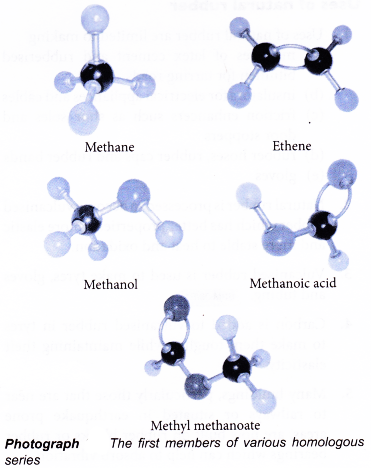
What is the homologous series of Hydrocarbons
What do you mean by homologous series?
Homologous series
- Organic compounds are grouped into different homologous series. Alkanes form a homologous series and so do alkenes.
- A homologous series is a group or family of organic compounds that has certain characteristics:
(a) Members of the series can be represented by a general formula.
(b) Successive members differ from each other by –CH2.
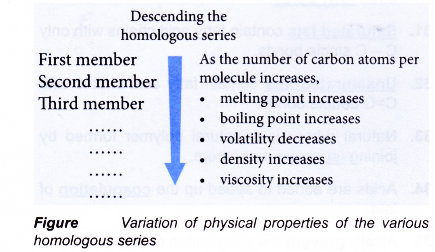
(c) Physical properties change gradually with increasing number of carbon atoms per molecule.
(d) Members have similar chemical properties because they have the same functional group.
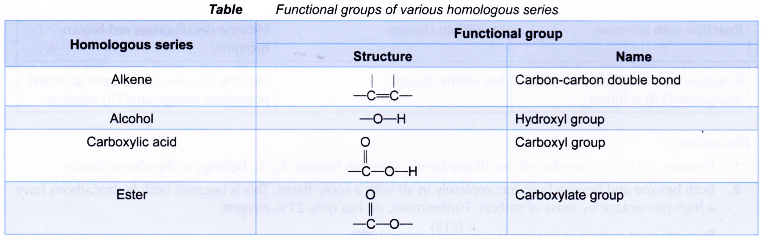
(e) Members can be prepared by similar methods. - A functional group is a special group of atoms attached to an organic molecule. This group of atoms determines the chemical properties of the molecule because it represents the most common site of chemical reactivity. Chemical reactions occur at the functional group.
- Table shows the functional groups of various homologous series.
There is another classification based on Homologous series.
The series of carbon compounds in which two successive compounds differ by –CH2 unit is called homologous series.
Eg: 1) CH4, C2H6, C3H8 …
2) CH3OH, C2H5OH, C3H7OH …
If you observe above series of compounds, you will notice that each compound in the series differs by –CH2 unit by its successive compound.
Homologous series of organic compounds have following characteristic features.
1) They have one general formula.
Eg: alkanes (CnH2n+2); alkynes(CnH2n-2); alcohols (CnH2n+1)OH etc.
2) Successive compounds in the series possess a difference of (-CH2) unit.
3) They possess similar chemical properties due to the same functional group
Eg: alcohols, aldehydes and carboxylic acids have functional groups C–OH, C–CHO and C-COOH respectively.
4) They show a regular gradation in their physical properties (see the table-1).
For example: we may take alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids etc. as homologous series. The individual members of a homologous series are called homologs.
Observe the following tables 1, 2 and 3. They represent three different homologous series.
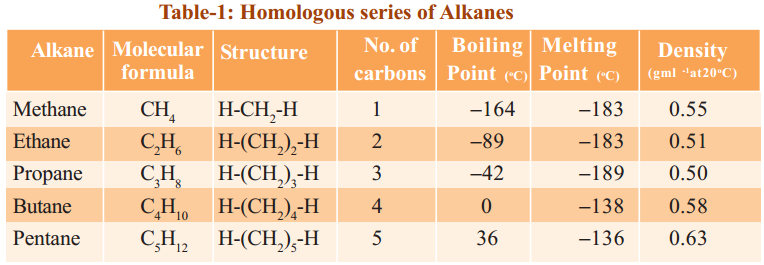
The general formula of this homologous series Alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n = 1,2,3…
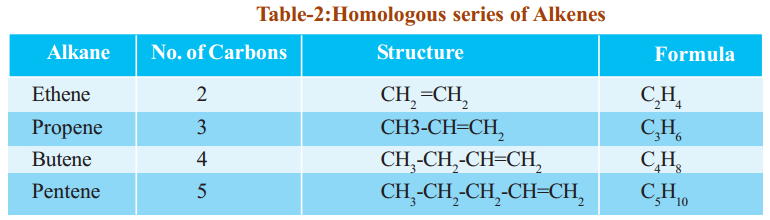
Alkenes have general molecular formula CnH2n, where ‘n’ is 2, 3, 4, …
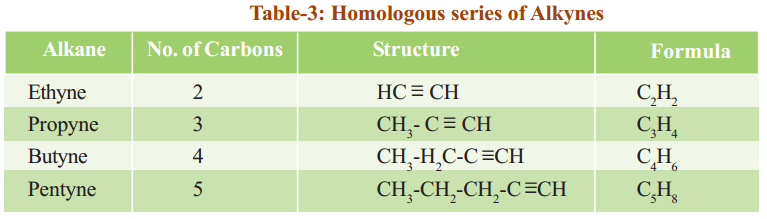
Alkynes have general molecular formula CnH2n-2, where ‘n’ is 2, 3, 4, …
Read More:
- Binding of Carbon with other Elements
- Allotropes of Carbon
- Catenation in Carbon
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- sp3 Hybridized Carbon atom
- Hybridization of the Carbon atoms in Acetylene
- Versatile Nature of Carbon
- What are the Characteristics of Compounds
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
People also ask
- What are carbon compounds?
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- How are alkanes formed?
- What is an alkene in chemistry?
- What is an isomerism?
- What is alcohol and how is it made?
- How are carboxylic acids formed?
- How esters are formed?
- What are fats and oils?
- How palm oil is extracted?
- Order in Homologous Series
- What is the monomer of natural rubber?
- Which acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex?
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- Properties and Uses of Ethanol
- Properties and Uses of Ethanoic Acid