Stratified Sampling Advantages And Disadvantages: Stratified Sampling is a likelihood Sampling strategy and a type of irregular Sampling in which the populace is separated into at least two gatherings (layers) as per one or more normal credits. These traits can be sex, age, pay, level of instruction and so forth as per the points and goals of the review.
Stratified Sampling means to ensure that the example addresses explicit sub-gatherings or layers. As needs are, utilization of a defined examining strategy includes separating the populace into various subgroups (layers) and choosing subjects from every layer in a proportionate way. The figure underneath delineates an oversimplified model where a test gathering of 10 respondents is chosen by separating the populace into male and female layers to accomplish an equivalent portrayal of the two sexes in the example bunch.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Stratified Sampling? Advantages and Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling 2022
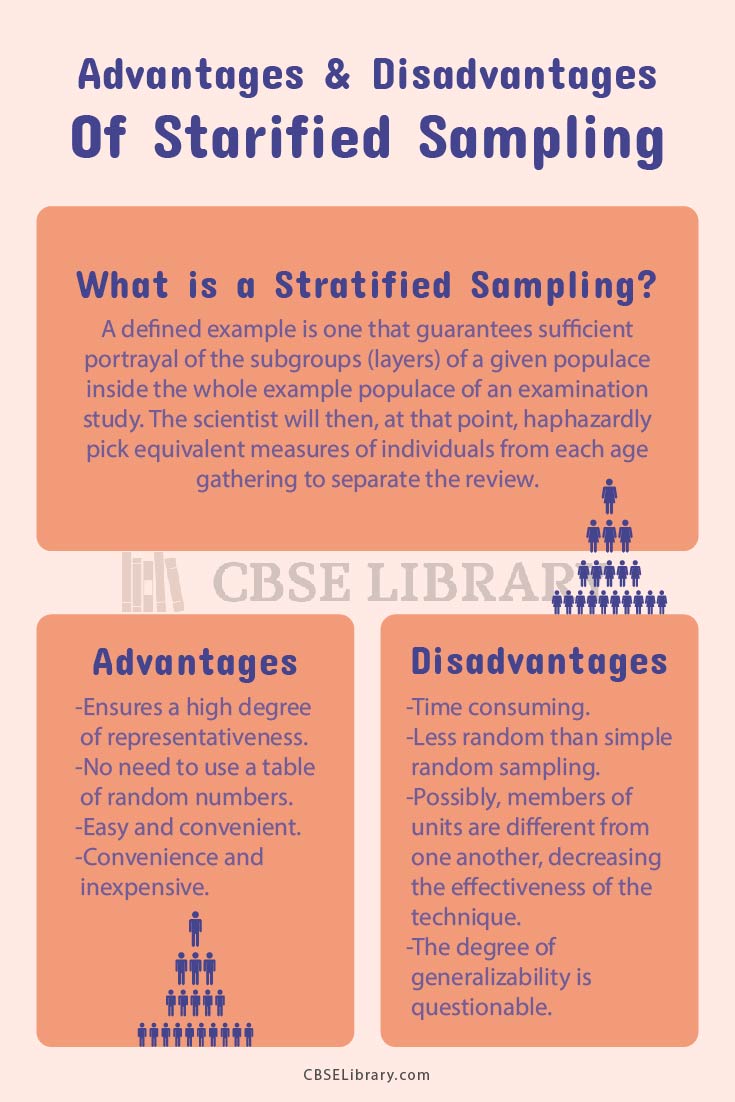
A defined example is one that guarantees sufficient portrayal of the subgroups (layers) of a given populace inside the whole example populace of an examination study. The scientist will then, at that point, haphazardly pick equivalent measures of individuals from each age gathering to separate the review.
Critically, layers utilized in this method shouldn’t cover, since, supposing that they did, a few people would have a higher gamble of being pick than others. This would make a slanted example which would make the examination one-sided and the outcomes invalid. Defined Random Sampling (SRS) utilizes the most widely recognized layers, like age, orientation, instructive fulfilment, financial status, and identity.
There are a few situations where specialists ought to pick Stratified Sampling over other inspecting types. Then, when the specialist needs to investigate subgroups inside a populace, this is utilized. This approach is frequently utilized by scientists when they need to inspect cooperation between at least two subgroups, or when they need to research a populace’s uncommon limits.
With this kind of Sampling, the specialist is ensured to remember subjects from every subgroup for the last example. Interestingly, basic arbitrary Sampling doesn’t guarantee that subgroups inside the example are addressed similarly or proportionately.
- Advantages of Stratified Sampling
- Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling
- Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling
- FAQ’s Pros and Cons of Stratified Sampling
Advantages of Stratified Sampling
- Stratified Sampling is better than straightforward arbitrary examining on the grounds that the most common way of separating lessens inspecting blunder and guarantees a more prominent degree of portrayal.
- This Sampling strategy catches key attributes of the populace in the example.
- On account of the decision of Stratified arbitrary Sampling sufficient portrayal, all things considered, can be guaranteed.
- At the point when there is homogeneity inside layers and heterogeneity between layers, the evaluations can be as exact (or considerably more exact) similarly as with the utilization of straightforward arbitrary Sampling.
Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling
- The utilization of separated irregular Sampling requires the information on layers enrollment deduced. The prerequisite to having the option to effortlessly recognize layers in the example casing might make troubles in viable levels.
- Covering issues might happen such that a few subjects might fall into various subgroups. This can bring about the deception of the populace.
- The research cycle might take more time and end up being more costly because of the additional stage in the examining method.
- The decision of a defined Sampling strategy adds specific intricacy to the examination plan.
Comparison Table for Advantages and Disadvantages of Stratified Sampling
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ensures a high degree of representativeness | Time consuming |
| No need to use a table of random numbers | Less random than simple random sampling |
| Easy and convenient | Possibly, members of units are different from one another, decreasing the effectiveness of the technique |
| Convenience and inexpensive | The degree of generalizability is questionable |
Stratified Sampling can be separated into the accompanying two gatherings: proportionate and unbalanced. Use of proportionate Stratified Sampling strategy includes deciding example size in every layer in a proportionate way to the whole populace. For instance, in the event that the whole populace for exploration is 5000 individuals, in proportionate Stratified Sampling, the gathering can be partitioned into five layers with 1000 individuals in every layer.
In unbalanced Stratified Sampling, going against the norm, quantities of subjects selected from every layer doesn’t need to be proportionate to the complete size of the populace. On the off chance that unbalanced Stratified Sampling is applied in an examination with 5000 individuals, the populace can be partitioned into five layers with the following inconsistent quantities of the populace in every layer: 1000, 1500, 1200, 800 and 500.
FAQ’s Pros and Cons of Stratified Sampling
Question 1.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Stratified Sampling?
Answer:
Utilizing a defined example would frequently accomplish higher precision than a straightforward irregular example, given the layers are picked to such an extent that delegates of a similar layer are pretty much as comparable as conceivable concerning the new trademark. The greater the distinctions between layers, the higher the accuracy gained. One significant disservice of Stratified Sampling is that the choice of suitable layers for an example might be troublesome. A subsequent drawback is that organizing and assessing the outcomes is more troublesome contrasted with a straightforward irregular examination.
Question 2.
What is the use of Stratified Sampling?
Answer:
There are a few situations where specialists ought to pick Stratified Sampling over other Sampling types. Then, when the scientist needs to dissect subgroups inside a populace, this is utilized. This approach is frequently utilized by specialists when they need to look at collaborations between at least two subgroups, or when they need to examine a populace’s strange limits. With this kind of Sampling, the specialist is ensured to remember subjects from every subgroup for the last example. Conversely, basic arbitrary inspecting doesn’t guarantee that subgroups inside the example are addressed similarly or proportionately.
