Selina Concise Biology Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Respiratory System
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Biology. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Biology ICSE SolutionsChemistryPhysicsMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Biology Chapter 5 Respiratory System
Synopsis —
- The energy released during respiration is stored as chemical energy in the form of ATP — adenosine tri-phosphate.
- Aerobic respiration —
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
Anaerobic respiration —
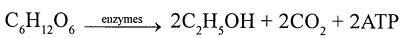
- During vigorous exercise, the cells respire anaerobically and form lactic acid which accumulate in the muscle cells causing fatigue and pain.
- The respiration in humans occur in three phases:
- Breathing
- Gaseous Transport
- Cellular respiration
- The oxygen inhaled in combines with haemoglobin present in the red blood cells forming an unstable compound called oxyhaemoglobin.
- The nasal chamber has got hairy lining to prevent dust particles from reaching the lungs. The lining also has mucous to trap germs and dust.
- The common passage for the food and air is the pharynx.
- Trachea is also called the wind pipe.
- The voice box or the Adam’s apple is the larynx which contains ligamentous folds called vocal cords.
- Incomplete closure of epiglottis during swallowing causes coughing.
- The trachea is formed of incomplete C-shaped cartilaginous rings which keep them permanently distended.
- The lungs are protected outside by the two membranes called outer and inner pleura.
- Left lung is slightly smaller than the right lung.
- Left lung has two lobes while the right lung has three lobes.
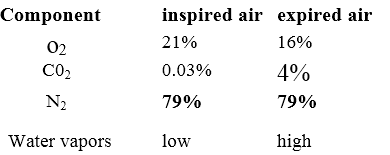
- Breathing is an involuntary act.
- Even after maximum forced expiration, some air is left in the lungs called residual volume.
- In normal adults, the breathing rate is 12-18/minute while a newborn breathes at about 60 breaths per minute.
- Asphyxiation is a condition in which blood becomes venous by the accumulation of excess carbon dioxide and the oxygen supply is diminished.
- The gas composition in artifical respiration is 95% oxygen, 5% carbon-di-oxide.
- Snoring: Vibration of soft palate during breathing when mouth is kept open while sleeping.
- Sneezing: It is a protective mechanism through which a foreign irritant particle is thrown out of the lungs suddenly and forcefully.
- Hiccups: Jerky incomplete inspiration due to blockage of the respiratory tract.
Review Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Put a tick (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the following statements.
(i) In humans, taken in of the air through nostrils into the nasal cavity is called
(a) Inhalation
(b) Exhalation
(b) Cellular respiration
(d) Internal respiration
(ii) The front opening of the wind pipe is guarded by —
(a) Glottis
(b) Exoglottis
(c) Epiglottis
(d) Trachea
(iii) The process during which food is oxidised and energy is released is called
(a) Cellular respiration
(b) Excretion
(c) Digestion
(d) Transpiration
Short Answer Questions
1. Answer briefly the following:
- Why do our body cells require oxygen ?
Ans. Body cells require oxygen for the break down of glucose and release energy for carrying out various life functions. - What is the difference between breathing and respiration?
Ans. Breathing is a simple physical process of drawing in air through the nostrils and expelling it out.
Respiration is a chemical process which involves the breakdown of food and release energy. - Name the by-product formed during the oxidation of food.
Ans. The by- products formed are
1. carbon-di-oxide
2. water - Name the agency which transports oxygen to all parts of the body.
Ans. Blood . - What is the role of epiglottis during swallowing ?
Ans. Epiglottis closes the wind pipe at the time of swallowing.
Question 2.
Describe in brief the function of ribs and diaphragm in breathing.
Answer:
- Ribs muscles—During inhalation, the ribs muscles contract and push the ribs upward and outward.
During exhalation these relax and cause the ribs to return to original position. - Diaphragm: During inhalation it becomes flattened while during exhalation it relaxes and moves up and back into convex (dome) shape.
Question 3.
Name the gas which is expelled out during expiration. Where is it originally produced in our body ?
Answer:
The gas which is expelled during expiration is carbon-di¬oxide. It is produced as a result of oxidation of glucose in the tissues. (Cellular respiration)
Question 4.
Name the following:
- Respiratory process
- in which oxygen is not utilized.
Ans. Cellular respiration - Respiratory process in which oxygen is utilized.
Ans. Gaseous transport - The microscopic air-sacs of the lungs.
Ans. Alveoli - The two membranes which protect the lungs.
Ans. Outer pleura, inner pleura
Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Why is a respiratory system necessary ?
Answer:
Respiratory system is very important for the body. Respiration in human beings is divided into two distinct parts. The first part involves taking in oxygen from the air or what we commonly call breathing. The respiratory system is responsible for breathing in and out of air, and exchange of gases. The main parts of the respiratory system consist of the nostrils, trachea or wind pipe and lungs.
The blood, then, transports the oxygen to the individual cell where it is used for the chemical process of respiration. This is known as cellular respiration.The second part involves taking out carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of cellular function.
Question 2.
What factors are most likely to affect the breathing rate ?
Answer:
Breathing is a necessary function for human beings. It supplies oxygen for a process called cellular respiration, which is how cells manufacture the energy they need for their life functions.
There are lots of things that can affect the rate of breathing in humans and they are:
- Exercise is one of those things, particularly aerobic exercise. Aerobic exercise is any exercise that causes the person to breathe more, such as running jogging, playing basketball, football, running track, or playing soccer.
- Even Breathing rate also changes while the person is sleeping, sitting at rest or even after climbing the stairs.
- Another factor that can influence breathing rate is allergic reactions to stimuli from the environment, such as pollen. This can inflame the passageways leading to the lungs, making them smaller, requiring more air.
- Smoking is a habit that can influence the development of lung cancer, which in turn influences the rate a person breathes.
- Nervous conditions and reactions to stimuli also influence the breathing rate, such as the fumed “fight or flight” syndrome.
Question 3.
What happens to the energy liberated during respiration?
Answer:
The energy liberated during respiration is utilised for carrying out various life processes.
Some of the energy liberated during the breakdown of the glucose molecule, is in the form of heat, but a large part of it is converted into chemical energy called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). Any activity inside the cell is carried out by the energy released by these ATP molecules.
Question 4.
What do you understand by inhalation and exhalation ? How are they different from each other ?
Answer:
The physical process, by which the air containing oxygen is drawn into the lungs and air containing carbon dioxide is forced out from lungs is called breathing. Breathing involves two steps, inhalation (inspiration) and exhalation (expiration).
Inhalation (Inspiration)
- Ribs move upwardsand outwards.
- Diaphragm is pushed downwards and flattens.
- Volume of chest cavity increases.
- Lungs expand, air pressure becomes low.
- Atmospheric air at higher pressure rushes into the lungs
Exhalation (Expiration)
- Ribs move downwards and inward.
- Diaphragm moves upwards and becomes dome shaped.
- Volume of chest cavity decreases.
- Lung size reduces, air pressure becomes high.
- Air rushes out of lungs as atmospheric air pressure is lower.
Question 5.
What do you understand by the term respiratory diseases ? Name any three common respiratory diseases.
Answer:
Any of the diseases and disorders that affect human respiration are called Respiratory diseases. Diseases of the respiratory system may affect any of the structures and organs that have to do with breathing, including the nasal cavities, the pharynx (or throat), the larynx, the trachea (or windpipe), the bronchi and bronchioles, the tissues of the lungs, and the respiratory muscles of the chest cage.
- Bronchitis — It is a respiratory infection in which the lining of the bronchi becomes inflamed. As this irritated membrane begins to swell, it narrows or shuts off the bronchial passages, resulting in breathlessness and coughing spells.
- Asthma — It is a chronic disease that also causes inflammation and swelling in the airways. But this happens periodically. During an asthmatic attack, a patient experiences tightness in the chest, shortness of breath and wheezing. This condition improves considerably with medication.
- Pneumonia — It is a respiratory infection caused by a bacteria. This bacteria enters the air sacs, multiplies there and the air sacs may get filled with fluid. This disease causes chest pain, chills and high fever.
Question 6.
State the cause and treatment for the following diseases
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
Answer:
- Tuberculosis — Cause: Caused by bacteria that can spread by air, dust or sputum.
Treatment: BCG vaccine, antibiotic — Streptomycin. - Pneumonia — Cause: Mainly caused by bacteria inhaled through air or by contact.
Treatment: Antibiotics—Penicillin. - Bronchitis — Cause: This respiratory infection is mainly caused by a virus. Air pollution and smoking can also cause bronchitis.
Treatment: Drinking plenty of fluids, following a well balanced diet, frequent hand washing and adequate rest can prevent and improve bronchitis.