New Simplified Chemistry Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Physical and Chemical Changes
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Simplified ChemistryChemistryPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Points to Remember:
- All changes are classified into two types
- Physical change
- Chemical change.
- Physical Change— A physical change is a temporary change in which no new substance is formed and chemical composition remains same. e.g. Melting of ice.
- Chemical Change— A chemical change is a permanent change, in which a new substance is formed whose chemical composition and physical properties are different, e.g. Burning of a candle.
- Chemical Reaction— Any chemical change in matter involving its transformation into one or more new substances is called a chemical reaction.
- Chemical Equations—A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using the symbols and the formulae of the substances involved in the reaction.
- The substances that react with one another are called reactants, and the new substances thus formed are called products.
- A balanced chemical reaction is one in which the number of the atoms of each element on the reactant side is equal to the number of atoms of that element on the product side.
- The law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor be destroyed.
- A chemical equation gives both qualitative and quantitative information about reactants and products.
- The type of chemical reaction in which two substances combine to form a new substance is known as combination reaction.
- The type of chemical reaction in which a substance breaks up on heating to form two or more simpler substances, which can be either elements or compounds, known as decomposition reaction.
ACTIVITIES & DEMONSTRATIONS
Demonstrations & Discussions – By the Teacher
Classifying – changes into physical & chemical with the help of charts or match the following or by putting X

EXERCISE
Question 1.
Change is the law of nature and occur in our everyday life, at all times and in all places.
Differentiate between the following changes with a suitable example.
(a) Desirable and undesirable change.
(b) Periodic and non-periodic change
(c) Slow and fast change.
(d) Natural and man-made change
(e) Reversible and irreversible change.
Answer:
(a) Desirable and undesirable change
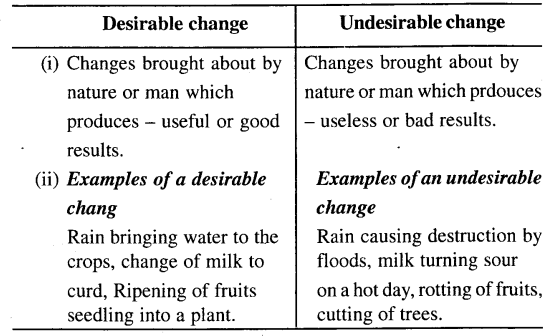
(b) Periodic and non-periodic change
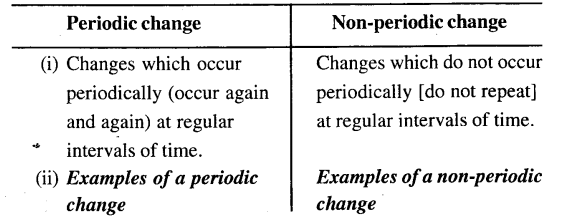

(c) Slow and fast change.
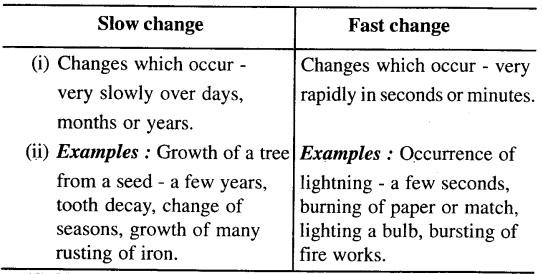
(d) Natural and man-made change
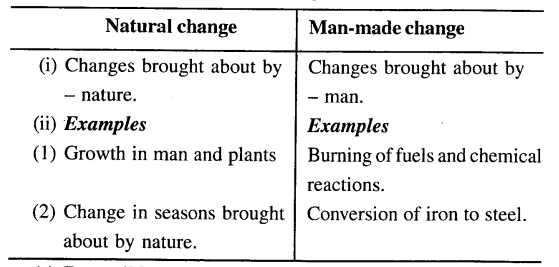
(e) Reversible and irreversible change.


Question 2.
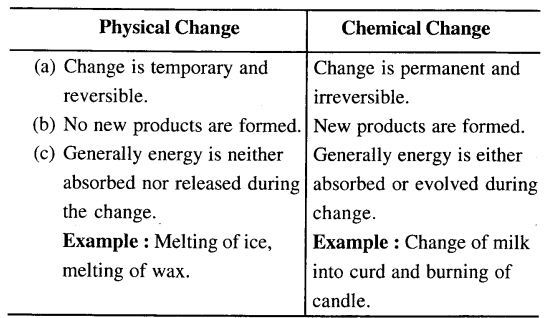
Differentiate between a physical change and a chemical change with reference to –
(a) Nature of change e. temporary and reversible or permanent and irreversible.
(b) Formation of products.
(c) Energy change taking place during the respective change.
Answer:
Question 3.
Give three reasons why melting of wax, is considered a physical change while burning of a candle, a chemical change.
Answer:
Melting of wax is a temporary and reversible change on cooling, wax solidifies and no new product is formed while burning of candle is a permanent change i.e. products are not convertible, new substance is formed having different composition & different properties.
Question 4.
State the observations seen, when milk in a dish is kept aside for a few hours or more. Is the change which occurs – a physical change or a chemical change. Give reasons.
Answer:
On keeping aside – the milk in a dish for a few hours or more. The change observed – will be that the milk has changed into curd. The change is permanent and cannot be reversed. New substance curd is formed. It is a chemical change.
Question 5.
State what is meant by the term – inter conversion of matter. Is inter conversion of matter a physical change or a chemical change.
Answer:
Inter conversion of matter involves, matter changing from one state to another and back to its original state, by change in temperature or pressure. It is a physical change in which one state of matter changes into another state and back again to its original state.
Question 6.
Ice kept in a beaker, slowly melts and turns into water. The water in the beaker on solidification Le. freezing turns back to ice. Give four reasons why the change from ice to water and water back to ice is considered a physical change.
Answer:
Both change are physical changes since
- The change is – temporary
- It is a reversible change
[heating and cooling reverse the change]
heating of ice – turns it into water,
cooling of ice – turns it back into ice - No new products are formed since both ice and water are chemically – ‘H20’
- Properties of the original substance are not altered.
Question 7.
Explain the term – ‘sublimation’. Is sublimation of naphthalene – a physical or a chemical change. Give reasons.
Answer:
It is the conversion of a solid – directly into gaseous [vapour] state and on cooling directly back to solid state – without changing into liquid state.
It involves a change of state-and hence it is a physical change.
Question 8.
Ammonium chloride is also a sublimable solid. Give a reason why sublimation of ammonium chloride involves a physical and a chemical change.
Answer:
Sublimation of ammonium chloride – [NH4C1]
Ammonium chloride sublimes on heating and dissociates into ammonia [NH3] and hydrogen chloride [HC1], which recombine on cooling to give back – NH4C1
![]()
Dissociation – is a chemical change.
Hence, sublimation of such substances involves both – a physical and a chemical change.
Question 9.
State why addition of sodium chloride to water is considered a physical change, while addition of dilute sulphuric acid to zinc is considered a chemical change.
Answer:
Addition of sodium chloride to water is considered as a physical change because it does not form any new substance . but when addition of dilute sulphuric acid is added to zinc. They forms zinc-sulphate hence it is considered as a chemical change.
Question 10.
Photosynthesis is a natural process by which green plants manufacture food in the presence of sunlight.
(a) Are any new products formed during the above process.
(b) Can the change be reversed or is irreversible.
(c) State the conclusions which can be drawn, to represent photosynthesis as a physical or a chemical change.
Answer:
(a) The change is permanent and new products are formed – i.e. glucose and oxygen.
(b) The change cannot be reversed. It is irreversible.
(c) Carbon dioxide and water cannot be obtained back from glucose and oxygen hence it is chemical change.
Question 11.
Give reasons why – separation of mixtures e.g. iron from a mixture of iron and sulphur is a physical change, but heating a mixture of iron and sulphur is considered a chemical change.
Answer:
Physical change
- There is no change in the specific properties of the constituents.
Example: The particles of iron can be separated from sulphur with the help of a magnet or by dissolving sulphur in carbon disulphide. - No new substance is formed.
Example: The mixture of iron and sulphur does not form any new substance. - There is not net release or absorption of energy.
Example: When iron and sulphur particles are mixed, heat energy is neither given out nor absorbed. - It is a temporary change and can be reversed by removing the cause of the change.
Example: The particles of iron can be separated from the mixture with the help of a magnet. removing the cause of change.
Chemical change
- There is a specific change in the prorperties of the – constituents.
Example: The particles of iron or sulphur cannot be separated by a magnet or carbon disulphide. - A new substance is formed.
Example: Iron sulphide is the new substance formed when iron and sulphur are heated. - There is a net release or absorption of energy when a chemical change takes place.
Example: When iron sulphide is formed, the test tube gets red hot on account of the release of a large amount of heat energy. - It is a permanent change and cannot be reversed by removing the cause of the change.
Example: The particles of iron can be separated from the mixture with the help of a magnet.removing the cause of change.
Question 12.
Explain in brief the involvement of energy in – physical and chemical changes.
Answer:
Involvement of energy in physical and chemical changes
- Physical changes use energy to change the state of matter,
- Chemical changes release or absorb energy when changing a substance into a new substance.
Energy is released during a decomposition of a substance while energy is absorbed during formation of a new substance.
Objective Type Questions
Physical & Chemical Changes
1. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate words for each of the statements given below:
- Germination of seeds is considered a chemical change
- If a change is permanent & irreversible it is considered a chemical change
- Heating a piece of iron, is considered a physical change, while heating a piece of coal [carbon] is considered a chemical change
- Chemical changes may involve exchange of energy in the form of light and heat.
- Change of milk of curd is a desirable change
2. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false write – the correct statement.
- Desirable changes are meaningful, while undesirable changes are unfavourable.
True. - During physical changes, the composition of the original substance is not altered, but the properties of the original substance are altered.
True. - During a chemical change the composition of the original substance is not altered and the change is irreversible.
False.During a chemical change the composition of the original substance is altered and the change is irreversible. - Melting of butter and wax are examples of chemical changes.
False. Melting of butter and wax are examples of physical changes. - Melting of ice is an exothermic, irreversible chemical change.
False. Melting of ice is an endothermic, reversible physical change.
3. Match the examples of changes in List I with the correct.

Answer:

4. Fill in the blanks with the correct words for each of the statements given below:
- Sublimation is considered a change of state of matter.
- Sublimation involves a physical change
- During sublimation a solid on heating turns directly into vapour and on cooling back to solid.
- Ammonium chloride, a sublimable solid undergoes dissociation on heating.
- Sublimation of iodine is an example of physical change
5. Name the following:
- The product/s obtained during ‘photosynthesis’ – which is a chemical change.
Ans. Glucose and Oxygen. - The term involved in the change of state from – ‘water to ice’ – which is a physical change.
Ans. Freezing Point. - The final product of the physical change involved during ‘melting of a piece of wax’.
Ans. Wax [CxHy] - The type of change e. physical or chemical involved – ‘during respiration in human beings’.
Ans. Chemical Change. - The type of change physical or chemical involved – ‘when a substance undergoes a change in state, colour or size’.
Ans. Physical Change.