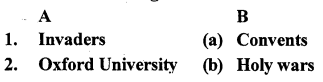ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics – The Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdom
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 7 History & CivicsGeographyMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
Important Words
- Harihara I and Bukka Raya I were the two brothers who established the Vijayanagar kingdom.
- Raichur Doab was the fertile area lying between river Krishna and river Tungabhadra.
- Domingo Paes was a Portuguese traveller who visited the Vijayanagar kingdom in the 16th century CE.
- Abdur Razzaq was a Persian traveller who visited the Vijayanagar kingdom in the 15th century CE.
- Deccanis were the local nobles in the Bahmani kingdom.
- Pardesis were the foreign nobles in the Bahmani kingdom.
Time To Learn
I. Fill in the blanks:
- After the death of Mahmud Gawan the Bahamani kingdom declined.
- The Vijayanagara rulers built the Vithalswami temple.
- The Battle of Talikota was fought in 1565.
- The Vijayanagara empire was founded by Harihara and Bukka Raya.
- Occupation of Golconda, Konkan coast was the main reason behind the Bahamani-Vijayanagara conflict.
II. Match Column A with Column B

Answer:

III. State whether the following statements are True or False:
- The battle of Talikota was fought in
False. The battle of Talikota was fought in 1565. - Before coming to the Bahamani kingdom, Mahmud Gawan was a Persian merchant.
True. - The Bahamani rulers fought with the Vijayanagara rulers over the occupation of the Gangetic Doab.
False. The Bahamani rulers fought with the Vijayanagara rulers over the occupation of the Raichur Doab. - Nicoli Conti and Abdul Razzak visited the Vijayanagara kingdom as foreign travellers.
True.
IV. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
Describe briefly the administration of Vijayanagara rulers.
Answer:
- The Vijayanagar rulers paid great attention to the welfare of people. Most of the land revenue and other taxes were used for public welfare.
- The king was the highest court of appeal. The criminals were severely punished.
Question 2.
Why did the Bahamani kingdom break up and what was the result?
Answer:
There were many reasons which led to the break up of the Bahamani kingdom. Religious intolerance, constant wars with neighbours, the pleasure seeking style of the rulers and mutual quarrels between Deccani and the Irani groups were the main causes. Moreover the later Bahamani rulers were weak and incompetent. After the death of Gawan, the Bahamani kingdom crumbled as there were no competent ministers. As a result Bahamani kingdom broke into five independent states of Bijapur, Golkunda, Ahmednagar, Berar and Bidar which were later conquered by the Mughals.
Question 3.
What was the contribution of the Vijayanagara rulers in the development of art and architecture?
Answer:
The Vijaynagara rulers were great patrons of art, architecture and learning. The city was adorned with beautiful temples. The Hazara Rama and Vithalaswami temple, built by Krishnadev Raya at Hampi, are most remarkable temples.Both the temples are exquisite. Their mandapas, gopurams and towers over the sanctum are beautifully sculptured. They also built The Elephants’ Stable at Vijayanagara.
Question 4.
Discuss the reasons for the conflict between the Bahamani and Vijayanagara empires.
Answer:
The reasons for the conflict between the Vijayanagar and Bahamani kings were the following :
- Both the kingdoms claimed Raichur doab lying between Krishna and Tungabhadra because of its fertile and rich land.
- Both wanted to conquer Golconda because of its diamond mines.
- Both of them were ambitious and wanted to control the whole inusila-peninsula.As such the Bahamani and Vijayanagar kingdom were continuously at war with each other,
Question 5.
Discuss the achievements of Krishnadev Raya.
Answer:
- Krishnadeva encouraged foreign trade with the Portuguese who had established trade centres on the Malabar Coast.
- He earned rich revenue by imposing custom duties and other taxes.
- He took active steps to promote agriculture. Irrigation facilities were develpoed by building dams and canals.
- Krishnadeva Raya was a great patron of art and literature.
- He maintainted a magnificent court and encouraged poets and learned men.
V. Tell my why!
Question 1.
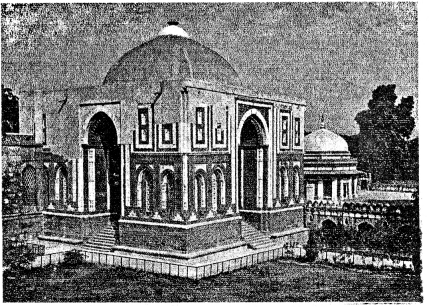
The Gol Gumbaz is called an architectural wonder.
Answer:
The Gol Gumbaz at Bijapur is an architectural wonder. It is the tomb of Muhammad Adil Shah. Its dome is said to be the largest in the world. It has an unparalled acoustic system. Any sound made in the inner gallery of the Gol Gumbaz gives rise to multiple echoes and returns it to the person several times.
Question 2.
Vijayanagara needed to keep a large army.
Answer:
Because of the conflicts between the Bahamani and Vijayanagara kingdom’s.
Question 3.
The Krishna-Tungabhadra doab was a much sought-after area.
Answer:
Because the empire Vijayanagara was situated on Krishna- Tungabhadra doab.And this doab and the people living in the Krishna-Tungabhagra doab memorises some of the Vijayanagar empire and these oral traditions combined with archaeological finds, monuments and inscriptions and other records helped scholars to rediscover the /ijayanagara Empire.
VI. Picure study:
This is a picture of a temple at a capital city:

1.Name the temple.
Ans. Virupaksha Temple.
2. Name the empire and the capital city where it was built.
Ans. Vijayanagara empire and Hampi was capital.
3.Who was the greatest ruler of the empire? Mention the name of the book written by him.
Ans. Krishnadeva Raya was the greatest ruler of the empire. Veera-Saivanruta, Bhava-Chinta-Ratna were the books written by him.
Additional Questions
(The Vijayanagara and Bahamani Kingdomes)
A. Fill in the blanks:
- Vijayanagar was established by two brothers, Harihara and Bukka Rai.
- The Vijayanagar kingdom which was ruled by sixteen kings, was very powerful for 230 years and became the centre of Hindu civilization and culture.
- The Raichur Doab became a battleground for the prolonged struggle between the Vijayanagar and Bahmani kingdoms.
- Each province in the Vijayanagar kingdom was placed under a Governor who was responsible for the administration of that province.
- The two main sources of revenue for the Vijayanagar kingdom were taxes on land and trade.
- The Bahmani kingdom was established by Alauddin Hassan. It lasted for about 200 years and was ruled by eighteen kings.
B. Match the following:

Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer:
1. The greatest ruler of the Vijayanagar kingdom was Harihara/Bukka Raya I/Krishnadeva Raya.
Ans. The greatest ruler of the Vijayanagar kingdom was Krishnadeva Raya.
2. The Vijayanagar kingdom was divided into six/nine/eight provinces.
Ans. The Vijayanagar kingdom was divided into six provinces.
3. The province/village/district was at the bottom rung of the administrative ladder in the Vijayanagar kingdom.
Ans. The village was at the bottom rung of the administrative ladder in the Vijayanagar kingdom.
4. The Bahmani kingdom reached the height of its glory under the leadership of Mahmud Gawan/Alauddin Bahman Shah/Adil Shah
Ans. The Bahmani kingdom reached the height of its glory under the leadership of Mahmud Gawan.
5. The Bahmani rulers patronized Hinduism/Buddhism/ Islam.
Ans. The Bahmani rulers patronized Mam.
D. State whether the following are true or false:
- The founders of the Vijayanagar kingdom brought the whole of South India, from the Tungabhadra to Cape Comorin, under their control.
True.
- The Vijayanagar kingdom had established trade relations with the Dutch.
False. Correct: The Vijayanagar kingdom had established trade relations with the Portuguese. - Vijayanagar was one of the wealthiest kingdoms in the Deccan in the 15th and 16th centuries CE.
True. - Mahmud Gawan slept on a mat and ate in earthen vessels.
True.
- The Bahmani rulers used Persian and Arabic as court languages.
True. –
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
1. How did the collapse of the Sultanate impact North India?
Ans. North India was rocked by political turmoil and instability.
2. What was Krishnadeva Raya’s contribution to literature and art?
Ans. Krishnadeva Raya was a great patron of art and literature. He was himself a Sanskrit scholar and a good Telegu poet. He maintained a magnificent court and encouraged poets and learned men.
3. What is the significance of the Battle of Talikota?
Ans. In the battle of Talikota the five kingdoms of Bijapur, Ahmadanagar, Berar, Golconda and Bidar formed an alliance against Vijayanagar kingdom and gave it a crushing defeat. Due to this battle the Hindu empire in the South was totally finished.
4. What major change was introduced in the village administration of the Vijayanagar kingdom?
Ans. The village administration was at the bottom of the administrative ladder. The old feudal system was revived and hereditary officers governed the village.
5. What measures did the Vijayanagar rulers take to develop agriculture?
Ans. During the regin of Vijayanagar rulers forests were cleared to bring more land under cultivation. Many canals, irrigation tanks and dams were built to improve and develop agriculture.
6. Why were there no major social or cultural changes in the Vijayanagar kingdom?
Ans. The Vijayanagar rulers followed ancient Vedic customs ; therefore there was no major social or cultural changes during that time. The Society was quite conservative and was governed by religious norms. The caste system was rigid and Brahmanas were considered superior and these religious supremos did not allow to have much social or cultural changes.
7. Give one example to show that the Vijayanagar kings were tolerant and liberal.
Ans. The Vijayanagar rulers were staunch Hindus but they were tolerant and liberal in their outlook. They employed Muslims in their army and administration. There was no discrimination between Christians, Jews, Muslims and Hindus.
8. Name any one foreign traveller whose observations are an important literary source of information about the Vijayanagar kingdom.
Ans. Two important sources of information about the Vijayanagar empire had been received from travellers like Domingo Paes from Portugal and Abdur Razzaq from Persia.
9.What was the extent of the Bahmani kingdom?
Ans. Bahmani kingdom stretched from the Arabian Sea to the Bay of Bengal and it also included the whole of northern Deccan with the river Krishna as its southern boundary.
10. Give one example to show that Mahmud Gawan was a patron of learning.
Ans. Mahmud Gawan was a learned man and a patron of learning. He built a madarasa in the capital city of Bidar and donated his private collection of 3,000 books. He gave scholarships to poor and deserving students.
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
What did Krishnadeva Raya do to make the make the Vijayanagar kingdom powerful and prosperous?
Answer:
Krishnadeva Raya took various steps to make the Vijayanagar empire rich and prosperous like:
- He encouraged foreign trade with the Portuguese.
- He collected good revenue from them by imposing custom duties and other taxes.
- He took active steps to promote agriculture.
- Importance was given for increasing irrigation facilities by building dams and canals.
Question 2.
Mention two important features of each of the following in the Vijayanagar kingdom: (a) central government (b) provincial government.
Answer:
(a) Central government:
- The king was the head of the administration and he was considered an absolute ruler and his will was law.
- A council of ministers chosen by him assisted him in administering the empire.
(b) Provincial government:
- The whole empire was divided into six provinces and each province was placed under the charge of a governor.
- The provinces were further divided into districts and each district consisted of a number of villages
Question 3.
Vijayanagar was one of the wealthiest kingdoms in the 15th and 16th centuries Explain.
Answer:
Vijayanagar was one of the wealthiest kingdoms in the 15th and 16th centuries ce. The development of agriculture and the promotion of trade and commerce enriched the treasury. The two main sources of revenue were taxes on land and trade.
The land tax varied from one third to one sixth of the produce, depending on the quality of the land, which was assessed before the tax was levied. Forests were cleared and more land was brought under cultivation. Irrigation tanks, canals and dams were built.
Flourishing trade enriched the kingdom. The market overflowed with foreign imports such as Arabian horses, Chinese silks and Sri Lankan elephants. The main items of export were cotton cloth, sandalwood, rice, sugar and spices.
Question 4.
Describe (a) the importance of trade in Vijayanagar and (b) the position of women in society.
Answer:
(a)
Krishnadeva Raja encouraged foreign trade with the Portuguese who had established trade centres on the Malabar Coast. He earned a rich revenue by imposing custom duties and other taxes on them. He took active steps to promote agriculture. Irrigation facilities were developed by building dams and canals.
(b)
Women in general were respected, but they did not – enjoy much freedom. Child marriage and sati were common practices. Some upper-class women, however, occupied high positions in society and participated in social, literary and even political life.
Question 5.
Briefly discuss the conflict between the Vijayanagar and Bahmani kingdoms over the Raichur Doab.
Answer:
The Raichur Doab was a fertile area, that touched the southern boundary of Bahmani kingdom and northern boundary of Vijayanagar empire. This area become a battleground for both the kingdoms as each one wanted to rule over it because it was a rich source of revenue. It constantly passed on from one hand to another till finally the issue was finished after the defeat of Vijayanagar in the Battle of Talikota
Question 6.
Give an account of the achievements of Mahmud Gawan.
Answer:
As a competent and successful general Mahmud Gawan enlarged the boundaries of the kingdom and recaptured the important port of Goa from the Vijayanagar kingdom.
He was also a capable administrator. He promoted and encouraged agriculture a great deal. As a result the kingdom become economically prosperous.
Mahmud Gawan was a learned man and a patron of learning. He built a madarasa in the capital city of Bidar and donated his private collection of 3,000 books. He gave scholarships to poor and deserving students
Question 7.
What was the actual position of the Bahmani kings in the administrative set-up?
Answer:
The Bahmani king in theory were powerful but in practice authority was depended on the strength of his army. Weak Sultans were controlled by the Ulemas and powerful nobles.
Question 8.
What did the Bahmani rulers do to patronize Islam?
Answer:
To patronize Islam the Bahmani rulers built many beautiful mosques in the capital cities of Gulbarga and Bidar. Madarasas and libraries were also set-up to promote Islamic studies and Persian and Arabic were used as court language.
Question 9.
Why were the sultans of the Deccan easily overpowered by the Mughal emperor of the north?
Answer:
The Sultans of the Deccan were in constant war among each other because of their mutual rivalries and due to this they also lost much of their wealth and become prey of the Mughal emperor of the North.
G Picture study:
This is a picture of the ruins of the capital city of a powerful kingdom in the Deccan which was founded by two brothers.

Question 1.
Identify the city and name the kingdom.
Answer:
Hampi, Vijaynagar kingdom.
Question 2.
Who was the greatest ruler of this kingdom?
Answer:
Krishnadeva Raya.
Question 3.
Mention any five achievements of this ruler.
Answer:
- Krishnadeva encouraged foreign trade with the Portuguese who had established trade centres on the Malabar Coast
- He earned rich revenue by imposing custom duties and other taxes.
- He took active steps to promote agriculture. Irrigation facilities were develpoed by building dams and canals.
- Krishnadeva Raya was a great patron of art and literature.
- He maintainted a magnificent court and encouraged poets and learned men.
Question 4.
Describe briefly the capital city of this kingdom.
Answer:
Hampi, the capital of Vijayanagar, was a splendid city. It was
surrounded by sevan walls and its total circumference was 96 kilometres (60 miles.) The streets were paved and well laid out. The city was studded with gardens, lakes, mansions and temples. Fresh sweet-scented flowers were sold in abundance. Everyone wore jewellery. Diamonds, rubies, pearls and emeralds were openly sold in crowded bazaars.
Question 5.
What is the most outstanding feature of the Gol Gumbaz?
Answer:
Gol Gumbaz has an enormous whispering dome. In this dome the whisper returns back nine times to the person who carries it out.