RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 12 Geometrical Constructions
Exercise 12A
Question 1:
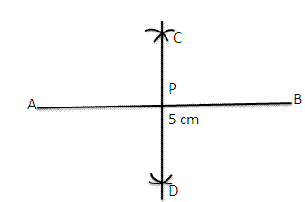
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 5 cm
(ii) With A as centre and radius equal to more than half of AB, draw two arcs, one above AB and the other below AB.
(iii) With B as a centre and the same radius draw two arcs which cuts the previously drawn arcs at C and D.
(iv) Join CD , intersecting AB at point P.
∴ CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB at the point P.
Question 2:
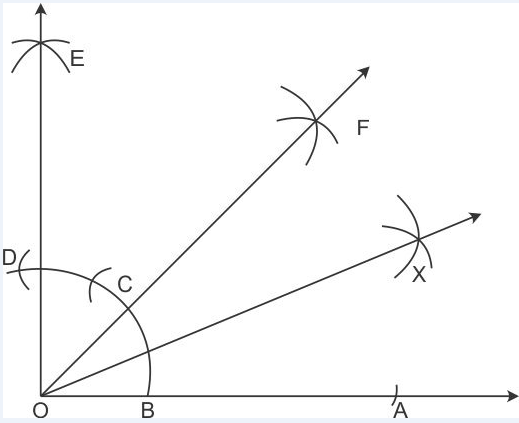
Step of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment OA.
(ii) AT A, draw ∠AOE=900, using ruler and compass.
(iii) With B as centre and radius more than half of BD, draw an arc.
(iv) With D as centre and same radius draw another arc which cuts the previous arc at F.
(v) Join OF. ∴ ∠AOF=450.
(vi) Now with centre B and radius more than half of BC, draw an arc.
(vii) With centre C and same radius draw another arc which cuts the previously drawn arc at X.
(viii) Join OX. ∴ OX is the bisector of ∠AOF.
Read More:
- Construction of an Equilateral Triangle
- Construction Of Similar Triangle As Per Given Scale Factor
- Construction Of A Line Segment
- Construction Of The Bisector Of A Given Angle
- Construction Of Perpendicular Bisector Of A Line Segment
- Construction Of An Angle Using Compass And Ruler
Question 3:
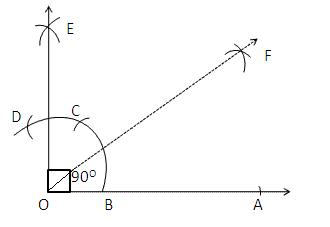
Step of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment OA.
(ii) With O as centre and any suitable radius draw an arc, cutting OA at B.
(iii) With B as centre and the same radius cut the previously drawn arc at C.
(iv) With C as centre and the same radius cut the arc at D.
(v) With C as centre and the radius more than half CD draw an arc.
(vi) With D as centre and the same radius draw another arc which cuts the previous arc at E.
(vii) Join E Now, ∠AOE =900
(viii) Now with B as centre and radius more than half of CB draw an arc.
(iv) With C as centre and same radius draw an arc which cuts the previous at F.
(x) Join OF.
(xi) ∴ F is the bisector of right ∠AOE.
Question 4:
Step of construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC=5cm.
(ii) With B as centre and radius equal to BC draw an arc.
(iii) With C as centre and the same radius draw another arc which cuts the previous arc at A.
(iv) Join AB and AC.
Then ∆ABC is the required equilateral triangle.
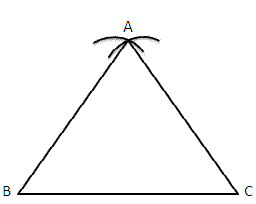
Question 5:
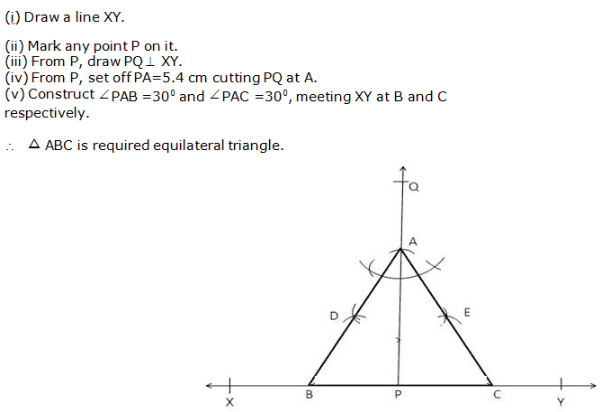
Question 6:
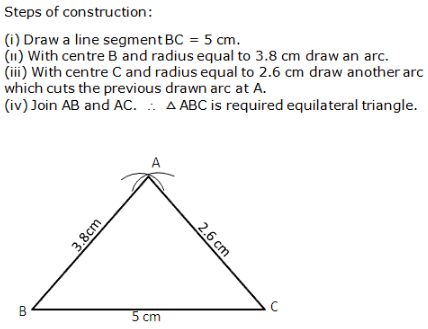
Question 7:
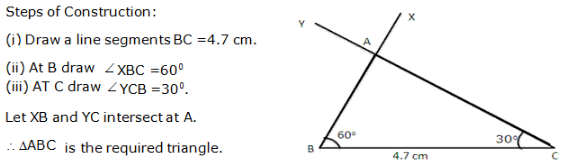
Question 8:
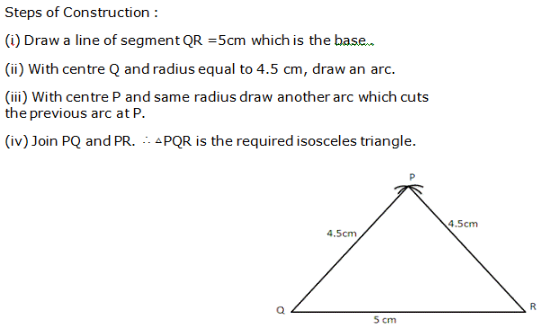
Question 9:
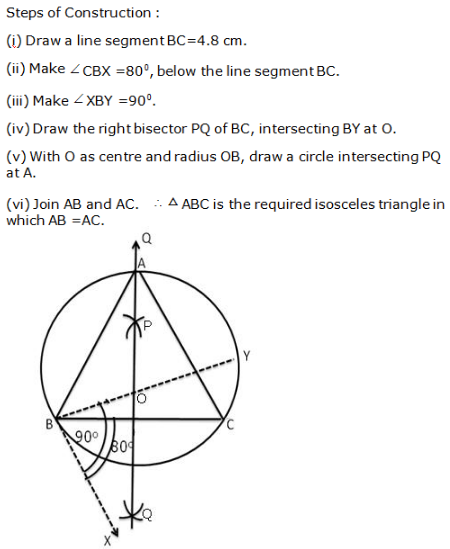
Question 10:
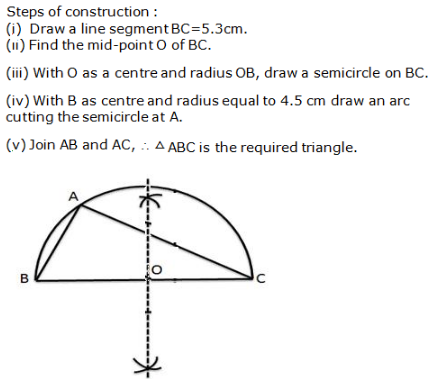
Question 11:
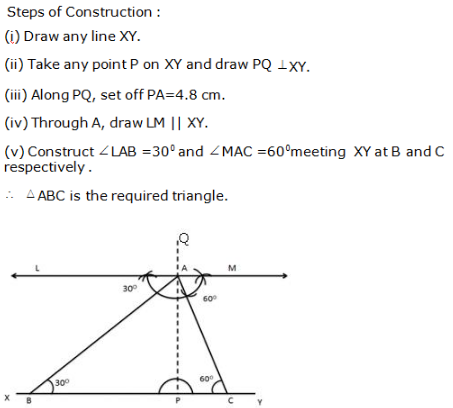
Question 12:
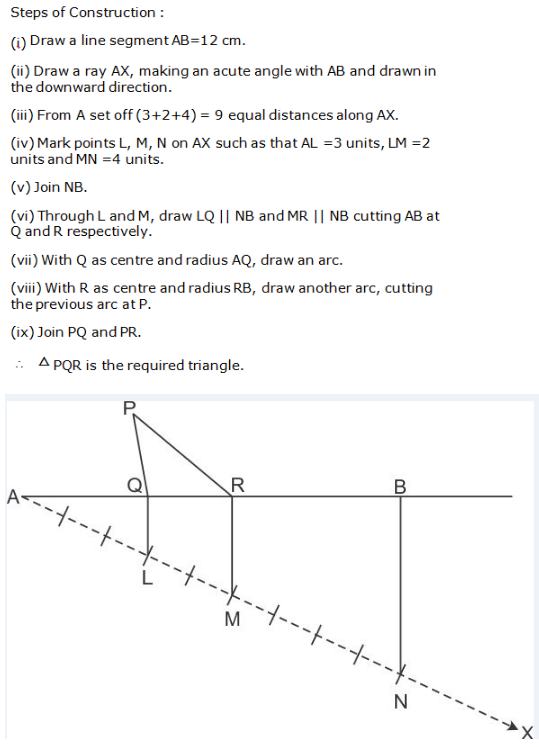
Question 13:
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw BC = 4.5 cm.
(ii) Construct ∠CBX = 600
(iii) Along BX set off BP =8cm.
(iv) Join CP.
(v) Draw the perpendicular bisector of CP to intersecting BP at A.
(vi) Join AC. ∴ ∆ABC is the required triangle.
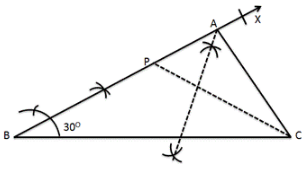
Question 14:
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw BC = 5.2 cm.
(ii) Construct ∠CBX = 300
(iii) Set off BP = 3.5 cm.
(iv) Join PC.
(v) Draw the right bisector of PC, meeting BP produced at A.
(vi) Join AC. ∴ ∆ABC is the required triangle.