + ∠ACD
⇒ 115° = x + 87° ⇒ x = 115°- 87° = 28°
Hence x = 28°