Undefined Terms Point, Line and Plane
Undefined Terms and Intuitive Concepts of Geometry
Undefined terms:
In geometry, definitions are formed using known words or terms to describe a new word. There are three words in geometry that are not formally defined. These three undefined terms are point, line and plane.
Point (an undefined term):
In geometry, a point has no dimension (actual size). Even though we represent a point with a dot, the point has no length, width, or thickness. Our dot can be very tiny or very large and it still represents a point. A point is usually named with a capital letter. In the coordinate plane, a point is named by an ordered pair, (x,y).
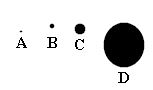
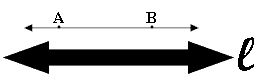
Line (an undefined term):
In geometry, a line has no thickness but its length extends in one dimension and goes on forever in both directions. Unless otherwise stated a line is drawn as a straight line with two arrowheads indicating that the line extends without end in both directions. A line is named by a single lowercase letter, , or by any two points on the line.
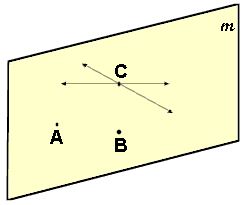
Plane (an undefined term):
In geometry, a plane has no thickness but extends indefinitely in all directions. Planes are usually represented by a shape that looks like a tabletop or a parallelogram. Even though the diagram of a plane has edges, you must remember that the plane has no boundaries. A plane is named by a single letter (plane m) or by three non-collinear points (plane ABC).
Intuitive Concepts:
There are a few basic concepts in geometry that need to be understood, but are seldom used as reasons in a formal proof.
| Collinear Points | points that lie on the same line. |
| Coplanar points | points that lie in the same plane. |
| Opposite rays | 2 rays that lie on the same line, with a common endpoint and no other points in common. Opposite rays form a straight line and/or a straight angle (180°). |
| Parallel lines | two coplanar lines that do not intersect |
| Skew lines | two non-coplanar lines that do not intersect. |
 A plane can be denoted by taking three or more points on it, which do not lie on the same line.
A plane can be denoted by taking three or more points on it, which do not lie on the same line. 


