Volume and Surface Area
Volume
Volume is the amount of three-dimensional space an object occupies, in cubic units, within a container.
Volume and Unit Cubes:
Volume is measured in cubic units. Think in three-dimensions.
The volume of an object can be represented by the number of unit cubes that can be placed within the object.
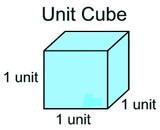
For some figures, the unit cubes fit “nicely” into the object, while other objects hold fractional parts of a unit cube.
The volume of this rectangular prism (“box”) is the total of the number of unit cubes it holds. There are a total of 16 unit cubes within the solid.
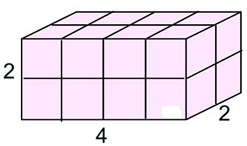
The volume = 16 cubic units
Volume as Area times Depth:
While counting the number of unit cubes within the rectangular prism,
a pattern can be seen that will help to determine the count of the cubes quickly.
Pattern: Find the number of cubes seen in one face and multiply times the number of rows of that face, going to the back of the figure.
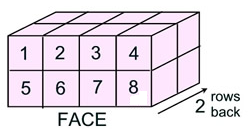
Volume = (cubes in face) • (rows going back)
= 8 • 2 = 16 square units
Pattern: A pattern similar to that shown above can be expressed using the term “area”. The number of cube faces seen in the face of the figure, comprise the area of the face of the figure. The new pattern is expressed as:
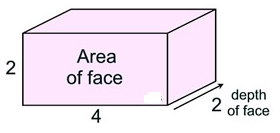
Volume = (area of face) • (depth of face)
= (4 • 2) • 2 = 16 square units
This will be a popular strategy to determine the volume of many solids.
This pattern utilizes a “limiting argument” with the area being a 2-dimensional cross section with no thickness. The thickness, however, can be theoretically considered very, very, very small so as not to affect calculations. These cross sections are stacked to the height of the figure, creating the formula V = B • h, with B the area of the base and h = height.
(In the example about consider the area of the face to be the base, and the depth to be the height; just tip it over.)
Surface area
Surface area is the total area that the surface of a three-dimensional object occupies, in square units.
Surface Area using a Net:
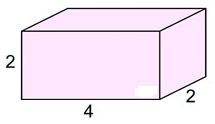
If you cut apart this box and flatten out the pieces, you will get a shape similar to the one at the right, called a net.
Several options are possible.
The advantage of examining the net is that you can see each of the faces of the figure, making computing the surface area easier.
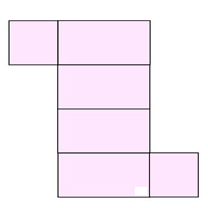
The surface area of this rectangular prism will be the sum of areas of all six shapes in the net.
Surface Area = (2•2) + (2•4) + (2•4) + (2•4) + (2•4) + (2•2) = 40 square units.
Working with different units:
- 1 square foot = 144 square inches
(a square foot is 1 ft. by 1 ft. which is also 12 in. by 12 in.) - 1 cubic foot = 1728 cubic inches
(a cubic foot is 1 ft. by 1 ft. by 1 ft. which is also 12 in. by 12 in. by 12 in.) - 1 cubic yard = 27 cubic feet
(a cubic yard is 1 yd. by 1 yd. by 1 yd. which is also 3 ft. by 3 ft. by 3 ft.)
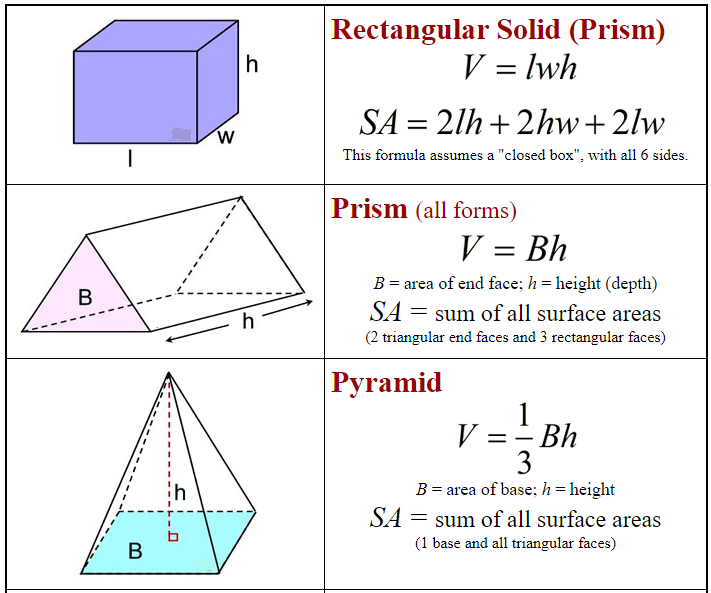
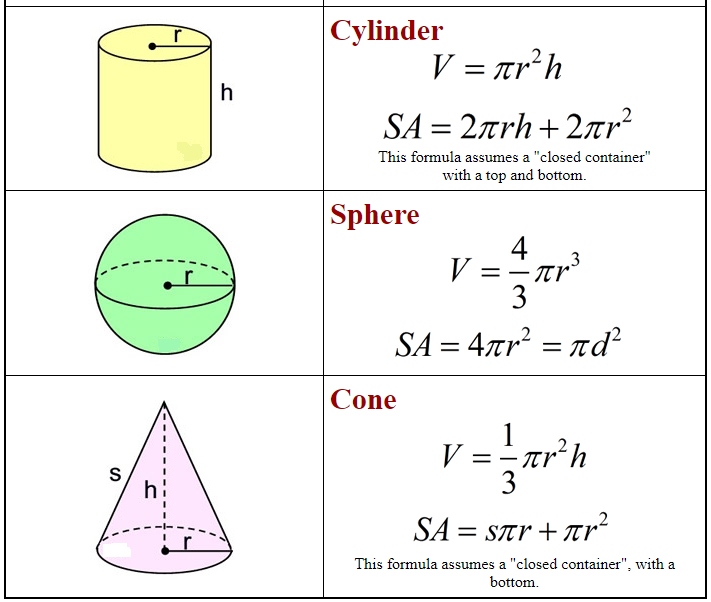
Formulas:
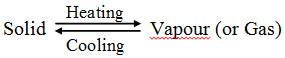 The solid substance which undergoes sublimation is said to ‘sublime’. the solid obtained by cooling the vapours of the solid is called a ‘sublimate’.
The solid substance which undergoes sublimation is said to ‘sublime’. the solid obtained by cooling the vapours of the solid is called a ‘sublimate’.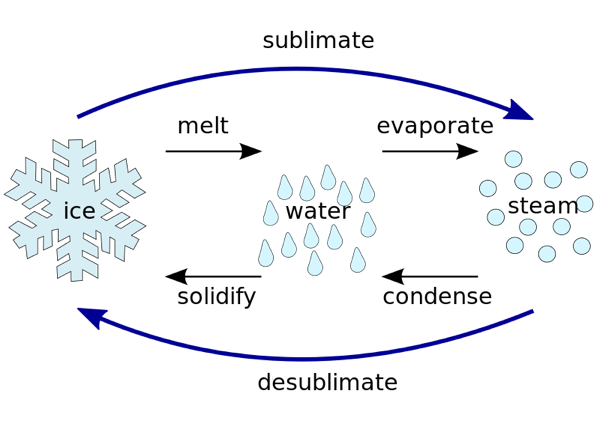 Ex. When solid ammonium chloride is heated, it directly changes into ammonium chloride vapour. And when hot Ammonium chloride vapour is cooled, it directly changes into solid ammonium chloride. Ammonium chloride, Iodine, Camphor, Naphthalene and Anthracene.
Ex. When solid ammonium chloride is heated, it directly changes into ammonium chloride vapour. And when hot Ammonium chloride vapour is cooled, it directly changes into solid ammonium chloride. Ammonium chloride, Iodine, Camphor, Naphthalene and Anthracene.