The Trail History and Civics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions – The Mauryan Empire
CSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
The Trail History and Civics for Class 6 ICSE Answers
Trail HistoryCivicsHistory & Civics Geography Biology Chemistry Physics Maths
Keywords
- Indika: was the account of the Mauryan period written by Megasthenes.
- Arthashastra: The book was written by Chanakya on politics.
- Dig vijaya: It means conquest of territories.
- Dhamma: vijaya It means conquest through dharma. Dhamma It is derived from the Sanskrit word dharma, meaning religious duty,
- Dharmamahamatras: They were special officials appointed to spread and enforce the principles of dhamma. Mahamatras They were officials appointed to carry out administrative work.
EXERCISES
A. Fill in the blanks:
- The main literary sources of information about the Mauryan period are Indika and Arthashastra.
- Chandragupta’s success in acquiring the throne of Magadha was largely due to the guidance and training of his adviser Chanakya.
- Chandragupta Mauiya was succeeded by his son Bindusara.
- The word dhamma is derived from the Sanskrit word dharma which means religious duty.
- Ashoka’s dhamma was based on human values and a code of conduct inspired by the teachings of Buddha.
B. Match the following:

Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer:
1. Indika was written by Kautilya/Megasthenes/Seleucus.
Ans: Indika was written by Megasthenes.
2. In 305 bce Alexander’s general Megasthenes/Seleucus/ Kautilya invaded India.
Ans. In 305 bce Alexander’s general Seleucus invaded India.
3. The Kalinga War was a turning point in the life of Dhana Nanda/Bindusara/Ashoka.
Ans. The Kalinga War was a turning point in the life of Ashoka.
4. Ashoka’s dhamma was based on the principles of Buddhism/Hinduism/Confucianism.
Ans. Ashoka’s dhamma was based on the principles of Buddhism.
5. Ashoka’s son was named Rahul/Chandragupta/ Mahendra.
Ans. Ashoka’s son was named Mahendra.
D. State whether the following are true of false:
- In 321 bce Dhana Nanda was overthrown by Chandragupta Maurya.
True.
- Chanakya was a wise brqhmana who had a personal grudge against Dhana Nanda.
True.
- Bindusara was the son of Ashoka.
False.
Correct: Bindusara was the father of Ashoka. - When Ashoka ascended the throne of Magadha, Bengal was the only kingdom outside Mauryan control.
False.
Correct: When Ashoka ascended the throne of Magadha, Kalinga was the only kingdom outside Mauryan control. - Ashoka replaced the policy of digvijaya with dhamma vijaya.
True.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
Question 1.
Mention any one important literary source of information about the Mauryan period.
Answer:
The main literary sources of information about the Mauryan period is Indika.
Question 2.
Who helped Chandragupta Maurya to become the ruler of Magadha?
Answer:
Chanakya helped Chandragupta Maurya to become the ruler of Magadha.
Question 3.
What was the extent of Chandragupta’s empire?
Answer:
Chandragupta’s empire was the first great empire in Indian history. By the end of his reign, the Maurya empire stretched from the Hindu Kush in the north-west to Bengal in the east, from the Himaylayas in the North to the Narmada in the South.
Question 4.
Which powerful kingdom was not under Mauryan control when Ashoka ascended the throne?
Answer:
Kalinga was the only powerful kingdom that was not under Mauryan control.
Question 5.
What was the extent of Ashoka’s empire?
Answer:
Ashoka’s empire stretched from the Himalayas in the North to Mysore in the South and from the Hindu Kush in the north-west to Brahmaputra in the east. It also included Kabul, Kandahar, Herat and the parts of Nepal and Kashmir.
Question 6.
What does the term ‘dhamma vijaya’ mean?
Answer:
Dhamma vijaya means conquest through dharma.
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
What happened to Alexander’s vast empire after his death?
Answer:
After Alexander’s death, fighting broke out between his generals for the control of his vast empire. Seleucus, one of Alexander’s generals, became the ruler of the territory stretching from Asia Minor to the Indus.
Question 2.
Why was Seleucus compelled to sign a treaty with Chandragupta Maurya? Mention two important terms of this treaty.
Answer:
Seleucus was compelled to sign a treaty with Chandragupta Maurya because Chandragupta Maurya defeated him.
According to this treaty he had to give eastern Afghanistan,Baluchistan and areas west of the Indus to Chandragupta. He gave his daughter to Chandragupta in marriage. In return,he received 500 war elephants.
Question 3.
Explain how the Kalinga War became a turning point in Ashoka’s life?
Answer:
The Kalinga war became a turning point in Ashoka’s life. Because, the death, destruction and great human suffering in this war filled Ashoka’s heart with sorrow and remorse.
Question 4.
Mention the main principles of Ashoka’s ‘Dhamma’.
Answer:
The Principles of dhamma were as follows.
- People should live in peace and harmony.
- Everyone should follow ahimsa.
- People should be truthful, charitable and kind to all.
Question 5.
Explain any five steps taken by Ashoka to propagate Dhamma in and outside India.
Answer:
To propagate dhamma, following steps were taken by Ashoka
- He ordered the construction of Buddhist monasteries.
- He sent learned Buddhist scholars to distant lands to spread Buddhism.
- He visited all the places associated with the life of Buddha.
- Special officers called Dhammamahamatras were appointed to spread and enforce the princples of dhamma throughout the kingdom.
- The principles of dhamma were engraved in Prakrit on rocks, pillars and caves so that people could read and follow them.
Question 6.
What arc edicts? Why were they composed in Prakrit?
Answer:
Edicts are order issued by a ruler. They are also source of valuable information of the Mauryan period.Edicts were composed in Prakrit because it was easy language to understand by the common people.
Question 7.
What did Ashoka do for the happiness and welfare of his subjects?
Answer:
He embraced Buddhism and devoted his life to the moral and material welfare of his subjects.
G Picture study.
This is the picture of an Ashokan edict.
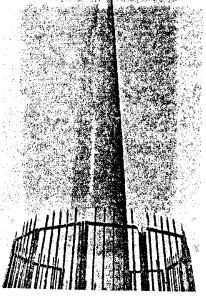
Question 1.
What are edicts?
Answer:
The edicts are a source of valuable information of the Mauryan period. Edicts are royal commands or proclamations.
Question 2.
How are Ashokan edicts useful?
Answer:
The edicts are a source of valuable information of the Mauryan period.
Question 3.
Where were these edicts inscribed?
Answer:
They were inscribed on rocks, polished stone pillars and caves.
Question 4.
In which language were they composed and in which script w ere they written?
Answer:
They were composed in Prakrit, the language of the people and written in Brahmi script. In the north-west they were written in Greek, Kharoshthi and Aramaic.
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Write the main sources of Information about Mauryan empire ?
Answer:
Indika by Megasthenes, Arthashastra by Chanakya, and the rock and pillar edicts of Ashoka are valuable sources of Information about Mauryan Empire.
Question 2.
Who was Chandragupta Maurya ?
Answer:
Chandragupta Maurya, the founder of the Maurya Empire was the greatest known ruler in the ancient history of India.
Question 3.
Who was Chanakaya ?
Answer:
Chanakaya was the chief advisor of Chandragupta. He was also known as Kautilya. He wrote book ‘Arthashastra’ on politics.
Question 4.
Who was Seleucus ?
Answer:
Seleucus was one of Alexander’s generals.
Question 5.
Why is Ashoka called as ‘Ashoka the Great’ ?
Answer:
Ashoka’s occupies an important place in history. He is regarded as one of the greatest rulers of India. He gave the best type of administration to his subject, Hospitals, schools were opened, wells were dug, trees were grown in large number, that is why he is called a ‘Ashoka the Great’.
Question 6.
What did Ashoka do to spread Buddhism outside India?
Answer:
Ashoka sent learned Buddhist scholars, his son Mahendra and daughter Sanghamitra to outside India to spread message of Buddhism.