Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions Value Added Tax
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 1 Value Added Tax. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 10 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 10 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Value Added Tax
Exercise 1(A)
Question 1.
Rajat purchases a wrist-watch costing ₹ 540. The rate of sales tax is 8%. Find the total amount paid by Rajat for the watch.
Solution:
Sale price of watch = ₹ 540
Rate of sales tax = 8%
Total amount paid by Rajat = ₹ 540 + 8% of ₹ 540
= ₹ 540 + \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) × 540
= ₹ 540 + ₹ 43.20
= ₹ 583.20
Question 2.
Ramesh paid ₹ 345.60 as sales tax on a purchase of ₹ 3,840. Find the rate of sales tax.
Solution:
Sale price = ₹ 3,840
Sales tax paid = ₹ 345.60
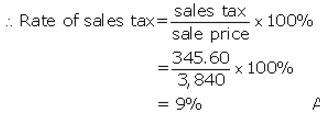
Question 3.
The price of a washing machine, inclusive of sales tax is ₹ 13,530/-. If the sales tax is 10%, find its basic cost price.
Solution:
Selling price of washing machine = ₹ 13,530
Rate of sales tax = 7%
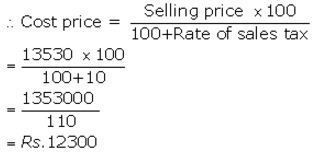
Question 4.
Sarita purchases biscuits costing ₹ 158 on which the rate of sales tax is 6%. She also purchases some cosmetic goods costing ₹ 354 on which the rate of sales tax is 9%. Find the total amount to be paid by Sarita.
Solution:
Sale price of biscuits = ₹ 158
Rate of sales tax on biscuits= 6%
Amount paid for biscuits= ₹ 158 + 6% of ₹ 158
= ₹ 158 + \(\frac { 6 }{ 100 }\) × 158
= ₹ 158 + ₹ 9.48
= ₹ 167.48
Sale price of cosmetic goods = ₹ 354
Rate of sales tax= 9%
Amount paid for cosmetic goods = ₹ 354 + 9% of ₹ 354
= ₹ 354 + \(\frac { 9 }{ 100 }\) × 354
= ₹ 354 + ₹ 31.86
= ₹ 385.86
Total amount paid by Sarita = ₹ 167.48 + ₹ 385.86
= ₹ 553.34
Question 5.
The marked price of two articles A and B together is ₹ 6,000. The sales tax on article A is 8% and that on article B is 10%. If on selling both the articles, the total sales tax collected is ₹ 552, find the marked price of collected of the articles A and B.
Solution:
Let the marked price of article A be ₹ x and article B be ₹ y.
The marked price of A and B together is ₹ 6,000.
⇒ x + y = 6,000 ……..(i)
The sales tax on article A is 8% and that on article B is 10%.
Also the total sales tax collected on selling both the articles is ₹ 552.
⇒ 8% of x + 10% of y = 552
⇒ 8x + 10y = 55,200 ……..(ii)
Multiply equation (i) by 8 and subtract it from equation (ii) we get,
2y = 7,200
⇒ y =3,600
Substituting y = 3,600 in equation (i) we get,
x + 3,600 = 6,000
⇒ x = 2,400
The marked price of article A is ₹ 2,400 and article B is ₹ 3,600.
Question 6.
The price of a T.V. set inclusive of sales tax of 9% is ₹ 13,407. Find its marked price. If sales tax is increased to 13%, how much more does the customer has to pay for the T.V.?
Solution:
(i) Total price paid for T.V. = ₹ 13,407
Rate of sales tax = 9%
Let sale price = ₹ y
According to question

New rate of sales tax = 13%
New total price for T.V. = ₹ 12,300+ 13% of ₹ 12,300
= ₹ 12,300 + \(\frac { 13 }{ 100 }\) × 12,300
= ₹ 12,300 + ₹ 1,599
= ₹ 13,899
More money paid = ₹ 13,899 – ₹ 13,407 = ₹ 492
Question 7.
The price of an article is ₹ 8,250 which includes sales tax at 10%. Find how much more or less does a customer pay for the article, if the sales tax on the article:
(i) increases to 15%
(ii) decreases to 6%
(iii) increases by 2%
(iv) decreases by 3%
Solution:
Let sale price of article = ₹ y
Total price inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 8,250
Rate of sales tax = 10%
According to question
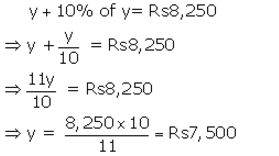
(i) New rate of sales tax = 15%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 15% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + \(\frac { 15 }{ 100 }\) × 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + ₹ 1,125 = ₹ 8,625
More money paid = ₹ 8,625 – ₹ 8,250 = ₹ 375
(ii) New rate of sales tax = 6%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 6% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + \(\frac { 6 }{ 100 }\) × 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 +₹ 450 = ₹ 7,950
Less money paid = ₹ 8,250 – ₹ 7,950 = ₹ 300
(iii) New rate of sales tax = (10+2)% = 12%
New total price = ₹ 7,500 + 12% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\) × 7,500
= ₹ 7,500+ ₹ 900 = ₹ 8,400
More money paid = ₹ 8,400 – ₹ 8,250 = ₹ 150
(iv) New rate of sales tax =(10-3)%= 7%
New total price = ₹ 7,500+ 7% of ₹ 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + \(\frac { 7 }{ 100 }\) × 7,500
= ₹ 7,500 + ₹ 525 = ₹ 8,025
Less money paid = ₹ 8,250 – ₹ 8,025 = ₹ 225
Question 8.
A bicycle is available for ₹ 1,664 including sales tax. If the list price of the bicycle is ₹ 1,600, find :
(i) the rate of sales tax.
(ii) the price, a customer will pay for the bicycle if the sales tax is increased by 6%.
Solution:
Price of bicycle inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 1,664
List price of bicycle = ₹ 1,600
(i) Sales tax= ₹ 1,664 – ₹ 1,600 = ₹ 64
![]()
(ii) New rate of sales tax =(4+6)% = 10%
New total price = ₹ 1,600+ 10% of ₹ 1,600
= ₹ 1,600 + \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) × 1,600
= ₹ 1,600 + ₹ 160
= ₹ 1,760
Question 9.
When the rate of sale-tax is decreased from 9% to 6% for a coloured T.V.; Mrs. Geeta will save ₹ 780 in buying this T.V. Find the list price of the T.V.
Solution:

Question 10.
A trader buys an unfinished article for ₹ 1,800 and spends ₹ 600 on its finishing, packing, transportation, etc. He marks the article at such a price that will give him 20% profit. How much will a customer pay for the article including 12% sales tax.
Solution:
Purchase price = ₹ 1,800
Expenditure = ₹ 600
Total price = ₹ 1,800+ ₹ 600 = ₹ 2,400
M.P. of article = ₹ 2,400 + 20% of ₹ 2400
= ₹ 2,400 + \(\frac { 20 }{ 100 }\) × 2400
= ₹ 2,400 + ₹ 480 = ₹ 2,880
Cost price for customer = ₹ 2,880+ 12% of ₹ 2,880
= ₹ 2,880 + \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\) × 2880
= ₹ 2,880 + ₹ 345.60
= ₹ 3,225.60
Question 11.
A shopkeeper buys an article for ₹ 800 and spends ₹ 100 on its transportation, etc. He marks the article at a certain price and then sells it for ₹ 1,287 including 10% sales tax. Find his profit as percent.
Solution:
C.P. of an article = ₹ 800
Expenditure = ₹ 100
Total C.P. = ₹ 800 + ₹ 100 = ₹ 900
Let sale price = ₹ y
Sale price inclusive of sales tax = ₹ 1,287
Rate of sales tax = 10%
Then y + 10% of y = ₹ 1,287
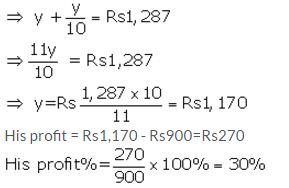
Question 12.
A shopkeeper announces a discount of 15% on his goods. If the marked price of an article, in his shop, is ₹ 6,000; how much a customer has to pay for it, if the rate of sales tax is 10%?
Solution:
Marked price of article = ₹ 6,000
Sale price after discount = ₹ 6,000 – 15% of ₹ 6,000
= ₹ 6,000 – ₹ 900
₹ 5,100
Rate of sales tax = 10%
Cost price for customer = ₹ 5,100 + 10% of ₹ 5,100
= ₹ 5,100+ ₹ 510
= ₹ 5,610
Question 13.
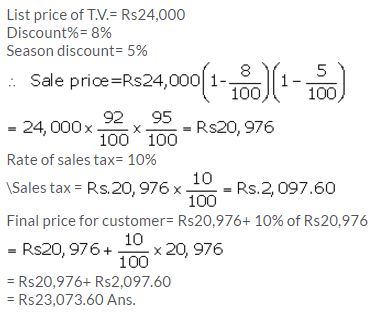
The catalogue price of a colour T.V. is ₹ 24,000. The shopkeeper gives a discount of 8% on the list price. He gives a further off season discount of 5% on the balance. But sales tax at 10% is charged on the remaining amount. Find :
(a) the sales tax a customer has to pay.
(b) the final price he has to pay for the T.V
Solution:
Exercise 1(B)
Question 1.
A shopkeeper purchases an article for ₹ 6,200 and sells it to a customer for ₹ 8,500. If the sales tax (under VAT) is 8%; find the VAT paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Purchase price for shopkeeper = ₹ 6,200
Sale price for shopkeeper = ₹ 8,500
Tax paid by the shopkeeper = 8% of 6,200 = ₹ 496
= \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) × 6,200
Tax charged by the shopkeeper= 8% of 8,500
= \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) × 8,500 = ₹ 680
Then VAT paid by the shopkeeper= ₹ 680 – ₹ 496 = ₹ 184
Question 2.
A purchases an article for ₹ 3,600 and sells it to B for ₹ 4,800. B, in turn, sells the article to C for ₹ 5,500. If the sales tax(under VAT) is 10%, find the VAT levied on A and B.
Solution:
Purchase price for A = ₹ 3,600
Tax paid by A = 10% of ₹ 3,600
= \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) × 3,600 = ₹ 360
Purchase price for B = ₹ 4,800
Tax paid by B to A = 10% of ₹ 4,800
= \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) × 4,800 = ₹ 480
Purchase price for C = ₹ 5,500
Tax paid by C to B = 10% of ₹ 5,500
= \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) × 5,500 = ₹ 550
VAT paid by A = ₹ 480 – ₹ 360 = ₹ 120
VAT paid by B = ₹ 550 – ₹ 480 = ₹ 70
Question 3.
A manufacturer buys raw material for ₹ 60,000 and pays 4% tax. He sells the ready stock for ₹ 92,000 and charges 12.5% tax. Find the VAT paid by the manufacturer.
Solution:
Purchase price for manufacture = ₹ 60,000
Tax paid by manufacturer = 4% of ₹ 60,000
= \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 }\) × 60,000 = ₹ 2,400
Sale price for manufacturer = ₹ 92,000
Tax charged by manufacturer = 12.5% of ₹ 92,000
= \(\frac { 12.5 }{ 100 }\) × 92,000 = ₹ 11,500
VAT paid by manufacturer = ₹ 11,500 – ₹ 2,400
= ₹ 9,100
Question 4.
The cost of an article is ₹ 6,000 to a distributor. He sells it to a trader for ₹ 7,500 and the trader sells it to a customer for ₹ 8,000. If the VAT rate is 12.5%; find the VAT paid by the :
(i)distributor
(ii)trader.
Solution:
Cost price for distributor = ₹ 6,000
Tax paid by distributor = 12.5% of ₹ 6,000
= \(\frac { 12.5 }{ 100 }\) × 6,000 = ₹ 750
Sale price for distributor= ₹ 7,500
Tax charged by distributor= 12.5% of ₹ 7,500
= \(\frac { 12.5 }{ 100 }\) × 7,500 = ₹ 937.50
VAT paid by distributor = ₹ 937.50 – ₹ 750
= ₹ 187.50
Sale price for trader = ₹ 8,000
Tax charged by trader = 12.5% of ₹ 8,000
= \(\frac { 12.5 }{ 100 }\) × 8,000 = ₹ 1000
VAT paid by trader= ₹ 1,000 – ₹ 937.50 = ₹ 62.50
Question 5.
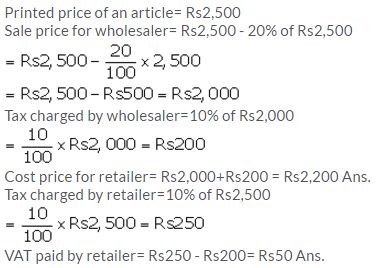
The printed price of an article is ₹ 2,500. A wholesaler sells it to a retailer at 20% discount and charges sales tax at the rate of 10%. Now the retailer, in turn, sells the article to a customer at its list price and charges the sales tax at the same rate. Find :
(i) the amount that retailer pays to the wholesaler.
(ii) the VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:
Question 6.
A retailer buys an article for ₹ 800 and pays the sales tax at the rate of 8%. The retailer sells the same article to a customer for ₹ 1,000 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Find:
(i) the price paid by a customer to buy this article.
(ii) the amount of VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:
Cost price for retailer = ₹ 800
Sales tax paid by retailer = 8% of ₹ 800
= \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) × 8,00 = ₹ 64
Sale price for retailer = ₹ 1,000
Tax charged by retailer = 8% of ₹ 1,000
= \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) × 1,000 = ₹ 80
Price paid by customer = ₹ 1,000 + ₹ 80 = ₹ 1,080
VAT paid by retailer = ₹ 80 – ₹ 64 = ₹ 16
Question 7.
A shopkeeper buys 15 identical articles for ₹ 840 and pays sales tax at the rate of 8%. He sells 6 of these articles at ₹ 65 each and charges sales tax at the same rate. Calculate the VAT paid by the shopkeeper against the sale of these six articles.
Solution:

Question 8.
The marked price of an article is ₹ 900 and the rate of sales tax on it is 6%. If on selling the article at its marked price, a retailer has to pay VAT = ₹ 4.80; find the money paid by him (including sales tax) for purchasing this article.
Solution:

Question 9.
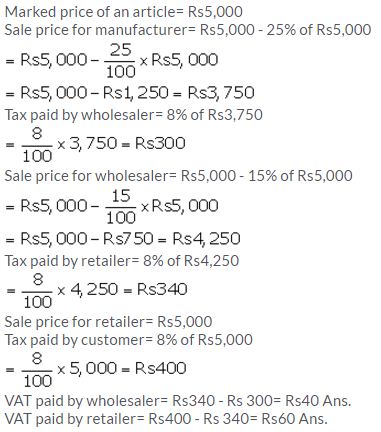
A manufacturer marks an article at ₹ 5,000. He sells this article to a wholesaler at a discount of 25% on the marked price and the wholesaler sells it to a retailer at a discount of 15% on its marked price. If the retailer sells the article without any discount and at each stage the sales tax is 8%, calculate the amount of VAT paid by :
(i) the wholesaler (ii) the retailer
Solution:
Question 10.
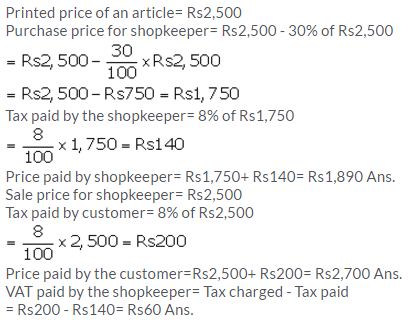
A shopkeeper buys an article at a discount of 30% and pays sales tax at the rate of 8%. The shopkeeper, in turn, sells the article to a customer at the printed price and charges sales tax at the same rate. If the printed price of the article is ₹ 2,500; find :
(i) the price paid by the shopkeeper.
(ii) the price paid by the customer.
(iii) the VAT (value added tax) paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Question 11.
A shopkeeper sells an article at its list price (₹ 3,000) and charges sales tax at the rate of 12%. If the VAT paid by the shopkeeper is ₹ 72, at what price did the shopkeeper buy the article inclusive of sales tax?
Solution:

Question 12.
A manufacturer marks an article for ₹ 10,000. He sells it to a wholesaler at 40% discount. The wholesaler sells this article to a retailer at a discount of 20% on the marked price. If retailer sells the article to a customer at 10% discount and the rate of sales tax is 12% at each stage; find the amount of VAT paid by the (i) wholesaler (ii) retailer.
Solution:
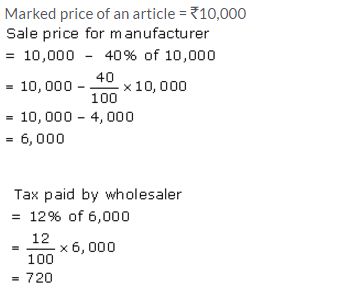

VAT paid by wholesaler = ₹ 960 – ₹ 720= ₹ 240
VAT paid by retailer = ₹ 1080 – ₹ 960= ₹ 120
Exercise 1(C)
Question 1.
Madan purchases a compact computer system for ₹ 47,700 which includes 10% rebate on the marked price and then a 6% sales tax on the remaining price. Find the marked price of the computer.
Solution:

Question 2.
An article is marked at ₹ 500. The wholesaler sells it to a retailer at 20% discount and charges sales tax on the remaining price at 12.5%. The retailer, in turn, sells the article to a customer at its marked price and charges sales tax at the same rate. Calculate:
(i) The price paid by the customer.
(ii) The VAT paid by the retailer.
Solution:
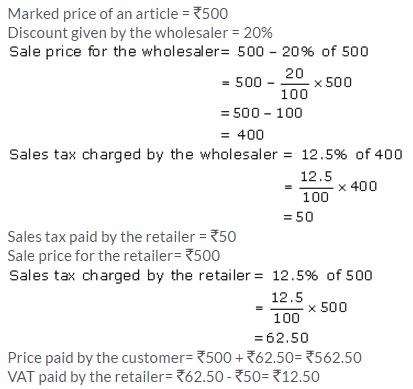
Question 3.
An article is marked at ₹ 4,500 and the rate of sales tax on it is 6%. A trader buys this article at some discount and sells it to a customer at the marked price. If the trader pays ₹ 81 as VAT; find:
How much per cent discount does the trader get?
The total money paid by the trader, including tax, to buy the article.
Solution:

Question 4.
A retailer sells an article for ₹ 5,350 including 7% sales tax on the listed price. If he bought it at a discount and has made a profit of 25% on the whole, find the rate of discount the retailer received.
Solution:

Question 5.
A shopkeeper buys a camera at a discount of 20% from the wholesaler, the printed price of the camera being ₹ 1,600 and the rate of sales tax being 6%. The shopkeeper sells it to a buyer at the printed price and charges tax at the same rate. Find:
The price at which the camera can be bought from the shopkeeper.
The VAT (Value Added Tax) paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:
Printed price of camera = ₹ 1,600
Discount% = 20%

Purchase price for the shopkeeper
= ₹ 1,280 + ₹ 76.80 = ₹ 1,356.80
Selling price for the shopkeeper = ₹ 1,600

Purchase price for a customer = ₹ 1,600 + ₹ 96 = ₹ 1,696
The price at which the camera can be bought from the shopkeeper is ₹ 1,696.
VAT paid by the shopkeeper= Tax charged – Tax paid
= ₹ 96 – ₹ 76.80 = ₹ 19.20
The VAT (Value Added Tax) paid by the shopkeeper is ₹ 19.20.
Question 6.
Tarun bought an article for ₹ 8,000 and spent ₹ 1,000 on its transportation. He marked the article at ₹ 11,700 and sold it to a customer. If the customer had to pay 10% sales tax, find:
(i) The customer’s price (ii) Tarun’s profit percent.
Solution:
Purchase price for = ₹ 8,000
Expense on transportation = ₹ 1,000
Cost price for Tarun = ₹ 8,000 + ₹ 1,000 = ₹ 9,000
Marked price by Tarun = ₹ 11,700

Question 7.
A shopkeeper sells an article at the listed price of ₹ 1,500 and the rate of VAT is 12% at each stage of sale. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of ₹ 36 to the Government, what was the price, inclusive of Tax, at which the shopkeeper purchased the article from the wholesaler?
Solution:

Question 8.
A shopkeeper bought a washing machine at a discount of 20% from a wholesaler, the printed price of the washing machine being ₹ 18,000. The shopkeeper sells it to a consumer at a discount of 10% on the printed price. If the rate of VAT (or sales tax) is 8%, find :
(i) The VAT paid by the shopkeeper.
(ii) The total amount that the consumer pays for the washing machine.
Solution:

Question 9.
Mohit, a dealer in electronic goods, buys a high class TV set for ₹ 61,200. He sells this TV set to Geeta, Geeta to Rohan and Rohan sells it to Manoj. If the profit at each stage is ₹ 2,000 and the rate of VAT at each stage is 12.5%, find:
(i) total amount of tax (under VAT) paid to the Government.
(ii) Money paid by Manoj to buy the TV set.
Solution:
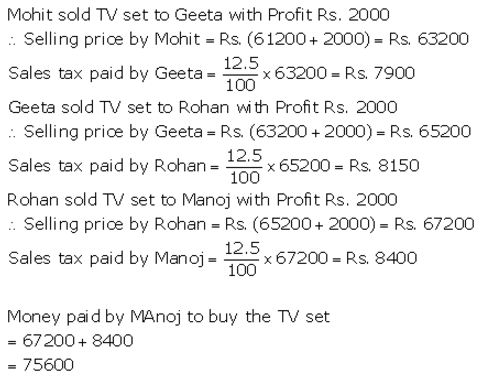
Question 10.
A shopkeeper buys an article at a discount of 30% of the list price which is ₹ 48,000. In turn, the shopkeeper sells the article at 10% discount. If the rate of VAT is 10%, find the VAT to be paid by the shopkeeper.
Solution:

Question 11.
A company sells an article to a dealer for 40,500 including VAT (sales-tax). The dealer sells it to some other dealer for 42,500 plus tax. The second dealer sells it to a customer at a profit of 3,000. If the rate of sales-tax under VAT is 8%, find :
(i) The cost of the article (excluding tax) to the first dealer.
(ii) The total tax (under VAT) received by the Government.
(iii) The amount that a customer pays for the article.
Solution:
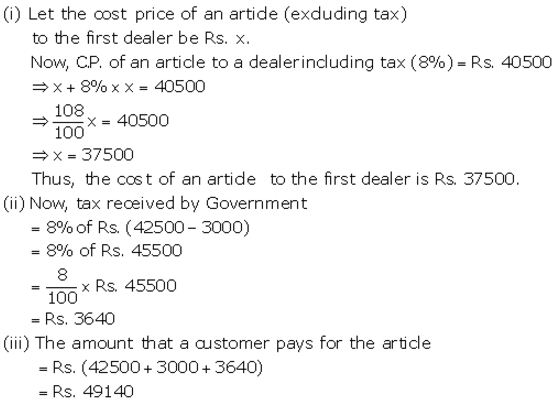
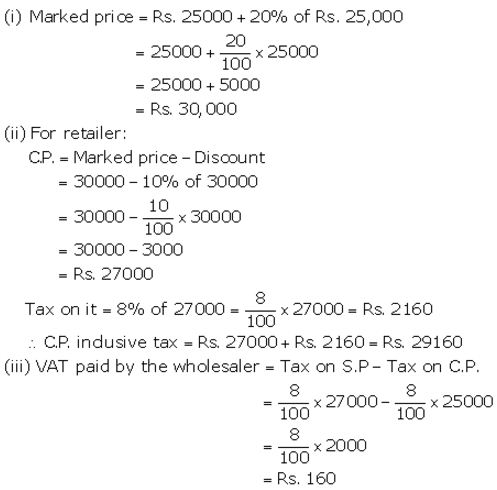
Question 12.
A wholesaler buys a TV from the manufacturer for ₹ 25,000. He marks the price of the TV 20% above his cost price and sells it to a retailer at 10% discount on the marked price. If the rate of VAT is 8%, find the :
(i) Marked price.
(ii) Reailer’s cost price inclusive of tax.
(iii) VAT paid by the wholesaler.
Solution:
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 10 ICSE Solutions