RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 19 Volume and Surface Areas of Solids
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 19 Volume and Surface Areas of Solids
Exercise 19A
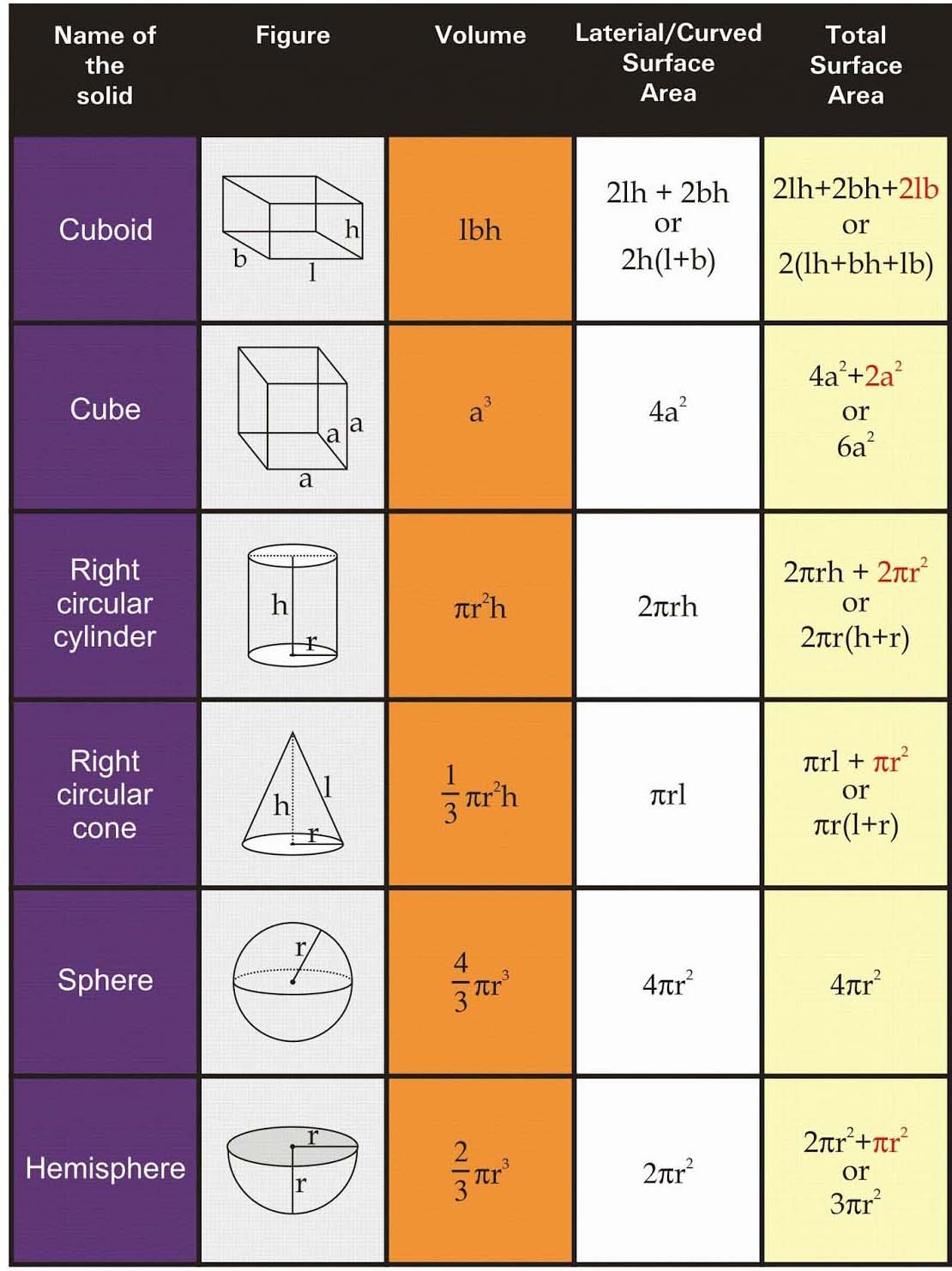
Question 1:
Radius of the cylinder = 14 m
And its height = 3 m
Radius of cone = 14 m
And its height = 10.5 m
Let l be the slant height

Curved surface area of tent
= (curved area of cylinder + curved surface area of cone)
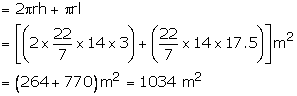
Hence, the curved surface area of the tent = 1034
Cost of canvas = Rs.(1034 × 80) = Rs. 82720
Read More:
Surface Area and Volume of a Cuboid
Surface Area and Volume of a Cube
Surface Area of a Sphere and a Hemisphere
Question 2:
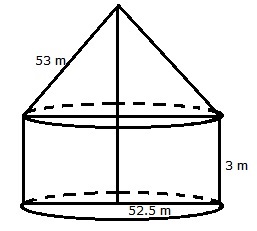
For the cylindrical portion, we have radius = 52.5 m and height = 3 m
For the conical portion, we have radius = 52.5 m
And slant height = 53 m
Area of canvas = 2rh + rl = r(2h + l)
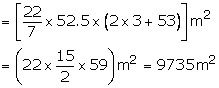
More Resources
Question 3:
Height of cylinder = 20 cm
And diameter = 7 cm and then radius = 3.5 cm
Total surface area of article
= (lateral surface of cylinder with r = 3.5 cm and h = 20 cm)

Question 4:
Radius of wooden cylinder = 4.2 cm
Height of wooden cylinder = 12 cm
Lateral surface area
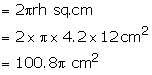
Radius of hemisphere = 4.2 cm
Surface area of two hemispheres
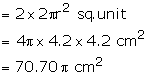
Total surface area = (100.8 + 70.56) π cm2
= 538.56 cm2
= 171.36 π
= 171.36 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) cm2
= 538.56 cm2
Further, volume of cylinder = πr2h = 4.2 × 4.2 × 12 π cm2
= 211.68 π cm2
Volume of two hemispheres = 2 × \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) πr3 cu.units
= \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) π × 4.2 × 4.2 × 4.2
= 98.784 cm3
Volume of wood left = (211.68 – 98.784) π
= 112.896 π cm3
= 112.896 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) cm3
= 354.816 cm3
Question 5:
Radius o f cylinder = 2.5 m
Height of cylinder = 21 m
Slant height of cone = 8 m
Radius of cone = 2.5 m
Total surface area of the rocket = (curved surface area of cone + curved surface area of cylinder + area of base)

Question 6:
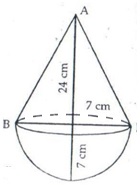
Height of cone = h = 24 cm
Its radius = 7 cm
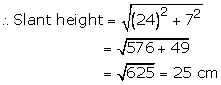
Total surface area of toy
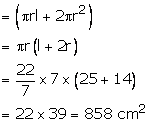
Question 7:
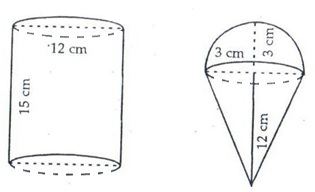
Height of cylindrical container h1 = 15 cm
Diameter of cylindrical container = 12 cm
Volume of container = ![]()
Height of cone r2 = 12 cm
Diameter = 6 cm
Radius of r2 = 3 cm
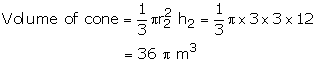
Radius of hemisphere = 3 cm
Volume of hemisphere = ![]()
Volume of cone + volume of hemisphere
= 36π + 18π = 54π
Number of cones
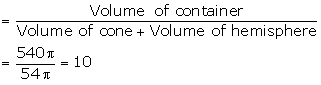
Number of cones that can be filled = 10
Question 8:
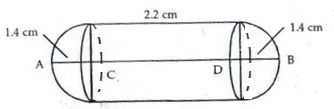
Diameter of cylindrical gulabjamun = 2.8 cm
Its radius = 1.4 cm
Total height of gulabjamun = AC + CD + DB = 5 cm
1.4 + CD + 1.4 = 5
2.8 + CD = 5
CD = 2.2 cm
Height of cylindrical part h = 2.2 cm
Volume of 1 gulabjamun = Volume of cylindrical part + Volume of two hemispherical parts

Volume of 45 gulabjamuns = 45 × 25.07 cm3
Quantity of syrup = 30% of volume of gulabjamuns
= 0.3 × 45 × 25.07 = 338.46 cm3
Question 9:
Diameter = 7cm, radius = = 3.5 cm
Height of cone = 14.5 cm – 3.5 cm = 11 cm

Total surface area of toy = ![]()
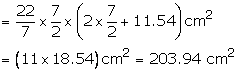
Question 10:
Diameter of cylinder = 24 m
Radius of cylinder = \(\frac { 24 }{ 2 } \) = 12 cm
Height of the cylinder = 11 m
Height of cone = (16 – 11) cm = 5 cm
Slant height of the cone l = ![]()
Area of canvas required = (curved surface area of the cylindrical part) + (curved surface area of the conical part)

Question 11:
Radius of hemisphere = 10.5 cm
Height of cylinder = (14.5 – 10.5) cm = 4 cm
Radius of cylinder = 10.5 cm
Capacity = Volume of cylinder + Volume of hemisphere

Question 12:
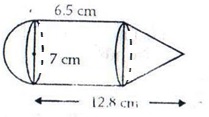
Height of cylinder = 6.5 cm
Height of cone = h2 = (12.8-6.5) cm = 6.3 cm
Radius of cylinder = radius of cone
= radius of hemisphere
= \(\frac { 7 }{ 2 } \) cm
Volume of solid = Volume of cylinder + Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere

Question 13:
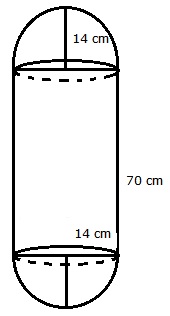
Radius of each hemispherical end = \(\frac { 28 }{ 2 } \) = 14 cm
Height of each hemispherical part = Its Radius
Height of cylindrical part = (98 – 2 × 14) = 70 cm
Area of surface to be polished = 2(curved surface area of hemisphere) + (curved surface area of cylinder)
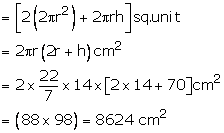
Cost of polishing the surface of the solid
= Rs. (0.15 × 8624)
= Rs. 1293. 60
Question 14:
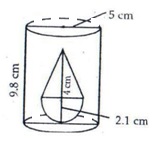
Radius of cylinder r1 = 5 cm
And height of cylinder h1 = 9.8 cm
Radius of cone r = 2.1 cm
And height of cone h2 = 4 cm
Volume of water left in tub = (volume of cylindrical tub – volume of solid)
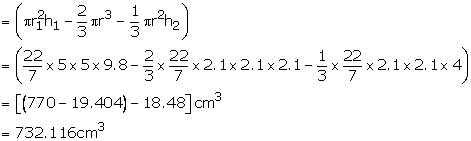
Question 15:
(i) Radius of cylinder = 6 cm
Height of cylinder = 8 cm
Volume of cylinder

Volume of cone removed

(ii) Surface area of cylinder = 2π = 2π × 6 × 8 cm2 = 96 π cm2

Question 16:
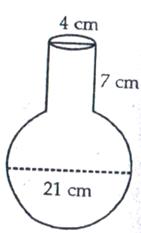
Diameter of spherical part of vessel = 21 cm

Question 17:
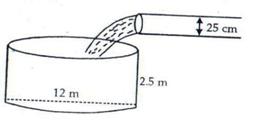
Height of cylindrical tank = 2.5 m
Its diameter = 12 m, Radius = 6 m
Volume of tank = ![]()
Water is flowing at the rate of 3.6 km/ hr = 3600 m/hr
Diameter of pipe = 25 cm, radius = 0.125 m
Volume of water flowing per hour
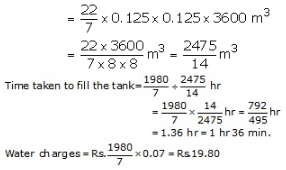
Question 18:
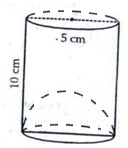
Diameter of cylinder = 5 cm
Radius = 2.5 cm
Height of cylinder = 10 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2h cu.units = 3.14 × 2.5 × 2.5 × 10 cm3 = 196.25 cm3
Apparent capacity of glass = 196.25
Radius of hemisphere = 2.5 cm
Volume of hemisphere

Actual capacity of glass = ( 196.25 – 32.608 ) cm3 = 163.54 cm3
Exercise 19B
Question 1:
Radius of the cone = 12 cm and its height = 24 cm
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) πr3 h = (\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \times 12\times 12\times 24) π cm3 = (48 × 24 )π cm3
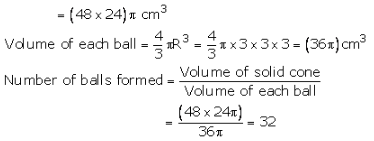
Question 2:
Internal radius = 3 cm and external radius = 5 cm

Hence, height of the cone = 4 cm
Question 3:
Inner radius of the bowl = 15 cm
Volume of liquid in it =
![]()
Radius of each cylindrical bottle = 2.5 cm and its height = 6 cm
Volume of each cylindrical bottle
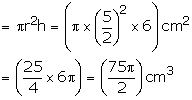
Required number of bottles = ![]()
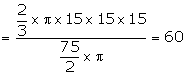
Hence, bottles required = 60
Question 4:
Radius of the sphere = \(\frac { 21 }{ 2 } \) cm
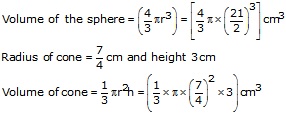
Let the number of cones formed be n, then
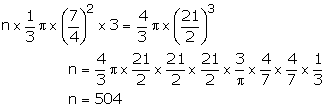
Hence, number of cones formed = 504
Question 5:
Radius of the cannon ball = 14 cm
Volume of cannon ball = ![]()
Radius of the cone = \(\frac { 35 }{ 2 } \) cm
Let the height of cone be h cm
Volume of cone = 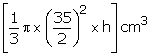
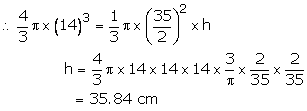
Hence, height of the cone = 35.84 cm
Question 6:
Let the radius of the third ball be r cm, then,
Volume of third ball = Volume of spherical ball – volume of 2 small balls

Question 7:
External radius of shell = 12 cm and internal radius = 9 cm
Volume of lead in the shell = 
Let the radius of the cylinder be r cm
Its height = 37 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2h = ( πr2 × 37 )
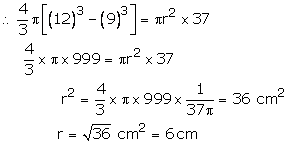
Hence diameter of the base of the cylinder = 12 cm
Question 8:
Volume of hemisphere of radius 9 cm
![]()
Volume of circular cone (height = 72 cm)
![]()
Volume of cone = Volume of hemisphere
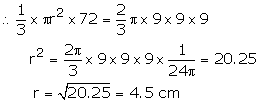
Hence radius of the base of the cone = 4.5 cm
Question 9:
Diameter of sphere = 21 cm
Hence, radius of sphere = \(\frac { 19 }{ 2 } \) cm
Volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = \((\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times \frac { 22 }{ 7 } \times \frac { 21 }{ 2 } \times \frac { 21 }{ 2 } \times \frac { 21 }{ 2 } ) \)
Volume of cube = a3 = (1 × 1 × 1)
Let number of cubes formed be n
∴ Volume of sphere = n × Volume of cube
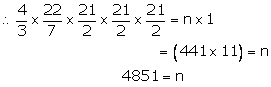
Hence, number of cubes is 4851.
Question 10:
Volume of sphere (when r = 1 cm) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 1\times 1\times 1) π cm3
Volume of sphere (when r = 8 cm) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 8\times 8\times 8) π cm3
Let the number of balls = n
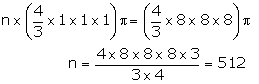
Question 11:
Radius of marbles = \(\frac { Diameter }{ 2 } =\frac { 1.4 }{ 2 } cm \)
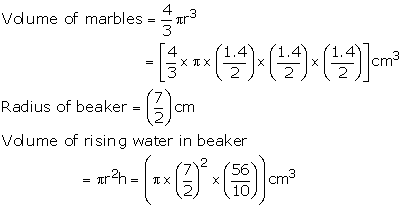
Let the number of marbles be n
∴ n × volume of marble = volume of rising water in beaker
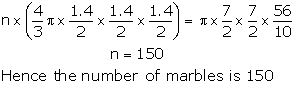
Question 12:
Radius of sphere = 3 cm
Volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 3\times 3\times 3) π cm3 = 36π cm3
Radius of small sphere = \(\frac { 0.6 }{ 2 } \) cm = 0.3 cm
Volume of small sphere = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 0.3\times 0.3\times 0.3) π cm3
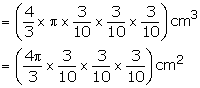
Let number of small balls be n
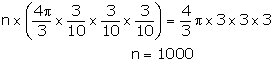
Hence, the number of small balls = 1000.
Question 13:
Diameter of sphere = 42 cm
Radius of sphere = \(\frac { 42 }{ 2 } \) cm = 21 cm
Volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 21\times 21\times 21) π cm3
Diameter of cylindrical wire = 2.8 cm
Radius of cylindrical wire = \(\frac { 2.8 }{ 2 } \) cm = 1.4 cm
Volume of cylindrical wire = πr2h = ( π × 1.4 × 1.4 × h ) cm3 = ( 1.96πh ) cm3
Volume of cylindrical wire = volume of sphere
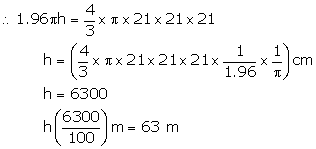
Hence length of the wire 63 m.
Question 14:
Diameter of sphere = 6 cm
Radius of sphere = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) cm = 3 cm
Volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) πr3 = (\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \times 3\times 3\times 3) π cm3 = 36π cm3
Radius of wire = \(\frac { 2 }{ 2 } \) mm = 1 mm = 0.1 cm
Volume of wire = πr2l = ( π × 0.1 × 0.1 × l ) cm2 = ( 0.01 πl ) cm2
36π = 0.01 π l
∴ \(l=\frac { 36 }{ 0.01 } =3600 \) cm
Length of wire = \(\frac { 3600 }{ 100 } \) m = 36 m
Question 15:
Diameter of sphere = 18 cm
Radius of copper sphere = \(\frac { 3600 }{ 100 } \) m = 36 m
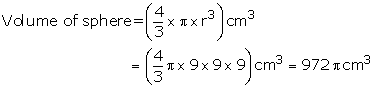
Length of wire = 108 m = 10800 cm
Let the radius of wire be r cm
= πr2l cm3 = ( πr2 × 10800 ) cm3
But the volume of wire = Volume of sphere

Hence the diameter = 2r = (0.3 × 2) cm = 0.6 cm
Question 16:
The radii of three metallic spheres are 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm respectively.
Sum of their volumes ![]()
![]()
Let r be the radius of sphere whose volume is equal to the total volume of three spheres.
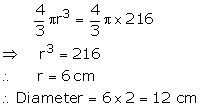
Exercise 19C
Question 1:
Here h = 42 cm, R = 16 cm, and r = 11 cm
Capacity = 
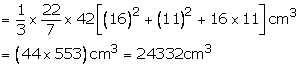
Question 2:
Here R = 33 cm, r = 27 cm and l = 10 cm
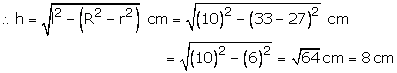
Capacity of the frustum
![]()
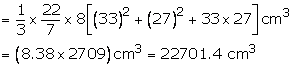
Total surface area
= ![]()

Question 3:
Height = 15 cm, R = \(\frac { 56 }{ 2 } \) cm = 28 cm and r = \(\frac { 42 }{ 2 } \) cm = 21 cm
Capacity of the bucket =


Quantity of water in bucket = 28.49 litres
Question 4:
R = 20 cm, r = 8 cm and h = 16 cm
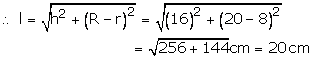
Total surface area of container = πl (R+r) + πr2

Cost of metal sheet used = Rs. \((1959.36\times \frac { 15 }{ 100 } ) \) = Rs. 293.90
Question 5:
R = 15 cm, r = 5 cm and h = 24 cm
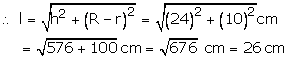
(i) Volume of bucket =
![]()
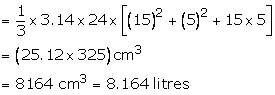
Cost of milk = Rs. (8.164 × 20) = Rs. 163.28
(ii) Total surface area of the bucket
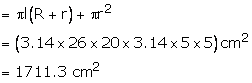
Cost of sheet = \(( 1711.3\times \frac { 10 }{ 100 } ) \) = Rs. 171.13
Question 6:
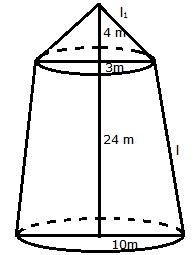
R = 10cm, r = 3 m and h = 24 m
Let l be the slant height of the frustum, then

Quantity of canvas = (Lateral surface area of the frustum) + (lateral surface area of the cone)
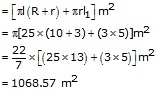
Question 7:
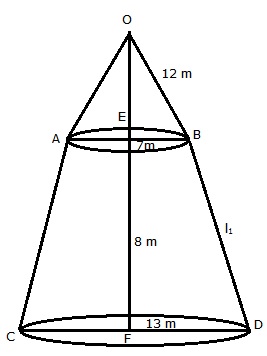
ABCD is the frustum in which upper and lower radii are EB = 7 m and FD = 13 m
Height of frustum = 8 m
Slant height l1 of frustum

Radius of the cone = EB = 7 m
Slant height l2 of cone = 12 m
Surface area of canvas required
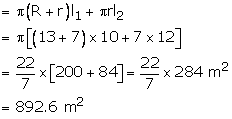
Question 8:
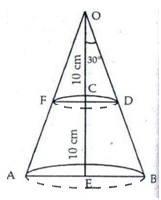
In the given figure, we have
∠COD = 30°, OC = 10 cm, OE = 20 cm
Let CD = r cm and EB = R cm
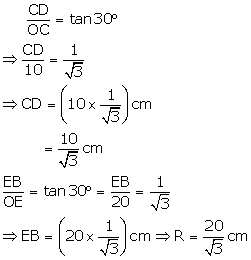
Also, CE = 10 cm
Thus, ABDF is the frustum of a cone in which
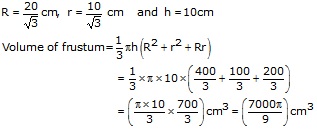
Volume of wire of radius r and length l
![]()
Volume of wire = Volume of frustum
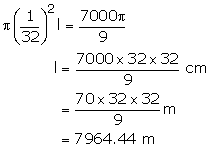
Length of the wire is 7964.44 m
Question 9:
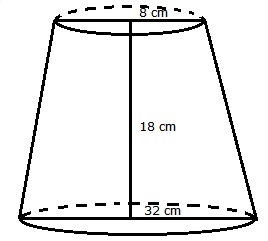
Radii of upper and lower end of frustum are r = 8 cm, R = 32 cm
Height of frustum h = 18 cm
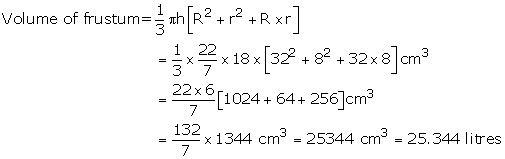
Cost of milk at Rs 20 per litre = Rs. 25.344 × 20 = Rs. 506. 88
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 19 Volume and Surface Areas of Solids are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. A Plus Topper try to provide online math tutoring for you.