ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Geography Voyage – Study of Weather
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Geography Voyage. You can download the Voyage Geography ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Geography Voyage for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 7 Geography History & CivicsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
VALUES AND LIFE SKILLS
Many people leave their pets in parked cars. They think they will be gone for a few minutes, or it will be alright to leave a window open. The temperature inside a parked car can rise up to more than 50°C in a matter of few minutes, irrespective of it being a hot or a cloudy day.
What would be the right thing to do if you see a pet locked inside a car on a hot day ?
Answer:
Leaving pets locked in cars is never safe. But when the weather gets warmer, it can be deadly. High temperatures can cause irreparable organ damage and even death. Protecting animals from an unnecessary death is a problem we can all agree to prevent.
EXERCISES
A. Write true or false. Correct the false statements.
1. A rise in temperature causes more condensation while a fall in temperature results in evaporation.
Answer. False.
Correct : Arise in temperature causes more evaporation while a fall in temperature results in condensation.
2. ‘4 o’clock showers’ are caused by cyclonic rainfall.
Answer. False.
Correct : ‘4 o’clock showers’ are caused by convection currents.
3. Heavy rainfall occurs on the leeward or rain shadow side of a highland.
Answer. False.
Correct : Little rainfall occurs on the leeward or rain shadow side of a highland.
4. The direction of wind blowing on the surface of the earth is affected by the Coriolis force.
Answer. True.
5. Cyclones and anticyclones are examples of variable winds.
Answer. True.
B. Fill in the blanks.
1. The temperature of a place depends upon its latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, ocean currents, winds, cloud cover and slope and aspect.
2. Pressure difference causes horizontal movement of air called wind and vertical movement of air called current.
3. Humidity refers to the amount of moisture or water vapour present in the air.
4. Planetary winds are also called permanent or prevailing winds.
5. The amount of cloud cover in the sky is expressed in discs (shaded in different proportions).
C. Answer the following questions in brief.
Question 1.
What are the elements that determine weather and climate?
Answer:
The elements that determine climate are the same as those weather, namely temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, precipitation, wind direction and speed, cloud cover, and sunshine.
Question 2.
Name the factors that determine the temperature at a place.
Answer:
The factors that affect the temperature of a place are latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, ocean currents, winds, cloud cover, and slope and aspect.
Question 3.
How do the following elements influence the weather of a place :
- temperature
- pressure?
Answer:
- Temperature : When the temperature of a place increases, the air gets heated, expands and rises. This leads to a decrease in air pressure in the area. When the temperature falls, the air gets cold, contracts, and descends downwards. This leads to an increase in air pressure. Thus, air pressure decreases with an increase in temperature. This is the reason why areas close to the equator generally have low air pressure.
- Pressure : Atmospheric pressure is the pressure that the atmopshere exerts on the surface of the earth because of its weight. There is a close relationship between pressure and temperature — high temperature means low pressure and vice versa. Pressure difference causes horizontal movement of air called wind and vertical movement of air called current, which together cause circulation of air in the atmosphere.
Question 4.
Name the various forms of precipitation.
Answer:
Rain, drizzle, snow, sleet, and hail are all different forms of precipitation.
Question 5.
How is cloud cover shown on a weather map? Give examples.
Answer:
The cloud cover in the sky is expressed in eighths of the total sky or oktas, which are shown in weather maps as discs shaded in different proportions.
D. Answer the following questions in one or two paragraph’s.
Question 1.
How is weather different from climate?
Answer:
Weather and climate are closely related terms but have different
meanings. Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions of a small area for a short period of time, usually 24 hours or one day, while climate is the average of the atmospheric conditions of a larger area, over a long period of time, usually 35 years.
Question 2.
What is condensation? Explain these different forms of condensation: fog, mist, and dew.
Answer:
Condensation is the process by which water vapour in the air gets converted into tiny droplets of water or ice. It is the opposite of evaporation. Evaporation takes place when air is dry, but condensation occurs only after air is saturated.
Fog and mist are formed at night, when air cools below its dew point near the earth’s surface. Fog is denser than mist and often dangerous because it reduces visibility. Dew forms in winter when the temperature is very low, but not below 0°C.
Question 3.
What do you understand by the term ‘4 o’clock showers’?
Answer:
In regions closer to the equator, the rate of evaporation is very high. Air gets heated because of the high temperature and starts rising in the form of convection currents. As it rises, it expands and cools. The cooling causes condensation, which results in heavy downpours. This rain is accompanied by thunder and lightning and since it mostly occurs around 4 p.m., it is often called the 4 o’ clock showers’.
Question 4.
What are planetary winds? Give a brief description of the Westerlies in the northern hemisphere.
Answer:
Planetary winds are also called permanent or prevailing winds as they blow the year round in the same areas. Westerlies blow in the middle latitudes between 30° and 60° latitude, and originate from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes towards the poles. Under the effect of the coriolis force, they become the South Westerlies in the north hemisphere and Northern Westerlies in the southern hemisphere.
Question 5.
What are local winds? Give a few examples.
Answer:
Local Winds blow for a short period of time over a very small area. Some local winds like Loo, Simoom, Chinook, and are warm winds. Others such as the Bora, Mistral, Buran, and Pampero are cold winds.
E. With the help of your atlas,encylopaedias, and the Internet, find out about the climate of these places.
- Mumbai
- Delhi
- Kolkata
- London
- New York
- Sydney
F. In your notebook, draw neat, labelled, coloured sketches of the three different types of rainfall. Alongside each diagram, briefly describe in your own words, how each type of rainfall occurs.
Answer:
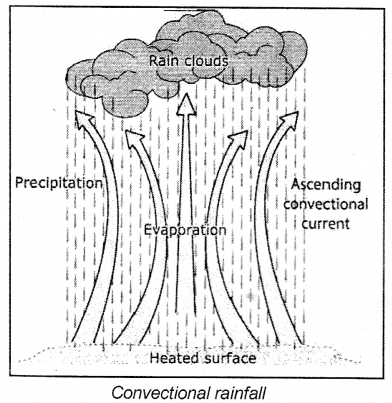
(a) Convectional Rainfall : In regions closer to the equator, the rate of evaporation is very high. Air gets heated because of the high temperature and starts rising in the form of convection currents. As it rises, it expands and cools. The cooling causes condensation, which results in heavy downpours. This rain is accompanied by thunder and lightning and since it mostly occurs around 4 p.m., it is often called the 4 o’clock showers’.
(b) Relief or Orographic Rainfall : Sometimes moisture-bearing winds are forced to rise because of the presence of a physical
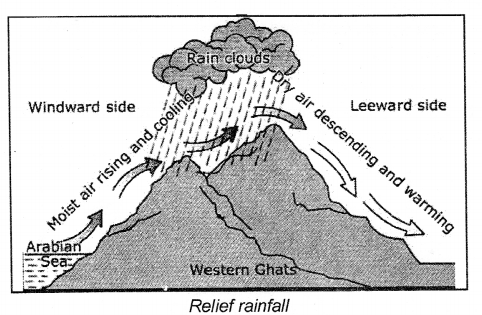
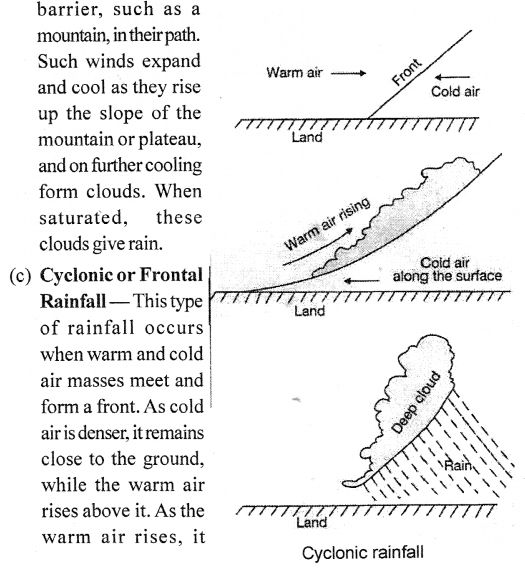
expands and cools, and the moisture in it condenses to form clouds. These clouds bring rainfall.
G. Picture study
Question 1.
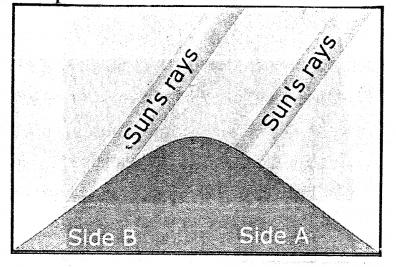
The diagram alongside illustrates one of the factors that affect temperature. What is it ?
Answer:
Aspect refers to the direction of a slope with respect to the sun’s rays. In the northern hemisphere, all the south-facing slope receive the direct rays of the sun and are, therefore, warmer, while the north-facing slopes are cooler. In the southern hemisphere, all the north-facing slopes receive more sunlight than the south-facing slopes.
Question 2.
Which side of the mountain is likely to have houses and be covered with trees ?
Answer:
Side B.