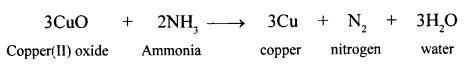
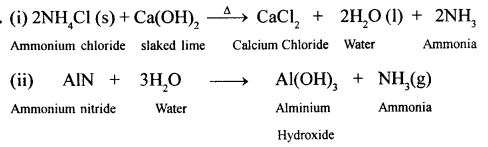
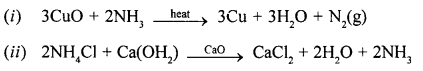
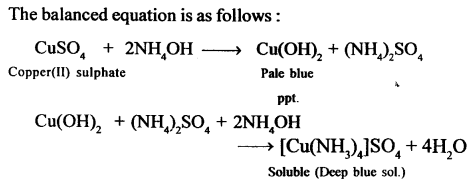
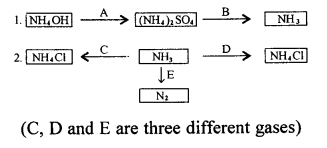
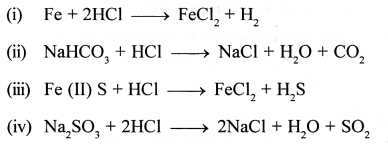
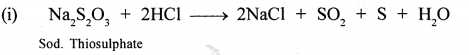
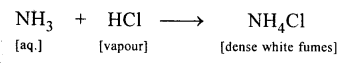
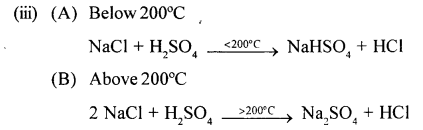
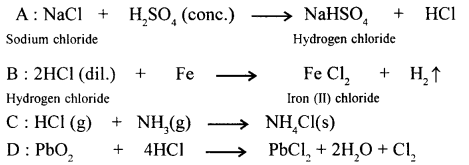
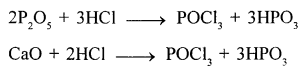
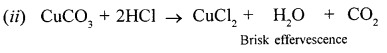
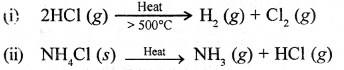
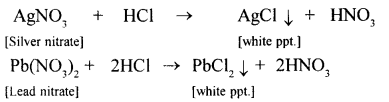
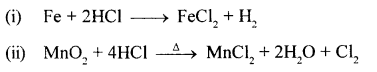
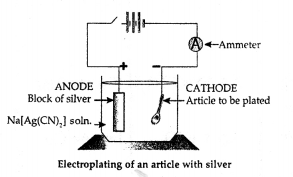
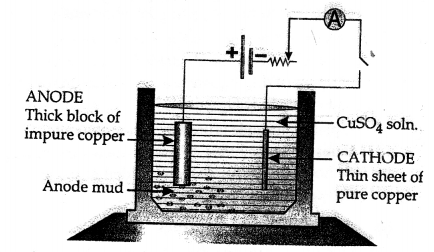
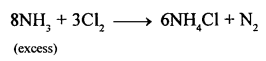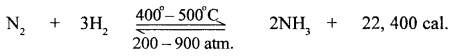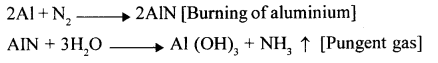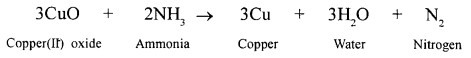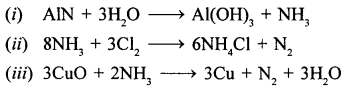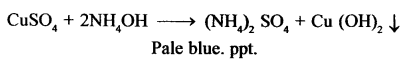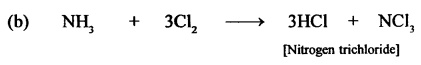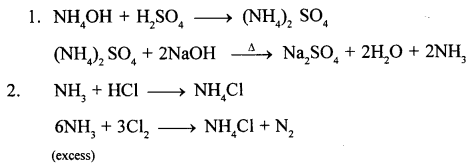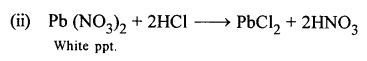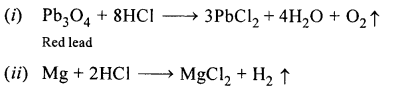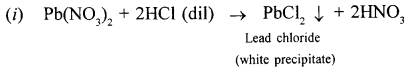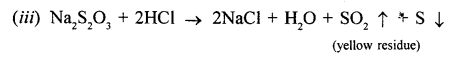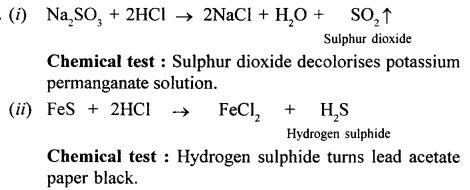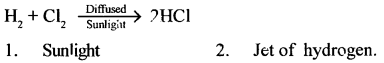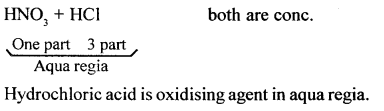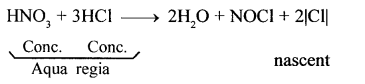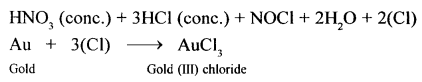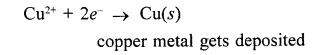New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions -Study Of Compounds – Nitric Acids
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Viraf J Dalal Chemistry Class 10 Solutions and Answers
Simplified ChemistryEnglishMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
QUESTIONS
2000
Question 1.
What do you see when concentrated nitric acid is added to copper.
Answer:
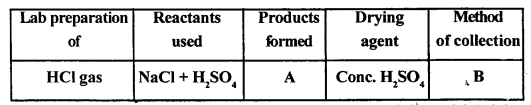
A pungent smelling reddish brown coloured gas (NO2) is produced and the solution turns greenish blue.
Cu + 4HNO3 (cone.) → Cu (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
2001
Question 1.
Name the gas produced in the reaction:
Action of concentrated nitric acid on copper.
Answer:
Nitrogen dioxide.
Question 2.
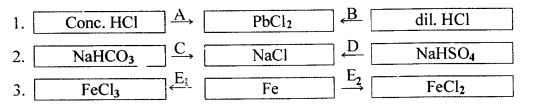
Choose the correct word from the brackets to complete the sentence. Sodium nitrate reacts with — (concentrated / dilute) sulphuric acid to produce nitric acid. Write equation for the same.
Answer:
Sodium nitrate reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid to produce nitric acid.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the equations for the following reaction : Between copper and concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 (cone.) → Cu (NO3)2 + 2H2O+ 2NO2
Question 4.
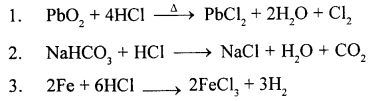
From the formulae listed below, choose, one, corresponding to the salt having the given description:
AgCl, CuCO3, CuSO4. 5H2O, KNO3, NaCl, NaHSO,, Pb(NO3)2, ZnCO3, ZnSO4.7H2O.
This salt gives nitrogen dioxide on heating.
Answer:
Pb(NO3)2
![]()
2002
Question 1.
Give equations for the action of heat on –
(1) NH4Cl
(2) NH4NO3.
State whether each reaction is an example of thermal decomposition or thermal dissociation.
(1) Dissociation
(2) decomposition
Answer:
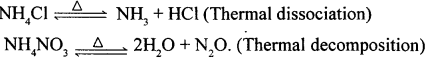
Question 2.
What compounds are required for the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
Answer:
Potassium nitrate and cone, sulphuric acid.
Question 3.
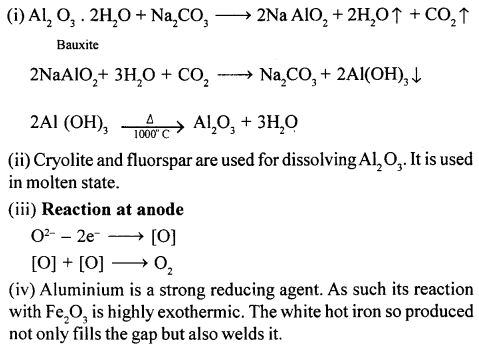
State why pure nitric acid takes on a yellowish brown colour when exposed to light.
Answer:
In the presence of sunlight nitric acid decomposes even at room temperature to give nitrogen dioxide, water and oxygen.
![]()
The NO2 so produced dissolves in cone. HNO3. The yellow colour of cone, nitric acid is due to NO2 dissolved in it.
Question 4.
Write an equation for the following reaction:
Copper and concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 (cone.) → Cu (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2.
Question 5.
The first step in the manufacture of HNO3 is the catalytic oxidation of NH3. Name the catalyst used.
Answer:
Platinum.
2003
Question 1.
Name a solution which gives nitrogen dioxide with copper.
Answer:
Concentrated nitric acid (HNO3).
Question 2.
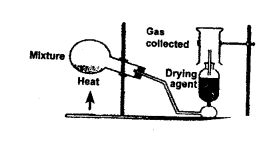
When nitric acid is prepared by the action of concentrated sulphuric acid on potassium nitrate, what is the special feature of the apparatus used.
Answer:
All glass apparatus is used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
Question 3.
Write the equation for the lab. preparation of H2NO3 from potassium nitrate and cone. H2SO4.
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Potassium nitrate prepared from KOH and nitric acid. State the type of reaction involved.
Answer:
Neutralization reaction.
Question 5.
State the cone, acid which will oxidise sulphur directly to H2SO4. Write the equation for the same.
Answer:
Hot and cone, nitric acid will oxidises sulphur directly to sulphuric acid.
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
2004
Question 1.
X, Y and Z are three crystalline solids which are soluble in water and have a common anion. To help you
to identify X, Y and Z, you are provided with the following experimental observations. Copy and complete the corresponding inferences in.
A reddish-brown gas is obtained when X, Y and Z are separately warmed with concentrated sulphuric acid and copper turnings added to the mixture. The common anion is the ion.
Answer:
[NO–] Nitrate
Question 2.
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of cone. HNO3 when added to copper turnings kept in a beaker.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
Question 3.
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of cone. HN03 when added to copper turnings kept in a beaker.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
2005
Question 1.
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of – sulphur and hot concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
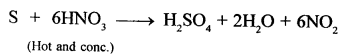
Question 2.
Dilute nitric acid is generally considered a typical acid except for its reaction with metals. In what way is dilute nitric acid different from other acids when it reacts with metals.
Answer:
Metals, lying above hydrogen in the electro chemical series, give hydrogen from the acid. In case of nitric acid which is a strong oxidising agent, hydrogen produced in the nascent state reduces excess nitric acid and produces water and a reduction productof nitric acid. The reduction product depends on the dilution of the acid.
Question 3.
Write the equation for the reaction of dilute nitric acid with copper.
Answer:
3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO
Question 4.
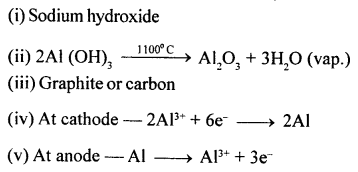
State why a yellow colour that appears in concentrated nitric acid when it is left standing in an ordinary glass bottle.
Ans.
It turns yellow because cone. HNO3 decomposes by the action of sunlight to give brown coloured NO2
![]()
The brown coloured NO2 dissolves in cone. HNO3, to give it a yellow colour.
2006
Question 1.
From the substances – Ammonium sulphate, Lead carbonate, Chlorine, Copper nitrate, Ferrous sulphate — State:
A compound which releases a reddish brown gas on reaction with concentrated sulphuric acid and copper turnings.
Answer:
Copper Nitrate.
Question 2.
State what is observed when nitric acid is kept in a reagent bottle for a long time.
Answer:
Brown vapours are seen in the reagent bottle and nitric acid turns yellowish in colour.
Question 3.
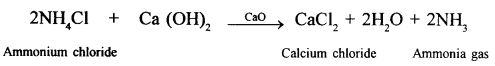
Explain why only all-glass apparatus should be used for the preparation of nitric acid by heating concentrated sulphuric acid and potassium nitrate.
Answer:
Nitric acid is highly corrossive and a strong oxidising agent. It attacks rubber and wooden corks. Therefore, all glass apparatus should be used for the preparation of nitric acid in the laboratory.
2007
Question 1.
In the laboratory preparation of nitric acid: Name the reactants A (a liquid) and B (a solid) used.
Answer:
(A) Cone, sulphuric acid (B) Potassium nitrate (Nitre)
Question 2.
Write an equation to show how nitric acid undergoes decomposition.
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
Write the equation for the reaction in which copper is oxidized by concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
2008
Question 4.
Identify the following substances: a dilute acid B which does not normally give hydrogen when reacted with metals but does give a gas when it reacts with copper.
Answer:
HNO3 (Nitric acid)
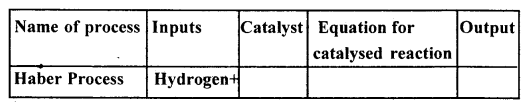
Question 2.
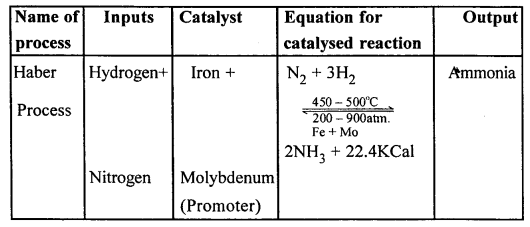
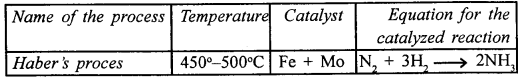
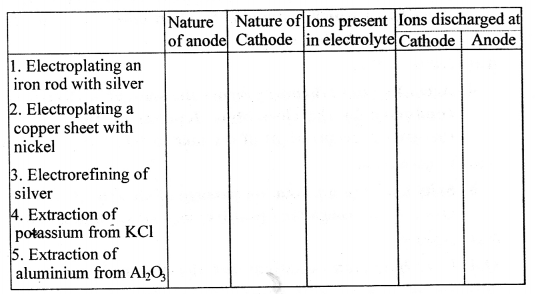
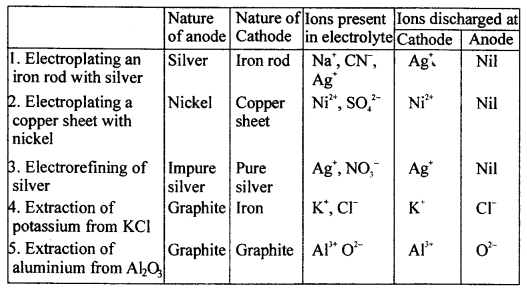
Copy and complete the following table relating to an important industrial process. Output refers to the product of the process not the intermediate steps.
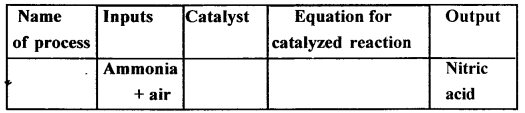
Answer:
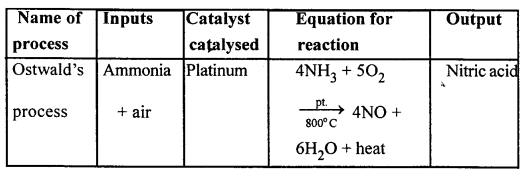 …
…
Question 3.
What is the property of nitric acid which allows it to react with copper ?
Answer:
Nitric acid works as an oxidising agent.
Question 4.
Write the equations for the following reactions: Dilute nitric acid and copper.
Answer:
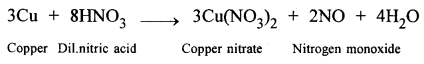
2009
Question 1.
Name the gas evolved (formula is not acceptable). The gas produced by the action of dilute nitric acid on copper.
Answer:
Nitric oxide (NO)
Question 2.
Match each substance A to E listed below with the appropriate description given below.|
(A) Sulphur
(B) Silver chloride
(C) Hydrogen chloride
(D) Copper (II) sulphate
(E) Graphite.
A non-metal which reacts with concentrated nitric acid to form its own acid as one of the product.
Question 3.
Correct the following statements.Copper reacts with nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide.
Answer:
Copper reacts with concentrated nitric acid to produce nitrogen dioxide.
2010
Question 1.
Select the correct answer from A, B, C D and E
(A) Nitroso Iron (II) sulphate
(B) Iron (III) chloride
(C) Chromium sulphate
(D) Lead (II) chloride
(E) Sodium chloride.
The compound which is responsible for the brown ring in the brown ring test for identify the nitrate ion.
Question 2.
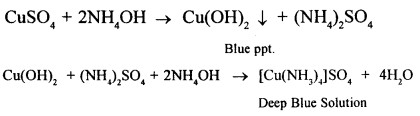
A blue crystalline solid X on heating gave a reddish brown gas Y, a gas which re-lights a glowing splint and a residue is black Identify X, Y and write the equation for the action of heat on X.
Answer:

(1) X = Copper nitrate [Cu(NO3)2]
Y = Nitrogen gas (NO2)
(2) ![]()
(3) Cu(NO3)2 + H2S → CuS ↓+ 2HNO3
2011
Question 1.
Choose from the list substances – Acetylence gas, aqua fortis, coke, brass, barium chloride, bronze, platinum. A catalyst used in the manufacture of nitric acid by Ostwald’s process.
Answer:
Platinum
Question 2.
State your observation when copper is heated with concentrated nitric acid in a hard glass test tube.
Answer:
At once reddish brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas are evolved. Gradually the copper dissolves in dilute nitric acid to form greenish blue solution of copper (II) oxide.
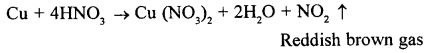
Question 3.
Choose the correct answer from the choices given – The brown ring test is used for detection of:
(A) C02–3
(B) NO-3
(c) SO23–
(D) cl-
Question 4.
(1) State the special feature of the apparatus used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid?
(2) State why the temperature of the reaction mixture of HNO3 is not allowed to rise above 200°C.
Answer:
- All glass apparatus is used because the vapours of nitric acid are corrosive and destroy materials like rubber and cork.
- The reaction mixture is not heated beyond 200 °C because at higher temperature:
The nitric acid would decompose:
4 HNO3 →4NO2 ↑+ 2H2O + O2 ↑
The residue, sodium sulphate or potassium sulphate, forms a hard crust that sticks to the glass. Hence, its removal becomes difficult.
Question 5.
Write a balanced equation for – Ferric hydroxide reacts with nitric acid.
Ans.
Fe (OH)3 + 3HNO3→ Fe (NO3)3 + 3H2O
2012
Question 1.
Name the gas produced when copper reacts with concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
Nitrogen dioxide.
Question 2.
State one observation for the following: Zinc nitrate crystals are strongly heated.
Answer:
Reddish brown gas is liberated residue is yellow when hot and white when cold.
Question 3.
Rewrite the correct statement with the missing word/s: Magnesium reacts with nitric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
Answer:
With very dilute nitric acid.
Question 4.
Give reasons for the following: Iron is rendered passive with fuming nitric acid.
Answer:
Iron forms coating of its oxide and nitrate which stops further reaction.
Question 5.
Give a balanced equation for the reactions: Dilute nitric acid and Copper carbonate.
Answer:
CuCO3 + 2HNO3→ Cu (NO3)2 + H2O + CO2
2013
Question 1.
Identify the gas evolved when:
- Sulphur is treated with concentrated nitric acid.
- A few crystals of KNO3 are heated in a hard glass test tube.
Answer:
- Nitrogen dioxide gas
- Oxygen gas
Question 2.
State two relevant observations for : Lead nitrate crystals are heated in a hard glass test tube.
Answer:
- Brown coloured pungent smelling gas – nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is produced.
- Buff coloured residue of PbO is obtained in the test tube.
- Oxygen produced relits a glowing splinter.
Question 3.
Give balanced equations for: Oxidation of carbon with concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
C + 4HNO3 → 2H2O + 4NO2 + CO2
2014
1. Fill in the blank from the choices given in the bracket:
Question 1.
Cold, dil. nitric acid reacts with copper to form________(Hydrogen, nitrogen dioxide, nitric oxide).
Answer:
Cold, dilute nitric acid reacts with copper to form nitric oxide. }
Question 2.
Give balanced equations for the following:
(1) Laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
(2) Action of heat on a mixture of copper and concentrated nitric acid.
Answer:
- Laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
- Action of heat on a mixture of copper and concentrated nitric acid.
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO
2015
Question 1.
State one appropriate observation for — When crystals of copper nitrate are heated in a test tube.
Answer:
The greenish blue crystals of copper nitrate will change to black residue of copper oxide and give reddish brown gas i.e., nitrogen dioxide on heating.
Question 2.
Identify the acid — The acid which is prepared by catalytic oxidation of ammonia.
Answer:
Nitric acid
Question 3.
Explain the following:
- Dil. HN03 is generally considered a typical acid but not so in its reaction with metals.
- When it is left standing in a glass bottle, concentrated nitric add appears yellow.
- In the laboratory preparation of nitric acid, an all glass apparatus is used.
Answer:
- It is because it does not liberate hydrogen gas when treated with metals. Instead it liberates oxides of nitrogen, such as nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, etc., as it is very powerful oxidising agent.
- Cone. Nitric acid on exposure to sunlight, slowly decomposes to form nitrogen dioxide gas which is reddish brown in color/. Nitrogen dioxide gas redissolves in the nitric acid and imparts it yellow colour.
- Nitric acid is a powerful oxidising agent and hence corrodes rubber or any other stoppers to avoid corrosion, we use all glass apparatus.
Question 4.
From the list of the following salts —
AgCl, MgCl2, NaHSO4, PbCO3, ZnCO3, KNO3, Ca(NO3)2 State the salt which on heating, evolves a brown coloured gas.
Answer:
On heating this salt, a brown-coloured gas is evolved is Ca(NO3)2
2016
Question 1.
Write balanced chemical equation for: Action of hot and concentrated nitric acid on copper.
Answer:
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2 ↑
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks using the appropriate words given in the bracket below:
(sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, nitric oxide, sulphuric acid)
- Cold, dilute, nitric acid reacts with copper to given nitric oxide.
- Hot, concentrated nitric acid reacts with sulphur to form sulphuric acid.
2017
Question 1.
Write the balanced chemical equation for –
- Action of cold and dilute nitric acid on copper,
- Action of cone. nitric acid on sulphur.
- Laboratory preparation of ni- trie acid.
Answer:
- 3Cu + 8HNO3 (dil.) → 3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO(g) + 4H2O
- S + 6HNO3(conc.) → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2 (g)
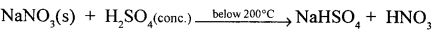
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
Question 1.
State how atmospheric nitrogen converts itself to nitric acid.
Ans.
- During lightning discharge, nitrogen in the atmosphere reacts with oxygen to form nitric oxide and further to nitrogen dioxide.
- The nitrogen dioxide dissolves in atmospheric moisture forming nitric acid.
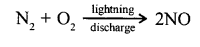
2NO + O2 →2NO2
4NO3+2HO + O2→ 4 HNO3 (acid Rain)
Question 2.
Give a word equation and balanced molecular equation for the laboratory preparation of nitric acid from (1) KN03 (2) NaNO3.
Answer:
(1)
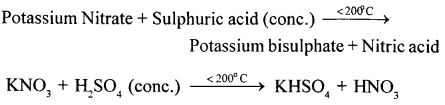
(2)
Sodium Nitrate + Sulphuric acid (conc.) Sodium Bisuiphate + Nitric acid
NaNO3 + H2S04 (conc.) NaHSO4 + HNO3
Question 3.
In the laboratory preparation of nitric acid from – KNO3 or NaNO3 State
- The acid used
- The type of apparatus used
- The precautions to be taken during the preparation
- The method of collection of the acid
- The method of identification of the product i.e. acid formed.
Answer:
- Cone, sulphuric acid
- Glass retort
- Precautions are:
- Use all glass apparatus with no wooden or rubber cork.
- Control the temperature carefully at nearly 200 °C.
- Concentrated nitric acid vapours – condense and are collected in the water-cooled receiver.
- The vapours obtained in the receiver on heating alone or with copper turnings evolve – reddish brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide which turns acidified ferrous sulphate solution brown – proving that the vapours are of nitric acid.
Question 4.
Give reasons for the following – pertaining to the above laboratory preparation of nitric acid
Question 4(1).
concentrated hydrochloric acid is not used as a reactant in the laboratory preparation.
Answer:
Cone. HCl is not used as a reactant in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid. It is due to the following reasons:
- HCl is a volatile acid.
- HNO3, if formed, will oxidise HCl to Cl,. In the process, HNO3 will get reduced to NO or NO,. This very little yield, if any, of HNO, will be obtained and that too will be contaminated with HCl.
Question 4(2).
The complete apparatus in the laboratory preparation does not contain parts made of rubber or cork.
Answer:
The complete apparatus is made of glass only – since the vapours of nitric acid being highly corrosive and attack rubber, cork, etc.
Question 4(3).
The reaction temperature is maintained below 200°C
Answer:
The reaction temperature is maintained below 200°C. This is because at higher temperatures, HNO3 decomposes to give NO2. The brown coloured NO2 dissolves in HNO3 to give it a yellow colour. Thus, if the temperature is allowed to go beyond 200°C, the product (HNO3) obtained is not pure (colourless).
Question 4(3).
At high temperatures the sodium sulphate or phtassium sulphate formed, forms a crust and sticks to the glass apparatus.
Answer:
Formation of a hard residual crust of the corresponding sulphate [Na2SO4 or K2SO4] which being a -poor conductor of heat, sticks to the glass and cannot be easily removed from the apparatus.
Question 5.
State the colour of
(1) pure nitric acid
(2) nitric acid obtained in the laboratory
(3) nitric acid obtained in the laboratory after passage of air or addition of water to it.
Answer:
- Pure nitric acid is colourless.
- Nitric acid obtained in laboratory is pale yellow in colour.
- The pale yellow colour of nitric acid disappears and hence it becomes colourless.
Question 6.
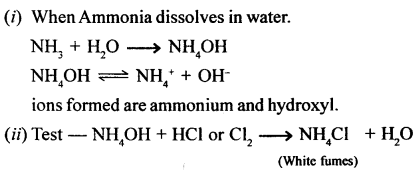
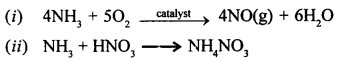
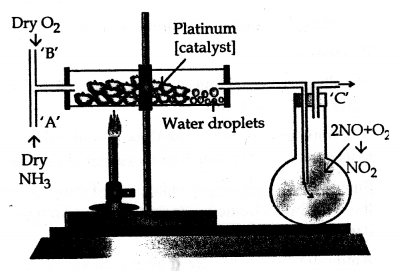
State which reaction of ammonia forms the first step of Ostwald’s process.
Answer:
The first step of Ostwald’s process involves catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide and water (steam).
![]()
Question 7.
Convert ammonia to nitric acid by the above process giving all conditions.
Answer:
Step I
![]()
Step II
![]()
Step III
4NO2 + 2H2O → 4HNO3
Question 8.
State how —
- a higher ratio of the reactant air
- exothermicity of the catalytic reaction
- use of low temp, in the conversion of NO to NO2 – affects each related step in Ostwald’s process.
Answer:
- Excess of air carries the reactions in forward direction as oxygen is needed in all the three reactions, leading to the formation of nitric acid.
- The exothermicity of catalytic reaction helps in stopping external heating, there by saving on energy.
- Low temperature (less than 50°C)
Question 9.
State why nitric acid
- Stains the skin
- Cannot be concentrated beyond 68% by boiling.
Answer:
- Nitric acid combines with protein of the skin forming a yellow compound Xanthoproteic acid, stains skin yellow.
- It is because at 68% concentration it forms a constant boiling mixture, i.e., if heated beyond this concentration then proportion of water vapour and nitric acid vapour, leaving the dilute acid does not change. Thus, it cannot be concentrated by boiling.
Question 10.
State two conditions which affect the decomposition of nitric acid.
Answer:
The conditions which affect the decomposition of nitric acid are:
- Presence of sunlight
- Higher temperature.
Question 11.
State the change in colour of pure concentrated nitric acid on initial and prolonged decomposition.
Answer:
Yellowish brown colour is changed to dark yellowish brown colour on prolonged decomposition.
Question 12.
State the cation responsible for turning moist neutral litmus red on reaction with dil. HNO3.
Answer:
Hydrogen |H+| ions and Nitrate ions.
Question 13.
State why nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent and yields varying products such as NO, NO2 on reaction with metals,non-metals etc.
Answer:
The oxidising property of nitric acid is based on the fact that when nitric acid undergoes decomposition, it yields nascent oxygen, which is very reactive.
2HNO3 (cone.) → H2O + 2NO2 + [O]
2HNO3 (dil.) → H2O + 2NO + 3[O]
This nascent oxygen oxidises metals, non-metals, organic and inorganic compounds. During the process, nitric acid itself gets reduced to various products (NO, NO2, N2O, NH3, etc.) depending upon the concentration of the acid, reaction temperature and activity of the metal with which it is reacting.
Question 14.
Give an equation for reaction of cone. HNO3 with
(1) carbon
(2) copper.
Answer:
- C + 4HNOs → CO2 + 2H2O + 4NO2
- 3Cu + 8HNO3 → 3Cu (NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO
Question 15.
Convert nitric acid to sulphuric acid using a non-metal.
Answer:
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
Question 16.
State how you would obtain
(1) Hydrogen
(2) Nitric oxide
(3) Nascent chlorine – from nitric acid. State the concentration of nitric acid used in each case.
Ans.
- Hydrogen from nitric acid: Cold, very dilute (1%) nitric acid reacts with metals like Mg and Mn to give H2.
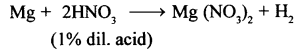
- Nitric oxide from nitric acid: Dilute nitric acid reacts with metals like Cu, Ag to give nitric oxide (NO).
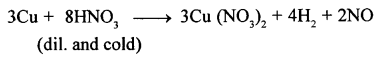
- Nascent chlorine from nitric oxide: A mixture of cone, nitric acid (I part) and cone, hydrochloric acid (III parts) (by volume) reacts with noble metals like gold and platinum. In this reaction, nascent chlorine is formed as an intermediate.
HNO3 (cone.) + 3HCl (cone.) → 2H2O + NOCL + 2|Cl|
Question 17.
State why hydrogen is liberated when zinc reacts with dil.HCl but not with dil. HNO3.
Answer:
Zinc displace hydrogen from dil. HCl.
Zn + 2HCl(dil.) → ZnCl2 + H2
However, when zinc reacts with dil HNO3, no hydrogen is obtained. This is because nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. Nitric acid oxidises the hydrogen produced to water and hence no hydrogen is liberated.
Question 18.
State a reason for the inactivity of iron and aluminium on reaction with fuming HNO3.
Answer:
Pure or fuming nitric acid renders metals like iron (Fe) and Al- passive i. e., inactive. This is due to the formation of a thin oxide coating on the surface of the metal which prevents further action.
Question 19.
State your observation when
(1) nitric acid is added to saw dust
(2) cone, nitric acid is heated
(a) in absence of copper
(b) in presence of copper.
Answer:
- Nitric acid being a strong oxidising agent decomposes to give nascent oxygen, which being very reactive, oxidises organic compounds to carbon dioxide and water. Saw dust is organic in nature. When hot cone. HNO3 is poured over saw dust, it burst into flames due to oxidation.
- (a)
When cone. HNO, is heated, it decomposes to give brown coloured pungent smelling gas nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
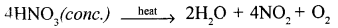 (b)
(b)
(b) When. ”cone. HNO3 is heated in the presence of copper, brown coloured, pungent smelling NO2 is formed alongwith blue coloured copper nitrate.
Cu + 4HNO(cone.)→ Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
Question 20.
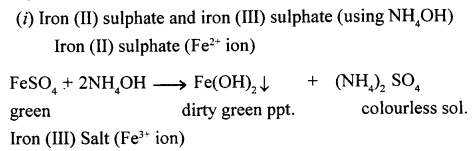
State how addition of nitric acid to acidified FeSO, serves as a test for the former.
Answer:
Nitric acid oxidises iron(II) sulphate to iron (III) sulphate with the liberation of nitric oxide gas.
6FeSO4 +3H2SO4 + 2HNO3 (dil. ) → 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 4H2O +2NO
The nitric oxide so formed reacts wtih more of iron(II) sulphate to form nitrosoferrous sulphate, which appears in the form of brown ring at the junction of liquids.
FeSO4 + NO → FeSO4.NO
Question 21.
Name three chemical products manufactured from nitric acid. Give two general uses of HNO3.
Answer:
- Three chemical products manufactured from nitric acid. Explosives (T.N.T., picric acid, nitrocellulose etc.)
- Fertilizers (Ammonium nitrate, calcium ammonium nitrate or C.A.N.)
- Dyes (Picric acid and other nitro dyes)
Two general uses of nitric acid
- For refinning of noble metals like gold, platinum etc.
- For etching on stainless steel.
UNIT TEST PAPER 7C — NITRIC ACID
Question 1.
Select the letters A, B, C, D or E, which form the gaseous products of the reactions from 1 to 5.
A: Nitrogen dioxide only
B: Nitric oxide only
C: Hydrogen
D: Nitrogen dioxide and oxygen
E: Nitrogen dioxide and carbon dioxide.
1. Reaction of manganese with cold very dil. nitric acid.
2. Reaction of sulphur with cone, nitric acid.
3. Reaction of zinc with dil. nitric acid.
4. Reaction of carbon with cone, nitric acid.
5. Heat on nitric acid.
Answer:
- (C) Hydrogen
- (A) Nitrogen dioxide only
- (B) Nitric oxide only
- (E) Nitrogen dioxide and carbon dioxide.
- (D) Nitrogen dioxide and oxygen.
Question 2.
Select the correct word from the list in bracket to complete each statement.
- The oxidised product obtained on reaction of H2S ghs with dil. HNO3 is ……… (sulphur dioxide / sulphur / sulphuric acid).
Ans. sulphur
- Aqua regia is a mixture of one part of…………… and three parts of……… (cone, hydrochloric acid/conc. nitric acid) in which nitric acid……….. (reduces/oxidises) hydrochloric acid to chlorine.
Ans. cone, nitric acid, cone, hydrochloric acid, oxidises
- Pure cone, nitric acid or fuming nitric acid renders the metal…………. (zinc/copper/iron) passive or inactive.
Ans. Iron
- A mineral acid obtained from cone, nitric acid on reaction with a non-metal is……….. (hydrochloric acid / sulphuric acid / carbonic acid).
Ans. sulphuric acid
- The reaction of……….. (calcium carbonate / calcium oxide/ calcium sulphite) with dilute nitric acid is an example of a neutralization reaction.
Ans. calcium oxide
Question 3.
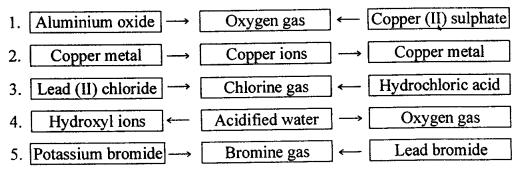
Give balanced equations for the following conversions A to E.
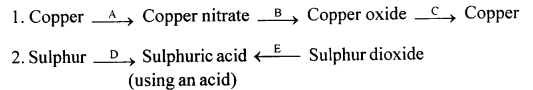
Answer:
1. A: Cu + 4HNO3→ Cu (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO
B:![]()
C : ![]()
2. D : S + 6HNO3→ H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
E : 3SO2 + 2H2O + 2HNO3 → 3H2SO4 + 2NO
Question 4.
Name the oxidised product when the following 1 to 5 react with nitric acid
- Sulphur (with cone, acid)
- Zinc (with dil. acid)
- Aqueous soln. of SO2 (with dil. acid)
- Acidified iron (II) sulphate (with dil. acid)
- Carbon (with cone, acid)
Answer:
1. H2SO4
2. Zn(NO3)2
3. H2SO4
4.Fe2(SO4)3 CO2
Question 5.
Give reasons for the following:
- Nitric acid is not manufactured from atmospheric nitrogen.
Ans. Direct conversion of atmospheric N2 into HNO3 is highly energy intensive process and hence very expensive.
- Nitric acid affects the skin if it accidently falls on it, staining the skin yellow.
Ans. Nitric acid has an extremely corrosive action on the skin – and causes painful blisters. It combines with the protein of the skin forming a yellow compound xanthoproteic acid and hence stains the skin yellow.
- The yellow colour of nitric acid obtained in the laboratory is removed by babbling air through it.
Ans. Yellow colour of the nitric acid is due to dissolved NO2. On bubbling air through it the NO2 is oxidised to HNO3 and the yellow colour of the acid disappears.
- Nitric acid finds application in the purification of gold.
Ans. Nitric acid is used for purification of gold because it can dissolve away all impurities of baser metals (Ag, Cu, etc.), leaving behing pure gold.
- Nitric acid is a stronger oxidising agent in the cone, state of the acid than in the dilute state.
Ans. Cone. HNO3 is a stronger oxidising agent than dil HNO3. It is due to the ease with which cone. HNO3 decomposes to give nascent oxygen, which acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
Question 6.
Answer the following questions pertaining to the brown ring test for nitric acid:
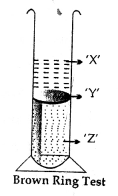
- Name the chemical constituent of the brown ring ‘Y’.
Ans. FeSO4.NO
- Which of the two solutions – iron (II) sulphate or cone, sulphuric acid, do ‘X’ and ‘Z’ represent.
Ans. X-FeSO4 Z-H2SO4 - State why the unstable brown ring decomposes completely on disturbing.
Ans. When test tube is disturbed, cone. H2SO4 mixes with water (in Fe2SO4 solution). Dilution of cone. H2SO4 with water is an exothermic process. The heat so produced assists in the decomposition of unstable brown ring.
- Give a reason why the brown ring does not settle down at the bottom of the test tube.
Ans. Cone. H2SO4), (density 1.98) is twice as heavy as water (density : 1). As such cone. H2SO4 settles down and iron(II) sulphate layer remains alone it resulting in the formation of brown ring at the junction.
- Name the gas evolved when acidified iron (II) sulphate reacts with dilute nitric acid in the brown ring test.
Ans. Nitric oxide (NO)
SOMETHING MORE TO DO
Question 1.
Perform ring test in the laboratory in the presence of your teacher.
Answer:
Brown ring test: Procedure – Take a solution of – a nitrate or dilute nitric acid in a test tube.
Add to it – a freshly prepared saturated solution of iron [II] sulphate.
Add – cone, sulphuric acid carefully from the sides of the test tube.
For More Resources
Hope given New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Nitric Acids helpful to you.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. We try to provide online math tutoring for you