ISC Commerce Previous Year Question Paper 2018 Solved for Class 12
Maximum Marks: 80
Time allowed: Three hours
- Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.
- Answer Question 1 (Compulsory) from Part I and five questions from Part II, choosing two questions from Section A, two questions from Section B and one question from either Section A or Section B.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
- Transactions should be recorded in the answer book.
- All calculations should be shown clearly.
- All working, including rough work, should be done on the same page as, and adjacent to the rest of the answer.
Part – I (20 Marks)
Answer all questions.
Question 1. [10 × 2]
Answer briefly each of the questions (i) to (x):
(i) Name the two dimensions of business environment.
(ii) What is meant by factoring ?
(iii) What is a debit card ?
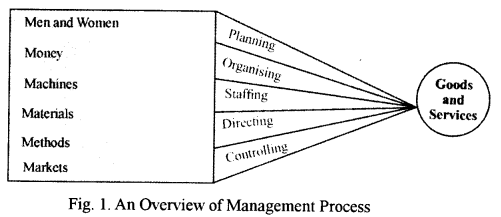
(iv) Why is management considered to be a discipline ?
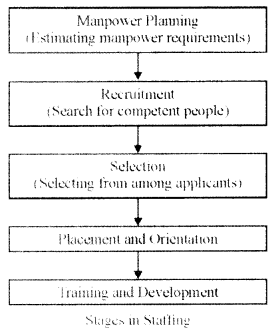
(v) Explain any two sources of external recruitment used in today’s world.
(vi) Name the four elements of directing, as a function of management.
(vii) Distinguish between achertisement and publicity.
(viii) Mention two types of markets, on the basis of the position of buyers and sellers.
(ix) The producer of Lime Fresh’ tea introduces ‘Buy one Get one’ scheme on all the products of ‘Lime Fresh’. Identify the promotional strategy’ used by the producer. State any one objective that could be met by this strategy.
(x) Expand the following terms :
(a) RTGS
(b) NEFT
Answer:
(i) The two dimensions of Business Environment are :
- Micro Environment
- Macro Environment
(ii) Factoring implies raising finance through the sale or mortgage of book debts. The finance companies provide finance to business concerns through outright purchase of accounts receivables. The debtors of the firm make payments to it which in turn forwards them to the finance company.
(iii) A people can get a debit card by depositing money in the bank. The card holder can make immediate payment for the goods purchased or sendees availed with the help of debit card availed provided the seller has the terminal facility. Debit card can also be used to withdraw money from the ATM.
(iv) Management is considered to be a discipline because it helps to improving discipline among the employees by exercising authority, assigning responsibility and introducing procedures of evaluation and control.
(v) Two sources of external recruitment used in today ‘s world are :
Advertisement : Advertisement in newspaper, business magazines and journal is very common source for fulfilling the senior positions in an organisation. The advantages of this method is that adequate information about the organisation and the job can be given to allow self-screening by prospective candidates.
Employment Exchange : Employment exchanges register the names of job seekers and maintain records of their qualifications, experience etc. These are run by the government and act as a link between the job-seekers and employers.
(vi) The elements of directing are :
- Supervision
- Motivation
- Leadership
- Communication
(vii) The difference between Advertisement and Publicity :

(viii) Primary and Secondary Market.
(ix) Sales promotion strategy is used by the producers.
Objective: It will increase the immediate sales.
(x) (a) RTGS: Real Time Gross Settlement.
(b) NEFT: National Electronic Funds Transfer.
Part – II (60 Marks)
Answer any five questions.
Question 2.
(a) Explain any three barriers to communication. [3]
(b) Explain any four features of Business Environment. [4]
(c) Discuss the need for the principles of management. [5]
Answer:
(a) Three barriers to Communication are :
Semantic Barriers : These are related with the problems in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or impressions. People interpret words and symbols in terms of their own experience and thinking. It includes faulty translations, technical jargon, unclarified assumptions etc.
Organisational Barriers : These arc related to organisation’s structure, authority, relationships, rules and regulations etc. Due to long lines of communication, flow of information gets delayed and distorted. Every layer of authority cuts off a bit of information, particularly in upward communication.
Personal Barriers: Personal factors like judgement, emotions and social values create a psychological distance between the sender and the receiver. When there is lack of mutual trust and confidence between sender and receiver of the message, communication is not effective.
(b) Business environment can be defined as the sum total of external factors that influence the functioning of a business enterprise. The main features of Business Environment arc given below:
Specific and general forces: Business environment is made up of both specific and general forces. General forces such as economic, social, political, legal conditions indirectly influence the business operations. Whereas specific forces refers to customers, competitors, investors etc. which have a direct effect on the day-to-day working of the business.
Dynamic nature: Business environment is dynamic in nature i.e., it keeps on changing. Entry of new competitors in the market, development of new technology , shifts in the preferences of consumers are examples of environmental changes.
Complexity: Business environment is complex because it consists of several interrelated elements which keeps on changing. Many forces constitutes the business environment. For example, it is difficult to know the impact of economic, social, political, technological and other forces on changes in demand for a product or service.
Uncertainty : Business environment is very uncertain as one cannot predict future events particularly changes in technology and fashion which occur fast and frequently. Its dynamic nature makes it more challenging to handle uncertainty.
(c) Principles of management are required for the following reasons :
Providing managers with useful sights into reality : With the help of principles of management, the organisation will increase the managerial efficiency by adding to their knowledge and ability to understand the various situations. These principles enables managers to solve problems in a methodical way without wasting time and effort in trial and error. It also help to improve the art of management by suggesting how things should be done to get good results.
To train managers : Principles of management provide a conceptual framework for scientific and systematic training and development of managers. It is central point of management theory . Formal methods of training managers in institutes and univ ersities are possible only when there are fundamental principles and concepts.
To evaluate managerial behaviour: Principles are help to prescribe what one should do to manage things in a given situation. These principles attempt to evaluate the behaviour of managers.
To fulfill the social goals : Management principles enable managers to make optimum use of human and material resources. The principles of management and management theory have been devised in such a way that they help in fulfilling these responsibilities. Managers coordinate efforts of the people so that individual objectives get translated into social attainments.
To improve research : Growing popularity and utility of management principles have attracted experts towards their study and analysis. It also help the managers in taking decisions based on the objective assessment of the situation, free of any bias and prejudice. It will helped in expanding the horizon of knowledge in management.
Question 3. .
(a) Discuss three advantages of ploughing hack of profit, from the company’s point of view. [3]
(b) Explain why management is considered to be a science. [4]
(c) What is labeling ? Explain four advantages of labeling. [5]
Answer:
(a) Ploughing back of profits refers to the process of retaining a part of the net profit year after year and reinvesting the same in business. There are some advantages of ploughing back of profits are :
(i) The company can undertake its plans for expansion, growth and modernization without bothering about conditions in the capital market.
(ii) Ploughing back of profits add to the financial strength and creditworthiness of the company.
(iii) Reserves created by ploughing back of profits can be used to stabilize the rate of dividend on equity shares.
(b) Management is considered to be science because :
Systematic Body of Knowledge : Management is a systematized body of knowledge based on cause and effect relationship e.g., genetic principle derived by Darwin. Like all other organized activity, management has its own vocabulary of terms through which managers communicate with each other.
Observations and Experiments: The principles of management have also been developed over a period of time, on the basis of experimentation and observation. Management experts and practitioners have developed the knowledge after careful analysis, inquiry and experience. Management deals with human beings and human behavior which cannot be scientifically predicted.
Cause and Effect Relationship : Management Principles builds the cause and effect relationship between various factors. For example, dual subordination leads to confusion.
Universal Validity of Principles : The principles of science are universally applicable i.e.. these principles hold tme under each and every situation. These principles have universal validity. These principles have to be modified according to the situation.
(c) La belling refers to designing the label and putting it on the package. A label is a small slip placed on the product to denote its nature, contents, ownership, destination etc. It is a medium through which the manufacturer gives necessary information to the user or consumer.
Various advantages of labeling are:
- A carefully designed label helps in attracting the customers and induces them to purchase the product.
- It avoids price variations by publishing the price on the label.
- It helps in identifying the product from among various products available in the market.
- It is a guarantee for the standard of the product. Hence, it raises the prestige of the product and of the manufacturer.
- It is social service to customers, who very often do not know anything about the product’s characteristics features.
Question 4.
(a) Give three points of difference between a product and a service. [3]
(b) What are the different types of short term financial assistance provided by the commercial banks to business houses ? [4[
(c) Explain any five types of debentures through which a company can collect borrowed capital from the public. [5]
Answer:
(a) Difference between a product and a service :
| Basis | A Product | A Service |
| (a) Storage | A product is durable and can be stored. | There is simultaneous production and consumption of services. |
| (b)Time Lag | Products can be brought in advance of need. | Services cannot be brought in advance of need. |
| (c) Tangibility | It can be seen, touched and felt. | Services cannot be seen and touched. |
(b) There are different types of short term financial assistance provided by the commercial banks to business houses :
Cash Credits: It is revolving credit agreement under which a borrower is allowed to borrow upto a certain limit. Cash credit is of two types : Clean Cash Credit and Secured Cash Credit. In both types of cash credit, the borrower has to pay interest only on the amount actually utilized.
Discounting of Bills: Commercial banks provide short term finance to business concerns by discounting their bills of exchange, promissory notes and hundies. Banks pay the price lower than the face value and charge some commission.
Loan and Advances: A loan is a direct advance made in lump sum which is credited to a separate loan account in the name of the borrow er. These are usually secured by pledge of specific assets which are in the actual or constructive possession of the bank.
Bank Overdrafts: Under this arrangement, a customer having a current account with the bank is allowed to overdraw his account uto a specified amount. Interest is charged on the amount actually overdrawn and not on the amount sanctioned by the bank.
(c) Five types of debentures are :
Mortgage and Unsecured Debentures : Mortgage debentures are those debentures which are secured by either a fixed charge or a floating charge on the assets of the company. In case, the company makes a default in payment, the debentureholders can recover their dues from the mortgage property. Whereas unsecured debentures are those debentures which are not secured by a charge.
Redeemable and Irredeemable Debentures: Redeemable debentures are repayable on a predetermined date or at any time prior to their maturity at the option of the company. Irredeemable debentures are those debentures that are not repayable during the lifetime of the company and hence will be repaid only when the company is wound up.
Bearer Debentures : Bearer debentures can be transferred by mere delivery as no record of such debentures is kept in the Register of Debentureholders. Payment of interest is made on production of coupons attached to the debenture. No legal formalities are required for their transfer and no formal notice or intimation to the company is necessary.
Registered Debentures : These arc the debentures, in respect of which the names, addresses and particulars of holdings of the debentureholders are entered in a register kept by the company. Such debentures can be transferred only by transfer deed or intimation to the company and not mere delivery.
(v) Convertible and Non-Convertible Debentures: In case of convertible debentures, the debentureholders arc given the option to convert their debentures into equity shares after a specified period. Debentureholder have an option of exchanging the whole or a part of amount of their debentures for shares. In case of non-convertible debentures, these are those debentures which do not earn the right to be converted into equity shares.
Question 5.
(a) Explain the need for consumer protection. [3]
(b) ‘Planning is not a guarantee of success.’ In this context, explain the limitations of Planning. [4]
(c) Explain the following principles of management, as advocated by Henry Fayol: [5]
(i) Stability of tenure
(ii) Discipline
(iii) Unity of command
(iv) Unit}’of Direction
(v) Order
Answer:
(a) Consumer protection is necessary due to following reasons :
Consumer is the purpose of business : Customer is the foundation of business and keeps it in existence. It is a consumer who not only relates to repeat sale but also provide positive feedback to other customers and thus results in an increased consumer base for business.
Business uses society’s resources : Business exercises considerable power and influence over society . It is the duty of the business to use the resources in such a way that the interests of society in general and consumers in particular are not damaged. Consumer’s protection aims at satisfying them and thus protect the long term interests of the business itself.
Ethics : Leading business houses all over the world have been founded on ethical values and they have followed high standards of ethics. To take care of consumer’s interests and to avoid any form of their exploitation is the moral duty of every business. Therefore, consumer protection is the ethical obligation of business.
(b) “Planning is not a guarantee of success.” It suffers from various limitations :
Planning may not work in dynamic environment: The environment in which a business exists is very dynamic. Changes in technology, changes in government policies, legislative enactments, industrial unrest in the country etc. are important external limitation of planning. Thus, it becomes very difficult to forecast the future when the economic policies of the gov ernment keeps on changing continuously.
Time-Consuming : Considerable time is required for collection, analysis and interpretation of information for planning. Sometimes, a lot of time is taken in formulating the plans, as a result of which very less time is left to implement these plans. Planning is not practicable during emergencies and crisis w hen on the spot decisions are necessary.
Rigidity : In an organisation, a well defined plan is drawn to achieve some specified goals within a specified period of time. Employees become more concerned with observing the programmes and procedures rather than achieving the goals. They have to strictly adhere to the formulated plans irrespectiv e of changes in the environment. Therefore, rigidity in plans may create difficulty in an organisation.
Costly Process : Planning is an expensiv e process. The cost is in terms of money, time and effort. Moreover, sometimes the cost incurred in formulating plans turn out to be higher than the benefits actually received from these plans. Management must exercise intelligent judgement to balance the expenses of preparing plans against the benefits derived from them.
(c) Stability of Tenure: According to Fayol. “Employee turnover should be minimized to maintain organisational efficiency”. Stability of tenure helps to develop loyalty and attachment on the part of employees. If an employee receives transfer order by the time he learns and gets settled in a job it will be leading to wastage of resources.
Discipline : Discipline implies obedience, respect of authority and observance of the established rules and regulations. To achieve proper discipline, skilled superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalities etc. are required.
Unity of Command : According to this principle, an individual employee should have only one superior from whom he should receive orders and to whom he should be responsible. If a subordinate has more than one boss, dual command will undermine authority’, weaken discipline, divide loyalty and create confusion, delays etc.
Unity of Direction : According to this principle, activities having the common goal must have one head and one plan. Each group of activities with the same objective must have one plan of action and must be under the control of one superior.
Order: According to Fayol. “People and material must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency “.
The order can be of two types :
- Material Order: It implies a proper place for everything and everything in its right place.
- Social Order: Arrangement of people is referred to as social order.
Question 6.
(a) Explain any three types of training that can be given to an employee. [3]
(b) What is Branding ? Give any three advantages of branding to the marketers. [4]
(c) Explain the various steps involved in the process of organizing. [5]
Answer:
(a) Types of training are :
Films : It helps to provide information and demonstrate skills that cannot be easily presented in lectures. Films in conjunction with conference can be a very effective method.
Vestibule Training: Employees learn their jobs on the equipment’s which they will be using while doing the actual job. This method is costly and it is used in case of sophisticated machinery and equipment.
Lectures : This method is used to convey specific information, rules and procedures. Audio-visuals are used to make lectures more interesting.
(b) Branding is the process of assigning a distinctive name or symbol to a product by which it is to be known and remembered. Branding enables a marketer to distinguish its products from its competitors’ products.
Advantages of branding are:
Product Identification : Branding helps customers in identifying the product. When a customer is satisfied with a particular brand of a product, he repeatedly purchases it. For example, a customer who is satisfied with Lux’ toilet soap need not inspect it every time he buys the product.
Product Differentiation : Branding enables a marketer to distinguish its product from its competitors’ products. This will help the firm to secure and control the market for its product.
Differential Pricing: Branding enables a firm to charge a different price for its product than that charged by its competitors. This is because when the customer becomes habitual or used to any particular brand of a product, they don’t mind paying higher price for it.
(c) The various steps involved in organizing process which are given below :
Division of Work: The first step in organizing is to divide the total work to be done into specific jobs. Division of work facilitates specialization in work and skills which is essential, as no individual can perform the entire work efficiently and effectively. While dividing work, care should be exercised to ensure that all the activities required to achieve organisational goals are identified.
(ii) Grouping Jobs or Activities : The process of grouping the activities of similar nature under same departments is called departmentalization. Work divided into jobs is combined to facilitate unify of effort. The departments so created are linked together on the basis of their interdependence. Following are the various ways of departmentalization:
- On the basis of functions.
- On the basis of type of products manufactured.
- On the basis of territory.
Assigning Duties : Each group of activities is assigned to an individual best suited to perform it. In order to ensure effective performance in an organisation, it is essential that a balance is created between the nature of a job and ability of the employee responsible for that job.
Delegation of Authority: After assignment of duties, appropriate authority is delegated to each individual. A chain of command from the top manager to the individual at the lowest level is created through delegation of authority .
Establishing Reporting Relationships : It creates hierarchy management in which top management enjoys maximum authority and as one moves downward, the authority’ decreases. It establishing reporting relationship facilitates coordination amongst various departments. Interrelationships between different positions are clearly defined so that everybody knows from whom he is to take orders and to whom he can issue orders.
Question 7.
(a) Explain any three disadvantages of borrowing funds from specialized financial institutions. [3]
(b) Briefly explain any four types of working capital required by a business concern. [4]
(c) Explain Maslow’s theory. [5]
Answer:
(a) The three disadvantages of borrowing funds from specialized financial institutions are :
- Certain restrictions such as restriction on dividend payment are imposed on the powers of the borrowing company by the financial institutions.
- The concern requiring finance from special financial institutions has to submit itself to a thorough investigation.
- The high interest rates charged by the financial institutions which makes this form of finance very extravagant.
(b) Working capital means the capital invested in working assets or current assets such as cash, stock of goods, debtors and short term investments etc. The various types of working capital are:
Permanent Working Capital: It refers to the minimum amount of working capital required permanently to operate the minimum level of business activity. It determine the financing requirement in the case of fixed assets is simply the cost of the asset. It is of two types: Initial and Regular working capital.
Variable Working Capital : It is the difference between net working capital and permanent working capital. The amount of temporary’ working capital depends upon the extent of extra demand in season. It is of two types : seasonal and special working capital.
Gross Working Capital : Gross working capital refers to the total amount of funds invested in the current assets.
Gross Working Capital = Book value of current assets
Net Working Capital : Net working capital means the excess of current assets over current liabilities. Current assets include cash at bank, sundry’ debtors, cash in hand, bills receivable etc. Current liabilities include bills payable, sundry creditors, short term loans etc.
Net Working Capital = Current assets – Current liabilities
(c) Maslow Theory: Abraham H. Maslow, an American psychologist has developed a classification of human needs which is known as ‘Hierarchy of Needs’. Needs are those desires, wants or urges of individuals which influence their behavior.
Types of Needs:
Physiological Needs : These are the basic needs which a person is required to satisfy first of all in order to survive in life. These include the need for air. water, food, sleep, sex etc. As these needs are concerned with the sheer survival, they are at the base in the hierarchy of needs. An organisation can satisfy the physiological needs of its employees by offering good salary and comfortable working conditions.
Safety and Security Needs : These needs arise after the satisfaction of physiological needs. These includes physical safety against danger and economic security against old age, sickness etc. An employer can satisfy safety needs of his employees by offering job security, pension, gratuity, housing etc.
Social and Affiliation Needs : These are related to the natural desire to socialise or interact with others. The person needs love, affection, a sense of belonging, association, friendship with others. Once the people get their physiological and safety needs satisfied, the affiliation needs become more active.
Ego Needs : Ego needs include factors like self respect, autonomy status, recognition and attention from others. Organisation can satisfy these needs by offering challenging jobs, recognizing good performance, providing good job titles etc.
Self Actualization Needs : Self actualization needs refers to need to grow and self fulfillment. These needs arise after the satisfaction of all previous needs i.e., physiological, safety, social, ego needs. For example, A manager may provide opportunities for continuous learning, encourage creativity, grant independence and allow risk taking to help employees satisfy their self actualization needs.
Question 8.
(a) Discuss the features of good packaging. [3]
(b) Explain the advantages of equity shares, as a source of finance. [4]
(c) Discuss any five functions of marketing. [5]
Answer:
(a) Packaging plays a very significant role in the marketing success or failure of many product especially for non-durable consumer products. It implies placing products in suitable packages for delivery of the product to customer or for the purpose of storage and transport.
A good package should have following features :
- It should be convenient to handle and use. It should be easy to open and close.
- It should be safe and should be capable of protecting the product.
- It lends individuality and prestige to the product.
- A good package can grab attention, describe the product and induce customers to buy it.
(b) Advantages of equity shares are:
- Equity shares impose no burden on the company resources because the dividend is payable only at the discretion of the management.
- The liability of equity shareholders is limited to the face value of shares subscribed by them.
- A company with substantial equity capital commands prestige in the investment market.
- Equity shareholders have the pre-emptive right to subscribe to new shares issued by company.
- The face value of an equity share is generally low.
- The value of investment in equity shares may increase manifold during boom and prosperity of the company-holders of these shares earn capital gains.
- Equity shares do not create any charge on the assets of the company.
- Shareholders are not required to pay income tax on dividends received from the company.
(c) According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is a social process by which individual groups obtain what the} need and want through creating offerings and freely exchanging products and sen ices of value with others”.
The various functions of marketing are given below :
Marketing Planning and Product Development: It involves making plans for increasing production and sales, .promotion of product etc. and also laying down a course of action for achieving these objectives. It relates to the decision of quality standards to be used for shape or design of the product, packing etc. in order to make product attractive. Product planning and development involves introduction and development of new products, improvement of the existing product and dropping out unprofitable items from the product line.
Standardization and Grading: Standardization is the general term which includes the establishment of standards for products, the inspection of products in order to determine the standard to which they conform and where necessary the sorting of products into lots conforming to established standards. Grading refers to a process of classifying products into different groups on the basis of their features like size, shape, quality etc. This assures the quality, price and packaging of product to the customers.
Storage or Warehousing: Storage refers to the holding and preservation of goods from . the time of production until the time of consumption. There is a need for storage of adequate stock of goods to meet the demand in case of contingencies and to avoid unnecessary delays in delivery. Warehousing is essential for commodities like wheat, sugar, rice etc. which are produced during the particular seasons but demanded throughout the year.
Transportation : It means physical movement of goods from the place of production to the place of consumption. It serves as a link between the producers and consumers who are located at different places. A business firm analyses its transportation needs on the basis of factors like nature of the product, cost, location of the target market etc. It also removes the barrier of distance and help to stabilize prices by matching supply with demand.
Pricing: The amount of money which a customer is required to pay for purchasing the product is known as product price. It is important function in marketing because it determines the sales volumes and the amount of profits. Thus, while determining the price for a product, various factors like type of customers, their income, product demand etc. should be considered.
Question 9.
Write short notes on the following :
(a) Meaning and Elements of Product Mix.
(b) Core banking solutions.
(c) Coordination, as the essence of management.
Answer:
(a) Product mix refers to the total number of products and items that a business firm offers to the market. It involves decisions concerning the quality; size, range, page. brand name, label, services. It also involves planning, developing and producing the right type of products and sendees to be marketed by the organisation. It includes :
Branding : Branding is the process of assigning a distinctive name or symbol to a product by which it is to be known and remembered.
Packaging: Packaging refers to covering, wrapping, crating, filling or compressing of goods to protect them from spoilage, breakage, leakage etc.
Labelling: Labelling refers to designing the label and putting it on the package. A label is a small slip placed on the product to denote its nature, contents, ownership, destination etc.
(b) Core Banking Solutions: Cofe banking is a banking service provided by a group of networked bank branches where customers may access their bank account and perform basic transactions from any of the member branch offices. Under this system, a customer becomes Customer of the bank’ rather than customer of a branch. Core banking functions will include transaction accounts, loans, mortgages and payments. Basically, it is the software applications for recording transactions, storing customer information, calculating interest and completing the process of passing entries in a single database. The basic goals of core banking are providing greater customer convenience and cutting down on operational expenses. CBS also known as ‘Centralized Banking Solutions’.
It provides following facilities :
- Updating of passbook at all CBS branches.
- Transfer of funds between the accounts in CBS.
- Customer may access their bank account from any of the branch offices.
(c) Coordination is not a separate function but very essence of management. According to George Terry, “Coordination deals with the task of binding efforts in order to ensure successful attainment of an objective. It is accomplishment by means of planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling”. It is an integral part of all the functions of management and not a separate function.
Planning requires coordination for:
- purpose and resources at hand.
- master plan of the enterprise and the plans of different divisions.
Organizing requires coordination so that:
- the whole work is systematically allocated and divided into different parts.
- establishing working relationship and clearly defines the lines of communication.
- promotes growth and diversification of an enterprise.
- leads to specialization which brings effectiveness in administration.
Staffing requires coordination for:
- matching the skills of workers with the jobs that should be assigned to them.
- ensures continuous growth and expansion of the business.
- improves job satisfaction and morale of employees.
Directing requires coordination :
- to ensures integration of employees’ efforts towards attainment of organisational goals.
- helps in initiating actions of people towards achieving organisational goals.
- To cope up with the changes in the business environment, directing function guides, initiates and motivates employees.
Controlling requires coordination for:
- proper balance between standards to be achieved and standard that have actually been achieved i.e., planned standards and actual performance.
- to cope with complexities arising out of expansion and diversification of business activities.