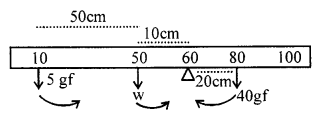
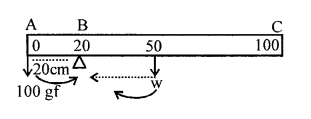
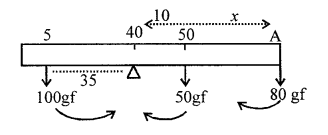
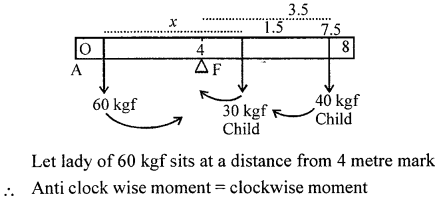
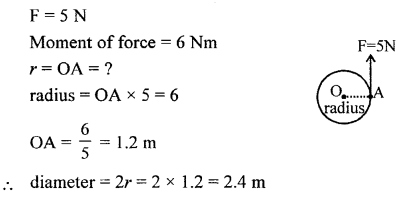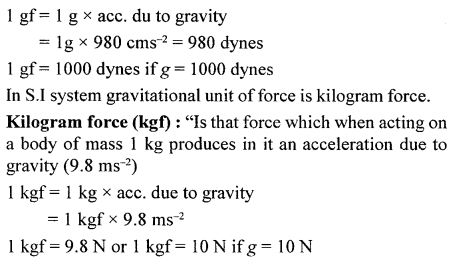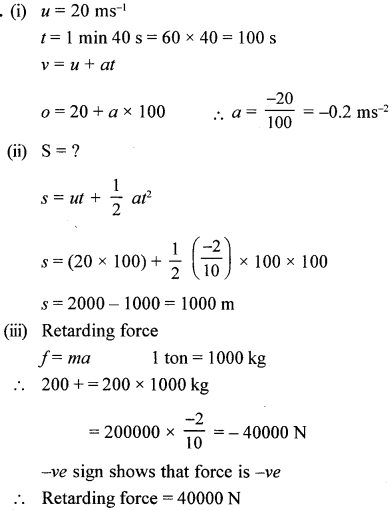A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Work, Power And Energy.
These Solutions are part of A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Work, Power And Energy.
Question 1.
(a) Define work.
(b) What are the conditions for doing work
(c) State the mathematical expression for work.
Answer:
(a) “When force is applied on the body and body moves (covers , some distance) in the direction of force, work is said to be done.”
Or
“Work is said to be done, when a force or its component causes a displacement in its own direction.”
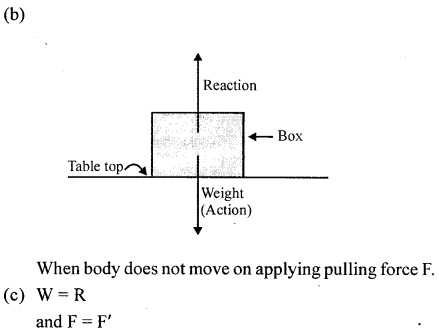
(b)
(1) Force should be applied.
(2) Displacement of body should be there.
(3) Work = Force x displacement
W = F x S
Question 2.
In which case work is done and why ?
(a) A man pushing a wall.
(b) A girl climbing a stair case
(c) A boy swimming in a tank.
(d) A man standing at a place and holding a suitcase in hand.
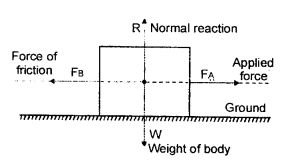
(e) A lady cooking food.
(f) A porter carrying a load on his head walking along a level road.
(g) A porter carrying a load and climbing upstairs.
Answer:
(a) A man pushing a wall does no work as wall does not move from its place and there is no displacement of wall in the direction of force.
(b) A girl climbing a staircase does work as component of force is in the direction of displacement.
(c) A boy swimming in a tank is doing work as force is applied in a direction opposite to the direction of displacement.
(d) The man is not doing work as displacement is zero.
(e) A lady cooking food is doing no work as displacement of lady is zero.
(f) A porter is doing no work as the direction of his displacement is at right angle (90°) and force of gravity is downward (vertically)
(g) Porter does work as component of force is in direction of displacement.
Question 3
A man climbs a slope and another walks the same distance on a level road. Who does more work and why ?
Answer:
The man who walk on a level road does no work as he is walking at right angle to the direction of gravitational force. Hence the man climbs a slope is doing more work.
Question 4.
(a) State the CGS and SI units of work.
(b) How is joule related to erg ?
Answer:
(a) CGS unit of work is erg or gcm2s2
S.I. unit of work is joule or kgm2s2
(b) 1 J = 107 ergs or 1 erg = 10-7 g
Question 5.
Define power. State two mathematical expressions for power.
Answer:
Work : “Rate of doing work is called power.”
Two mathematical expressions for power are :
\(\mathbf{P}=\frac{w}{t}\)
\(\mathrm{P}=\frac{\mathrm{F} \times \mathrm{S}}{t}=\mathrm{F} \times \frac{s}{t}=\mathrm{F} \times v\)
Question 6.
(a) State the absolute unit of power in SI system.
(b) What is horsepower ? What is its magnitude in SI unit ?
Answer:
(a) Absolute unit of power is watt.
(b) Horse power is unit of power used in engineering 1 H.P = 746 w .
Question 7.
(a) What is energy ? State and define SI unit of energy.
(b) Define potential energy. Give two examples of potential energy.
(c) Define kinetic energy. Give four examples of kinetic energy.
Answer:
(a) Energy : “Capacity of doing work”
S.I. unit of energy is Joule
(b)Potential energy: “Energy posserred by a body by virtue of it position or configuration is called potential energy.”
Example :
- A key to works on P.E. when we wind the key its shape changes and on unwinding this energy is used by to do work.
- A stone kept at a height, when drop can break a plate of glass because of P.E. possessed by it
(c) Kinetic energy: “Energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion.”
Examples :
- A bullet though of very small mass but moving with high speed and hence kinetic energy can peneterate a body.
- Running water of the river due its kinetic energy can rotate a turbine to produce electricity.
- A trunk running at high speed possesses kinetic energy and when hits a body can damage it.
- A shooting arrow possesses kinetic energy.
- Blowing wind possesses K.E.
Question 8.
What kind of energy is possessed by a body in the following cases ?
(a) A cocked-up spring and an air gun.
(b) A shooting arrow.
(c) A stone lying on the top of a housi.
(d) Water stored in the dam.
(e) An electron spining around the nucleus.
(f) A fish moving in water.
Answer:
(a) Potential energy, (stretched spring)
(b) Kinetic energy as arrow is in motion
(c) A stone lying on the top of a house has potential energy due to its position above the ground level.
(d) Water stored in dam has potential energy.
(e) An electron spining around the nucleus has kinetic energy.
(f) A fish moving in water has kinetic energy.
Question 9.
(a) State the law of conservation of energy.
(b) Prove mathematically the law of conservation of energy.
(c) Explain how a freely swinging pendulum obeys the law of conservation of energy.
(d) Name six kinds of energy familiar to you.
Answer:
(a) Law of conservation of energy : “Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
Though it can be transformed from one form to other.”
(b) Mathematical proof of law of conservation of energy :
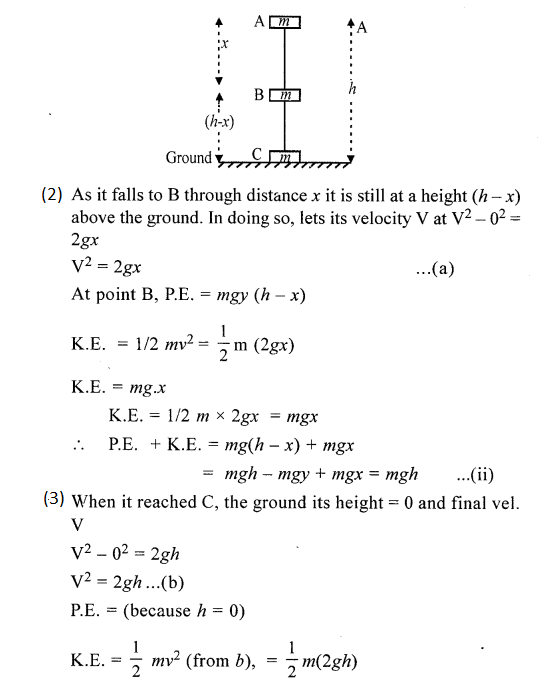
At A Consider a body of mass m at A at a height h above the ground level.
P.E. = mgh K.E. = 0 at rest.
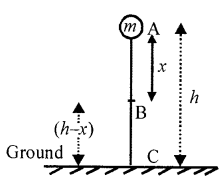
P.E. + K.E. = mgh + O = mgh …………….. (i)
Let it fall from A to B covering a distance x and still at (h-x) above ground.
In doing so
v2 – u2 = 2 gx
v2 – 0 = 2gx
v2 = 2gx …(a)
At B P.E = mg (h – x)
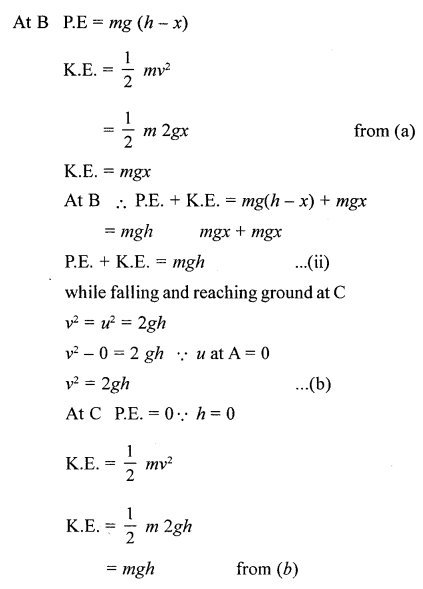
AT C P.E + K.E = 0 + mgh
P.E. + K.E. = mgh
Thus we find sum of P.E. + K.E. at A, B, C remains same mgh
Hence varifies the law of can servation of energy.
(c) Energy changes at B K.E. = O
at highest pt. vel. = O
P.E. = mgh
∴ the bob is at height h
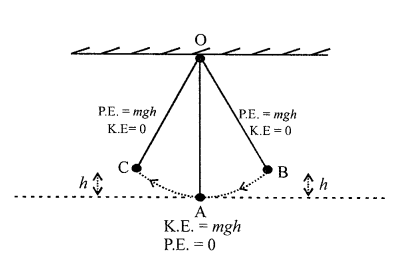
K.E. + P.E. = O + mgh = mgh …(i)
At A: As the bob moves towards A from B its height goes on decreasing and h at A is zero, but its vol. goes on increasing.
∴ At A, P.E. = 0 and K.E. = mgh
∴ P.E. + K.E. = 0 + mgh = mgh ….(ii)
At C : As the bob continues to move forward from B to C, its
velocity = 0 but height increases to h
∴ At C K.E. = 0 and P.E. = mgh
∴ K.E..+ P.E. = 0 + mgh
= mgh …(iii)
Thus we find that sum total of K.E. and P.E remains constant which is in accordance with conservation of energy.
(d) Six kinds of energy :
- E. (wind energy)
- Heat energy
- Sound energy
- Solar energy
- Electrical energy
- Nuclear energy
Question 10.
State the energy changes taking place in the following cases:
(a) Glowing of a torch bulb
(b) A toy car is wound and then allowed to move on the floor
(c) A truck climbing up a hill
(d) Water in a dam rotates a turbine coupled to a generator
(e) An air gun is loaded and then fired
(f) A piece of magnesium burns in air
(g) Water freezes in the freezing chamber of a fridge
(h) A stone dropped from a cliff
(i) Food eaten by humans
(j) Exposure of photographic film in sunlight
Answer:
(a) Electric energy into heat light energy.
(b) Potential energy into mechanical energy or kinetic energy.
(c) Heat energy into mechanical (P.E.) energy
(d) E. of water into electrical energy.
(e) Potential energy of spring into K.E. of bullet (pallel)
(f) Chemical energy into heat energy.
(g) Electrical energy into mechanical energy (to run compresor)
(h) Chemical energy into heat energy.
(i) Potential energy into kinetic energy.
(j) Light energy of Sun into chemical energy.
Question 11.
Give one example in each case
(a) when heat energy changes into kinetic energy.
(b) when kinetic energy changes into heat energy.
(c) when sound energy changes into electric energy.
(d) when electric energy changes into sound energy.
(e) when light energy changes into chemical energy.
(f) when chemical energy changes into light energy.
(g) when electric changes into magnetic energy.
(h) when magnetic energy changes into electric energy.
(i) when potential energy changes into electric energy.
(j) when electric energy changes into potential energy.
Answer:
(a) In steam engine heat energy moves the wheels of engine and changes into kinetic energy.
(b) When we rub the palms of our hands fast they become warm hence K.E changes into heat energy.
(c) Sound energy of microphone changes into electrical energy.
(d) Electrical energy changes into sound energy while flowing through the speaker.
(e) Exposure of photographic film in Sun light.
Or
During photosynthesis light energy changes into chemical energy.
(f) Burning of match stick by friction.
(g) The electrical energy in an electromagnet changes into magnetic energy.
(h) Motion of magnet in the coil i.e. in generaters.
(i) When water stored in dam rotates the turbine to produce electricity.
(j) During the pumping of water in an overhead tank by an electric motor pump, the electrical energy changes into kinetic energy of water. The kinetic energy of water then changes into potential energy.
Question 12.
Define kilowatt hour and convert it into joules
Answer:
Kilowatt hour : “When an electric power of one kilowatt flows through a conductor for one hour, then electrical energy which flows through the conductor is one kilowatt hour.”
1 KWH = 1000 W x 1h
1 KWH = 1000 W x (60 x 60) sec
= 1000 J/S x 3600 s
= 100000J
1 KWH = 105 J
Question 13.
Define electron volt and express it in joule.
Answer:
Electron volt : “The electric work done when an electron moves through an electric field at a potential difference of 1 volt.”
1 electron volt (eV) = charge on 1 electron x 1 volt
= 1.6 x 10-19C x IV
= 1.6 x 10-19 J [∵ 1C x IV = 1J)
1 [eV] = 1.6 x 1019 J
Multiple Choice Questions
Tick (✓ ) the most appropriate option.
1: A boy drags a load ‘L’ along horizontal plane AB by applying a force F. The boy does
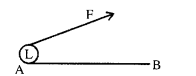
(a) no work
(b) some positive work
(c.) negative work
(d) none of these
2. The SI unit of work is joule. It is expressed in terms of mass, length and time as
(a) kg m2s-3
(b) kg m2s-2
(c) kg2 m2s-2
(d) kg m2s-2
3. The SI unit of power is watt. It is expressed in terms of mass, length and time as:
(a) kg m2s-3
(b) kg ms-3
(c) kg2 m2s-2
(d) kg ms-2
4. A stone resting on the roof ofa building has
(a) potential energy
(b) gravitational energy
(c) kinetic energy
(d) none of these
5. A falling raindrop has :
(a) only kinetic energy
(b) only potential energy
(c) both kinetic and potential energy
(d) none of these
6. One horse power is equal to :
(a) 764 W
(b) 746 W
(c) 700 W
(d) 1000 W
7. One electron volt is equal to :
(a) 6 x 10-17 J
(b) 6.1 x 10-19 J
(c) 6 x 10-19 J
(d) 1.6 x 10-10 J
8. Kilowatt hour is the commercial unit of:
(a) electric power
(b) electric energy
(c) electric force
(d) none of these
9. Power is the product of:
(a) force and velocity
(b) force and displacement
(c) force and acceleration
(d) force and time
10. An aeroplane is flying at an altitude of 10,000 m at a speed of 300 km/hour. The aeroplane at this height has :
(a) only kinetic energy
(b) only potential energy
(c) both kinetic and potential energy
(d) zero kinetic and potential energy
11. Kilocalorie is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of:
(a) one gram of water through 1°C
(b) 1 kg of water through 100°
(c) one kg of water through 1°C
(d) 1 kg of water through 10°C Arts.
12. When a flash light is switched on the electric energy
(a) directly changes to light energy
(b) first changes to light energy and then to heat energy
(c) first changes to heat energy and then to light energy
(d) none of above
13. A pendulum is swinging freely. The bob ofpendulum has:
(a) maximum K.E. at its extreme positions
(b) minimum K.E. at its mean position
(c) maximum K.E. at its mean position
(d) both (b) and (c)
14. A pendulum is oscillating freely. Its bob has :
(a) only kinetic energy
(b) maximum kinetic energy at extreme position
(c) maximum potential energy at its mean position
(d) a constant energy which is the sum of potential and kinetic energy
15. A ball of mass m is dropped from height ‘h ’.
(a) Potential energy of the ball at ground level is mgh.
(b) Potential energy of the ball at height h is mgh.
(c) kinetic energy of the ball at ground level is mgh
(d) both (b) and (c)
Numerical Problems on Work, Power & Energy
Practice Problems 1
Question 1.
A girl of mass 50 kg climbs a flight of 100 stairs each measuring 0.25 m in height, in 20s. Find
(a) force acting on the girl
(b) work done by the girl
(c) gain in potential energy
(d) power in (1) watts (2) Horse
[Taking g = 10 ms-2, 1 HP = 750 W]
Answer:
mass = 50 kg g = 10 ms-1
(a) Force acting on the girl F = mg
F = 50 x 10 = 500 N
(b) Work done by girl W = F x S
W = 500 x 25 = 12500 J
(c) Gain in pot. energy = mgh
50 x 10 x 25 = 12500 J
Or
Gain in P.E. = Workdone = 12500 J

Question 2.
A load of 220 kg is vertically pulled up by a crane through a vertical height of 16 m in 40 s. Calculate
(1) Force acting in the upward direction
(2) Total work done
(3) Horse power of the engine pulling the rope [Take g = 9.8 ms-2 ; 1 HP = 750 w]
Answer:
Mass m = 220 kg g = 9.8 ms-2 h= 16 m t = 40 s
(1) Force F = mg
= 220 x 9.8 = 2156 N
(2) Total work done = W = F x S
W = 2156 x 16 = 3496 J
(3) \(Horse power of engine \frac{3496}{40} \mathrm{J}=87.4 \mathrm{w}\)
\(=\frac{3496}{40 \times 750}=1.15 \mathrm{HP}\)
Practice Problems 2
Question 1.
A work of 1000 J is done on a body in 4 s, such that a displacement of 20 m is caused. Calculate
(a) force (b) power
Answer:
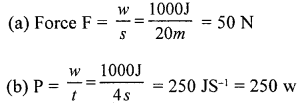
Question 2.
What force must be applied to a body through a distance of 10 m, such that it does a work of 4000 J. If the mass of the body is 20 kg, what is the acceleration of the body ?
Answer:
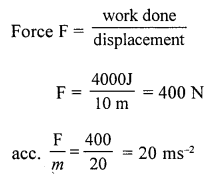
Question 3.
An engine of power 200 W, operates for 4 s. Find the work done by the engine. If the force developed by the engine is 100 N calculate the maximum displacement caused.
Answer:
p = 200 W t = 4 s
workdone = p x t
200 x 4 = 800 J
\(\text { displacement }=\frac{w}{\mathrm{F}}=\frac{800 \mathrm{J}}{100 \mathrm{N}}=8 \mathrm{m}\)
Practice Problems 3
Question 1.
Calculate the horse power of the motor of an elevator, which can carry 10 persons of average mass 60 kg
through a vertical height of 20 m in 30 s. [Take g = 10 N/ kg]
Answer:
Total mass of 10 persons = 60 x 10 = 600 kg
F = mg = 600 x 10 = 6000 N
displacement = h = 20 m t = 30 s
work done = w = F x h = 6000 x 20 J
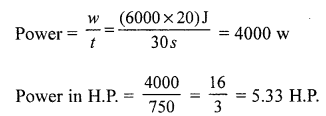
Question 2.
Calculate the power of an electric pump in horse power, which can lift 2000 m3 of water from a depth of 20 m in 25 minutes. [Take g = 10 ms 2 and 1 ml of water = 103 kg]
Answer:
1 m3 of water = 103 kg
∴ 2000 m3 of water has mass = m = 20 00 x 103 kg
wt. = force = mg = 2000 x 1o3 x 10N
Displacement = depth = 20 m
work done = F x S t = 25 min = (25 x 60) S

Question 3.
Calculate the height through which a crane can lift a load of 4 t, when its motor of 4 HP operates for 10 s.[Take g = 10 ms-2]
Answer:
h = 2 t= 10 s
mass = m = At = 4 x 1000 = 4000 kg
force F = mg = 4000 x 10 N
work done = F x h
= 4000 x 10 h
Power = 4HP = 4 x 750 w
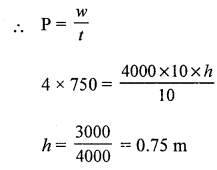
Question 4.
For how long must an electric motor pump of2 HP operate, so as to pump 5 m3 of water from a depth of 15 m.[Take g = 10 N/kg, 1 m3 of water = 103 kg]
Answer:
t = ?
power = 2HP = 2 x 750w
p x t = work done
2 x 750x; = (mass x g) x displacement
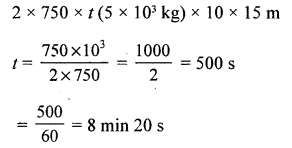
Practice Problems 4
Question 1.
An electric pump is 60% efficient and is rated 2 HP. Calculate the maximum amount of water it can lift through a height of 5 m in 40 s. [Take g = 10 ms-2 and 1 HP = 750 W]
Answer:
Power of lift pump = 2 HP
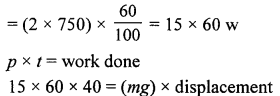
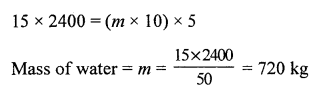
Question 2.
Calculate the time for which a motor pump of 10 HP and efficiency 80% must be switched on, so as to pump 20 m3 of water through a vertical height of 20 m.[Density of water = 1000 kg m3; g = 10 ms-2; 1 HP = 750 W]
Answer:
Power of motor pump =10 HP
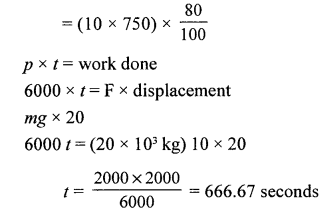
Question 3.
In a hydroelectric power station, 1000 kg of water is allowed to drop a height of 100 in in ¡ s. If the conversion of potential energy to electric energy is 60%, calculate the power output.
[Take g = 10 ms-2]
Answer:
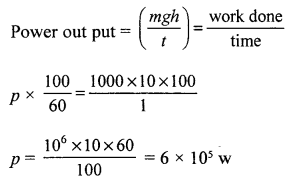
Practice Problems 5
Question 1.
A compressed spring is held near a small toy car of mass 0.15 kg. On the release of the spring, the toy car moves forward with a velocity of 10 ms’. Find the potential energy of the spring.
Answer:
mass of car m = 0.15 kg
velocity y = 10 ms-1
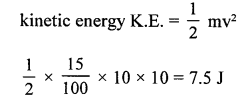
Question 2.
A catapult throws a stone of mass 0.10 kg with a velocity of 30 ms-1. If 25% of the RE. of the elastic band is wasted during transmission, find the magnitude of the potential energy.
Answer:
Let pot. energy = RE.
P.E. wasted = 25%
P.E. used 100—25 = 75%

Practice Problems 6
Question 1.
A body of mass 20 kg is moving with a velocity of 1 ms-1 Another body B of mass 1 kg is moving wills a velocity of 20 ms-1. Find the ratio of kinetic energy of A and B.
Answer:
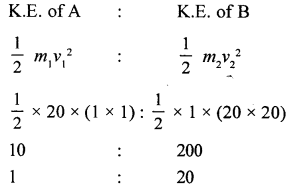
Question 2.
A bullet of mass 0.2 kg, moving with a velocity of 200 ms-1 , strikes a stationary wooden target of mass 5 kg. If all the energy is transferred to the wooden target, calculate the velocity with which the target towards direction.
Answer:
Let the other body (B) moves with kinetic energy of bullet = K.E. of wooden target (B)
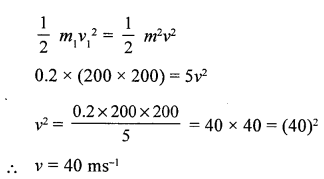
Practice Problems 7
Question 1.
A body of mass m has a velocity v. If the mass of the body increases 81 times, but the kinetic energy remains same, calculate the new velocity.
Answer:
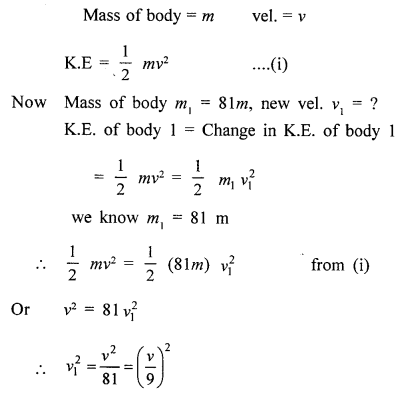
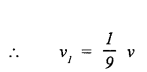
Question 2.
A body P has KE energy E. Another body Q, whose mass is 9 times than P, also has kinetic energy E. Calculate the ratio of velocities of P and Q.
Answer:
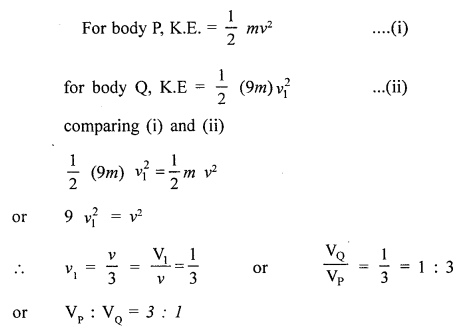
Practice Problems 8
Question 1.
(a) Force of gravity acting on the barrel. (Take g — 10 ms-2)
(b) Work done by the force in pulling body along the inclined plane
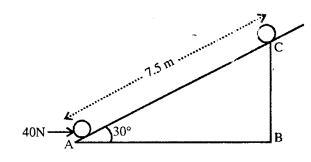
(c) Work done against the force of gravity.
Answer:
(a) Force of gravity F mg
F = 2.5 x 10 = 25
(b) Work done in pulling the body along the inclined plane = F x displacement
= 40x 7.5 J
W = 300 J
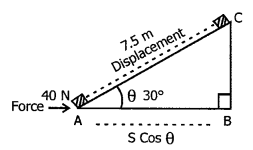
(c) Work done against force of gravity
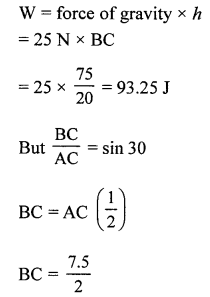
Question 2.
Adjacent diagram shows a body of mass 5 kg pulled up an inclined plane by a
force of 30 N.
(a) Calculate forced by gravity acting on body. (Take g = 10 ms-2)
(b) Work done by the force in pulling body along the inclined plane.
(c) Work done against the force of gravity.
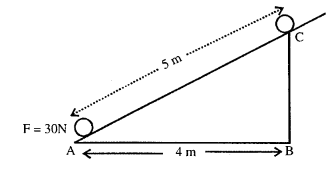
Answer:
Mass of body = 5 kg
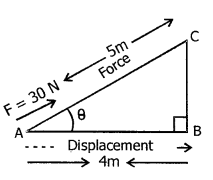
(a) Force of gravity acting on the body
F = mg
F = 5 x 10 = 50 N
(b) Work done by force in pulling the body along the inclined plane = F x displacement
W = 30 N x 5 m
= 150 J
(c) Work done against force of gravity
= (mg) x BC
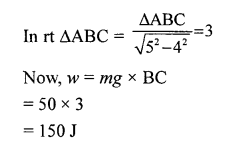
Practice Problems 9
Question 1.
A scooter develops a power of 1 HP while running at 36 km hr-1. Calculate the force generated by its engine.
Answer:
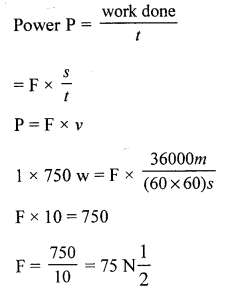
Question 2.
The engine of a car develops a power of 5 HP and force 500 N while running a uniform speed S. Calculate the value of S.
Answer:

Practice Problems 10.
Question 1.
The heart of a normal person beats 72 times in a minute and does a work of 1 joule per beat. What is power of the heart ?
Answer:
Work done per beat = 1 J
work done for 72 beats = 72 J
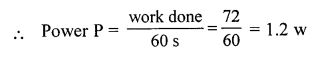
Question 2.
The heart of a deer chased by a tiger beats 200 times in a minute and does a work of 1.4 joules per beat. What is the power of heart ?
Answer:
Heart beats per minute = 200
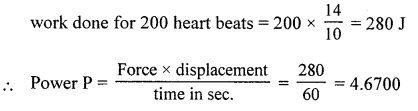
Practice Problems 11
Question 1.
A beam of electrons has an energy of 1 joule. How many electrons are in the beam ? [1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19]
Answer:
Let there are n electrons in beam
Energy of n electrons in beam = 1 J
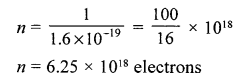
Question 2.
An accelerated electron has energy of 9.6 x 10-18 J. Express the energy in electron volts (eV)
Answer:

Practice Problems 12
Question 1.
Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass 100 g and having a momentum of 20 kg ms-1.
Answer:
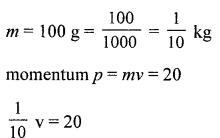
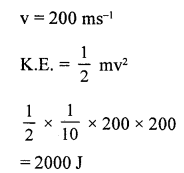
Question 2.
Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass 5 kg momentum 50 kg ms-1
Answer:
Mass m = 5 kg
move (Questions from ICSE Examination Papers) (Questions from ICSE Examination Papers) mentum p = mv = 50 kg ms-1
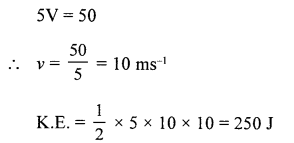
Practice Problems 13
Question 1.
A spring is kept compressed by a toy car of mass 100 g. On releasing the pressure the car moves out with a speed of 0.5 ms-1. Calculate the potential energy of the compressed spring.
Answer:
Kinetic energy = P.E.
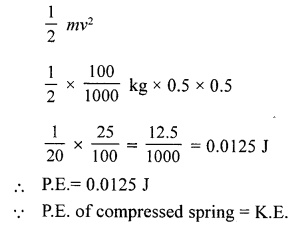
Question 2.
A lead pallet of mass 10 g leaves an air gun with a velocity of 40 ms-1 . What is the magnitude of potential energy stored by its spring?
Answer:

Questions from ICSE Examination Papers
2002
Question 1.
(a) A machine raises a load of 800 N through a height of 15 m in 5 s. Calculate the power at which the machine works.
(b) State the principle of conservation of energy.
Answer:
(a) Load = mg = 800 N
displacement h = 15 m, t = 5s P = ?

(b) Conservation of energy: “Energy can neither be created nor destroyed.”
Question 2.
(a) State SI unit of the momentum of a body.
(b) Define : (1) work (2) Power (3) Energy.
(c) How is work related to applied force ?
(d) By what factor does the kinetic energy of a moving body change, when its speed is reduced to one third of the initial velocity ?
(e) What does the unit kilowatt hour measure ?
(f) From the ground floor, a man comes up to the third floor of a building using a staircase. Another person comes up to the mine floor, using an elevator. Neglecting friction, compare the work done in two cases.
Answer:
(a) S.I. unit of momentum is kgms-1
(b)
- Work: “If force is applied on a body and body moves in the direction of force. Work is said to be done.”
- Power: “Rate of doing work is called power.
- Energy: “Capacity of doing work is called energy.”
(c) W α p
or W α F cos 0
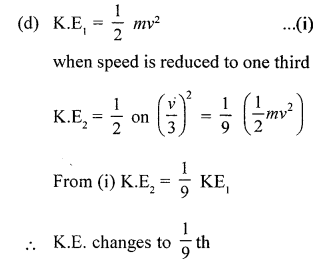
(e) Kilowatt hour measures Electrical energy consumed.
(f) Displacement in both cases is from ground floor to third floor work done in each case is same
i.e. 1 : 1
Question 3.
(a) The weights of two bodies are 2.0 N and 2.0 kgf respectively. What is the mass of each body ?
(g = 10 ms-2) .
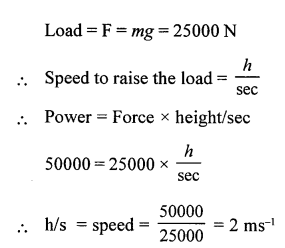
(b) If the power of a motor is 40 kW, at what speed can it raise a load of 20,000 N ?
Answer:
(a) Weight = mg = 2N
m x 10 = 2

2003
Question 4.
(a) The weights of two bodies A and B are 5.0 N and 5.0 kgf respectively. What is the mass of each body ?(g = 10 ms)
(b) If the power of a motor is 50 kW, at which speed can it raise a load of 25,000 N ?
Answer:
(a) wt. of body A = 5.0N
mg= 5
m x 10 = 5
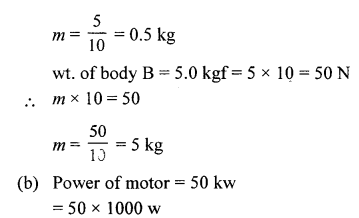
2004
Question 5.
(a) What energy changes take place in an oscillating pendulum ?
(b) Two objects A and B have masses in the ratio of 2:1 and are dropped from the same height.
Answer the following questions :
- What is the ratio of velocities of A and B, when they strike the ground ?
- What is the ratio offorces of A and B, when they strike the ground ?
Answer:
(a) At A
P.E. is max and K.E. is zero
As bob moves towards B, P.E. goes on decreasing K.E. goes on increasing
P.E. = zero K.E.max
As the bob moves to C
K.E. goes on decreasing and P.E. goes on increasing
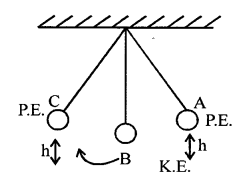
At C
P.E. is maximum and K.E. is zero
(b) (1) Mass of body B = m Mass of body A = 2m
They are dropped from the same height using
v2 – u2 = 2gh
v2 = 2gh is independent of mass and hence mass if not taken into account

Question 6.
A ball of mass 0.5 kg is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 8 m/s. Calculate the maximum potential energy it gains at the highest point.
Answer:
v2 – u2 = 2gh
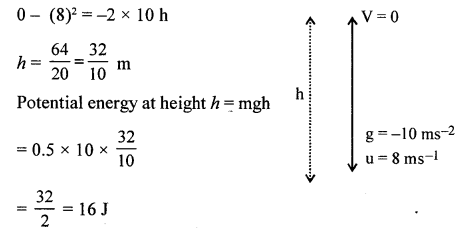
2005
Question 7.
(a) Which physical quantity does the electron volt measure? How is it related to SI unit of this quantity ?
(b) What would be the angle between force and displacement to get the (1) minimum work, (2) maximum work ?
(c)The work done by the heart is 1 J per Calculate the power of the heart, if it beats 72 times a minute.
(d) State the law of conservation of energy.
(e) Name the chief energy transformations that occur :
- in a loud speaker,
- in an electric ell.
Answer:
(a) Energy (electrical)
Relation with S.I. unit 1 ev = 1.6 x 10-19 J
(b) To get minimum work = 90°
To get maximum work = 0°
(c) See practice problem 10 Q. 1. page 56
(d) Law of conservation of energy :
“Energy can neither be created nor destroyed”
(e)
- Sound energy of man changes into electrical energy changes in microphones and electrical energy changes into sound energy, while flowing through the speaker.
- Chemical energy changes into electrical energy.
2006
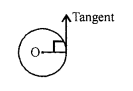
Question 8.
State the amount of work done by an object, when it moves in a circular path.
Answer:
Amount of work done when an object is moving in circular path is zero because the force acting and the displacement are at right angle.
Question 9.
Show that for the free fall of a body, the sum of mechanical energy at any point in its path is constant. Answer:
See Q. 9(b) Ex. 1
Question 10.
Define newton, in SI unit of force. State its relationship with CGS unit of force.
Answer:
- One newton is that force which when acting on a body of m ass 1 kg, produces an acceleration of
1 m s-2 in it. - S.I. unit of force is newton (N) and C.G.S. unit is dyne.
IN = 105 dyne.11.
Question 11.
Calculate the height through which a body of mass 0.5 kg should be lifted, if the energy spent for doing so is 1.0 joule. [g = 10 m/s2]2
Answer:
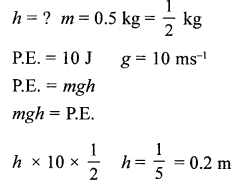
2007
Question 12.
Two bodies, A and B, of equal mass are kept at heights 20 m and 30 m respectively. Calculate the ratio of their potential entergies.
Answer:
∵ mass of body A = mass of body B = m
∴ P.E. of A : P.E. of body B
mgh, : mgh2
h1 : h2
20 : 30
2 : 3
Question 13.
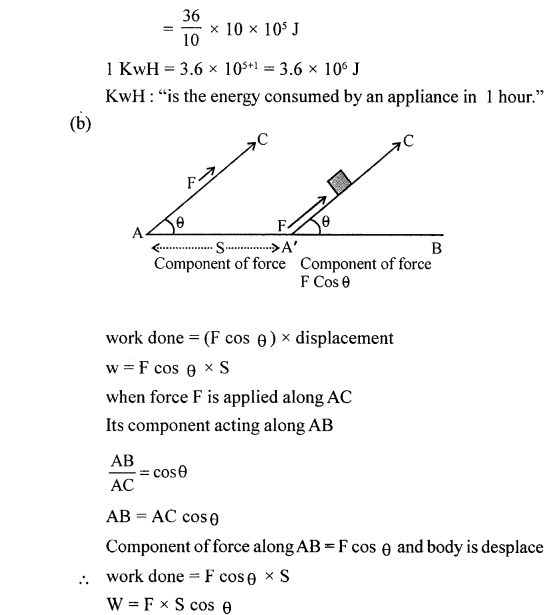
(a) Define kilowatt hour. How is it related to joule ?
(b) How can the work done be measured when force is applied at an angle to the direction of displacement ?
Answer:
(a) Kilowatt hour
kwH
1000 w x (60 x 60) s
1000 j/s x 3600 s
= 36 x 100000 J
1 KwH = 36 x 105 J
Question 14.
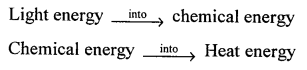
What is the main energy transformation that occurs during
(a) Photosynthesis in green leaves ;
(b) Charging of a battery ?
Answer:
(a) Energy changes during photosynthesis
(b) Charging of battery : Electrical energy supplied into chemical energy of battery than Chemical energy into electrical energy.
2008
Question 15.
(a) When an arrow is shot from a bow, it has kinetic energy in it. Explain briefly from where does it get its kinetic enrgy ?
(b) What energy conversions take place in the following when they are working (1) electric toaster (2) microphone ?
Answer:
(a) When an arrow is shot is gets its energy from the stretched bow/P.E. which in turn gets energy from the muscles of person stretching it.
i.e. P.E. of bow is transformed into K.E. of arrow.
(b)
- Electric energy is transformed into heat energy in a electric toaster.
- Sound energy of speaker is transformed into electric energy while flowing through a microphone.
Question 16.
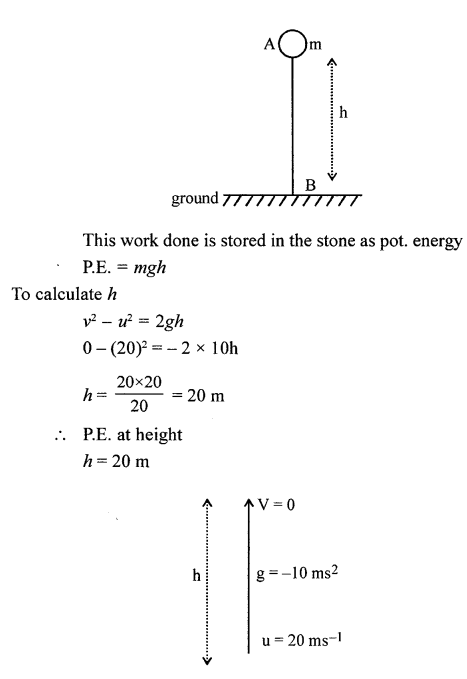
(a) A stone of mass 64.0 g is thrown vertically upward from the ground with an initial speed of 20.0 m/s. The gravitational potential energy at the ground level is considered to be zero. Apply the principle of conservation of energy and calculate the potential energy at the maximum height attained by the stone, (g – 10 ms-2)
(b) Using the same principle, state what will be the total energy of the body at its half-way point ?
Answer:
When a stone is thrown vertically upward, work has to be done against gravity. At maximum height h. the work done = force x displacement
W = mg x h
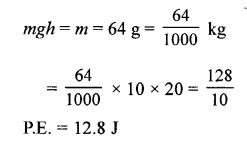
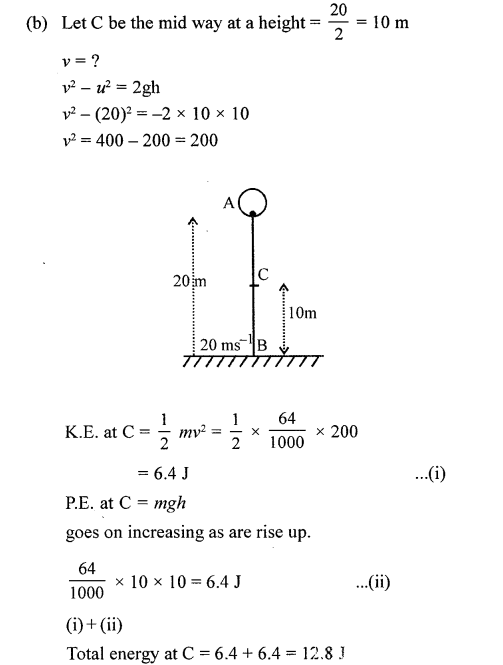
Question 17.
Define ‘joule’, the SI unit of work and establish a relationship between the SI and CGS units of work.
Answer:
Joule : “Is the work done when a force of 1 N displaces a body through 1 meter in the direction of force”.
Relation between S.I. and C.G.S. units
1J= 1 N x 1m

2009
Question 18(a).
What is the SI unit of energy ? How is the electron volt (eV) related to it ?
Answer:
Joule is SI unit of energy
Relation between eV and J
1 eV = charge on 1 electron x 1 V
1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 [∵ 1 Lx 1 V- 1 J]
J x 1V
1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J
Question 18(b).
State the energy changes that take place in the following when they are in use :
(1) a photovoltaic cell. (2) an electromagnet.
Answer:
- In photovoltaic cell, light energy is transformed into electrical energy.
- In an electromagnet, electrical energy is transformed into magnetic energy.
Question 18(c).
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with a velocity of 10ms-1. What will be the ratio of its initial kinetic energy and final kinetic energy, if the mass of the body is doubled and its velocity is halved ?
Answer:
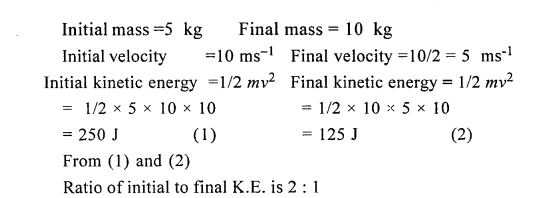
Question 19.
6.4 kJ of energy causes a displacement of 64 m in a body in the direction of force in 2.5 seconds. Calculate (1) the force applied (2) power in horse power (HP).(Take 1 HP = 746 W).
Answer:
- Energy = 6.4 kJ = 6.4 x 1000 J = 6400 J
S = 64 m in the direction of force
t = 2.5 sec F = ?
P = ? (in HP)
Energy = Work done = F x S in the direction of force
∴ F = Energy / S = 6400 / 64 = 100N -
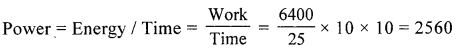
Power in Hp =2560/746=3.43 Hp
Question 20.
An object of mass ‘m’ is allowed to fall freely from point A as shown in the figure. Calculate the total mechanical energy of the object at: (1) Point A (2) Point B (3) Point C (4) State the law which is verified by your calculations in parts (1), (2) and (3).
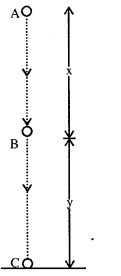
Answer:
(1)
At point A,
Mechanical energy means K.E. + P.E.
At height h above ground K.E. = 0 [ ∵ body is at real]
P.E. = mgh
KE + P.E. = 0 + mgh = mgh
Total mechanical energy = mgh …….(i)
K.E. mgh
K.E.+P.E.mgh+O=mgh
(4) The law which is verified in parts (I), (ii) and (iii) ¡s
conservation of energy i.e., total energy remains conserved.
It may change from one form to another.
2010
Question 21.
(a) A toy is acted upon by a force. State two conditions under which the work done could be zero.
Answer:
We know that W = FS cosθ. clearly, work done by the force will be zero if.
- ) S = 0 i.e., no displacement takes place
- If θ = 90°, then cos 90° = 0, and W = 0;.e., when the force acts perpendicular to the direction of motion.
(b) A spring is kept compressed by a small trolley of mass 0.5 kg lying on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure given below :
When the trolley is released, it is found to move at a speed of 2m s-1.
What potential energy did the spring possess when compressed?
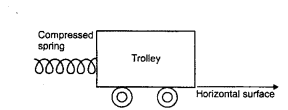
Answer:
When spring is compressed, there is a potential energy stored in it. When the trolley is released the potential energy of spring is converted into kinetic energy of the trolley
Question 22.
A body of mass 50 kg has a momentum of 3000 kg ms-1. Calculate :
- the kinetic energy of the body.
- the velocity of the body.
Answer:
(1) Mass m = 50 kg
Momentum P = mv = 3000
mv = 3000
50(v)=3000
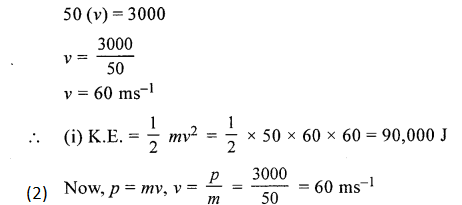
Question 23.
(a) A ball of mass 200 g falls a height of 5 m. What will be its kinetic energy when it just reaches the ground ? (g = 9.8 m s-2)
Answer:
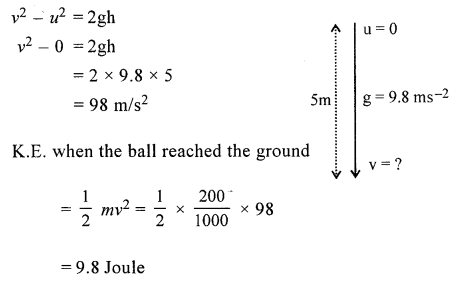
(b) What is energy degradation ?
Answer:
There is no degradation of energy as P.E. = mgh =
\(\left(\frac{200}{1000} \times 9.8 \times 5\right)=9.8 \mathrm{J}\) is transformed in K.E.=9.8J at ground
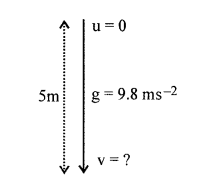
(c) Draw a diagram to show the energy changes in an oscillating simple pendulum. Indicate in your diagram the total mechanical energy in it remains constant during the oscillation.
Answer:
The variation of potential and kinetic energy is as shown. The total energy remains constant.
2012
Question 24(a).
(a) A ball is placed on a compressed spring. When the spring is released, the ball is observed to fly away.
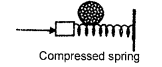
- What form of energy does the compressed spring possess?
- Why does the ball fly away ?
Answer:
(1) The compressed spring possesses potential energy.
(2) The potential energy of the spring on releasing changes to kinetic energy. It is the kinetic energy which makes the ball to fly away.
Question 24(b).
(1) State the energy conversion taking place in a solar cell.
(2) Give disadvantage of using a solar cell.
Answer:
(1) In a solar cell, the light energy directly changes to electric energy.
Disadvantage of using a solar cell
(2)
- Solar cell does not produce electric energy during night or in darkness.
- High cost
- Loss efficiency : A solar cell can convert only about 25% of the light.
Question 24(c).
A body of mass 0.2 kg falls from a height of 10 m to a height of 6 m above the ground level. Find the loss in potential energy taking place in the body, [g = 10 ms-2]
Answer:
Loss in potential energy = mass x g x loss of height
= 0.2 kg x 10 ms-2 x 4 m = 8 J
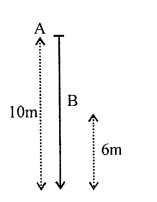
Question 24(d).
A moving body weighing 400 N possesses 500 J of kinetic energy. Calculate the velocity with which the body is moving, (g = 10 ms-2)
Answer:
Weight of the body = mg
m x 10 = 400
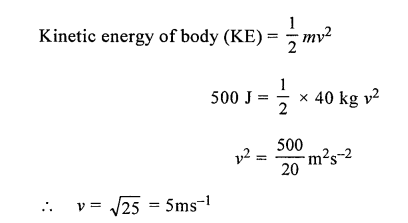
2013
Question 25(a).
(a) A force is applied on a body of mass 20 kg moving with a velocity of 40 ms-1. The body attains a velocity of 50ms-1 in 2 seconds. Calculate the work done by the body.
Answer:
m = 20 kg
u = 40 ms-1
v = 50 ms-1
t = 2s
a = ?
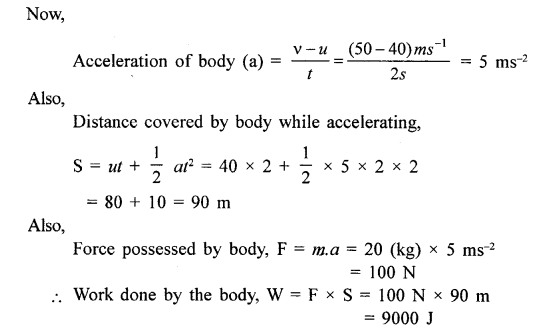
Question 25(b)
A girl of mass 35 kg climbs up from the first floor of a building at a height 4 m above the ground to the third floor at a height 12 m above the ground. What will be the increase in her gravitational potential energy ?(g = 10 ms-2).
Answer:
Mass of girl (m) = 35 kg
Height gained by girl (h) = (12 – 4) = 8 m
Increase in gravitational potential
energy = mgh = 35 (kg) x 10 ms-2 x 8 m
= 2800 J
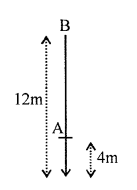
Question 25(c).
- State the Principle of conservation of energy.
- Name the form of energy which a body may possess even when it is not in motion.
Answer:
- Law of conservation of energy : Energy in a system cannot be created, nor be destroyed though, it can be transfered from one form to another.
- Potential energy.
2014
Question 26(a).
- When does a force do work?
- What is the work done by the moon when it revolves around the earth?
Answer:
- Work is said to be done only when the force applied on a body makes the body moves he., there is displacement of the body.
- No work is done as moon revolves around the earth in Circular Path and angle between force acting towards the center of circle and tangent at any point in circular path is 90°.
Question 26(b)
Calculate the change in the Kinetic energy of a moving body if its velocity is reduced to l/3rd of the initial velocity
Answer:

Question 26(c)
State the energy changes in the following devices while in use:
- A loud speaker.
- A glowing electric bulb.
Answer:
- First sound energy is converted into electrical energy in microphone. Then electrical energy is converted into sound energy in loud speaker.
- Electrical energy converted to light and heat energy.
Question 26(d)
The conversion of part of the energy into an undesirable form is called Dissipation of energy
Question 27(a).
A man having a box on his head, climbs up a slope and another man having identical box walks the same distance on a leveled road. Who does more work against the force of gravity and why ?
Answer:
Man climbs up a slope does more work because the work done by the man walking on a leveled road is zero.
Question 27(b).
A body is thrown vertically upward. Its velocity keeps on decreasing. What happens to its kinetic energy as its velocity becomes zero ?
Answer:
The K.E. is transformed into potential energy where K.E. is 0 (at the highest point) or velocity becomes zero.
2015
Question 28(a).
How is work done by a force measured when the force:
- is in the direction of displacement?
- is in an angle to the direction of displacement?
Answer:
- When force is in the direction of displacement θ= 0°, then cos0 = 1.
Hence, the work done by a force measured in the direction of displacement is
W = F x S
The work done is maximum and positive. - When the displacement is in the direction making an angle . with the direction of force,
Work done = Component of force in the direction of displacement x displacement
W.F = cosθ x s
Question 28(b).
State the energy in the following while in use:
- Burning of a candle.
- A steam engine.
Answer:
- Burning of a candle: Conversion of chemical energy to light and heat energy. When a candle bums, it gives light and heat.
- A steam engine : Conversion of heat energy into mechanical energy.In a steam engine, chemical energy of coal first changes to heat energy of steam, and then heat energy changes to mechanical energy.
Question 28(c).
(1) A scissor is a_________ multiplier
(2) 1 kWh =________ J.
Answer:
- A scissor is a force multiplier because the effort applied is less than the load.
- 1 kWh = 1 kilowatt x 1 hour
= 1000 J s- x 3600 s = 3.6 x 106 J
Question 28(d).
Rajan exerts a force of 150 N in pulling a cart at a constant speed of 10 m/s. Calculate the power exerted.
Answer:
Given that
Force = 150 N
Velocity = 10 ms-1
Power = F x v = 150 N x 10 ms-1
= 1500 w
Question 29.
(a) Name the physical quantity measured in terms of horse power.
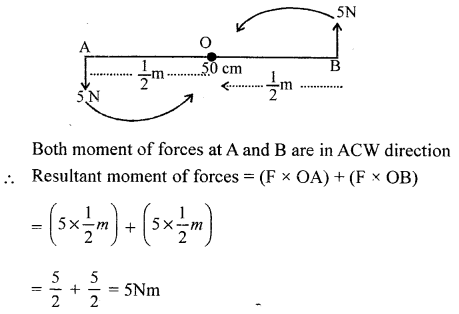
(b) A nut is opened by a wrench of length 20 cm. If the least force required is 2N, find the moment of force needed to loosen the nut.
(c) Explain briefly why the work done by a fielder when he takes a catch in a cricket match is negative.
Answer:
(a) Power is measured in horse power. 1 HP = 746 W
(b) According to the principle of moments, we have Moment of load about the fulcrum = Moment of effort about the fulcrum Load x Load arm = Effort x Effort arm
Given that the effort arm = 20 cm = 0.2 m, the minimum force E = 2 N
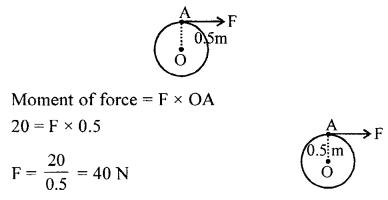
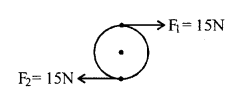
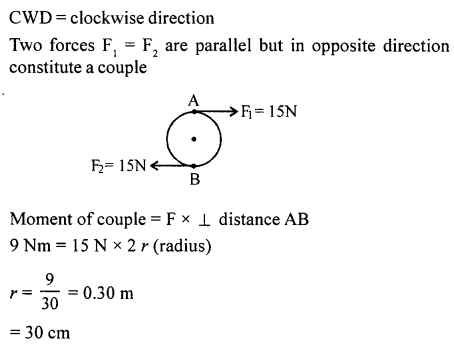
Therefore, the moment of load or the moment of force = 0.2 93 Work, Power and Energy x 2 = 0.4 NmThe moment of force needed to loosen the nut = 0.4 Nm
(c) The work done by a fielder when he takes a catch in a cricket match is negative because the force applied by the fielder is in the direction opposite to the displacement of the ball. The angle between the force applied and the displacement of the ball is 180° We know that work done = -F.s
2016.
Question 30.
A boy weighing 40 kgf climbs up a stair of 30 steps each 20 cm high 4 minutes and a girl weighing 30 kgf does the same in 3 minutes compare
(a) Work done by them
(b) Power developed by them
Answer:
Given:
Force of gravity of the boy, Fb = 40 kg x 10 Nkg1
= 400N
Time taken by him tb= 4 minutes = 4 x 60 s = 240 s
Force of gravity of the girl, Fg = 30 kgf x 10 Nkg-1
= 300 N
Time taken by her, tg = 3 minutes = 3 x 60 s=180 s
Distance covered by both in 30 steps is D = 30 x 20 = 600 cm = 6 m
While climbing, both have to do work against the force of gravity, 1
(1) Work done by the boy in climbing the stairs:
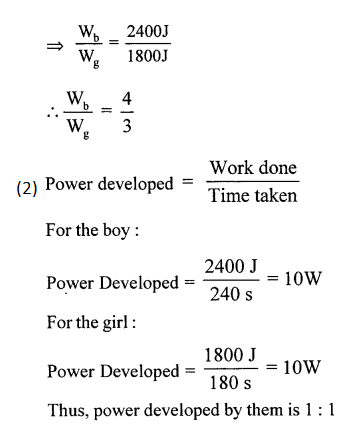
Wb = F x D = 400 N x 6 m
Wb = 2400 j
Work done by the girl in climbing the stairs:
Wb = F x D = 300 N x 6
Wg= 1800 J
More Resources
- A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 History and Civics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English Literature and Language
- Merchant of Venice Workbook Answers – ICSE Class 10 English
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Poems Workbook Answers
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Short Stories Workbook Answers
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English – A Collection of Poems & Short Stories
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
Hope given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Work, Power And Energy are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. APlusTopper try to provide online science tutoring for you.