A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -1
These Solutions are part of A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -1.
SECTION I (40 MARKS)
Attempt all questions from this section
Question 1.
(a) It is possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain. [2]
(b)
- When does a force do work ?
- What is the work done by the moon when it revolves around the earth ? [2]
(c) A boy of mass 30 kg is sitting at a distance of 2 m from the middle of a see-saw. Where should a boy of mass 40 kg sit so as to balance the see-saw? [2]
(d)
- What is meant by the term ‘moment of force’?
- If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign then will the turning tendency of the force be clockwise or anticlockwise? [2]
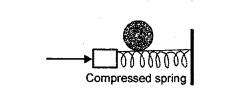
(e) A ball is placed on a compressed spring. When the spring is released, the ball is observed to fly away.
- What form of energy does the compressed spring posses?
- Why does the ball fly away? [2]
Answer:
(a) Yes. Motion of a stone tied to a strong thread in a circular path at constant speed in the horizontal plane is an accelerated motion with constant speed.
Explanation : Consider a stone of mass (m) tied to a strong thread of radius (r), whirled around the point ‘O’ at a constant speed in the horizontal plane, in the clockwise direction.
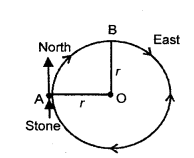
When the stone is at point A, then its motion is directed towards the North. When the stone reaches the point B, then its motion is directed towards East along the tangent drawn to the circumference of the circular path at point B.
From the above two positions, it is clear that when the stone is moving along a circular path, the direction of motion with respect to time (speed) is not the same. In fact the direction changes from point to point. Thus, we can say that the stone may be moving with a uniform speed, but is not moving with a uniform velocity, i.e., it is moving with a variable velocity along the circular path. As the stone is moving with a variable velocity, therefore,
it must have an accelerated motion.
(b)
- Work is said to be done only when a force or its component causes a displacement in its own direction.
- Work done by the moon when it revolves around earth is Zero. (In one complete revolution net displacement is zero)
(c)
- Let the distance of 40 kg from the mean position be ‘x’m. Using principle of moments,
30 x 2 = 40 x X
x = 1.5m
(d)
- Turning effect of force acting on a body about an axis is called moment of force.
- Clockwise.
(e)
- Potential Energy
- Since P.E. is converted into K.E. and is also transferred to the ball. Hence, the ball flies away.
Question 2.
(a) Samir exerts a force of 150 N in pulling a cart at a constant speed of 10 m/s. Calculate the power exerted. [2]
(b) A body of mass 0.2 kg falls from a height of 10 m to a height of 6 m above the ground. Find the loss in potential energy taking place in the body. [g = 10 m s-2] [2]
(c)
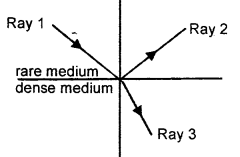
- Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
- A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially
(d) You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens? [2]
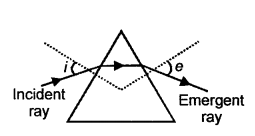
(e) A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence T passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence V.
- How is the angle of emergence ‘e’ related to the angle of incidence ‘i’?
- What can you say about the value of the angle of deviation in such a situation ? [2]
Answer:
(a) Let Time (t) = 1s,
∴ Speed (s) = 10 m
Force (F) = 150 N
Work Done = F x s = 150 x 10 = 1500 Nm = 1500 J
Power exerted = 1500J/1s= 1500 W
(b) Mass, m = 0.2 kg, h = 10 m, g = 10 m s-2 Loss in P.E. = mgh
= 0.2 x 10 x (10 – 6)
= 0.2 x 10 x 4 = 8 J.
(c)
- The absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum
(or air) to the speed of light in that medium i.e., μ = c/v - Ray 2
(d) On moving the printed piece of paper before the lens, if the image is always diminished then it is a concave lens otherwise it is a convex lens.
(e)
- Angle of incident ∠i = Angle of emergence∠e
- The angle of deviation is the angle of minimum deviation
Question 3.
(a)
- What is meant by Dispersion of light’ ?
- In the atmosphere which colour of light gets scattered the least ? [2]
(b) Which characteristic of sound will change if there is a change in
- its amplitude
- its waveform [2]
(c)
- Name one factor which affects the frequency of sound emitted due to vibrations in an air column.
- Name the unit used for measuring the sound level. [2]
(d) An electrical appliance is rated at 1000 kVA, 220V. If the appliance is operated for 2 hours, calculate the energy consumed by the appliance in :
(1) kWh (2) joule [2]
(e) Calculate the equivalent resistance between P and Q from the following diagram : [2]
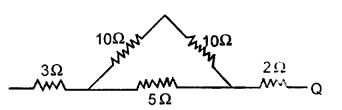
Answer:
(a)
- The phenomenon of splitting of white light of a prism into its constituent colours is called dispersion of light.
- Red colour.
(b)
- Loudness
- Quality or Timbre.
(c)
- Length of air column.
- Decibel (dB)
(d) Energy consumed in KWh = Power x Time
= 1000 x 2 = 2000 kWh
(e) Energy consumed in J = 2000 x 3.6 x 105:J.
= 7.2 x 109 J.
The two 10 Ω resistors are in series and they are parallel to the 5Ω resistor.

Net resistance between P and Q = 3 + 4 + 2 = 9Ω.
Question 4.
(a) (1) What is an a.c. generator or Dynamo used for?
(2) Name the principle on which it works. [2]
(b) Differentiate between heat capacity and specific heat capacity. [2]
(c) A hot solid of mass 60 g at 100°C is placed in 150 g of water at 20°C. The final steady temperature recorded is 25°C.
Calculate the specific heat capacity of the solid. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1]. [2]
(d) (1) What is the value of the speed of gamma radiations in air or vacuum?
(2) Name a material which exhibits fluorescence when cathode rays fall on it. [2]
(e) Which of the radioactive radiations :
(1) can cause severe genetic disorders.
(2) are defected by an electric field. [2]
Answer:
(a)
- An a.c. generator or dynamo is used to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy.
- Faraday’s law of Electromagnetic induction.
(b)
- Specific heat capacity is defined on unit mass but heat capacity is defined on entire mass.
- Specific heat capacity depends on the mass of the body but heat capacity does not depend on the mass of the body.
(c) Heat gained Heat lost (Principle of calorimetry)
150 x 4.2 x (25 – 20) = 60 x C x (100 – 25)
150 x 4.2 x 5 = 60 x C x 75
C = 0.7 Jg-1C-1
(d)
- Speed of gamma radiations in air = 3 x 108 m s-1.
- Zinc suiphide.
(e)
- Radioactive radiations which can cause severe genetic disorders : Gamma (γ )-radiations
- Radioactive radiation which are deflected on electric field : Alpha (α) and beta (β)- radiations.
SECTION II (40 MARKS)
Attempt any four questions from this section
Question 5.
(a)
(1) Which of the following remains constant in uniform circular motion : Speed or Velocity or both?
(2) Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction. [3]
(b)
(1) State the class of levers and the relative positions of
load (L), effort (E) and fulcrum (F) in each of the following cases. 1. A bottle opener 2. Sugar tongs [3]
(2) Why is less effort needed to lift a load by single fixed pulley as compared to
lifting the load directly?[3]
(c)
(1) A moving body weighing 400 N possesses 500 J of kinetic energy. Calculate the velocity with which the body is moving, (g = 10 m s-2).
(2) In what way does an ideal machine differ from a practical machine? [4]
Answer:
(a)
- Speed remains constant,
- Centripetal force directed towards the centre.
(b)
- A bottle opener — Class II lever Load between Fulcrum and Effort
- Sugar Tongs — Class II lever
Effort between Fulcrum and Load.Less effort is required because mechanical advantage increases.
(c)
- Let W = mg ; m=400/10 =40kg
We know that K.E.
500 =1/2 mv2
500 =1/2 ×40×v2
v2= 25
v=5m s-2 - For an ideal machine efficiency is 1 but for a practical machine efficiency is always less than 1. This is due to the following two reasons :
- A part of the input is wasted in moving the parts of the machine.
- A part of the input is wasted in overcoming friction between the various parts of the machine.
Question 6.
(a).
- What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
- How is it related to the refractive index of the medium?
- Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above? [3]
(b) A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right angled prism ABC as shown in the given diagram
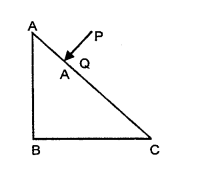
- Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
- What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
- Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
(c) A converging lens is used to obtain an image of an object placed in front of it.The inverted image is formed between F2 and 2F2 of the lens.
(1) Where is the object placed ?
(2) Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the formation of the image obtained.
Answer:
(a)
- Critical angle is the angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 900.
- aμg = cosec ic where ic is the critical angle.
- Depth remain the same. Apparent depth = Actual depth.
(b)
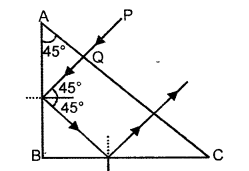
- Angle of deviation (δ) = 180°
- Prism binocular.
(c)
- Object is placed Beyond 2Ft
-
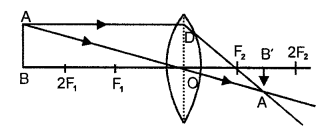
Question 7.
(a)
- What is meant by Resonance?
- State two ways in which Resonance differs from Forced vibrations. [3]
(b)
- A man standing between two cliffs produces a sound and hears two successive echoes at intervals of 3 s and 4s respectively. Calculate the distance between the two cliffs.
The speed of sound in the air is 330 m s-2. - Why will an echo not be heard when the distance between the source of sound and the reflecting surface is 10 m?
(c) The diagram given below shows the displacement-time graph for a vibrating body.
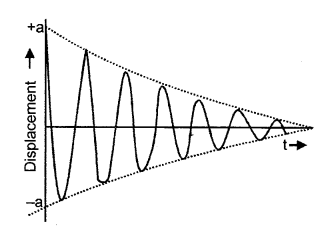
- Name the type of vibrations produced by the vibrating body.
- Give one example of a body producing such vibrations.
- Why is the amplitude of the wave gradually decreasing?
- What will happen to the vibrations of the body after some time? [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) When the frequency of an externally applied periodic force on a body is equal to the natural frequency of the body, the body readily begins to vibrate or free to vibrate with an increased amplitude. This phenomenon is known as resonance.
Resonance
- Vibration are of large amplitude.
- Frequency of an external applied periodic force is equal or an integral multiple to the natural frequency of the body.
Forced Vibrations
- Vibrations are usually small amplitude
- Frequency need not be equal or integral multiple to the natural frequency of the body.
(b)
- d1 = 495m and d2 = 660m
Dist. between the two cliffs = 495 + 660 = 1155 m. - No echo will be heard because least distance of distinct hearing in 17 m.
(c)
- Damped vibrations.
- Tuning fork vibrating in air.
- Due to friction, energy is continuously lost.
- After some time, the amplitude gradually decreases finally stops.
Question 8.
(a)
- A cell is sending current in an external circuit How the terminal voltage compare with the e.m.f. of the cell?
- What is the purpose of using a fuse in an electrical circuit?
- What are the characteristic properties of fuse wire? [3]
(b)
- Write an expression for the electrical energy spent in the flow of current through an electrical appliance in terms of I, R and t.
- At what voltage is the alternating current supplied to our houses?
- How should the electric lamps in a building be connected? [3]
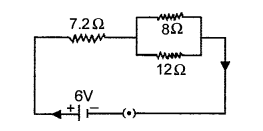
(c) Three resistors are connected to a 6V battery as shown in the figure given alongside.Calculate :
- the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
- total current in the circuit.
- potential difference across the 7.2 Q resistor. [4]
Answer:
(a)
- Terminal voltage < e.m.f.
- An electric fuse is a safety device which limits the current flowing in an electric circuit.
High resistance and Low melting point.
(b)
- We know that E = Vlt = I2R/
- 220 V – 240 V
- In a building, electrical lamps are connected in parallel.
(c)
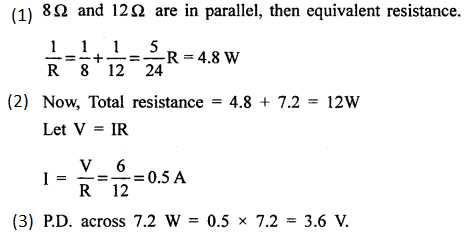
Question 9.
(a)
- Write an expression for the heat energy liberated by a hot body.
- Some heat is provided to a body to raise its temperature by 25°C. What Will be the corresponding rise in temperature of the body as shown on the kelvin scale ?
- What happens to the average kinetic energy of the molecules as ice melts at 0°C? [3]
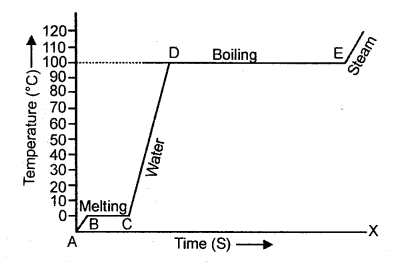
(b) A piece of ice at 0°C is heated at a constant rate and its temperature recorded at regular intervals till steam is formed at 100°C. Draw a temperature – time graph to represent the change in phase. Label the different parts of your graph. [3]
(c) 40 g of ice at 0°C is used to bring down the temperature of a certain mass of water at 60°C to 10°C. Find the mass of water used. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 C-1 [Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 x 103 J kg-1] [4]
Ans.
(a)
- ΔQ = me Δt
where m → mass, c → specific heat capacity; Δt → change in temperature. - Since ΔQ α Δt
Hence the corresponding rise in temperature of the body in kelvin 25 K. - Average kinetic energy of the molecules increases.
(b)
(c)
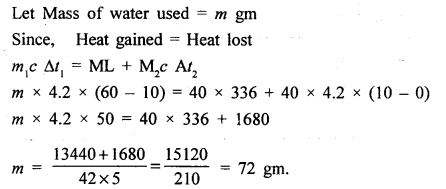
Question 10.
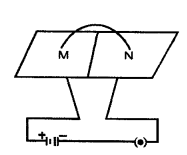
(a) The diagram given below shows a current carrying loop or a circular coil passing through a sheet of cardboard at a points M and N.
The sheet of cardboard is sprinkled uniformly with iron filings.
- Copy the diagram and draw an arrow on the circular coil to show the direction of current flowing through it.
- Draw the pattern of arrangement of the iron filings when current is passed through the loop. [3]
(b)
- Define nuclear fusion.
- Which of the two, fusion or fission is a nuclear chain reaction? Explain. [3]
(c) A certain nucleus X has a mass number 14 and atomic . number 6. The nucleus X change to after the loss of a particle.
- Name the particle emitted.
- Represent this change in the form of an equation.
- A radioactive substance is oxidized. What change would you expect to take place in the nature of its radioactivity? Give a reason for your answer. [4]
Answer:
(a)
- M to N
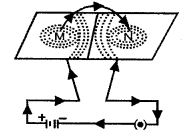
- Anticlockwise around M
Clockwise around N
(b)
- Nuclear fusion : The process of combining lighter nuclei (atomic mass less than 20) into heavier nuclei is called nuclear fusion.
- Fission is a nuclear chain reaction. As one atom of U235 can liberate three neutrons when the atom, of
- U235 is bombarded with a slow moving neutron. If all of these neutrons (or more than one) are utilised to break further U235 atoms, a kind of chain reaction starts with spontaneous release of a large amount of heat energy. Thus nuclear fission is chain reaction.
(c)
- 3-particle
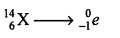
- No change because radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon and oxidation is concerned with outermost orbit.
More Resources
- A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 History and Civics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English Literature and Language
- Merchant of Venice Workbook Answers – ICSE Class 10 English
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Poems Workbook Answers
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Short Stories Workbook Answers
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English – A Collection of Poems & Short Stories
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
Hope given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -1 are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. APlusTopper try to provide online science tutoring for you.