Selina Concise Biology Class 9 ICSE Solutions Digestive System
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 9 Chapter 11 Digestive System. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 9 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 9 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology Chapter 11 Digestive System
Exercise 1
Solution A.
- (iii) stomach into intestine
- (i) HCl and pepsin
- (iii) colon
- (iii) Premolars, molars – Grinding
Solution B.1.
![]()
Solution B.2.
The two reflexes which occur when a person chews and swallows food are:
- Reflex when a person chews – Secretion of saliva
- Reflex when a person swallows – Tongue presses upward and back against the roof (palate)
Solution B.3.
(ii) Both the statements are wrong. Small intestine is longer (7 metres) than large intestine (1.5 metres). Also, large intestine is so called because of its width which is larger than that of small intestine.
Solution C.1.
Digestion is the process of breaking down complex food materials into simpler substances by the action of enzymes.
Need for a digestive system:
- Large complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins and lipids need to be broken down to simpler molecules. These simpler molecules can then be absorbed and utilized by the body.
- The breaking down of complex food molecules into their simpler form is possible only through the process of digestion.
- During digestion, large complex macromolecules present in food are converted into small simpler molecules, which can be simplified in different compartments of digestive system only.
Solution C.2.
| SUBSTRATE | END PRODUCTS |
| Starch | Maltose |
| Proteins | Small peptides and amino acids |
| Fats | Fatty acids and glycerol |
Solution C.3.
Vitamins are used in their original form by the cells. They do not require digestion. They are either water soluble or fat soluble, hence no enzyme is required to digest vitamins. They are absorbed directly from the digestive tract, transported by blood to the cells, and the cells absorb and use them whenever they need. Besides, vitamins themselves act as catalysts or enzymes in essential chemical reactions that take place in the body.
Solution C.4.
It is very important to chew our food thoroughly as chewing of food helps to break down complex food materials into simpler substances. The act of chewing stimulates the salivary glands to release saliva. The saliva helps to moisten the food and form bolus, which can be swallowed easily. Saliva also contains special enzymes that help to break down carbohydrates.
Solution C.5.
Rectum acts as a temporary storage site for undigested food. It has voluntary smooth muscles that remove the faeces out of the body through the anus.
Solution C.6.
Roughage is a dietary fibre that largely consists of cellulose. It cannot be digested by our body as our body does not contain cellulose-digesting enzymes.
Examples of roughage:
- Fruits
- Green leafy vegetables
Solution C.7.
Adaptations of ileum for the absorption of digested food:
- Very long to provide more surface area for absorption
- Presence of large number of villi to further increase the surface area
Solution C.8.
Functions of hydrochloric acid:
- It gets mixed with food and kills the bacteria present in food.
- It activates pepsin to act on proteins.
Solution D.1.
Vegetarian menu for dinner:
| Foodstuffs | Weight (gm/ml) |
| Cereals | 320 |
| Pulses | 70 |
| Green leafy vegetables | 100 |
| Root vegetables | 75 |
| Fruits | 75 |
| Milk | 600 |
| Fat and oil | 30 |
| Brown sugar and jaggery | 30 |
Solution D.2.
Main characteristics of an enzyme:
- It is a protein and therefore, gets destroyed by heating.
- It acts only on one kind of substance called the substrate. So, it is very specific.
- It acts as a catalyst, so it can be used again and again.
- It only affects the rate of a chemical reaction and always speeds up the reaction.
- It always forms the same end products from the fixed substrate.
- It acts best only at a particular pH.
- It acts best within a narrow temperature range, usually between 35°C-40°C.
Solution D.3.
The small intestine is the most important organ of the digestive system as it serves both, for digestion and absorption. It receives two digestive juices; the bile and the pancreatic juice in the duodenum. These two juices virtually complete the digestion of starch, proteins, carbohydrates, etc. After the breakdown of food, the small intestine absorbs simple substances such as glucose, amino acids, etc.
Solution D.4.
Liver is an important organ in our body as it serves the following functions:
- Production of bile
- Control of blood sugar levels
- Control of amino acid levels
- Synthesis of foetal red blood cells
- Produce fibrinogen and heparin
- Regulate blood volume
- Destroy dead red blood cells
- Store vitamin and minerals
- Excrete toxic and metallic poisons
- Produce heat
- Detoxification
Solution D.5.
(i) Peristalsis: Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the alimentary canal that pushes the food along the gut.
(ii) Omnivore: Omnivores are organisms that consume both plants and animals.
(iii) Pylorus: Pylorus is the passage at the lower end of the stomach that opens into the duodenum.
(iv) Kilocalorie: A kilocalorie is a unit of energy. It is the energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 Celsius.
(v) Basal metabolic rate: Basal metabolic rate refers to the minimum amount of energy in the form of calories that our body requires to complete its normal functions.
Solution D.6.
| REGION | ENZYME | ACTION ON FOOD |
| Stomach | Pepsin | Acts on proteins and converts it into polypeptides |
| Small intestine | ||
| Duodenum | Amylopectin | Acts on starch and converts it into maltose |
| Trypsin | Acts on remaining proteins, proteoses and peptones to produce peptides and amino acids | |
| Ileum | Erepsin | Acts on proteins and polypeptides and converts them into small peptides and amino acids |
| Sucrase | Acts on sucrose and converts it into glucose and fructose | |
| Lactase | Acts on lactose and converts it into glucose and galactose | |
Solution D.7.
Importance of water in our body:
- Water is the major component of blood, which carries nutrients and oxygen, to and from all the cells.
- It is the major component of saliva and mucous, which lubricate the membranes that line our digestive system beginning with the mouth.
- It helps in regulating the temperature of the body.
- Water is very essential for digestion as well as absorption of food.
Solution D.8.
Test for starch:
- Takethe food item to be tested. Put it into a test-tube containing water and boil to make a solution.
- Cool the solution and add 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution to it.
- Blue-black colour of the solution indicates the presence of starch in the food item.
Test for proteins:
- Take the food item to be tested in a test tube.
- Add few drops of dilute nitric acid to it.
- Heat the test-tube gently.
- Rinse off the acid with water and add few drops of ammonium hydroxide to it.
- Colour changefrom colourless to yellow and then from yellow to orange redindicates the presence of protein in the food item.
Solution E.1.
Solution E.2.
While swallowing saliva in the mouth, the larynx is pulled upwards to bring it close to the back of the tongue, when a flap called epiglottis closes its opening. Then, it goes towards the oesophagus.
Solution E.3.
| Organ | Enzyme | Food acted upon | Find product |
| Stomach | Pepsin | Proteins | Polypeptide |
| Mouth | Amylase | Starch | Disaccharide |
| Ileum | Maltase | Maltose | Glucose |
Solution E.4.
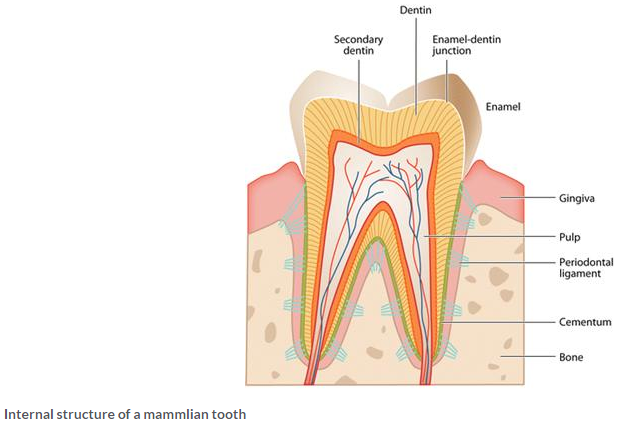
(a)
1 → Enamel
2 → Dentine
3 → Pulp
4 → Gum
5 → Crown
6 → Cement
(b) The tooth shown in the diagram has only one root, so it is an incisor or canine which is used for biting and piercing.
(c) The part labelled ‘3’ (pulp) is a soft connective tissue present in the pulp cavity of the tooth. It consists of blood capillaries, lymph vessels and nerve fibres. These extend from the crown of the tooth and open through the pulp cavity at the base of the root.
(d) Type of teeth in the mouth of an adult:
- Incisors (8) → Used for biting and cutting
- Canines (4) → Used for holding and tearing of food
- Premolars (8) → Used for grinding and crushing of food
- Molars (12)→ Used for grinding and crushing of food
Solution E.5.
a) A total of 20 teeth are present in the given dentition.
(b) The given dentition is that of a herbivore because there are no canines present in the dentition. Canines are required by carnivores as they help in holding and tearing of food. The teeth of herbivores are used for cutting, gnawing, and biting, while the teeth of carnivores are sharper and more suited for catching, killing and tearing the prey.
(c) The given dentition is likely to be present in any herbivore such as deer.
(d)

More Resources for Selina Concise Class 9 ICSE Solutions