Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions Atmospheric Pollution
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Atmospheric Pollution
Page No: 128
Question 1.
Define the following terms:
pollution
pollutant
air pollution
Solution:
Pollution may be defined as contamination of air, water or soil by undesirable amounts of materials or heat and is caused by the concentration of substances which have harmful effects.
Toxic and otherwise harmful substances which have an undesirable impact on different components of the environment and life forms are known as pollutants.
Air pollution means degradation of air quality due to concentration of harmful contaminants which affect human, plant and animal lives.
Question 2.
Name any four gaseous pollutants.
Solution:
Sulphur dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons.
Question 3.
Name the compounds of sulphur that cause air pollution. Also state the harmful effects of sulphur compounds.
Solution:
Compounds of sulphur like sulphur dioxide, sulphur trioxide and hydrogen sulphide are pollutants.
Harmful effects of oxides of sulphur:
- It causes headache, vomiting and even death due to respiratory failure.
- It destroys vegetation and weakens building materials/constructions.
- It mixes with smoke and fog to form smog, which is very harmful.
It is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen into sulphur trioxide (SO3) which combines with water to form sulphuricacid.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) →2SO3(g)
SO3(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
Question 4.
State:
natural sources of air pollution
man-made sources of air pollution
Solution:
Volcanoes, decaying vegetation, forest fires and dust storms.
Automobiles, factories, industrial processes and decay of crop residue in rural areas.
Question 5.
a. How do oxides of nitrogen enter the atmosphere?
b. What are their harmful effects?
Solution:
Nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) enter the atmosphere in the following ways:
- On burning of fuels in furnaces, temperature increases. At high temperature, nitrogen and oxygen present in air combine to form oxides of nitrogen.
- When fuel burns in an internal combustion engine, oxides of nitrogen are produced, and they enter the atmosphere as exhaust gases from automobile engines.
- Nitric acid is formed by the reaction between atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen in the presence of electric discharge, which occurs during thunderstorms when there is lightning.
- Nitric oxide further reacts with atmospheric oxygen and ozone to form nitrogen dioxide.
Harmful effects of the oxide of nitrogen
- Nitrogen dioxide is very harmful to plants and animals.
- It causes irritation in the mucous membrane.
- Large concentrations of NO2 may cause serious lung diseases.
- Nitrogen dioxide causes serious injury to vegetation; it damages plant leaves.
- In sunlight, nitrogen dioxide oxidises hydrocarbons to form photochemical smog. Photochemical smog causes eye irritation, asthma attacks and nasal and throat infections.
Question 6.
State the origin and health impact of smog.
Solution:
Smog is a dark, thick, dust and soot-laden fog pollutant which is a combination of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur and of partially oxidised hydrocarbons and their derivatives produced by industries and automobiles.
Smog is noxious and irritating. It reduces visibility, induces respiratory troubles and can cause death by suffocation.
Question 7.
What are the harmful effects of oxides of sulphur?
Solution:
Harmful effects of oxides of sulphur:
- It causes headache, vomiting and even death due to respiratory failure.
- It destroys vegetation and weakens building materials/constructions.
- It mixes with smoke and fog to form smog, which is very harmful.
It is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen into sulphur trioxide (SO3) which combines with water to form sulphuricacid.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) →2SO3(g)
SO3(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
Question 8.
State the main sources and effects of carbon monoxide.
Solution:
Carbon monoxide is formed by incomplete combustion of fuels in homes, factories and automobiles.
Effects of carbon monoxide are as follows:
- It is a highly poisonous gas.
- It reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood by an amount equivalent to the amount of haemoglobin converted to carboxyhaemoglobin.
Haemoglobin + CO → Carboxyhaemoglobin - Because heart and brain are the two tissues most sensitive to oxygen depletion, they show the most serious effects of carbon monoxide exposure.
- In high concentrations, carbon monoxide may kill by paralysing normal brain action.
Question 9.
Give the mechanism of the action of carbon monoxide.
Solution:
- It is a highly poisonous gas.
- When inhaled, it passes through the lungs directly into the blood stream. There it combines with haemoglobin, the substance which carries oxygen to body tissues. Because haemoglobin binds with carbon monoxide 200 times more strongly than oxygen, even low concentrations of carbon monoxide in air have magnified effects on the body.
- It reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood by an amount equivalent to the amount of haemoglobin converted to carboxyhaemoglobin.
Haemoglobin + CO → Carboxyhaemoglobin
Question 10.
How can we control carbon monoxide poisoning?
Solution:
Carbon monoxide pollution can be controlled in the following ways:
- By switching over from internal combustion engines to electrically powered cars.
Many pollution control devices are now installed in cars. Most of these devices help reduce pollution by burning gasoline completely. Complete combustion of gasoline produces only carbon dioxide and water vapour.
2C8H18 + 5O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O - By using substitute fuels for gasoline: Natural gas in both compressed (CNG) and liquefied forms (LNG) is now increasingly being used as fuel. Alcohols are other feasible substitutes.
- By using catalytic convertors: Nitrogen oxide is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen in the presence of finely divided platinum or palladium as a catalyst.

Page No: 130
Question 1.
Why does rain water have pH less than 7?
Solution:
Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form weak carbonic acid which is slightly acidic having pH about 5.6.
Hence, the pH of rain water usually ranges between 5.6 and 3.5; at times, it can be as low as 2.
Question 2.
pH of acid rain is sometimes as low as 2. Explain.
Solution:Normal rain is only slightly acidic having pH about 5.6.
This is because carbon dioxide reacts with it to form weak carbonic acid.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
pH of acid rain usually ranges between 5.6 and 3.5; at times, it can be as low as 2.
Question 3.
Explain the formation of acid rain due to:
1. Oxides of sulphur
2. Oxides of nitrogen
Solution:
- Sulphur is a non-metallic element found in coal and fuel oil. When these fuels are burned, sulphur combines with oxygen in air to form its gaseous oxides, sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3).
S + O2 → SO2
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 - Sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide react with water to form H2SO4 which is the main cause of acid rain.
2SO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 - Nitric acid is formed by the combination of nitrogen and oxygen. Nitrogen and oxygen combine in the presence of thunder and lightning. Oxides of nitrogen are also produced by internal combustion engines.
N2 + O2 → 2NO - Nitrogen oxide then gets oxidised in the atmosphere to nitrogen dioxide.
2NO +O2 → 2NO2
- Nitrogen dioxide combines with water to form a mixture of nitrous acid and nitric acid.
2NO2 + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
Question 4.
What are the causes of acid rain?
Solution:
The main causes of acid rain are the formation of mineral acids such as carbonic acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid during rains.
Question 5.
Give the impact of acid rain:
1. on plants
2. on soil
3. on water bodies
Solution:
Acid rain causes loss of nutrients from plants, thus damaging their leaves.
It removes calcium and potassium both basic ingredients of soil, thus making it lose its fertility which ultimately damages forests.
Acid rain has serious ecological impacts as it affects water bodies too. The water of lakes and rivers is gradually becoming acidic due to acid rain which is affecting aquatic life.
Question 6.
How does a scrubber help in reducing the formation of acid rain?
Solution:
A scrubber can also be used to reduce the formation of acid rain. It is a device which absorbs gaseous pollutants. It is used for removing sulphur dioxide from a smoke stack, and usually consists of a fine spray of water and gas rising from the stack, which is passed through the scrubber where water absorbs sulphur dioxide.
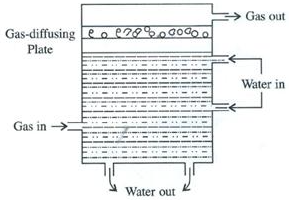
Page No: 131
Question 1.
What do you understand by Green House effect?
Solution:
Heating of the Earth and its environment due to solar radiation trapped by carbon dioxide and water vapour in the atmosphere is called greenhouse effect.
Question 2.
What are green house gases? How are they responsible for global warming?
Solution:
Gases which contribute to the greenhouse effect are called greenhouse gases. These gases are carbon dioxide, water vapour, oxides of nitrogen, methane, ozone and chlorofluorocarbons. Sunlight reaching Earth consists of three types of radiation-UV radiation, visible radiation and IR radiation. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, most UV radiation is absorbed by ozone; 30% of IR radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, heating it up. As the Earth’s surface becomes hot, it starts emitting radiation with less energy than the incoming radiation and thus with longer wavelength. Some emitted IR radiation escapes from the Earth’s surface and some are absorbed by CO2, thus remaining on the Earth. Trapped radiation warms the Earth’s surface and lower layers of the atmosphere.

Question 3.
State the sources and effects of the following gases:
1. Carbon dioxide
2. Methane
3. Water vapour
Solution:
Sources of carbon dioxide:
- Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and petroleum
- Industrial processes such as manufacture of lime and those in fermentation units
- Biological decay of plants
- Respiration by animals, human beings and plants
Effects of carbon dioxide:
- Greenhouse effect and global warming
Sources of methane:
- Anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in soil, water and sediments
- Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels
Effects of methane:
- Greenhouse effect and global warming
Sources of water vapour:
- Burning of hydrocarbons
- Evaporation and transpiration
Effects of water vapour:
- Greenhouse effect and global warming
Question 4.
State the ways of reducing the presence of green house gases.
Solution:
Ways of reducing the presence of greenhouse gases:
- Minimise the use of automobiles: Depending on the situation, one can use a bicycle, the public transport system and car pools.
- Plant more trees to increase green cover.
- Avoid burning of dry leaves and wood.
- Avoid smoking. It is illegal to smoke in public places and work places, because smoke is harmful not only for the one who is smoking but also for others sitting nearby.
- Help people in understanding global warming; most people are unaware of it.
Question 5.
State the effects of green house gases on the atmosphere.
Solution:
Effects of global warming
- Rise in sea level: Due to global warming, glaciers and polar ice caps have started to melt, and gradually this may lead to an increase in the sea level. This will in turn flood several coastal areas in countries such as India, Bangladesh, the Netherlands and the Maldives.
- Global warming will cause more water to evaporate from water bodies, thus forming more water vapour. Because water vapour also contributes to the greenhouse effect, global warming will further increase.
- Global warming can lead to changes in the rain pattern and thus shift in crop zones. For example, wheat-producing zones will shift from Russia and Canada to the less fertile polar regions.
- Change in rain pattern due to global warming will also affect trees and plants in forests which are natural habitats of wild life. With destruction of forests, many species of wild life will also begin to die out.
Question 6.
State the role of a green house in growing plants.
Solution:
A greenhouse collects light and converts it to heat. It also stores thermal energy and helps moderate temperature and produces a controlled environment for plants to grow and thrive. It even offers protection from wind, rain, snow and other weather elements and protects fruits from invading pests and animals.
Question 7.
Our atmosphere acts as a green house. Explain.
Solution:
Our atmosphere contains greenhouse gases such as CO2, water vapour, O3, CH4, oxides of nitrogen and CFCs and allows the sunrays to come in. Sunlight reaching the Earth consists of three types of radiation-UV radiation, visible radiation and IR radiation. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, most UV radiation is absorbed by ozone; 30% of IR radiation reaches the Earth’s surface, heating it up. As the Earth’s surface becomes hot, it starts emitting radiation with less energy than the incoming radiation and thus with longer wavelength. Some emitted IR radiation escapes from the Earth’s surface and some are absorbed by CO2, thus remaining on the Earth. Trapped radiation warms the Earth’s surface and lower layers of the atmosphere.

Question 8.
How can we reduce global warming?
Solution:
Ways of reducing global warming:
- Minimise the use of automobiles: Depending on the situation, one can use a bicycle, the public transport system and car pools.
- Plant more trees to increase green cover.
- Avoid burning of dry leaves and wood.
- Avoid smoking. It is illegal to smoke in public places and work places, because smoke is harmful not only for the one who is smoking but also for others sitting nearby.
- Help people in understanding global warming; most people are unaware of it.
Page No: 134
Question 1.
What is a pollutant?
Solution:
The toxic substances that have an undesirable impact on different components of the environment and are injurious to life and property are known as pollutants.
Question 2.
What is the effect of the following pollutants on living beings (one in each case)?
Fluorides
Smoke particles
Lead
Mercury compounds
Smog
Nitrogen oxide
Solution:
Effect of Pollutant on living beings:
- Fluorides: Effects teeth and bones.
- Smoke Particles: Cause asthma and lung diseases.
- Lead: Damages the nervous and digestive systems and can cause cancer .
- Mercury compounds: They cause disease like Minamata commonly found in fishermen.
- Smog: It reduces visibility and induces respiratory troubles.
- Nitrogen Oxide: Causes death of many plants.
Question 3.
What is air pollution? How does this pollution take place?
Solution:
Air pollution: Deterioration of air quality around us is called air pollution. It is defined as the presence of a contaminant in the atmosphere in a concentration large enough to injure human, plant and animal life.
Air pollution takes place due to the presence of gaseous pollutants like oxides of sulphur, hydrocarbons, smoke, oxides of carbon, oxides of nitrogen, dust, particulate pollutants like mist, spray and fume.
Question 4.
What are the components of clean, dry air?
Solution:
Components of air is:
| Pure Air components | By Volume percentage | Concentration parts per million (ppm) |
| Nitrogen | 78.09 | 780,900 |
| Oxgyen | 20.94 | 209,400 |
| Inert Gases Argon | 0.93 | 9300 |
| Neon | 18 | |
| Helium | 5 | |
| Krypton | 1 | |
| Xenon | 1 | |
| Carbon-dioxide | 0.03 | 315 |
| Methane | 1 | |
| Hydrogen | 0.5 | |
| Natural pollutants Oxides of nitrogen Ozone | 0.52 |
Question 5.
Name some particulate pollutants.
Solution:
Particulate Pollutant are dust, smoke, mist, spray and fume.
Question 6.
Why is cigarette-smoking harmful?
Solution:
Cigarette smoking is harmful not only for one who is smoking but also for sitting nearby and so one should avoid it. Tobacco smoke causes lung cancer and asthma.
Question 7.
What is smog? State its damaging effects.
Solution:
Smog: A smog is a pollutant which is a combination of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen, partially oxidized hydrocarbons and their derivatives produced by industries and automobiles from a dark, thick dust and soot laden fog known as smog.
Damaging Effect: Smog is noxious and irritating. It reduces visibility, induce respiratory troubles and can cause death by suffocation.
Photochemical Smog damages the tissues of certain plants and even decreases the yield of citrus fruits and grapes.
Question 8.
What do you understand by ppm?
Solution:
ppm means parts per million. That is, share in 10, 00000.
Question 9.
Describe the major air pollutants. How does carbon monoxide pollute our environment?
Solution:
Major air pollutants are: Large amounts of Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide, H2S, Chlorine, HCl, Hydrocarbons and particulates. Particulate matter like sand, dust etc. Secondary pollutant like (PAN) peroxyaryl.
Question 10.
How do you propose to control:
a. carbon monoxide emission
b. SOx emission
Solution:
Control of: (i) Carbon monoxide, CO emission:
Emission of CO can be controlled by :
- Switching over from internal combustion engine to electrically powered cars. (b) Using alcohols, CNG, LNG in place of gasoline.
- By using Catalytic Mufflers or Convertors.
- Using pollution control devices to burn gasoline completely.
- Using lead free petrol.
- By using catalytic convertors
Nitrogen oxide is reduced to nitrogen and oxygen in the presence of finely divided platinum or palladium as catalyst.
2NO → N2 + O2
2NO2 → N2 + 2O2 - Carbon monoxide changes to carbon dioxide in the presence of finely divided platinum as catalyst.
CO → CO2 + H2O
(ii) (SOx) oxides of Sulphur emission: Oxides of sulphur (SO, SO) emission can be reduced by-
(a) Using coal or oil that has low sulphur content. (b) By using Scrubber, a device that absorbs gaseous pollutants.
Question 11.
Give the composition, causes and effects of acid rain.
Solution:
Acid rain
Factories in big cities release nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide as their wastes. These gases dissolve in rainwater during rains and form nitrous acid and sulphurous acid. As the rain falls, these acids come down to the ground as an acid rain.
The normal rain is slightly acidic having a pH about 56 as carbon dioxide gas reacts with it to form a weak carbonic acid.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
(Carbonic acid)
The pH of acid rain ranges between 56 – 35 and in some cases pH can go even lower than 2.
The two forms of deposition of acid rains are:
- Dry deposits-Particles containing sulphates and nitrates
- Wet deposits-dew, rain, fog, smoke
Formation of acid rain
- Acid rain refers to rain which has pH less than 5.6. It is mainly caused by atmospheric pollutants.
- Natural sources: Bacterial decomposition, forest fires, volcanic eruptions.
- Man made sources: Industries and smelting plants, automobile exhausts, power plants etc.
- Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur interact with water vapour in presence of sunlight in the atmosphere to form nitric acid and sulphuric acid mist respectively. This mist remains as vapours at high temperatures and condenses at low temperatures. These acids mix with rain (snow or fog) and fall down on the Earth resulting in acid rain.
Causes of acid rain
- The formation of mineral acids like carbonic acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid is the main cause of acid rain.
Formation of Nitric acid and Nitrous acid
- Nitrogen and oxygen (that is oxides of nitrogen) combines in the presence of thunder and lightning to form nitric acid.
- They are also produced by internal combustion engines (automobile engines). This then gets oxidized in the atmosphere to nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide combines with water to form a mixture of nitrous acid and nitric acid.
N2 + O2 → 2NO
(Nitrogen oxide)
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
(Nitrogen dioxide)
2NO2 + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
(Nitrous acid) (Nitric acid)
Formation of Sulphuric acid and Sulphurous acid
Impurities in the coal: Coal used in power plants contains upto 4% sulphur. On combustion it forms pollutant sulphur dioxide (i.e, oxides of sulphur).
S + O2 → SO2
(Sulphur dioxide)
Sulphur dioxide reacts with water vapour to form sulphurous acid.
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
(Sulphurous acid)
Sulphur dioxide can also be oxidized to sulphur trioxide.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
(Sulphur trioxide)
Sulphur trioxide reacts with water vapour to form sulphuric acid.
SO3 + H2O H2SO4
(Sulphuric acid)
Impact of Acid rain
Changes the acidity of soil: The acids present in the acid rain like, nitric acid, nitrous acid and sulphuric acid, sulphurous acid increases the acidity of soil. It removes calcium and potassium minerals i.e., basic ingredients from the soil losing their fertility.
The hydrogen ions H+ which are added to the soil, when acid rain falls on the Earth interact chemically with existing soil minerals.
![]()
Affects water bodies and marine organisms: The water of lakes and rivers is becoming acidic, which may no longer support aquatic life.
Material damage: It increases corrosion of metals, disintegrates paper and leather. Weakens building materials such as statues, marbles, sculptures, limestone, slate, mortar etc. These materials become pitted and weakened mechanically. The Taj Mahal in India faces this problem.
CaCO3 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + CO2 + H2O
CaCO3 + 2HNO3 → Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
Impact on living things: It damages forests. Acid rain gets absorbed by plants, animals directly or indirectly toxicity enters food chain affecting humans. They can affect a person’s breathing, at sufficiently high concentrations. Sulphur dioxide irritates the upper respiratory tract, which serve to expel soot particles and dust in the inhaled air. At even lower concentrations, it does still greater harm by injuring lung tissues.
Question 12.
Explain the effect of sulphur dioxide on the atmosphere.
Solution:
Harmful effects of oxides of sulphur:
- It causes headache, vomiting and even death due to respiratory failure.
- It destroys vegetation and weakens building materials/constructions.
- It mixes with smoke and fog to form smog, which is very harmful.
- It is oxidised by atmospheric oxygen into sulphur trioxide (SO3) which combines with water to form sulphuric acid (H2SO4). Sulphuric acid is the cause of acid rain.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g)
SO3(g) + H2O →H2SO4(aq)
Question 13.
Explain the formation of ozone in the atmosphere.
Solution:
In the atmosphere ozone is formed by the action of ultraviolet rays of the sun on oxygen.
3O2 (g) → 2O3(g)
The high energy UV radiations break oxygen molecules into oxygen atoms.
O2 + Far UV → O + O
Oxygen molecule Oxygen atoms
Oxygen atom reacts with oxygen molecule to form ozone.
O + O2 → O3
Atom Molecule Ozone
The Net reaction is:
3O2 + Far UV → 2O3
Question 14.
What is the function of ozone in the atmosphere?
Solution:
It is formed by the action of ultraviolet rays of the Sun on oxygen.
O3 → O + O2
Ozone layer acts as a blanket in the atmosphere 16 km height above the Earths surface.
It absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays (UV radiations) coming from the Sun and prevents them to reach the surface of the Earth.
Ultraviolet rays have very harmful effects on living things. It causes skin cancer. It destroys many organic species which are necessary for life.
Thus it protects the life on earth from harmful effects of Ultra Violet Rays. Which can cause (a) Skin cancer (b) destroy many organic species necessary for life.
Question 15.
State the chemicals responsible for ozone layer destruction.
Solution:
Chemicals responsible for ozone destruction free radical chlorine (Cl) and nitrioxide (NO) are responsible for ozone depletion i.e. react with O3Free radical chlorine (Cl) is produced by UV rays from chlorofluoro carbons enter the atmosphere because of excessive use as solvents, Aerosol, Spray, Propellants, Refrigerants and blowing agents for plastic foams.
Chemicals responsible for the depletion of ozone layer
Fuel of planes: Burning of fuels of planes emits large quantity of nitric oxide and other gases in the atmosphere. Nitric oxide reacts with ozone and form nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen trioxide. This causes depletion of ozone.
NO(g) + O3(g) → NO2(g) + O2(g)
(Nitrogen dioxide)
NO2(g) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O2(g)
(Nitrogen trioxide)
Excessive use of chlrofluro carbon: It is released by refrigerators and air conditioning systems.
It causes reduction of ozone layer that protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays (UV radiations) of the Sun.
The chlorofluro carbons are decomposed by the ultraviolet rays to highly reactive chlorine which is produced in the atomic form.
![]()
The free radical [Cl] reacts with ozone to form chlorine monoxide.
Cl + O3 → ClO + O2
(Chlorine monoxide)
This causes depletion of ozone layer. Chlorine monoxide then reacts with atomic oxygen to produce more chlorine free radicals.
ClO + O → Cl + O2
(Free radical)
Again this free radical destroys ozone and the process continues giving rise to depletion of ozone layer.
Question 16.
Name any two:
natural sources of atmospheric pollution.
gases which are responsible for the formation of acid rain.
Solution:
Natural sources of atmospheric pollution:
- Decay of plants and animals
- Disintegration of rocks and soil
- SO2 and NO2 are gases responsible for acid rain
Question 17.
Explain the term ‘global warming’. State two ways by which global warming can be reduced.
Solution:
Global warming is the increase in temperature of Earth due to enhanced concentration of greenhouse gases (CFCs) in the atmosphere.
Two ways to reduce global warming:
- Plant more trees to increase green cover
- Minimise the use of automobiles
Question 18.
State two effects of ozone depletion.
Solution:
Effects of ozone depletion:
- UV rays of the Sun reach Earth and cause sun burn, premature ageing of the skin and skin cancer.
- UV radiation can also damage several parts of the eyes, including the lens, cornea, retina and conjunctiva.
Question 19.
What is the cause of acid rain? Give any two impacts of acid rain.
Solution:
Causes:
Sulphur and nitrogen oxides are emitted by burning fossil fuels. Such smoke and gases entering the atmosphere make a dilute soup of sulphuric and nitric acids. This falls on the land surface in the form of acid rain damaging the things on Earth.
Impacts:
- Acid rain accelerates the decay of building materials and paints, including buildings, statues and sculptures which are part of our nation’s culture and heritage.
- Acid rain causes respiratory problems in humans, especially for people suffering from asthma. It may cause throat irritation, dry cough and severe headache.
Question 20.
Explain the methods of preventing acid rain.
Solution:
Methods of preventing acid rain:
- By using coal or oil which has low sulphur content. This reduces the emission of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen responsible for acid rain.
- By using a scrubber, a device which absorbs gaseous pollutants.
Question 21.
State an advantage of CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
Solution:
Using CNG causes less pollution. It does not contain lead, and it has low maintenance cost.
Question 22.
State how CFC break ozone layer.
Solution:
Depletion of O3 by CFC:
CFC is broken by UV rays of sunlight to produce [Cl] atom or free radical [Cl] which is highly reactive in the atomic form and it forms ClO(g) with O2.
CFCl3 → CFCl2 + Cl(atom)
Cl(g) + O3(g) → ClO(g) + O2(g)
This depletes ozone.
ClO further produces more[Cl] free radical and destroys more of O3,thereby resulting in ozone depletion.
ClO(g) + O(g)→ Cl(g) + O2(g)
Question 23.
Describe the methods of saving ozone layer.
Solution:
Methods to protect the ozone layer:
- Using alternative products such as HCFCs (hydrochlorofluorocarbons)
- Montreal Protocol, an international treaty, helps prevent ozone depletion.
Question 24.
Fill in the blanks:
The pollutants such as NO2, SO2 and SO3 dissolved in the moisture of air are the cause of ____________________.
Excessive release of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is the cause of __________ effect which produces global warming.
Ozone layer prevents the harmful ________ radiation of the sun to reach the earth.
Decrease of the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere is the cause of formation of __________ holes.
Ozone depletion is mainly caused by the active __________ atoms generated from CFC in the presence of UV radiation.
Solution:
- acid rain
- greenhouse
- ultraviolet
- ozone
- chlorine
Question 25.
Select the correct answer:
a. Excessive release of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is the cause of
i. Depletion of ozone
ii. formation of polar vartex
iii. global warming
iv. formation of smog
b. Inhalation of air polluted with carbon monoxide is dangerous because:
i. CO combines with O2 dissolved in blood.
ii. CO combines with haemoglobin of blood.
iii. CO removes water from the body and causes dehydration.
iv. CO causes coagulation of proteins in the body
c. Decrease of amount of ozone in stratosphere is called depletion of zone and it is caused by
i. UV radiations of sun
ii. Use of CFC compounds
iii. excessive use of detergents
iv. Use of polychlorinated biphenyls
Solution:
- global warming
- CO combines with haemoglobin of blood.
- Use of CFC compounds
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 9 ICSE Solutions