What is the half life of a radioactive element?
Half-life:
- Radioactive decay is a random process. This means that all the unstable nuclei have the same probability to decay at a certain instant. It is not possible to predict when a particular nucleus is going to decay.
- The unstable nuclei will decay at different times, some decay earlier while others will decay at a much later time. Therefore, the number of undecayed nuclei decreases with time.
- The half-life of a radioactive sample is the time taken for the number of undecayed nuclei in the sample to be reduced to half of its original number.
- However, this applies only when the number of undecayed nuclei in the sample is very large. If the number is small, then the number of undecayed nuclei left after one half-life is only expected to be halved. This means that the actual number left may be slightly more or slightly less.
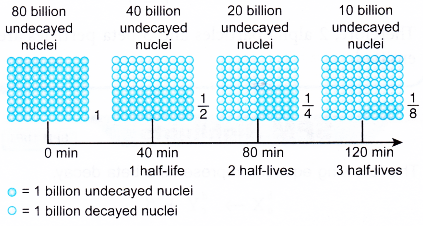
- Xenon-140 has a half-life of 40 minutes.
It takes 40 minutes for the number of undecayed nuclei to decrease to half its original number. Figure illustrates the decay of xenon-140 over 3 half-lives.
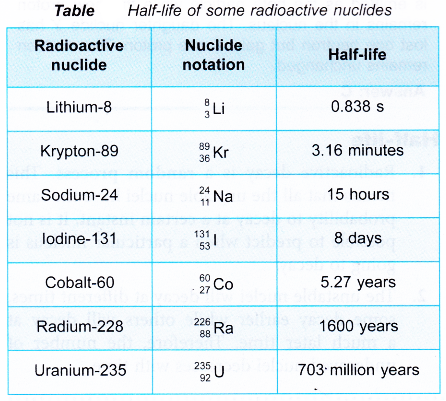
- Some radioactive nuclides have very short half-lives while others have very long half lives. Table gives the half-lives of some radioactive nuclides.
People also ask
- What is the Radioactive Isotope?
- Radioactivity: Types of Radioactive Emissions
- How do you detect radioactivity?
- What is nucleus of an atom?
- What are the different types of radioactive decay?
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- Importance of Proper Management of Radioactive Substances
Half-life and Activity
- The activity of a radioactive substance is the number of decays per second of the unstable nuclei.
- The activity is also called the decay rate.
- As the number of undecayed nuclei decreases with time, the activity of the radioactive substance also decreases with time.
- For a radioactive substance with a relatively short half-life, the change in the activity can be measured by a GM tube connected to a ratemeter as shown in Figure.
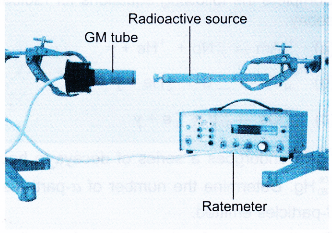
- The activity of the radioactive source is given by the count rate recorded by the ratemeter.
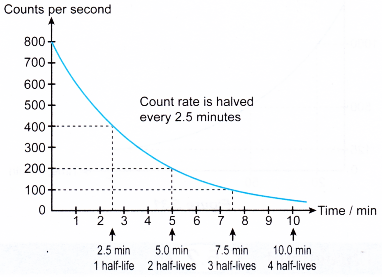
- The count rate is recorded at regular time intervals and a graph of the count rate against time is plotted to obtain the decay curve.
- Figure shows the decay curve for antimony-133 which has a half-life of 2.5 minutes.
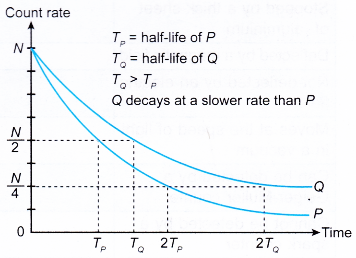
- A radioactive nuclide with a short half-life will decay at a faster rate than another radioactive nuclide that has a longer half-life.
- Figure shows the decay curve for two radioactive nuclides, P and Q.
Half Life Problems and Answers
1. Tin-108 has a half-life of 10.3 minutes. A radioactive sample contains 72 g of tin-108. Determine the mass of tin-108 that has decayed and that has not decayed after 30.9 minutes.
Solution:
The mass of tin-108 that has not decayed will be halved every 10.3 minutes.
30.9 minutes is equivalent to 30.9/10.3 = 3 half-lives.
The decay process is as follows:
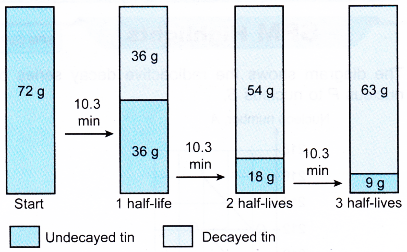
After 30.9 minutes, 9 g of tin-108 has not decayed and 63 g of tin-108 has decayed.
2. The radioactive atoms in a substance decay to become stable atoms. It was found that after 136 s, 93.75% of the atoms have decayed. What is the half-life of the substance?
Solution:
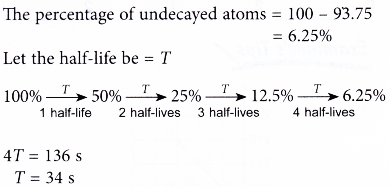
3. A sample of protactinium-234 of mass 100 g has a half-life of of 6.7 hours.
(a) What fraction of the sample has not decayed after 20.1 hours?
(b) What is the mass of undecayed protactinium-234 after this period of time?
Solution:

4. Figure shows the decay curve of a radioactive sample.
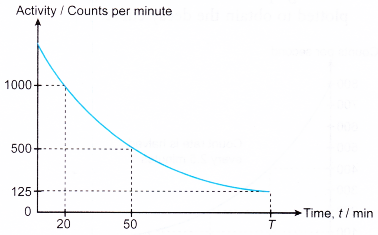
(a) What is the half-life of the sample?
(b) State the value of T.
Solution:
